273aa3fccf9967228f3d6c38cd176d35.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Currency Derivatives (or chapter 7)
Currency Derivatives (or chapter 7)
 Agenda § How forex futures quoted & used for speculation? § Futures vs. forwards? § How forex options are quoted? § Speculate w/ forex options. § Distinction b/n buying & writing options? § How forex options are valued?
Agenda § How forex futures quoted & used for speculation? § Futures vs. forwards? § How forex options are quoted? § Speculate w/ forex options. § Distinction b/n buying & writing options? § How forex options are valued?
 § § Forex Futures Future delivery of standard amount of currency @ fixed time & price. Traded @ Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). Specifications: • • • Size –notional principal, in even multiple. Method of stating exchange rates – “American terms” used. Maturity date –mature on 3 rd Wed/ 01, 03, 04, 06, 07, 09, 10, or 12. Last trading day – contracts may trade through 2 nd business day prior to maturity. Collateral & maintenance margins –purchaser/trader must deposit initial margin or collateral. – Daily marked-to-market • Settlement – round turn fee. • Use of a clearing house as a counterparty
§ § Forex Futures Future delivery of standard amount of currency @ fixed time & price. Traded @ Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). Specifications: • • • Size –notional principal, in even multiple. Method of stating exchange rates – “American terms” used. Maturity date –mature on 3 rd Wed/ 01, 03, 04, 06, 07, 09, 10, or 12. Last trading day – contracts may trade through 2 nd business day prior to maturity. Collateral & maintenance margins –purchaser/trader must deposit initial margin or collateral. – Daily marked-to-market • Settlement – round turn fee. • Use of a clearing house as a counterparty
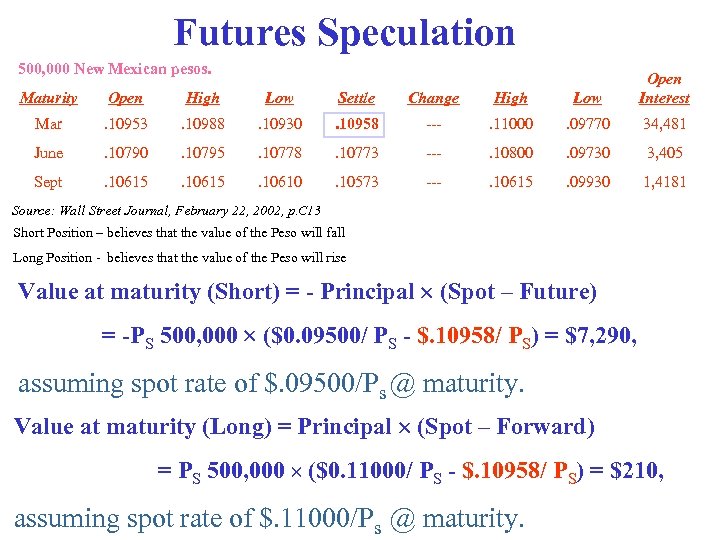 Futures Speculation 500, 000 New Mexican pesos. Maturity Open High Low Settle Change High Low Open Interest Mar . 10953 . 10988 . 10930 . 10958 --- . 11000 . 09770 34, 481 June . 10790 . 10795 . 10778 . 10773 --- . 10800 . 09730 3, 405 Sept . 10615 . 10610 . 10573 --- . 10615 . 09930 1, 4181 Source: Wall Street Journal, February 22, 2002, p. C 13 Short Position – believes that the value of the Peso will fall Long Position - believes that the value of the Peso will rise Value at maturity (Short) = - Principal (Spot – Future) = -PS 500, 000 ($0. 09500/ PS - $. 10958/ PS) = $7, 290, assuming spot rate of $. 09500/Ps @ maturity. Value at maturity (Long) = Principal (Spot – Forward) = PS 500, 000 ($0. 11000/ PS - $. 10958/ PS) = $210, assuming spot rate of $. 11000/Ps @ maturity.
