e75dcf2f3d5289e821e67ec1c74eeb54.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 35
 Currency Futures and Options
Currency Futures and Options
 Spot Exchange Rates n Spot transactions are done immediately. A spot rate is the current domestic currency price of a foreign currency
Spot Exchange Rates n Spot transactions are done immediately. A spot rate is the current domestic currency price of a foreign currency
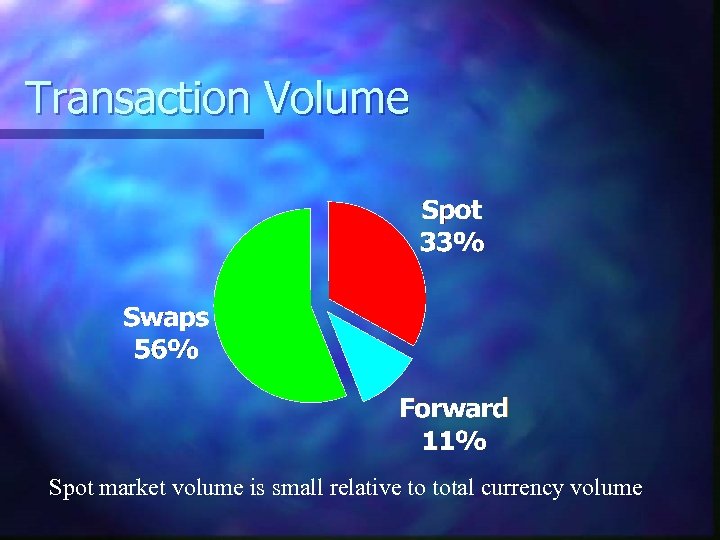 Transaction Volume Spot market volume is small relative to total currency volume
Transaction Volume Spot market volume is small relative to total currency volume
 Forward Contracts Forward contracts are purchases/sales of currencies to be delivered at a specific forward date (30, 90, 180, or 360 days) n Example n CAD/USD 1 month 3 months 6 months 12 months . 7641. 7583. 7563. 7537. 7525
Forward Contracts Forward contracts are purchases/sales of currencies to be delivered at a specific forward date (30, 90, 180, or 360 days) n Example n CAD/USD 1 month 3 months 6 months 12 months . 7641. 7583. 7563. 7537. 7525
 Forward Contracts Suppose that the current CAD/USD exchange rate is. 7641. n Microsoft anticipates labor expenses from Canadian operations (payable in Canadian Dollars) in 30 Days. n A Canadian Prescription Drug Importer is expecting a shipment of Viagra from Pfizer in 30 days (payment due in dollars) Microsoft would be worried about the dollar depreciating while the Canadian importer worries about the dollar appreciating.
Forward Contracts Suppose that the current CAD/USD exchange rate is. 7641. n Microsoft anticipates labor expenses from Canadian operations (payable in Canadian Dollars) in 30 Days. n A Canadian Prescription Drug Importer is expecting a shipment of Viagra from Pfizer in 30 days (payment due in dollars) Microsoft would be worried about the dollar depreciating while the Canadian importer worries about the dollar appreciating.
