2075158fbf71c3f7df52ff6dd5a2bd80.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 Culture and Organisation in a Multinational Firm
Culture and Organisation in a Multinational Firm
 Structure of the presentation • Meaning of culture • Cultrural dimensions -national culture *Trompenaars and Hofstede -organizational culture • Case study
Structure of the presentation • Meaning of culture • Cultrural dimensions -national culture *Trompenaars and Hofstede -organizational culture • Case study
 What’s culture? • A shared system of meanings • About groups-not about individual behavior • Learned-not inherited • Transgenerational • Patterned • Not “wright” or “wrong”
What’s culture? • A shared system of meanings • About groups-not about individual behavior • Learned-not inherited • Transgenerational • Patterned • Not “wright” or “wrong”
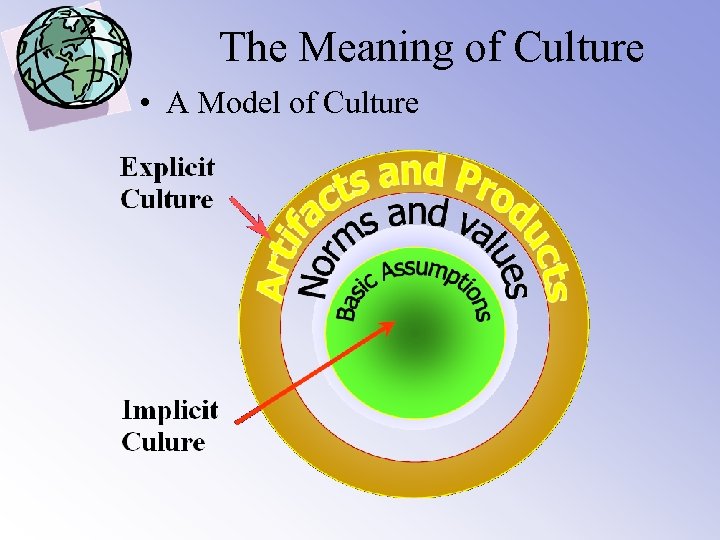 The Meaning of Culture • A Model of Culture
The Meaning of Culture • A Model of Culture
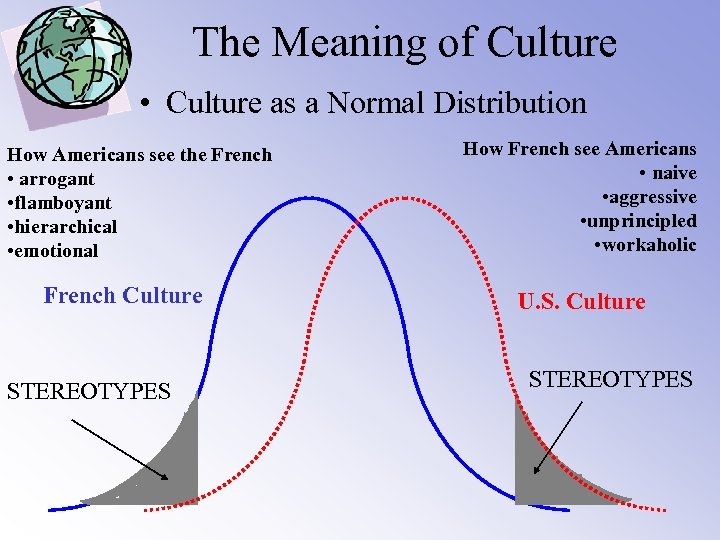 The Meaning of Culture • Culture as a Normal Distribution How Americans see the French • arrogant • flamboyant • hierarchical • emotional French Culture STEREOTYPES How French see Americans • naive • aggressive • unprincipled • workaholic U. S. Culture STEREOTYPES
The Meaning of Culture • Culture as a Normal Distribution How Americans see the French • arrogant • flamboyant • hierarchical • emotional French Culture STEREOTYPES How French see Americans • naive • aggressive • unprincipled • workaholic U. S. Culture STEREOTYPES
 Is their one best way of managing and organising? • No! Why? • Each culture has different meanings • One fact can have different meanings in different cultures • Example : the walkman • Hofstede and Trompenaars
Is their one best way of managing and organising? • No! Why? • Each culture has different meanings • One fact can have different meanings in different cultures • Example : the walkman • Hofstede and Trompenaars