Futures Speculation 500, 000 New Mexican pesos. Maturity Open High Low Settle Change High Low Open Interest Mar . 10953 . 10988 . 10930 . 10958 --- . 11000 . 09770 34, 481 June . 10790 . 10795 . 10778 . 10773 --- . 10800 . 09730 3, 405 Sept . 10615 . 10610 . 10573 --- . 10615 . 09930 1, 4181 Source: Wall Street Journal, February 22, 2002, p. C 13 Short Position – believes that the value of the Peso will fall Long Position - believes that the value of the Peso will rise Value at maturity (Short) = - Principal (Spot – Future) = -PS 500, 000 ($0. 09500/ PS - $. 10958/ PS) = $7, 290, assuming spot rate of $. 09500/Ps @ maturity. Value at maturity (Long) = Principal (Spot – Forward) = PS 500, 000 ($0. 11000/ PS - $. 10958/ PS) = $210, assuming spot rate of $. 11000/Ps @ maturity.
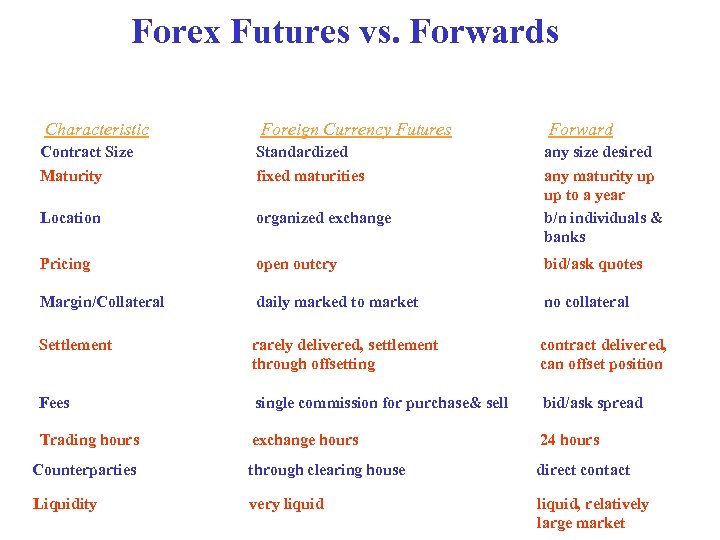 Forex Futures vs. Forwards Characteristic Foreign Currency Futures Forward Contract Size Maturity Standardized fixed maturities Location organized exchange any size desired any maturity up up to a year b/n individuals & banks Pricing open outcry bid/ask quotes Margin/Collateral daily marked to market no collateral Settlement rarely delivered, settlement through offsetting contract delivered, can offset position Fees single commission for purchase& sell bid/ask spread Trading hours exchange hours 24 hours Counterparties through clearing house direct contact Liquidity very liquid, relatively large market
Forex Futures vs. Forwards Characteristic Foreign Currency Futures Forward Contract Size Maturity Standardized fixed maturities Location organized exchange any size desired any maturity up up to a year b/n individuals & banks Pricing open outcry bid/ask quotes Margin/Collateral daily marked to market no collateral Settlement rarely delivered, settlement through offsetting contract delivered, can offset position Fees single commission for purchase& sell bid/ask spread Trading hours exchange hours 24 hours Counterparties through clearing house direct contact Liquidity very liquid, relatively large market
 Initial Margin Requirements § Held as collateral by broker. § Usually 2 -4% of contract value. § Margin amount same for short & long positions. § Buyer holds a long position (seller – short). § If settlement price higher than yesterday, buyer has a § § positive settlement for the day. Long position now worth more. Exact opposite for seller (zero-sum game).
Initial Margin Requirements § Held as collateral by broker. § Usually 2 -4% of contract value. § Margin amount same for short & long positions. § Buyer holds a long position (seller – short). § If settlement price higher than yesterday, buyer has a § § positive settlement for the day. Long position now worth more. Exact opposite for seller (zero-sum game).