 Forward Contracts Commercial Bank Microsoft approaches a commercial bank with an offer to buy Canadian dollars forward 30 days The bank negotiates a price of. 7583 per CAD for 1 M CAD The Canadian drug importer approaches a commercial bank with an offer to sell Canadian dollars forward 30 days
Forward Contracts Commercial Bank Microsoft approaches a commercial bank with an offer to buy Canadian dollars forward 30 days The bank negotiates a price of. 7583 per CAD for 1 M CAD The Canadian drug importer approaches a commercial bank with an offer to sell Canadian dollars forward 30 days
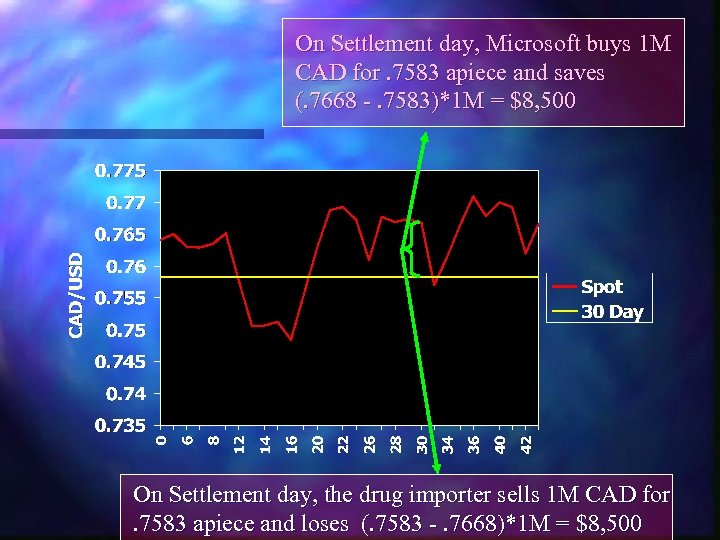 On Settlement day, Microsoft buys 1 M CAD for. 7583 apiece and saves (. 7668 -. 7583)*1 M = $8, 500 On Settlement day, the drug importer sells 1 M CAD for. 7583 apiece and loses (. 7583 -. 7668)*1 M = $8, 500
On Settlement day, Microsoft buys 1 M CAD for. 7583 apiece and saves (. 7668 -. 7583)*1 M = $8, 500 On Settlement day, the drug importer sells 1 M CAD for. 7583 apiece and loses (. 7583 -. 7668)*1 M = $8, 500
 Non-Deliverable Forwards n Note that the currencies need not actually be delivered. A non-deliverable forward specifies that only the profits/losses will be exchanged on settlement day.
Non-Deliverable Forwards n Note that the currencies need not actually be delivered. A non-deliverable forward specifies that only the profits/losses will be exchanged on settlement day.
 Forward Premiums/Discounts n In the previous example: CAD =. 7641 30 Day =. 7583 Forward Premium = . 7583 -. 7641 100 360 30 = -9. 1% Annualized The 30 Day CAD is selling at a discount of 9. 1%
Forward Premiums/Discounts n In the previous example: CAD =. 7641 30 Day =. 7583 Forward Premium = . 7583 -. 7641 100 360 30 = -9. 1% Annualized The 30 Day CAD is selling at a discount of 9. 1%
 Futures Contracts Forward contracts are written on an individual basis. Futures are standardized, traded commodities (Chicago Mercantile Exchange) n JPY: 12, 500, 000 Yen n GBP: 62, 500 Pounds n Euro: 125, 000 Euro n CAD: 100, 000 Canadian Dollars n Therefore, to make the previous trade (buy 1 M CAD, you would purchase 10 futures contracts) n
Futures Contracts Forward contracts are written on an individual basis. Futures are standardized, traded commodities (Chicago Mercantile Exchange) n JPY: 12, 500, 000 Yen n GBP: 62, 500 Pounds n Euro: 125, 000 Euro n CAD: 100, 000 Canadian Dollars n Therefore, to make the previous trade (buy 1 M CAD, you would purchase 10 futures contracts) n
