6a7ef6e86c46091b454682c2a8d1279f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 Culture Hearths
Culture Hearths
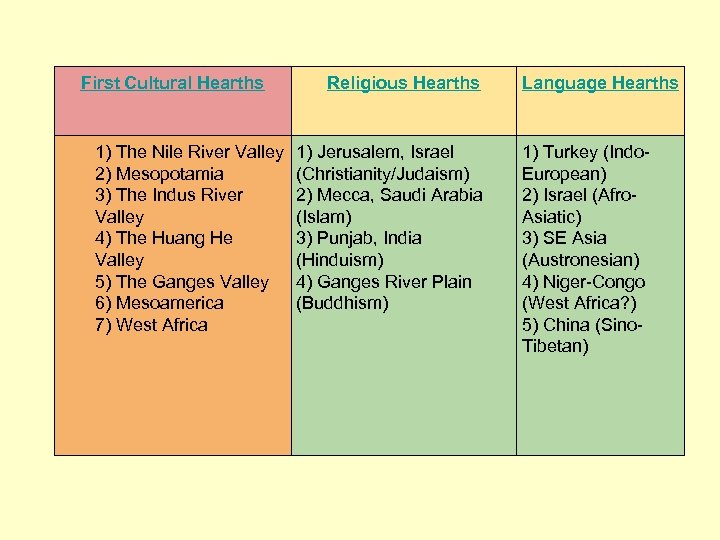 First Cultural Hearths 1) The Nile River Valley 2) Mesopotamia 3) The Indus River Valley 4) The Huang He Valley 5) The Ganges Valley 6) Mesoamerica 7) West Africa Religious Hearths 1) Jerusalem, Israel (Christianity/Judaism) 2) Mecca, Saudi Arabia (Islam) 3) Punjab, India (Hinduism) 4) Ganges River Plain (Buddhism) Language Hearths 1) Turkey (Indo. European) 2) Israel (Afro. Asiatic) 3) SE Asia (Austronesian) 4) Niger-Congo (West Africa? ) 5) China (Sino. Tibetan)
First Cultural Hearths 1) The Nile River Valley 2) Mesopotamia 3) The Indus River Valley 4) The Huang He Valley 5) The Ganges Valley 6) Mesoamerica 7) West Africa Religious Hearths 1) Jerusalem, Israel (Christianity/Judaism) 2) Mecca, Saudi Arabia (Islam) 3) Punjab, India (Hinduism) 4) Ganges River Plain (Buddhism) Language Hearths 1) Turkey (Indo. European) 2) Israel (Afro. Asiatic) 3) SE Asia (Austronesian) 4) Niger-Congo (West Africa? ) 5) China (Sino. Tibetan)
 Modern Culture Hearths and Cultural Diffusion §Because cultures develop over time, new dominant areas of dominant culture do to. §Today's modern culture hearths are places such as the United States and major world cities like London and Tokyo. §Areas such as these are considered modern culture hearths because their major cultural ideas have spread throughout much of the world. §Take for instance the popularity of sushi--cultural diffusion from Tokyo. §The presence of Starbucks in places like France, Germany, Moscow, and even in China is cultural diffusion from the United States.
Modern Culture Hearths and Cultural Diffusion §Because cultures develop over time, new dominant areas of dominant culture do to. §Today's modern culture hearths are places such as the United States and major world cities like London and Tokyo. §Areas such as these are considered modern culture hearths because their major cultural ideas have spread throughout much of the world. §Take for instance the popularity of sushi--cultural diffusion from Tokyo. §The presence of Starbucks in places like France, Germany, Moscow, and even in China is cultural diffusion from the United States.