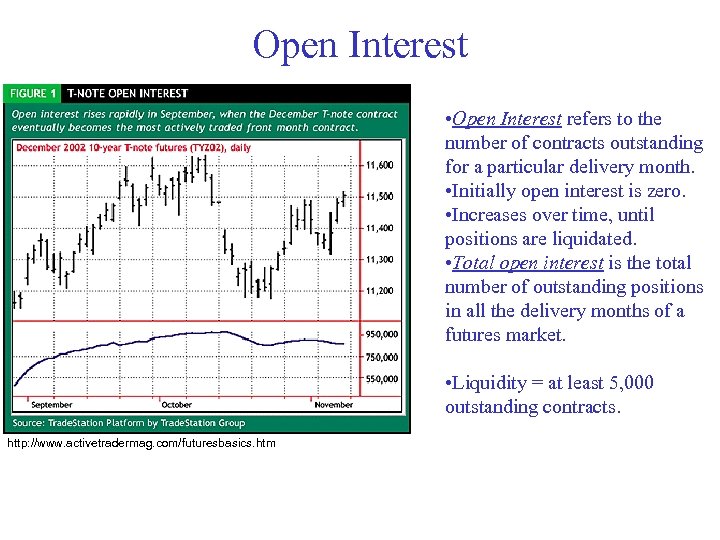 Open Interest • Open Interest refers to the number of contracts outstanding for a particular delivery month. • Initially open interest is zero. • Increases over time, until positions are liquidated. • Total open interest is the total number of outstanding positions in all the delivery months of a futures market. • Liquidity = at least 5, 000 outstanding contracts. http: //www. activetradermag. com/futuresbasics. htm
Open Interest • Open Interest refers to the number of contracts outstanding for a particular delivery month. • Initially open interest is zero. • Increases over time, until positions are liquidated. • Total open interest is the total number of outstanding positions in all the delivery months of a futures market. • Liquidity = at least 5, 000 outstanding contracts. http: //www. activetradermag. com/futuresbasics. htm
 Reversing Trades § Rare in forward markets – 90% of all contracts lead to § delivery. Common in futures markets – only 1% of contracts lead to delivery!
Reversing Trades § Rare in forward markets – 90% of all contracts lead to § delivery. Common in futures markets – only 1% of contracts lead to delivery!
 Forex Option § Gives right but not obligation to buy/sell amount of currency @ fixed price for given time period • Call – buyer has right to purchase • Put – buyer has right to sell • Buyer = holder & seller = writer. § Two option types § Price elements • American: may exercise during life of option. • European: may not exercise until maturity. • Strike (exercise price): exchange rate @ which foreign currency • • can be purchased/ sold. Premium, price of option Spot rate
Forex Option § Gives right but not obligation to buy/sell amount of currency @ fixed price for given time period • Call – buyer has right to purchase • Put – buyer has right to sell • Buyer = holder & seller = writer. § Two option types § Price elements • American: may exercise during life of option. • European: may not exercise until maturity. • Strike (exercise price): exchange rate @ which foreign currency • • can be purchased/ sold. Premium, price of option Spot rate
 Forex Options § May be classified as: • At-the-money (ATM): exercise price = spot rate. • In-the-money (ITM) options profitable, excluding • premium, if exercised immediately. Out-of-the-money (OTM) options not profitable, excluding premium, if exercised immediately. § Markets for derivatives: • OTC Market • Organized exchanges - Chicago Mercantile and the Philadelphia Stock Exchange – Option Clearinghouse Corporation
Forex Options § May be classified as: • At-the-money (ATM): exercise price = spot rate. • In-the-money (ITM) options profitable, excluding • premium, if exercised immediately. Out-of-the-money (OTM) options not profitable, excluding premium, if exercised immediately. § Markets for derivatives: • OTC Market • Organized exchanges - Chicago Mercantile and the Philadelphia Stock Exchange – Option Clearinghouse Corporation
 Futures Contracts vs. Options § Futures Contract – you’ve agreed to purchase/sell the contract. No backing out. Can offset/ exit by buying/selling to someone else. • Buy = long; sell = short. § Option – contract that gives you the right but not the obligation to purchase/sell something at prespecified terms. No commitment.
Futures Contracts vs. Options § Futures Contract – you’ve agreed to purchase/sell the contract. No backing out. Can offset/ exit by buying/selling to someone else. • Buy = long; sell = short. § Option – contract that gives you the right but not the obligation to purchase/sell something at prespecified terms. No commitment.