 Futures Contracts Chicago Mercantile Exchange Microsoft makes an offer to buy 10, 30 Day Futures Contracts The CME simultaneously buys 10 contracts from Microsoft and sells 10 contracts from the drug importer The Canadian drug importer makes an offer to sell 10, 30 day Futures contracts
Futures Contracts Chicago Mercantile Exchange Microsoft makes an offer to buy 10, 30 Day Futures Contracts The CME simultaneously buys 10 contracts from Microsoft and sells 10 contracts from the drug importer The Canadian drug importer makes an offer to sell 10, 30 day Futures contracts
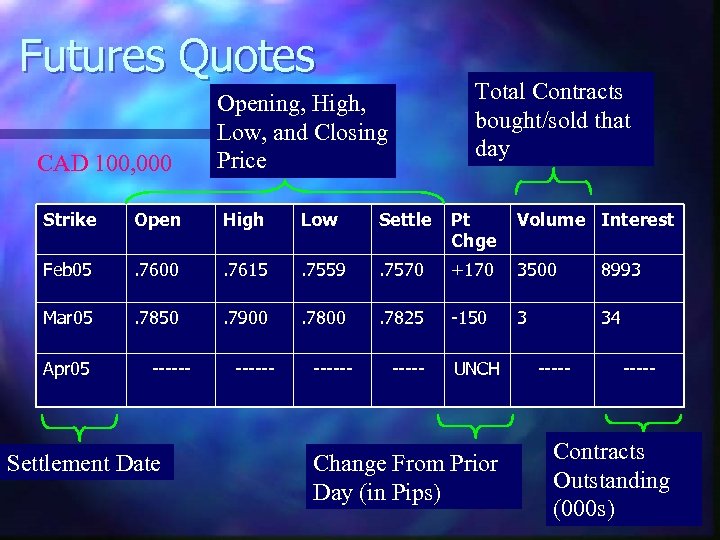 Futures Quotes CAD 100, 000 Total Contracts bought/sold that day Opening, High, Low, and Closing Price Strike Open High Low Settle Pt Chge Volume Interest Feb 05 . 7600 . 7615 . 7559 . 7570 +170 3500 8993 Mar 05 . 7850 . 7900 . 7825 -150 3 34 Apr 05 ------ Settlement Date ------ UNCH Change From Prior Day (in Pips) ----- Contracts Outstanding (000 s)
Futures Quotes CAD 100, 000 Total Contracts bought/sold that day Opening, High, Low, and Closing Price Strike Open High Low Settle Pt Chge Volume Interest Feb 05 . 7600 . 7615 . 7559 . 7570 +170 3500 8993 Mar 05 . 7850 . 7900 . 7825 -150 3 34 Apr 05 ------ Settlement Date ------ UNCH Change From Prior Day (in Pips) ----- Contracts Outstanding (000 s)
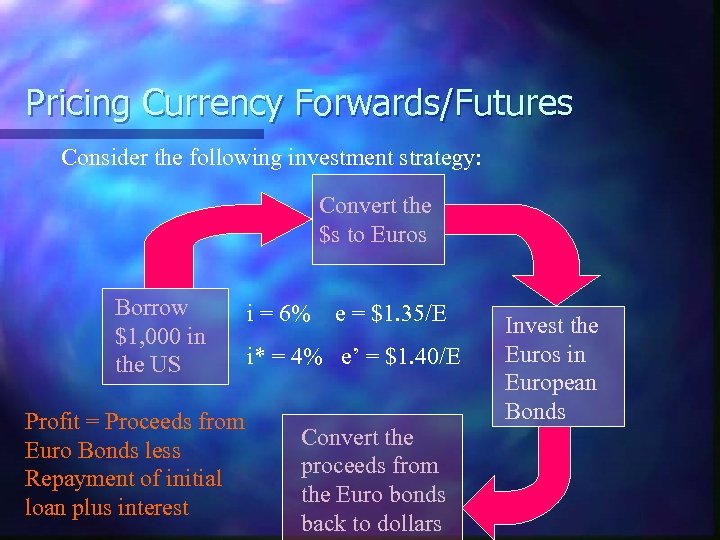 Pricing Currency Forwards/Futures Consider the following investment strategy: Convert the $s to Euros Borrow $1, 000 in the US Profit = Proceeds from Euro Bonds less Repayment of initial loan plus interest i = 6% e = $1. 35/E i* = 4% e’ = $1. 40/E Convert the proceeds from the Euro bonds back to dollars Invest the Euros in European Bonds
Pricing Currency Forwards/Futures Consider the following investment strategy: Convert the $s to Euros Borrow $1, 000 in the US Profit = Proceeds from Euro Bonds less Repayment of initial loan plus interest i = 6% e = $1. 35/E i* = 4% e’ = $1. 40/E Convert the proceeds from the Euro bonds back to dollars Invest the Euros in European Bonds