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 DEFINITION Culture Hearth: - heartland - source area - innovation center - place of origin of a major culture * “civilization incubator”
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 DEFINITION Culture Hearth: - heartland - source area - innovation center - place of origin of a major culture * “civilization incubator”
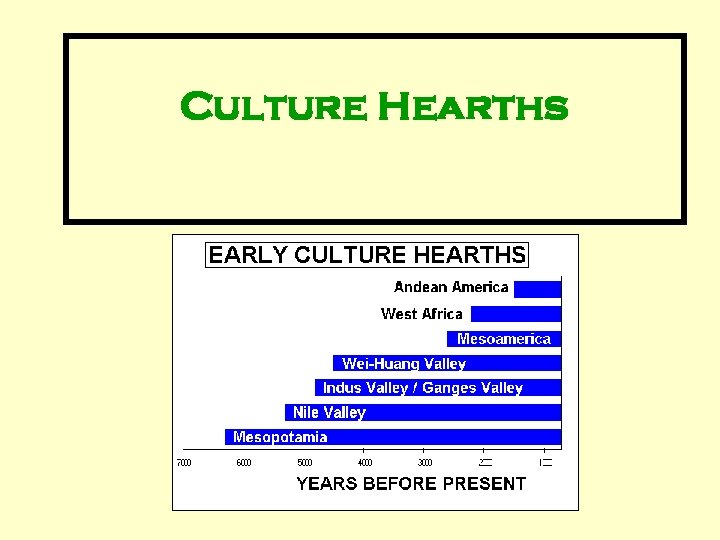
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 Primary Culture Hearths of the World: Fertile Crescent (8000 BCE) India (7000 BCE) Huang Ho (5000 BCE) West Africa (2000 BCE) Mesoamerica & S. America (8000 -3000 BCE) A cultural hearth is the heartland of a particular culture.
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 Primary Culture Hearths of the World: Fertile Crescent (8000 BCE) India (7000 BCE) Huang Ho (5000 BCE) West Africa (2000 BCE) Mesoamerica & S. America (8000 -3000 BCE) A cultural hearth is the heartland of a particular culture.
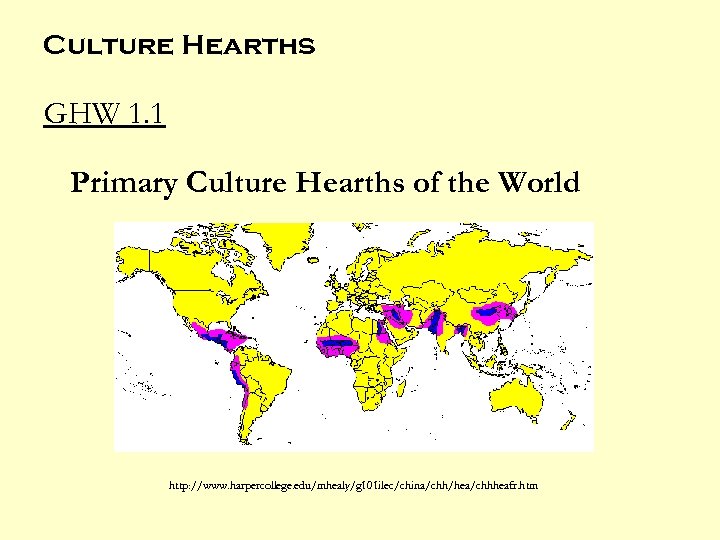 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 Primary Culture Hearths of the World http: //www. harpercollege. edu/mhealy/g 101 ilec/china/chh/hea/chhheafr. htm
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 Primary Culture Hearths of the World http: //www. harpercollege. edu/mhealy/g 101 ilec/china/chh/hea/chhheafr. htm
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 Fertile Crescent location: - Neolithic Revolution ca. 8000 BCE - several early settlements: Jericho et al. - organized societies appear concurrently: Mesopotamia: Sumer (3200) Unification of Egypt (3100)
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 Fertile Crescent location: - Neolithic Revolution ca. 8000 BCE - several early settlements: Jericho et al. - organized societies appear concurrently: Mesopotamia: Sumer (3200) Unification of Egypt (3100)
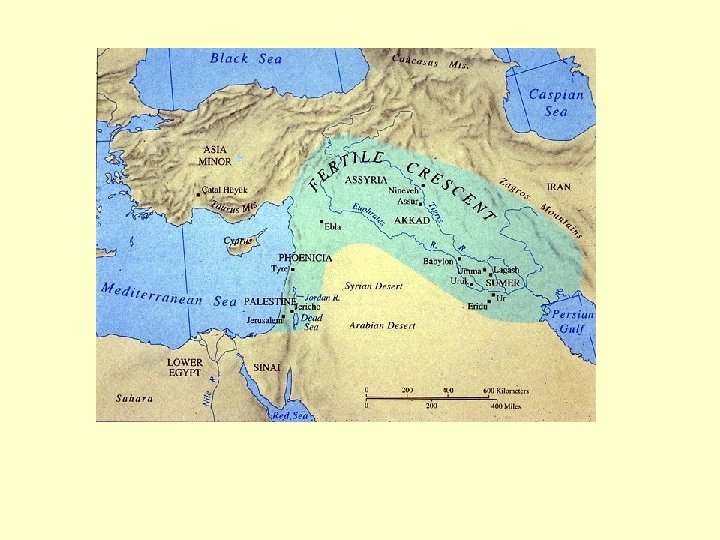
 Mesopotamia • for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modernday Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran. • Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires
Mesopotamia • for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modernday Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran. • Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the Akkadian, Babylonian and Assyrian empires
 Mesopotamia • As early as 500 B. C people were farming in Southern Mesopotamia. This flat swampy region was well suited for agriculture. • The Tigris and Euphrates rivers often flooded there in the spring. • The floods left behind a fertile mud called silt, which enriched the soil. • It’s geography led to the developing methods to control water.