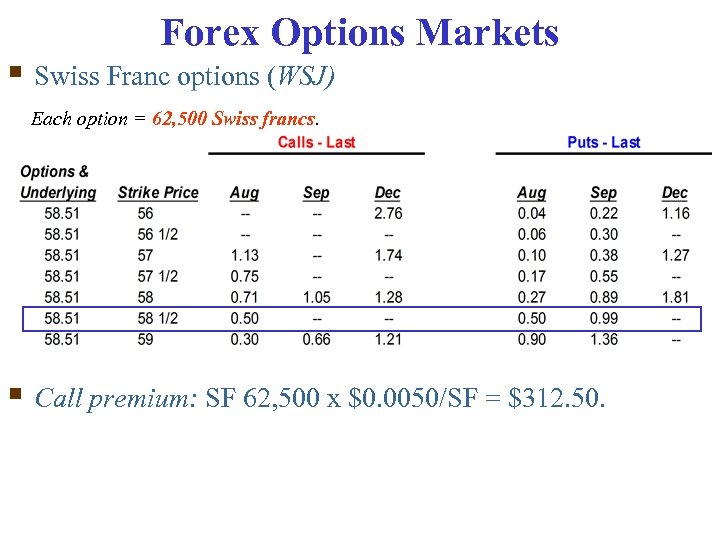 Forex Options Markets § Swiss Franc options (WSJ) Each option = 62, 500 Swiss francs. § Call premium: SF 62, 500 x $0. 0050/SF = $312. 50.
Forex Options Markets § Swiss Franc options (WSJ) Each option = 62, 500 Swiss francs. § Call premium: SF 62, 500 x $0. 0050/SF = $312. 50.
 Speculation § Assume spot rate: $0. 5851/SF, 6 m forward: $0. 5760/SF. § Spot market • $100, 000. Expect six month spot SF $0. 6000/SF. • Step 1: purchase SF 170, 910. 96 @ spot $0. 5851/SF. • Step 2: sell at target spot rate of $0. 60/SF. § Forward market • Step 1: Buy forward SF 173, 611. 11 x $0. 576/SF= • $100, 000. Step 2: In 6 m, fulfill forward & sell proceeds in spot market Sfr 173, 611. 11 x $0. 6000/Sfr = $104, 166. 67. § Options market • Long Call, Short Call, Long Put, Short Put.
Speculation § Assume spot rate: $0. 5851/SF, 6 m forward: $0. 5760/SF. § Spot market • $100, 000. Expect six month spot SF $0. 6000/SF. • Step 1: purchase SF 170, 910. 96 @ spot $0. 5851/SF. • Step 2: sell at target spot rate of $0. 60/SF. § Forward market • Step 1: Buy forward SF 173, 611. 11 x $0. 576/SF= • $100, 000. Step 2: In 6 m, fulfill forward & sell proceeds in spot market Sfr 173, 611. 11 x $0. 6000/Sfr = $104, 166. 67. § Options market • Long Call, Short Call, Long Put, Short Put.
 For Example… § Suppose that: • you have $10 m. • Wish to speculate on Euro • S = $ 0. 885/ EUR, F 30 = $ 0. 900/ EUR. – You expect S 30 = $ 0. 844/ EUR (EUR depreciates). – Arbitrage strategy? – You expect S 30 = $ 0. 944/ EUR (EUR appreciates). – Arbitrage strategy?
For Example… § Suppose that: • you have $10 m. • Wish to speculate on Euro • S = $ 0. 885/ EUR, F 30 = $ 0. 900/ EUR. – You expect S 30 = $ 0. 844/ EUR (EUR depreciates). – Arbitrage strategy? – You expect S 30 = $ 0. 944/ EUR (EUR appreciates). – Arbitrage strategy?