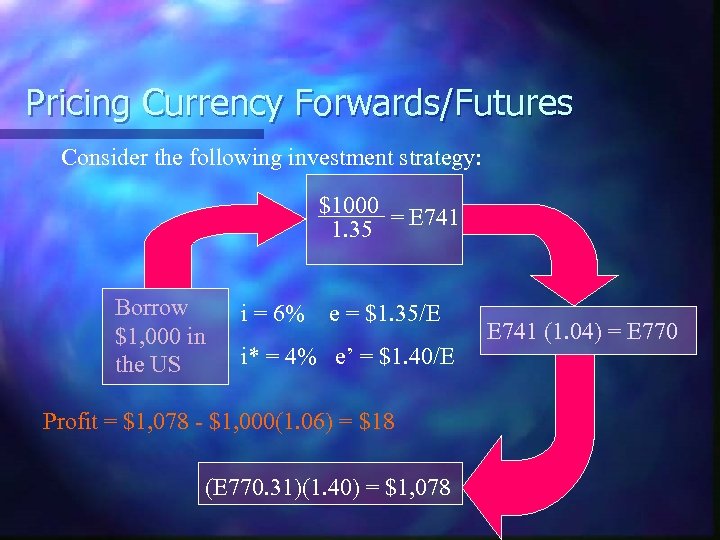 Pricing Currency Forwards/Futures Consider the following investment strategy: $1000 = E 741 1. 35 Borrow $1, 000 in the US i = 6% e = $1. 35/E i* = 4% e’ = $1. 40/E Profit = $1, 078 - $1, 000(1. 06) = $18 (E 770. 31)(1. 40) = $1, 078 E 741 (1. 04) = E 770
Pricing Currency Forwards/Futures Consider the following investment strategy: $1000 = E 741 1. 35 Borrow $1, 000 in the US i = 6% e = $1. 35/E i* = 4% e’ = $1. 40/E Profit = $1, 078 - $1, 000(1. 06) = $18 (E 770. 31)(1. 40) = $1, 078 E 741 (1. 04) = E 770
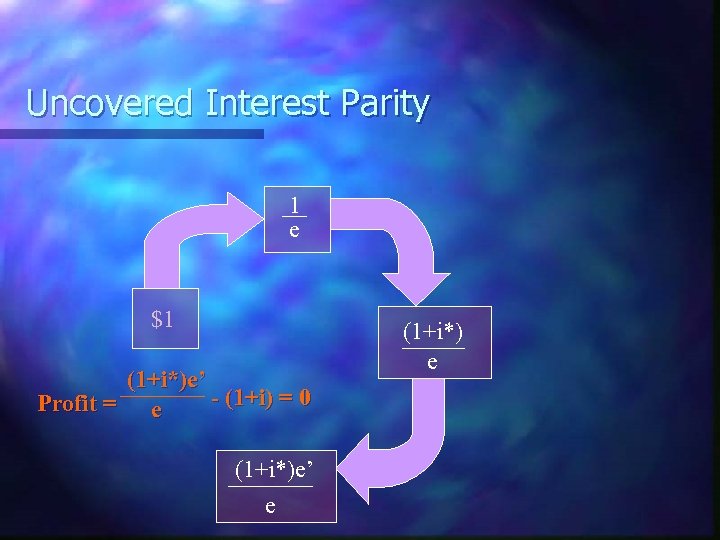 Uncovered Interest Parity 1 e $1 (1+i*)e’ - (1+i) = 0 Profit = e (1+i*)e’ e (1+i*) e
Uncovered Interest Parity 1 e $1 (1+i*)e’ - (1+i) = 0 Profit = e (1+i*)e’ e (1+i*) e
 Uncovered Interest Parity Uncovered parity suggests that you shouldn’t EXPECT to make money this way! Profit = This is the expected future exchange rate (1+i*)e’ - (1+i) = 0 e i – i* = Expected Change in the Exchange Rate 6% – 4% = 2% (An expected 2% dollar depreciation) Expected e’ = $1. 35/E (1. 02) = $1. 38
Uncovered Interest Parity Uncovered parity suggests that you shouldn’t EXPECT to make money this way! Profit = This is the expected future exchange rate (1+i*)e’ - (1+i) = 0 e i – i* = Expected Change in the Exchange Rate 6% – 4% = 2% (An expected 2% dollar depreciation) Expected e’ = $1. 35/E (1. 02) = $1. 38
 Covered Interest Parity You could eliminate all your risk by “locking in” your future exchange rate with a futures contract $1000 = E 741 1. 35 Borrow $1, 000 in the i = 6% e = $1. 35/E US, Buy a futures contract for $1, 078 at i* = 4% F = $1. 40/E Profit = $1, 078 - $1, 000(1. 06) = $18 (E 770. 31)(1. 40) = $1, 078 E 741 (1. 04) = E 770
Covered Interest Parity You could eliminate all your risk by “locking in” your future exchange rate with a futures contract $1000 = E 741 1. 35 Borrow $1, 000 in the i = 6% e = $1. 35/E US, Buy a futures contract for $1, 078 at i* = 4% F = $1. 40/E Profit = $1, 078 - $1, 000(1. 06) = $18 (E 770. 31)(1. 40) = $1, 078 E 741 (1. 04) = E 770
 Covered Interest Parity Covered parity is a zero arbitrage condition between spot and forward rates This is the futures/forward rate (1+i*)F - (1+i) = 0 Profit = e i – i* = Forward Premium/Discount Given the 2% interest differential, Forward/Futures should be selling at a 2% premium (= $1. 38)