Mesopotamia • As early as 500 B. C people were farming in Southern Mesopotamia. This flat swampy region was well suited for agriculture. • The Tigris and Euphrates rivers often flooded there in the spring. • The floods left behind a fertile mud called silt, which enriched the soil. • It’s geography led to the developing methods to control water.
 Mesopotamia • Early civilizations first developed in Mesopotamia over six thousand years ago. Some of the first cities were established. • A writing system was developed. • Empires were created and monumental buildings were constructed.
Mesopotamia • Early civilizations first developed in Mesopotamia over six thousand years ago. Some of the first cities were established. • A writing system was developed. • Empires were created and monumental buildings were constructed.
 Mesopotamia • People created methods to control water. • They dug basins (holes) to store rainwater, and cannels to carry water to fields and dikes to control flooding. • As a result of their water projects they had to assign jobs and allocate resources. Resulting in appointed leaders and government formed.
Mesopotamia • People created methods to control water. • They dug basins (holes) to store rainwater, and cannels to carry water to fields and dikes to control flooding. • As a result of their water projects they had to assign jobs and allocate resources. Resulting in appointed leaders and government formed.
 Sumerian Culture • Sumerian’s developed the first writing called cuneiform. • To produce this writing they had to chisel into stone or clay tablets using a sharp tool called styluses.
Sumerian Culture • Sumerian’s developed the first writing called cuneiform. • To produce this writing they had to chisel into stone or clay tablets using a sharp tool called styluses.

 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 India: - early agricultural sites date from 7000 BCE - Harappan society arises ca. 3000 - dependent upon rich floodplains of Indus - develop cotton textiles & dyes by 2000 - impt. trade contacts w/ Fertile Crescent - Aryan migration into India ca. 1500
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 India: - early agricultural sites date from 7000 BCE - Harappan society arises ca. 3000 - dependent upon rich floodplains of Indus - develop cotton textiles & dyes by 2000 - impt. trade contacts w/ Fertile Crescent - Aryan migration into India ca. 1500
 India’s Geography • One of the greatest river valley civilizations originated along the Indus River. – Flows across the NW edge of the Indian subcontinent. • Subcontinent is divided into 3 geographic zones: – Far North: Himalaya and Hindu Kush mountains – Northern Plains: middle of the subcontinent – Southern part: Deccan Plateau • Flooding in the Northern Plains is caused by heavy rains – Monsoon: season winds – India’s first civilization depended on the monsoons to bring water. – Could also destroy crops and homes.
India’s Geography • One of the greatest river valley civilizations originated along the Indus River. – Flows across the NW edge of the Indian subcontinent. • Subcontinent is divided into 3 geographic zones: – Far North: Himalaya and Hindu Kush mountains – Northern Plains: middle of the subcontinent – Southern part: Deccan Plateau • Flooding in the Northern Plains is caused by heavy rains – Monsoon: season winds – India’s first civilization depended on the monsoons to bring water. – Could also destroy crops and homes.
 Indus Valley Civilization • Hunters and gathers: first people here • Farming communities came second – These communities grew into India’s first civilization. • Civilization started around 2500 BC when a system of writing was developed. – 2 large cities: Harappa and Mohenjo Darao • Sometimes called the Harappan civilization because of the ruins found. • Civilizations were carefully planned; suggesting a strong central authority. • Economy: focus on agriculture and trade. • Reasons for decline: flooding, disappearance of the river; invasion and disease.
Indus Valley Civilization • Hunters and gathers: first people here • Farming communities came second – These communities grew into India’s first civilization. • Civilization started around 2500 BC when a system of writing was developed. – 2 large cities: Harappa and Mohenjo Darao • Sometimes called the Harappan civilization because of the ruins found. • Civilizations were carefully planned; suggesting a strong central authority. • Economy: focus on agriculture and trade. • Reasons for decline: flooding, disappearance of the river; invasion and disease.