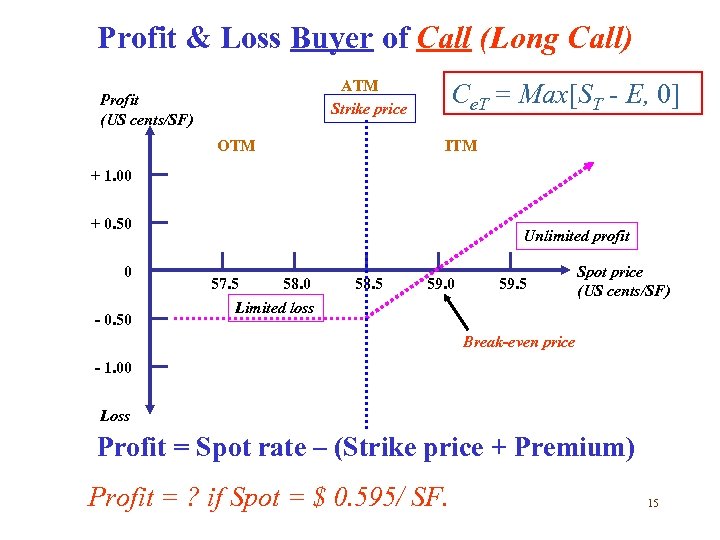 Profit & Loss Buyer of Call (Long Call) ATM Strike price Profit (US cents/SF) OTM Ce. T = Max[ST - E, 0] ITM + 1. 00 + 0. 50 0 - 0. 50 Unlimited profit 57. 5 58. 0 Limited loss 58. 5 59. 0 59. 5 Spot price (US cents/SF) Break-even price - 1. 00 Loss Profit = Spot rate – (Strike price + Premium) Profit = ? if Spot = $ 0. 595/ SF. 15
Profit & Loss Buyer of Call (Long Call) ATM Strike price Profit (US cents/SF) OTM Ce. T = Max[ST - E, 0] ITM + 1. 00 + 0. 50 0 - 0. 50 Unlimited profit 57. 5 58. 0 Limited loss 58. 5 59. 0 59. 5 Spot price (US cents/SF) Break-even price - 1. 00 Loss Profit = Spot rate – (Strike price + Premium) Profit = ? if Spot = $ 0. 595/ SF. 15
 Profit & Loss Writer of Call (Short Call) ATM Strike price Profit (US cents/SF) Ce. T = Max[ST - E, 0] + 1. 00 + 0. 50 0 Break-even price Limited profit 57. 5 58. 0 58. 5 59. 0 - 0. 50 59. 5 Spot price (US cents/SF) Unlimited loss - 1. 00 Loss Profit = Premium – (Spot rate - Strike price). Profit = ? if Spot = $ 0. 595/ SF. 16
Profit & Loss Writer of Call (Short Call) ATM Strike price Profit (US cents/SF) Ce. T = Max[ST - E, 0] + 1. 00 + 0. 50 0 Break-even price Limited profit 57. 5 58. 0 58. 5 59. 0 - 0. 50 59. 5 Spot price (US cents/SF) Unlimited loss - 1. 00 Loss Profit = Premium – (Spot rate - Strike price). Profit = ? if Spot = $ 0. 595/ SF. 16
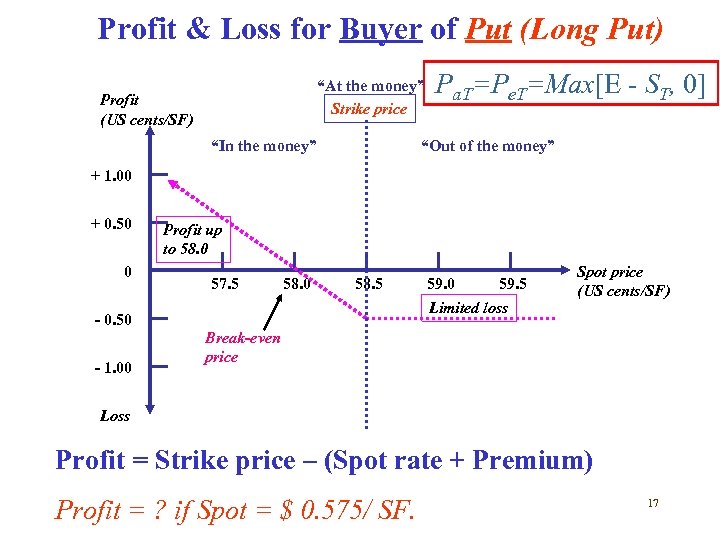 Profit & Loss for Buyer of Put (Long Put) “At the money” Strike price Profit (US cents/SF) “In the money” Pa. T=Pe. T=Max[E - ST, 0] “Out of the money” + 1. 00 + 0. 50 0 Profit up to 58. 0 57. 5 58. 0 58. 5 - 0. 50 - 1. 00 59. 5 Limited loss Spot price (US cents/SF) Break-even price Loss Profit = Strike price – (Spot rate + Premium) Profit = ? if Spot = $ 0. 575/ SF. 17
Profit & Loss for Buyer of Put (Long Put) “At the money” Strike price Profit (US cents/SF) “In the money” Pa. T=Pe. T=Max[E - ST, 0] “Out of the money” + 1. 00 + 0. 50 0 Profit up to 58. 0 57. 5 58. 0 58. 5 - 0. 50 - 1. 00 59. 5 Limited loss Spot price (US cents/SF) Break-even price Loss Profit = Strike price – (Spot rate + Premium) Profit = ? if Spot = $ 0. 575/ SF. 17