 Cultural differences : Trompenaars • • Universalism-particularism Individualism-communitarianisme Neutral-emotional Specific-diffuse Achievement-ascription Sequential-synchronic Inner-directed and outer-directed
Cultural differences : Trompenaars • • Universalism-particularism Individualism-communitarianisme Neutral-emotional Specific-diffuse Achievement-ascription Sequential-synchronic Inner-directed and outer-directed
 1. Universalism-Particularism Universalism Particularism • • • Flexibility • It depends on the circumstance • Make exeptions • At ease with ambiguity Consistency Standards and rules Clarity Uniform procedures
1. Universalism-Particularism Universalism Particularism • • • Flexibility • It depends on the circumstance • Make exeptions • At ease with ambiguity Consistency Standards and rules Clarity Uniform procedures
 1. Universalism-Particularism • A Car Accident What right has your friend? A. My friend has a definite right as a friend to expect me to testify to the lower figure. B. He has some right as a friend to expect me to testify to the lower figure. C. He has no right as a friend to expect me to testify to the lower figure.
1. Universalism-Particularism • A Car Accident What right has your friend? A. My friend has a definite right as a friend to expect me to testify to the lower figure. B. He has some right as a friend to expect me to testify to the lower figure. C. He has no right as a friend to expect me to testify to the lower figure.

 2. Individualism. Communitarianism Individualism Communitarianism • I • Achieving alone • Ex. Vacations taken in pairs, even alone • We (part of a group) • Decisions taken in group • Ex. Vacations in group