Covered Interest Parity Covered parity is a zero arbitrage condition between spot and forward rates This is the futures/forward rate (1+i*)F - (1+i) = 0 Profit = e i – i* = Forward Premium/Discount Given the 2% interest differential, Forward/Futures should be selling at a 2% premium (= $1. 38)
 Forward rates as Predictors of the Future? Expected Percentage Change Forward Premium/Discount = i – i* = in Spot Rate Covered Interest Parity Uncovered Interest Parity Expected Percentage Forward Premium/Discount = Change in Spot Rate
Forward rates as Predictors of the Future? Expected Percentage Change Forward Premium/Discount = i – i* = in Spot Rate Covered Interest Parity Uncovered Interest Parity Expected Percentage Forward Premium/Discount = Change in Spot Rate
 Currency Options With options, you have the right to buy/sell currency, but not the requirement n Call: The right to buy at a specific “strike price” n Put: The right to sell at a specific “strike price” n The option belongs to the buyer of the contract. If you sell a put, you are REQUIRED to buy if the holder of the put chooses to exercise the option. n The buyer must pay an up front price for the contract n
Currency Options With options, you have the right to buy/sell currency, but not the requirement n Call: The right to buy at a specific “strike price” n Put: The right to sell at a specific “strike price” n The option belongs to the buyer of the contract. If you sell a put, you are REQUIRED to buy if the holder of the put chooses to exercise the option. n The buyer must pay an up front price for the contract n
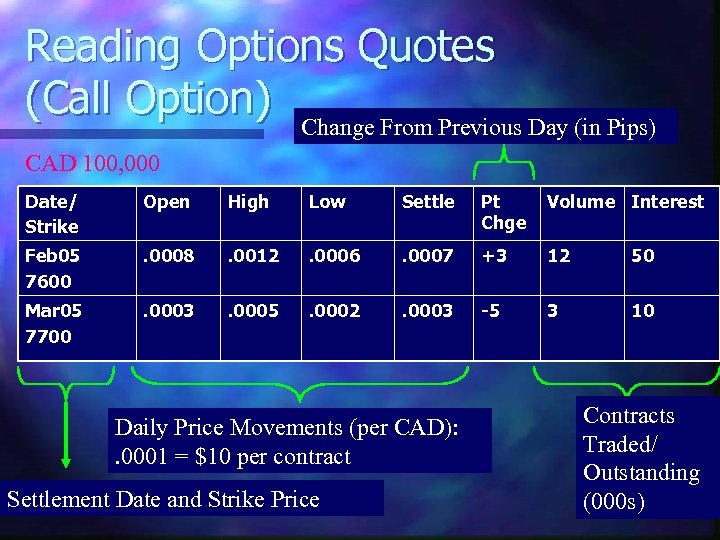 Reading Options Quotes (Call Option) Change From Previous Day (in Pips) CAD 100, 000 Date/ Strike Open High Low Settle Pt Chge Volume Interest Feb 05 7600 . 0008 . 0012 . 0006 . 0007 +3 12 50 Mar 05 7700 . 0003 . 0005 . 0002 . 0003 -5 3 10 Daily Price Movements (per CAD): . 0001 = $10 per contract Settlement Date and Strike Price Contracts Traded/ Outstanding (000 s)
Reading Options Quotes (Call Option) Change From Previous Day (in Pips) CAD 100, 000 Date/ Strike Open High Low Settle Pt Chge Volume Interest Feb 05 7600 . 0008 . 0012 . 0006 . 0007 +3 12 50 Mar 05 7700 . 0003 . 0005 . 0002 . 0003 -5 3 10 Daily Price Movements (per CAD): . 0001 = $10 per contract Settlement Date and Strike Price Contracts Traded/ Outstanding (000 s)