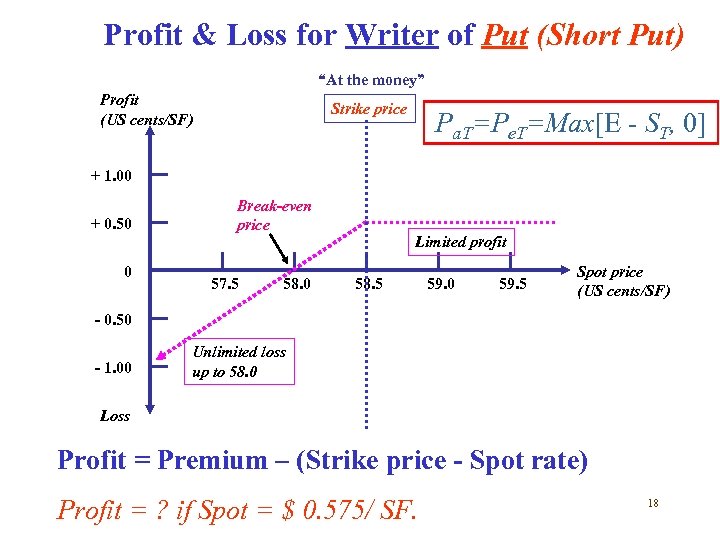 Profit & Loss for Writer of Put (Short Put) “At the money” Profit (US cents/SF) Strike price Pa. T=Pe. T=Max[E - ST, 0] + 1. 00 + 0. 50 0 Break-even price 57. 5 58. 0 Limited profit 58. 5 59. 0 59. 5 Spot price (US cents/SF) - 0. 50 - 1. 00 Unlimited loss up to 58. 0 Loss Profit = Premium – (Strike price - Spot rate) Profit = ? if Spot = $ 0. 575/ SF. 18
Profit & Loss for Writer of Put (Short Put) “At the money” Profit (US cents/SF) Strike price Pa. T=Pe. T=Max[E - ST, 0] + 1. 00 + 0. 50 0 Break-even price 57. 5 58. 0 Limited profit 58. 5 59. 0 59. 5 Spot price (US cents/SF) - 0. 50 - 1. 00 Unlimited loss up to 58. 0 Loss Profit = Premium – (Strike price - Spot rate) Profit = ? if Spot = $ 0. 575/ SF. 18
 For Example… § Suppose that: • • • You wish to speculate on fall of Yen vs. $. Current S = Yen 120/ $ (or $. 00833/Yen). Maturity: 90 days. Expected S 90 = Yen 140/$ (or $. 00714). Two options available: Call on Yen Put on Yen – Strike: – Premium: Yen 125/$ (or $. 008/ Yen) $. 00046 1. What option to buy? 2. Break even price on option of choice? 3. If S= Yen 140/ $, what is net profit? Yen 125/$. (or $. 008/ Yen) $. 00003
For Example… § Suppose that: • • • You wish to speculate on fall of Yen vs. $. Current S = Yen 120/ $ (or $. 00833/Yen). Maturity: 90 days. Expected S 90 = Yen 140/$ (or $. 00714). Two options available: Call on Yen Put on Yen – Strike: – Premium: Yen 125/$ (or $. 008/ Yen) $. 00046 1. What option to buy? 2. Break even price on option of choice? 3. If S= Yen 140/ $, what is net profit? Yen 125/$. (or $. 008/ Yen) $. 00003
 Option Pricing § Market value = Time value + Intrinsic Value § Intrinsic Value –gain if option exercised § immediately. Will reach zero when the option is OTM. At maturity, option value = intrinsic value. Time Value – reflects a gamble that the option might be more profitable (more in-the-money) as time passes (i. e. before time of expiry).