2. Individualism. Communitarianism Individualism Communitarianism • I • Achieving alone • Ex. Vacations taken in pairs, even alone • We (part of a group) • Decisions taken in group • Ex. Vacations in group

 3. Neutral-Affective Neutral Affective • Do not reveal what they are, thinking or feeling • Cool • Seem monotone • Physical contact = taboo • Reveal thoughts and feelings • Emotional • Heated, vital and animated • Seem dramatical
3. Neutral-Affective Neutral Affective • Do not reveal what they are, thinking or feeling • Cool • Seem monotone • Physical contact = taboo • Reveal thoughts and feelings • Emotional • Heated, vital and animated • Seem dramatical

 4. Specific-Diffuse Specific • Principles and behaviour independent of the person being addressed • Work and life are separated • Direct, to the point, purposeful in relating Diffuse • Everything depends of the context and the person • Work and private life are often very close • Indirect, seemingly aimless forms of relating
4. Specific-Diffuse Specific • Principles and behaviour independent of the person being addressed • Work and life are separated • Direct, to the point, purposeful in relating Diffuse • Everything depends of the context and the person • Work and private life are often very close • Indirect, seemingly aimless forms of relating
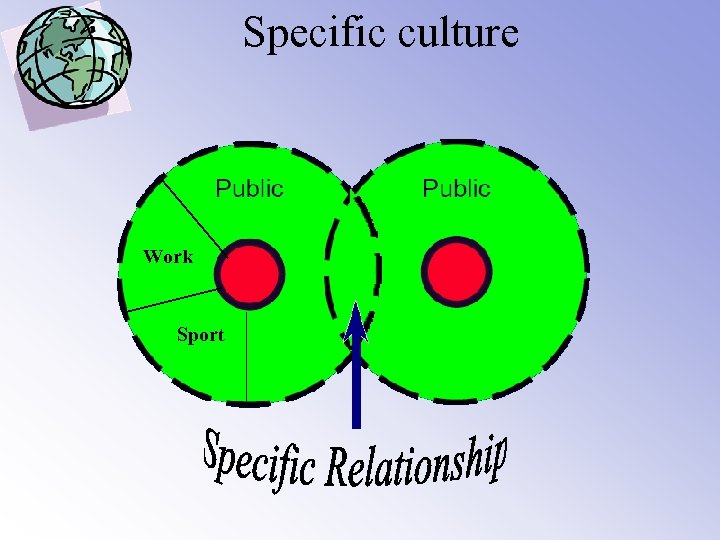 Specific culture Work Sport
Specific culture Work Sport
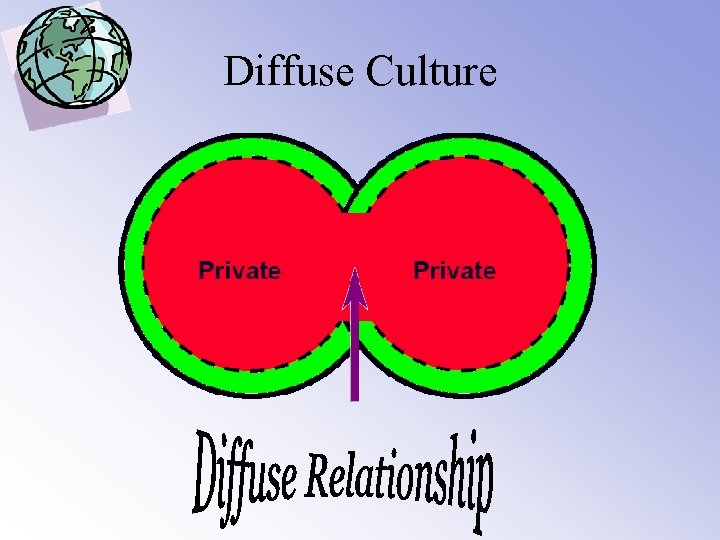 Diffuse Culture
Diffuse Culture
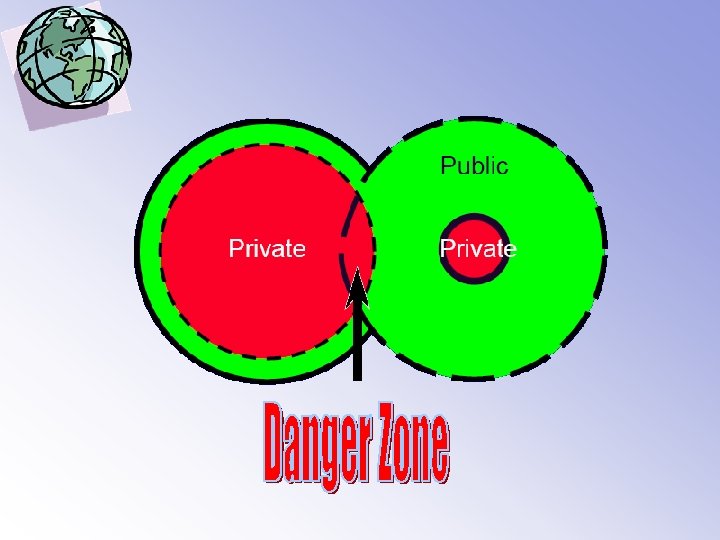
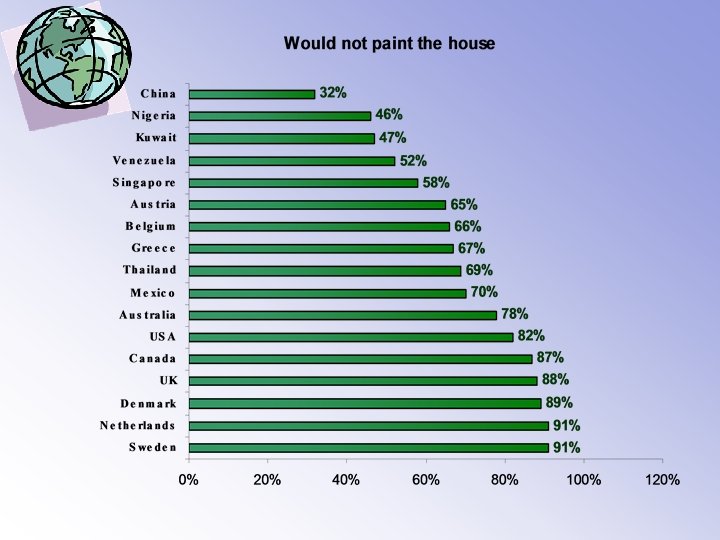
 A Boss asking to paint the house • The colleague argues You don’t have to paint the house if you don’t feel like it. He is your boss in the company. Ouside the company, he has little authority. • The subordinate argues: Despite the fact that I don’t feel like it, I will paint the house anyway. He is my boss and you cannot ignore it outside your work either.