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 Huang Ho (Yellow River): - Neolithic Revolution ca. 5000 BCE - rich soils but floods = need for dikes, dredging - small societies flourish, 5000 -3000 BCE - emergence of centralizing hereditary monarchies: Xia (ca. 2200 -1750) & Shang (ca. 1750 -1100) - major influence of Indo-Europeans: bronze, chariots - Zhou dynasty (1122 -256): classical Chinese civilization
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 Huang Ho (Yellow River): - Neolithic Revolution ca. 5000 BCE - rich soils but floods = need for dikes, dredging - small societies flourish, 5000 -3000 BCE - emergence of centralizing hereditary monarchies: Xia (ca. 2200 -1750) & Shang (ca. 1750 -1100) - major influence of Indo-Europeans: bronze, chariots - Zhou dynasty (1122 -256): classical Chinese civilization
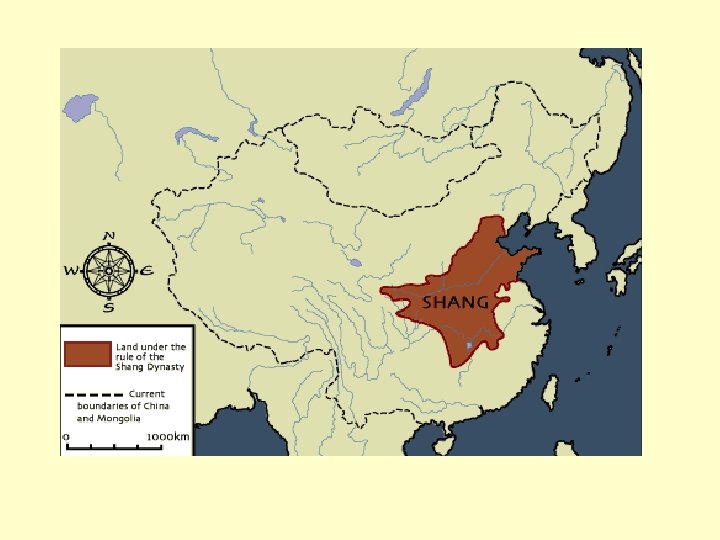
 China’s Geography • The first Chinese civilizations grew in river valleys created by: – The Chang Jiang river (AKA the Yangzi) – The Huang He River (AKA the Yellow River) • First civilization here was ruled by the Xia dynasty. • Annual floods left behind rich soil in both valleys. • The Huang He valley also benefited from losses (a fine dusty soil carried into China by desert winds). • Mountains, hills and desert protected early Chinese civilizations from invaders.
China’s Geography • The first Chinese civilizations grew in river valleys created by: – The Chang Jiang river (AKA the Yangzi) – The Huang He River (AKA the Yellow River) • First civilization here was ruled by the Xia dynasty. • Annual floods left behind rich soil in both valleys. • The Huang He valley also benefited from losses (a fine dusty soil carried into China by desert winds). • Mountains, hills and desert protected early Chinese civilizations from invaders.
 The Shang Dynasty • Since no evidence if the Xia dynasty has been found, most historians date Chinese civilization to the beginning of the Shang dynasty; around 1766 BC. • Most Shang kings ruled their capital of Anyang where they were surrounded by a court (gathering of wealthy nobles). • Shang rulers appointed governors to keep order in distant parts of the kingdom. • Most people in Shang China were farmers. • The Shang believed in an afterlife in which a ruler would still need his riches and servants. • Shang religion centered on ancestor worship. – Used oracle bones to seek advice from dead ancestors. • Were skilled at making items out of bronze, learned how to build huge structures and created a precise calendar based on the cycles of the moon.
The Shang Dynasty • Since no evidence if the Xia dynasty has been found, most historians date Chinese civilization to the beginning of the Shang dynasty; around 1766 BC. • Most Shang kings ruled their capital of Anyang where they were surrounded by a court (gathering of wealthy nobles). • Shang rulers appointed governors to keep order in distant parts of the kingdom. • Most people in Shang China were farmers. • The Shang believed in an afterlife in which a ruler would still need his riches and servants. • Shang religion centered on ancestor worship. – Used oracle bones to seek advice from dead ancestors. • Were skilled at making items out of bronze, learned how to build huge structures and created a precise calendar based on the cycles of the moon.