Option Pricing § Market value = Time value + Intrinsic Value § Intrinsic Value –gain if option exercised § immediately. Will reach zero when the option is OTM. At maturity, option value = intrinsic value. Time Value – reflects a gamble that the option might be more profitable (more in-the-money) as time passes (i. e. before time of expiry).
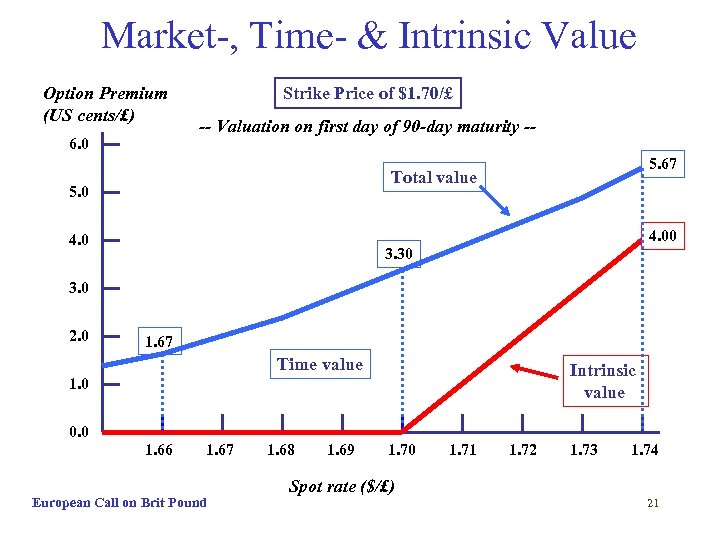 Market-, Time- & Intrinsic Value Option Premium (US cents/£) 6. 0 Strike Price of $1. 70/£ -- Valuation on first day of 90 -day maturity -5. 67 Total value 5. 0 4. 0 3. 30 3. 0 2. 0 1. 67 Time value Intrinsic value 1. 0 0. 0 1. 66 1. 67 European Call on Brit Pound 1. 68 1. 69 1. 70 1. 71 1. 72 1. 73 1. 74 Spot rate ($/£) 21
Market-, Time- & Intrinsic Value Option Premium (US cents/£) 6. 0 Strike Price of $1. 70/£ -- Valuation on first day of 90 -day maturity -5. 67 Total value 5. 0 4. 0 3. 30 3. 0 2. 0 1. 67 Time value Intrinsic value 1. 0 0. 0 1. 66 1. 67 European Call on Brit Pound 1. 68 1. 69 1. 70 1. 71 1. 72 1. 73 1. 74 Spot rate ($/£) 21
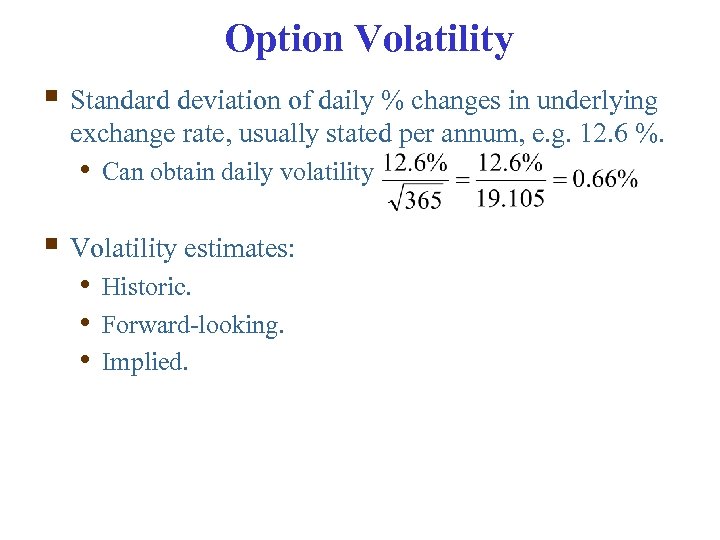 Option Volatility § Standard deviation of daily % changes in underlying exchange rate, usually stated per annum, e. g. 12. 6 %. • Can obtain daily volatility § Volatility estimates: • Historic. • Forward-looking. • Implied.