A Boss asking to paint the house • The colleague argues You don’t have to paint the house if you don’t feel like it. He is your boss in the company. Ouside the company, he has little authority. • The subordinate argues: Despite the fact that I don’t feel like it, I will paint the house anyway. He is my boss and you cannot ignore it outside your work either.
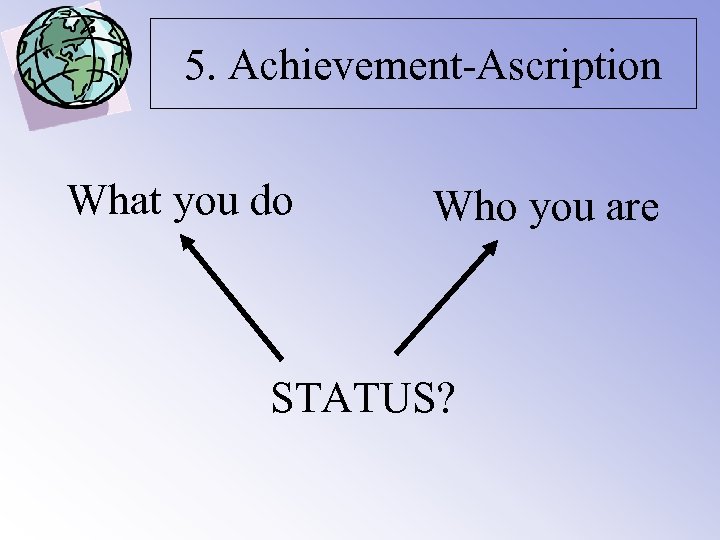 5. Achievement-Ascription What you do Who you are STATUS?
5. Achievement-Ascription What you do Who you are STATUS?
 5. Achievement-Ascription Achievement • Competence determines status • Respect is based on achieving your job • Senior managers are of varying age Ascription • Extensive use of titles(who you are) • Respect is gained through your status (background) • Senior manager is mostly male, middle-aged and qualified by his background
5. Achievement-Ascription Achievement • Competence determines status • Respect is based on achieving your job • Senior managers are of varying age Ascription • Extensive use of titles(who you are) • Respect is gained through your status (background) • Senior manager is mostly male, middle-aged and qualified by his background
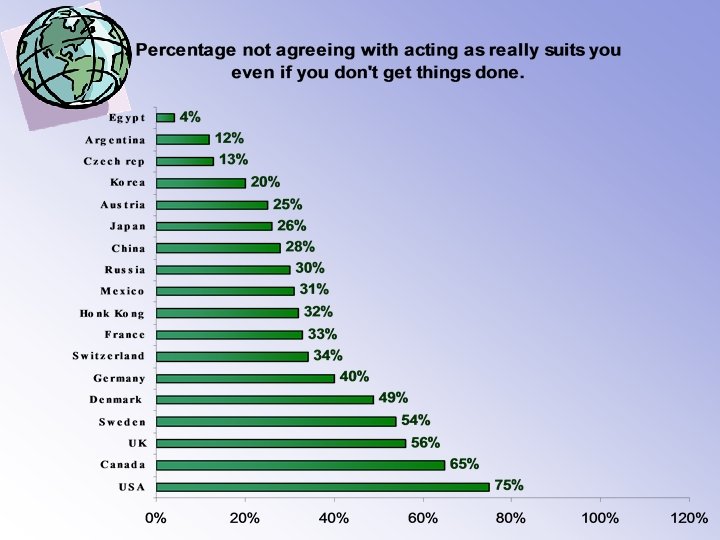
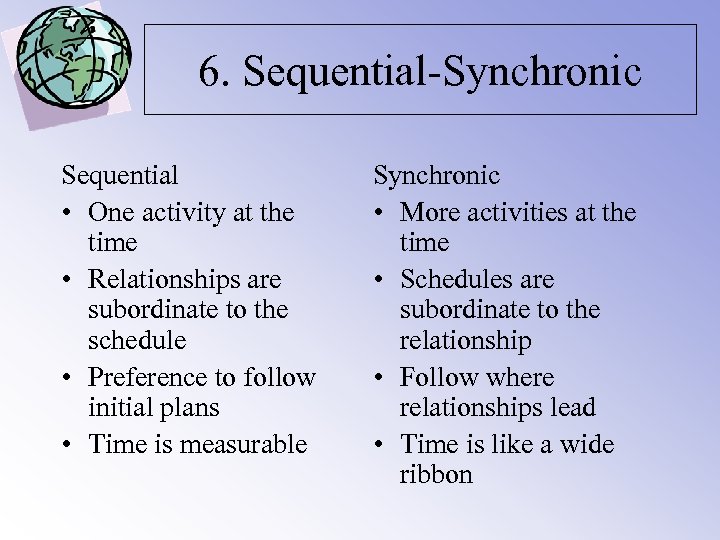 6. Sequential-Synchronic Sequential • One activity at the time • Relationships are subordinate to the schedule • Preference to follow initial plans • Time is measurable Synchronic • More activities at the time • Schedules are subordinate to the relationship • Follow where relationships lead • Time is like a wide ribbon
6. Sequential-Synchronic Sequential • One activity at the time • Relationships are subordinate to the schedule • Preference to follow initial plans • Time is measurable Synchronic • More activities at the time • Schedules are subordinate to the relationship • Follow where relationships lead • Time is like a wide ribbon