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 West Africa: - early Sudanic agricultural influence - incremental Bantu migrations, 3000 -1000 BCE - spread across central and southern Africa - enabled by agricultural surpluses & iron - diffusion: - W. African yams & grains - 90 million Bantu-speakers today
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 West Africa: - early Sudanic agricultural influence - incremental Bantu migrations, 3000 -1000 BCE - spread across central and southern Africa - enabled by agricultural surpluses & iron - diffusion: - W. African yams & grains - 90 million Bantu-speakers today
 Impact of Geography • Africa has four distinct climate zones: – Mild climate of the north: 10% – Sahara and Kalahari Deserts: 40% – Rain forest: 10% – Savannas: 40%
Impact of Geography • Africa has four distinct climate zones: – Mild climate of the north: 10% – Sahara and Kalahari Deserts: 40% – Rain forest: 10% – Savannas: 40%
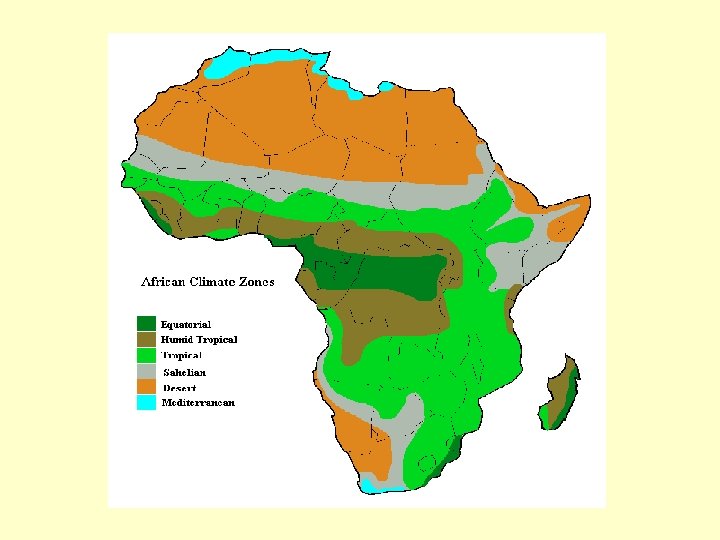
 Impact of Geography • Landforms of Africa: – In the north, mountains run along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea. – The Nile River empties into the Mediterranean, and the Sahara is the largest desert in the world. – The so-called hump of Africa extends to the Atlantic Ocean in the west. Here the Sahara gradually gives way to grasslands, while the coastal regions are mostly tropical jungles.
Impact of Geography • Landforms of Africa: – In the north, mountains run along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea. – The Nile River empties into the Mediterranean, and the Sahara is the largest desert in the world. – The so-called hump of Africa extends to the Atlantic Ocean in the west. Here the Sahara gradually gives way to grasslands, while the coastal regions are mostly tropical jungles.
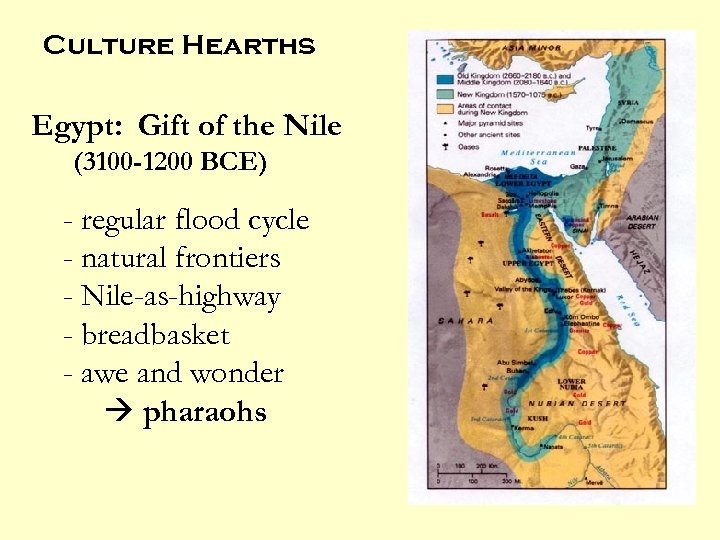 Culture Hearths Egypt: Gift of the Nile (3100 -1200 BCE) - regular flood cycle - natural frontiers - Nile-as-highway - breadbasket - awe and wonder pharaohs
Culture Hearths Egypt: Gift of the Nile (3100 -1200 BCE) - regular flood cycle - natural frontiers - Nile-as-highway - breadbasket - awe and wonder pharaohs
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 2 Egypt: 2 nd Pyramid of Giza (Khafra, 2558 -2532)
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 2 Egypt: 2 nd Pyramid of Giza (Khafra, 2558 -2532)
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 2 Common Factors of Decline: - increased contacts with hostile neighbors - ecological degradation & exhaustion - over-attractive agricultural hearths (? ) - internal disorder all in evidence in Egypt by 1200 BCE