Option Volatility § Standard deviation of daily % changes in underlying exchange rate, usually stated per annum, e. g. 12. 6 %. • Can obtain daily volatility § Volatility estimates: • Historic. • Forward-looking. • Implied.
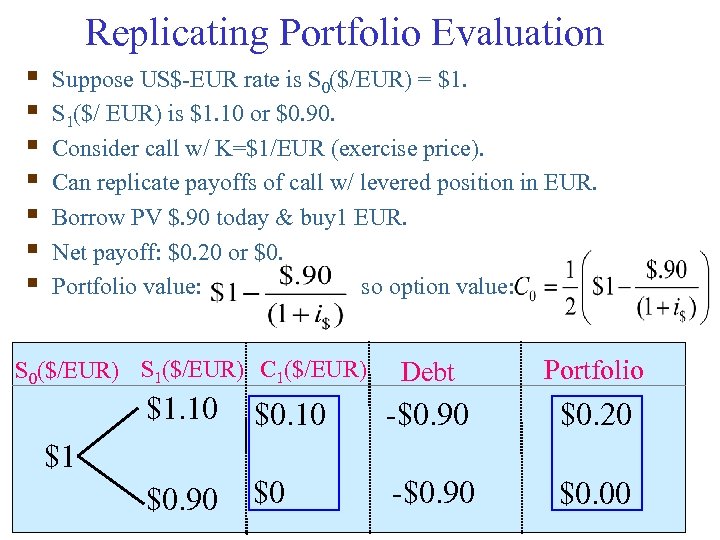 Replicating Portfolio Evaluation § § § § Suppose US$-EUR rate is S 0($/EUR) = $1. S 1($/ EUR) is $1. 10 or $0. 90. Consider call w/ K=$1/EUR (exercise price). Can replicate payoffs of call w/ levered position in EUR. Borrow PV $. 90 today & buy 1 EUR. Net payoff: $0. 20 or $0. Portfolio value: so option value: S 0($/EUR) S 1($/EUR) C 1($/EUR) Debt Portfolio $1. 10 $0. 10 -$0. 90 $0. 20 $0. 90 $0 -$0. 90 $0. 00 $1
Replicating Portfolio Evaluation § § § § Suppose US$-EUR rate is S 0($/EUR) = $1. S 1($/ EUR) is $1. 10 or $0. 90. Consider call w/ K=$1/EUR (exercise price). Can replicate payoffs of call w/ levered position in EUR. Borrow PV $. 90 today & buy 1 EUR. Net payoff: $0. 20 or $0. Portfolio value: so option value: S 0($/EUR) S 1($/EUR) C 1($/EUR) Debt Portfolio $1. 10 $0. 10 -$0. 90 $0. 20 $0. 90 $0 -$0. 90 $0. 00 $1
 Rogue Trading: Good Fellas… § Nick Leeson @ Barings. • 1995, managed to bankrupt Barings Brothers (UK). § John Rusnak @ Allied Irish Bank. • 2002, lost $691 m on behalf of Allied Irish Bank (Baltimore office).
Rogue Trading: Good Fellas… § Nick Leeson @ Barings. • 1995, managed to bankrupt Barings Brothers (UK). § John Rusnak @ Allied Irish Bank. • 2002, lost $691 m on behalf of Allied Irish Bank (Baltimore office).
 Things to remember § Futures terminology. § Futures vs. Forwards. § Speculation • In spot & forward markets. • In option markets. § How forex options are quoted? § Distinction b/n buying & writing options. § How forex options are valued?
Things to remember § Futures terminology. § Futures vs. Forwards. § Speculation • In spot & forward markets. • In option markets. § How forex options are quoted? § Distinction b/n buying & writing options. § How forex options are valued?