 7. Inner-directed VS outer-directed Inner-directed Outer-directed • Environment is in • I am in control • Dominating attitude • Flexible attitude, • Discomfort when the willing to compromise environment seems out • Comfort with of control waves, cycles if these are natural
7. Inner-directed VS outer-directed Inner-directed Outer-directed • Environment is in • I am in control • Dominating attitude • Flexible attitude, • Discomfort when the willing to compromise environment seems out • Comfort with of control waves, cycles if these are natural
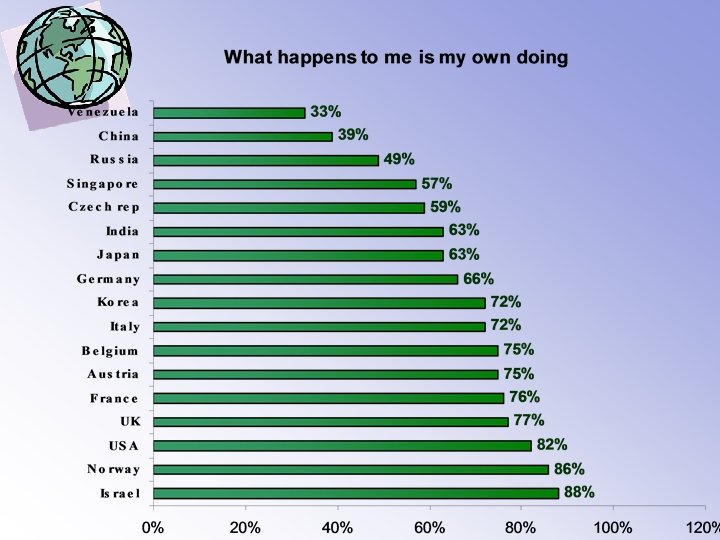
 Cultural differences : Geert Hofstede • Power distance • Uncertainty avoidance • Individualism • mascunility
Cultural differences : Geert Hofstede • Power distance • Uncertainty avoidance • Individualism • mascunility
 1. Power distance the extent to which power is accepted High power distance Low power distance • • • Flat structure • Decentralized • Less supervisory personnel Obey blindly Steep structure Centralized A lot of supervisory personnel
1. Power distance the extent to which power is accepted High power distance Low power distance • • • Flat structure • Decentralized • Less supervisory personnel Obey blindly Steep structure Centralized A lot of supervisory personnel
 2 Uncertainty avoidance High avoidance Low avoidance • High need for security • Strong belief in experts • Important structures • More written rules • Lower labor turnover • Example: Germany Japan • Accepting risk • Life must go on Less structural • Fewer written rules • Higher labor turnover • Example: Great-Britain Denmark