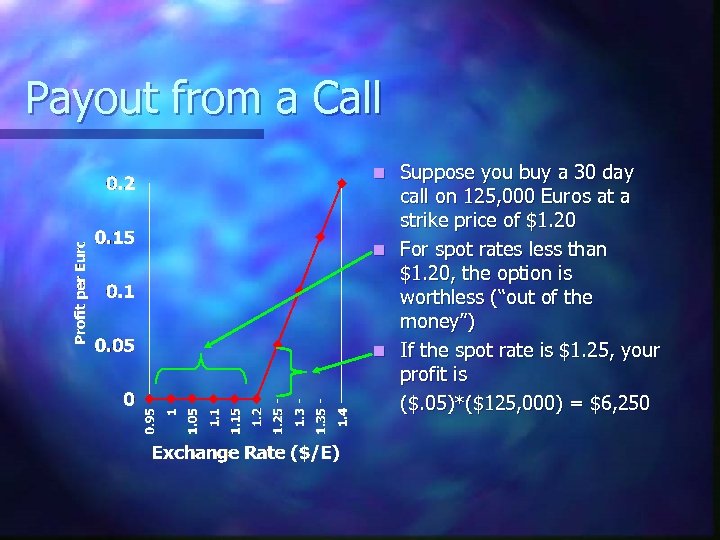 Payout from a Call Suppose you buy a 30 day call on 125, 000 Euros at a strike price of $1. 20 n For spot rates less than $1. 20, the option is worthless (“out of the money”) n If the spot rate is $1. 25, your profit is ($. 05)*($125, 000) = $6, 250 n
Payout from a Call Suppose you buy a 30 day call on 125, 000 Euros at a strike price of $1. 20 n For spot rates less than $1. 20, the option is worthless (“out of the money”) n If the spot rate is $1. 25, your profit is ($. 05)*($125, 000) = $6, 250 n
 Pricing a Call Option n If the future price of a Euro is $1. 25 at expiration (30 days from now) with certainty, the contract guarantees a $6, 250 payout in 30 days ($. 05 per Euro). Suppose the interest rate is currently 5% Call Price = Present Value of $6, 250 in one month = $6, 250/(1. 05) = $5, 952. 38 (. 047 per Euro) A call option price should be positively related to the (expected) future exchange rate and negatively related to the interest rate
Pricing a Call Option n If the future price of a Euro is $1. 25 at expiration (30 days from now) with certainty, the contract guarantees a $6, 250 payout in 30 days ($. 05 per Euro). Suppose the interest rate is currently 5% Call Price = Present Value of $6, 250 in one month = $6, 250/(1. 05) = $5, 952. 38 (. 047 per Euro) A call option price should be positively related to the (expected) future exchange rate and negatively related to the interest rate
 Pricing a Call Option n If the future price of a Euro has a 50% chance of decreasing to $1 and a 50% chance of increasing to $1. 50 at expiration (30 days from now). Suppose the interest rate is currently 5% Expected Payout = (. 5)($0) + (. 5)($. 30*125, 000) = $18, 750 Call Price = Present Value of $18, 750 in one month = $18, 750/(1. 05) = $17, 857. 14 (. 143 per Euro) A call option price should be positively related to the variance of the exchange rate.
Pricing a Call Option n If the future price of a Euro has a 50% chance of decreasing to $1 and a 50% chance of increasing to $1. 50 at expiration (30 days from now). Suppose the interest rate is currently 5% Expected Payout = (. 5)($0) + (. 5)($. 30*125, 000) = $18, 750 Call Price = Present Value of $18, 750 in one month = $18, 750/(1. 05) = $17, 857. 14 (. 143 per Euro) A call option price should be positively related to the variance of the exchange rate.