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 2 Common Factors of Decline: - increased contacts with hostile neighbors - ecological degradation & exhaustion - over-attractive agricultural hearths (? ) - internal disorder all in evidence in Egypt by 1200 BCE
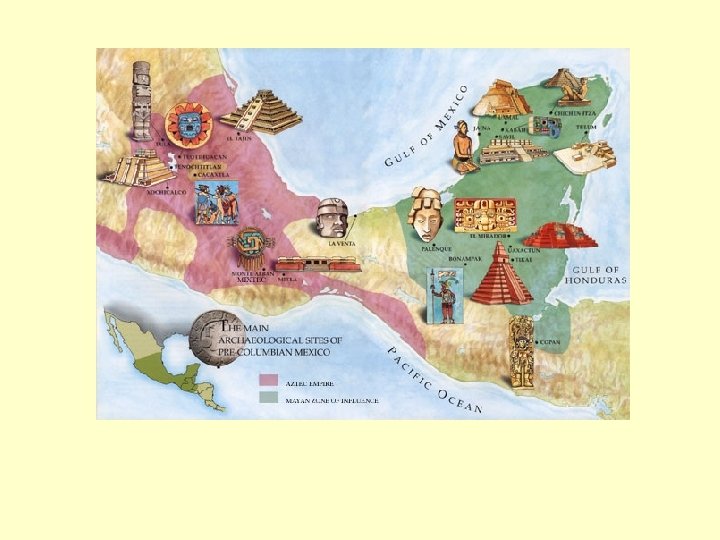
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 Mesoamerica & South America: - migrations to W. hemisphere ca. 13, 000 BCE(? ) - early agriculture in Mesoamerica by 7000 - maize cultivation begins ca. 4000 - no large domestic animals (hence no wheel) - only small villages; no large cities until later - Olmec rulers (fl. 1200 -400) compel building of large ritual centers, drainage projects, & artistic objects (heads) - Olmec destroy own civilization; Maya inherit later
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 1 Mesoamerica & South America: - migrations to W. hemisphere ca. 13, 000 BCE(? ) - early agriculture in Mesoamerica by 7000 - maize cultivation begins ca. 4000 - no large domestic animals (hence no wheel) - only small villages; no large cities until later - Olmec rulers (fl. 1200 -400) compel building of large ritual centers, drainage projects, & artistic objects (heads) - Olmec destroy own civilization; Maya inherit later
 Maya, Aztec, and Inca Civilizations
Maya, Aztec, and Inca Civilizations
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 3 Columbian Exchange and European Conquerors the radical global diffusion of: - people - animals - ideas * plants & food crops * pathogens
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 3 Columbian Exchange and European Conquerors the radical global diffusion of: - people - animals - ideas * plants & food crops * pathogens
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 3 EXAMPLE Columbian Exchange: DEMOGRAPHICS New World: disaster - smallpox, measles, influenza, et al. - 90% mortality - s. 16 -18: 100 million dead - adult losses = esp. devastating
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 3 EXAMPLE Columbian Exchange: DEMOGRAPHICS New World: disaster - smallpox, measles, influenza, et al. - 90% mortality - s. 16 -18: 100 million dead - adult losses = esp. devastating
 Columbian Exchange: SMALLPOX http: //www. bt. cdc. gov/agent/smallpox-images/smallpox 1. htm
Columbian Exchange: SMALLPOX http: //www. bt. cdc. gov/agent/smallpox-images/smallpox 1. htm
 Culture Hearths GHW 1. 3 Columbian Exchange: DEMOGRAPHICS Old World: boon - new crops = population explosion - s. 16 -18: growth of 475 million! - European pol & econ expansion WORLD HEGEMONY
Culture Hearths GHW 1. 3 Columbian Exchange: DEMOGRAPHICS Old World: boon - new crops = population explosion - s. 16 -18: growth of 475 million! - European pol & econ expansion WORLD HEGEMONY