2 Uncertainty avoidance High avoidance Low avoidance • High need for security • Strong belief in experts • Important structures • More written rules • Lower labor turnover • Example: Germany Japan • Accepting risk • Life must go on Less structural • Fewer written rules • Higher labor turnover • Example: Great-Britain Denmark
 3. Individualism-Collectivism Individualism Collectivism • I • Belonging to a group • Greater individual initiative • Less individual initiative
3. Individualism-Collectivism Individualism Collectivism • I • Belonging to a group • Greater individual initiative • Less individual initiative
 4. Masculinity • = dominant values are success, money and things • Earnings, recognition and achievement is important • Independent decision makers Femininity • = dominant values are caring for others and the quality of life • Cooperation • Friendly atmosphere • Employment security • Group decision makers
4. Masculinity • = dominant values are success, money and things • Earnings, recognition and achievement is important • Independent decision makers Femininity • = dominant values are caring for others and the quality of life • Cooperation • Friendly atmosphere • Employment security • Group decision makers
 Organizational culture • Definition of organizational culture • Characteristics • The interaction with national culture • Four categories for organizational culture
Organizational culture • Definition of organizational culture • Characteristics • The interaction with national culture • Four categories for organizational culture
 1/ Definition • Assumptions that are developed by a group through her existence • New members should adopt this way of thinking in order to fit with the organisation • The organizational culture of a MNC can differ a lot from one country to an other