 Black - Scholes
Black - Scholes
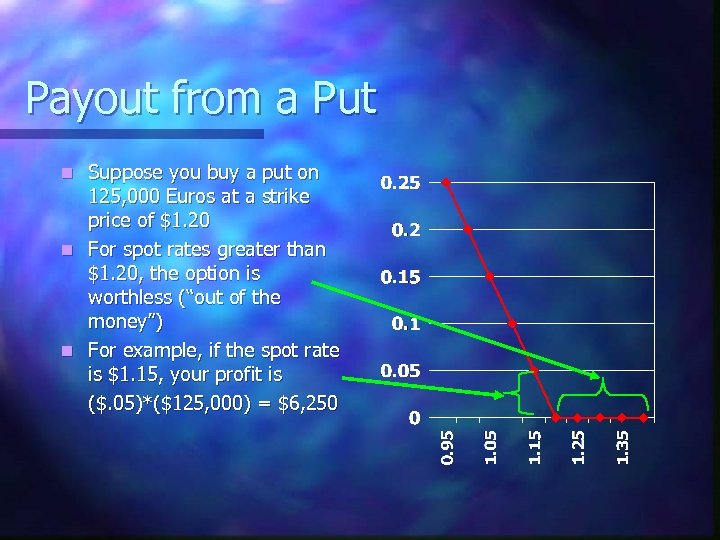 Payout from a Put Suppose you buy a put on 125, 000 Euros at a strike price of $1. 20 n For spot rates greater than $1. 20, the option is worthless (“out of the money”) n For example, if the spot rate is $1. 15, your profit is ($. 05)*($125, 000) = $6, 250 n
Payout from a Put Suppose you buy a put on 125, 000 Euros at a strike price of $1. 20 n For spot rates greater than $1. 20, the option is worthless (“out of the money”) n For example, if the spot rate is $1. 15, your profit is ($. 05)*($125, 000) = $6, 250 n
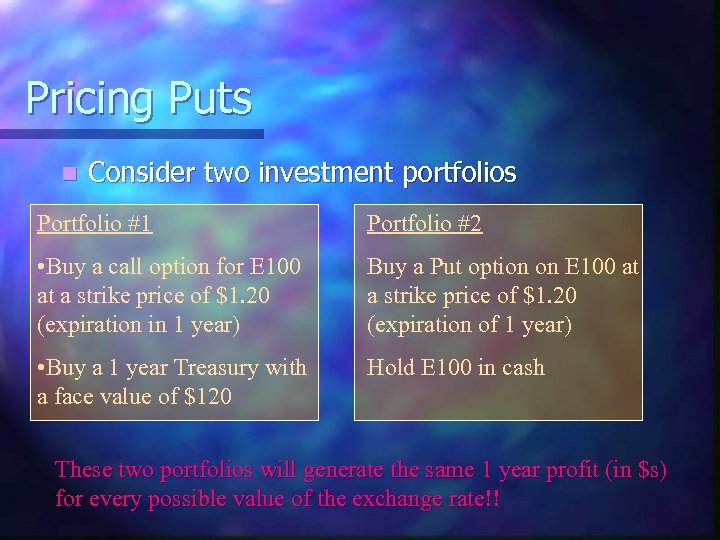 Pricing Puts n Consider two investment portfolios Portfolio #1 Portfolio #2 • Buy a call option for E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration in 1 year) Buy a Put option on E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration of 1 year) • Buy a 1 year Treasury with a face value of $120 Hold E 100 in cash These two portfolios will generate the same 1 year profit (in $s) for every possible value of the exchange rate!!
Pricing Puts n Consider two investment portfolios Portfolio #1 Portfolio #2 • Buy a call option for E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration in 1 year) Buy a Put option on E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration of 1 year) • Buy a 1 year Treasury with a face value of $120 Hold E 100 in cash These two portfolios will generate the same 1 year profit (in $s) for every possible value of the exchange rate!!