1/ Definition • Assumptions that are developed by a group through her existence • New members should adopt this way of thinking in order to fit with the organisation • The organizational culture of a MNC can differ a lot from one country to an other
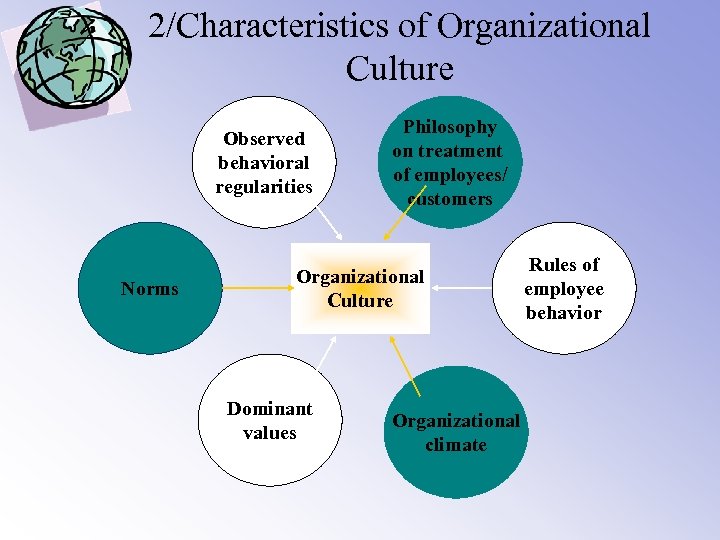 2/Characteristics of Organizational Culture Observed behavioral regularities Norms Philosophy on treatment of employees/ customers Organizational Culture Dominant values Organizational climate Rules of employee behavior
2/Characteristics of Organizational Culture Observed behavioral regularities Norms Philosophy on treatment of employees/ customers Organizational Culture Dominant values Organizational climate Rules of employee behavior
 3/ Interaction between national and organizational culture • National cultural values are significant • The values people bring to work can’t be changed easily
3/ Interaction between national and organizational culture • National cultural values are significant • The values people bring to work can’t be changed easily
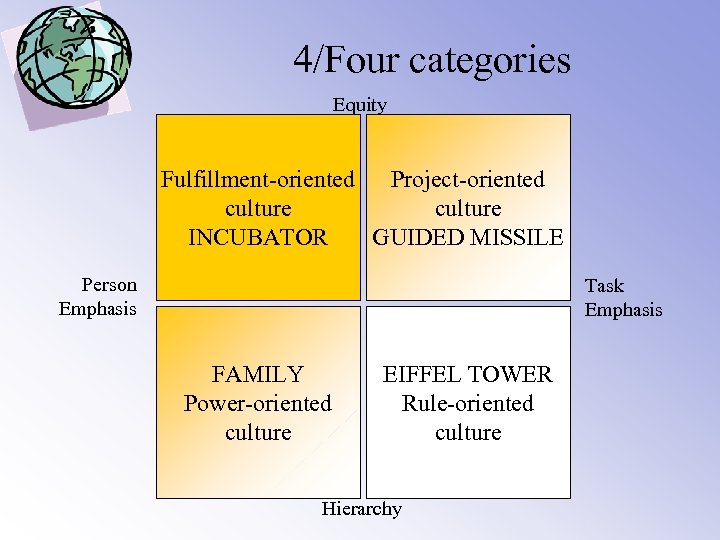 4/Four categories Equity Fulfillment-oriented Project-oriented culture INCUBATOR GUIDED MISSILE Person Emphasis Task Emphasis FAMILY Power-oriented culture EIFFEL TOWER Rule-oriented culture Hierarchy
4/Four categories Equity Fulfillment-oriented Project-oriented culture INCUBATOR GUIDED MISSILE Person Emphasis Task Emphasis FAMILY Power-oriented culture EIFFEL TOWER Rule-oriented culture Hierarchy
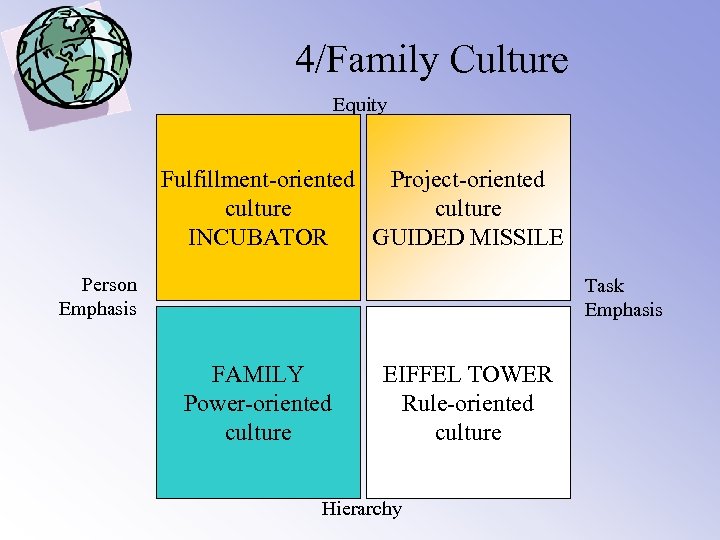 4/Family Culture Equity Fulfillment-oriented Project-oriented culture INCUBATOR GUIDED MISSILE Person Emphasis Task Emphasis FAMILY Power-oriented culture EIFFEL TOWER Rule-oriented culture Hierarchy
4/Family Culture Equity Fulfillment-oriented Project-oriented culture INCUBATOR GUIDED MISSILE Person Emphasis Task Emphasis FAMILY Power-oriented culture EIFFEL TOWER Rule-oriented culture Hierarchy