 n Suppose the exchange rate is $1. 25/E Portfolio #1 Portfolio #2 • Buy a call option for E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration in 1 year) Buy a Put option on E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration of 1 year) • Buy a 1 year Treasury with a face value of $120 Hold E 100 in cash Payout = ($. 05)(100) + $120 Call Payout Bond Payout = $0 + $125 Put Payout Value of Euros
n Suppose the exchange rate is $1. 25/E Portfolio #1 Portfolio #2 • Buy a call option for E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration in 1 year) Buy a Put option on E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration of 1 year) • Buy a 1 year Treasury with a face value of $120 Hold E 100 in cash Payout = ($. 05)(100) + $120 Call Payout Bond Payout = $0 + $125 Put Payout Value of Euros
 n Suppose the exchange rate is $1. 10/E Portfolio #1 Portfolio #2 • Buy a call option for E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration in 1 year) Buy a Put option on E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration of 1 year) • Buy a 1 year Treasury with a face value of $120 Hold E 100 in cash Payout = $0 + Call Payout $120 Bond Payout = ($. 10)(100) + $110 Put Payout Value of Euros
n Suppose the exchange rate is $1. 10/E Portfolio #1 Portfolio #2 • Buy a call option for E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration in 1 year) Buy a Put option on E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration of 1 year) • Buy a 1 year Treasury with a face value of $120 Hold E 100 in cash Payout = $0 + Call Payout $120 Bond Payout = ($. 10)(100) + $110 Put Payout Value of Euros
 n Two portfolios with equal returns should have equal cost Portfolio #1 Portfolio #2 • Buy a call option for E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration in 1 year) Buy a Put option on E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration of 1 year) • Buy a 1 year Treasury with a face value of $120 Hold E 100 in cash Cost Euro) (per Call Strike Price = Price + (1+i) Cost = Put Price + exchange rate (per Euro)
n Two portfolios with equal returns should have equal cost Portfolio #1 Portfolio #2 • Buy a call option for E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration in 1 year) Buy a Put option on E 100 at a strike price of $1. 20 (expiration of 1 year) • Buy a 1 year Treasury with a face value of $120 Hold E 100 in cash Cost Euro) (per Call Strike Price = Price + (1+i) Cost = Put Price + exchange rate (per Euro)
 Put/Call Parity Call Strike Price + (1+i) = Put Price + exchange rate Given the price of a call option, the current exchange rate and the current interest rate, we can price a put.
Put/Call Parity Call Strike Price + (1+i) = Put Price + exchange rate Given the price of a call option, the current exchange rate and the current interest rate, we can price a put.
 Currency Swaps Currency swaps are contracts to convert known income/payment streams from one currency to another – think of them as a portfolio of forwards with varying maturities/strikes n As with forward contracts, swaps are individualized and not traded. n
Currency Swaps Currency swaps are contracts to convert known income/payment streams from one currency to another – think of them as a portfolio of forwards with varying maturities/strikes n As with forward contracts, swaps are individualized and not traded. n
 Currency Swaps n Suppose that IBM wishes to raise funds by issuing a 5 year Swiss Franc denominated Eurobond with a face value of CHF 100, 000 and fixed annual coupon payments of 6%. Up front, IBM receives CHF 100, 000. IBM plans on using the proceeds to finance domestic operations
Currency Swaps n Suppose that IBM wishes to raise funds by issuing a 5 year Swiss Franc denominated Eurobond with a face value of CHF 100, 000 and fixed annual coupon payments of 6%. Up front, IBM receives CHF 100, 000. IBM plans on using the proceeds to finance domestic operations
 Currency Swaps 0 Yrs 1 Yrs 2 Yrs 3 Yrs IBM owes CHF 6, 000 IBM Collects CHF 100, 000 IBM Wishes to hedge its currency exposure 4 Yrs 5 Yrs IBM owes CHF 6, 000 IBM owes CHF 106, 000
Currency Swaps 0 Yrs 1 Yrs 2 Yrs 3 Yrs IBM owes CHF 6, 000 IBM Collects CHF 100, 000 IBM Wishes to hedge its currency exposure 4 Yrs 5 Yrs IBM owes CHF 6, 000 IBM owes CHF 106, 000
 Currency Swaps 0 Yrs 1 Yrs 2 Yrs 3 Yrs IBM buys CHF 6, 000 @. 845 IBM buys CHF 6, 000 @. 830 IBM buys CHF 6, 000 @. 800 IBM Sells CHF 100, 000 @. 844 IBM enters into a swap agreement with 4 Yrs 5 Yrs IBM buys CHF 6, 000 @. 840 IBM buys CHF 106, 000 @. 836 This swap is very similar to buying/selling six separate futures contracts and is priced in a similar fashion
Currency Swaps 0 Yrs 1 Yrs 2 Yrs 3 Yrs IBM buys CHF 6, 000 @. 845 IBM buys CHF 6, 000 @. 830 IBM buys CHF 6, 000 @. 800 IBM Sells CHF 100, 000 @. 844 IBM enters into a swap agreement with 4 Yrs 5 Yrs IBM buys CHF 6, 000 @. 840 IBM buys CHF 106, 000 @. 836 This swap is very similar to buying/selling six separate futures contracts and is priced in a similar fashion