 4/ Family culture • • Power-oriented culture Diffuse relationships Status is ascribed (parent figures) Intuitive and error-correcting way of thinking People are seen like family members Father makes the changes Management by subjectives In conflict: do not lose your power
4/ Family culture • • Power-oriented culture Diffuse relationships Status is ascribed (parent figures) Intuitive and error-correcting way of thinking People are seen like family members Father makes the changes Management by subjectives In conflict: do not lose your power
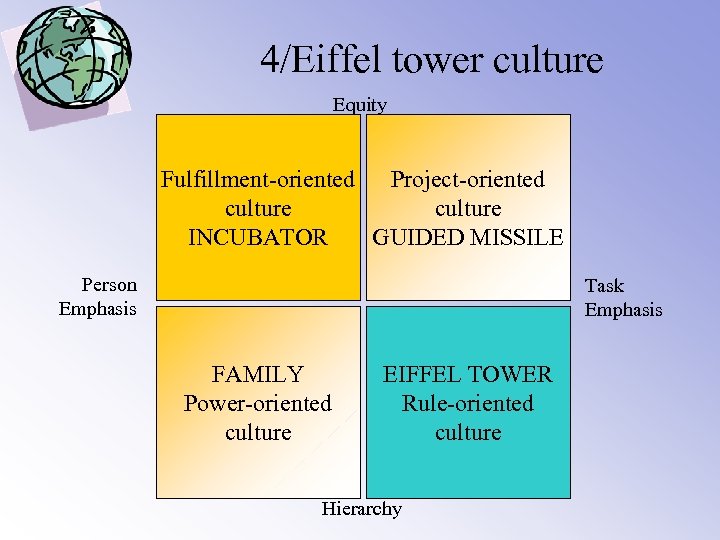 4/Eiffel tower culture Equity Fulfillment-oriented Project-oriented culture INCUBATOR GUIDED MISSILE Person Emphasis Task Emphasis FAMILY Power-oriented culture EIFFEL TOWER Rule-oriented culture Hierarchy
4/Eiffel tower culture Equity Fulfillment-oriented Project-oriented culture INCUBATOR GUIDED MISSILE Person Emphasis Task Emphasis FAMILY Power-oriented culture EIFFEL TOWER Rule-oriented culture Hierarchy
 4/ eiffel tower culture • • • Role-oriented culture Specific relationships Status is ascribed to superior roles Rationally thinking People are seen like human ressources Change through rules and procedures Management by job description Criticism is accusation of irrationalism Everything is planned, structured
4/ eiffel tower culture • • • Role-oriented culture Specific relationships Status is ascribed to superior roles Rationally thinking People are seen like human ressources Change through rules and procedures Management by job description Criticism is accusation of irrationalism Everything is planned, structured
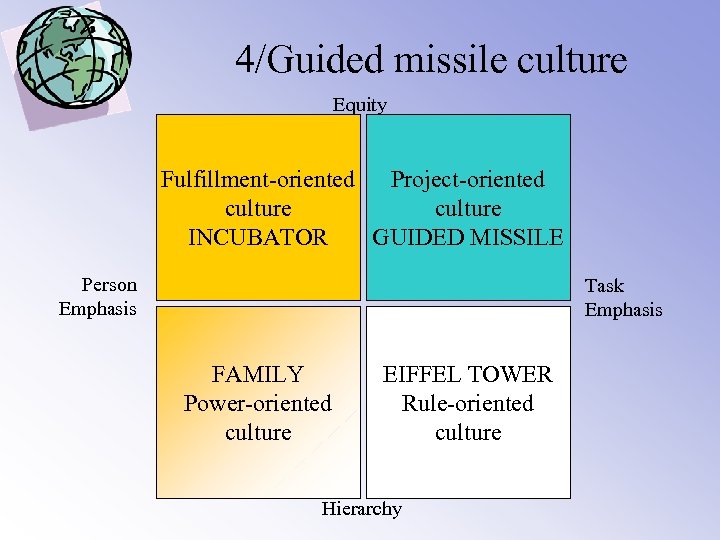 4/Guided missile culture Equity Fulfillment-oriented Project-oriented culture INCUBATOR GUIDED MISSILE Person Emphasis Task Emphasis FAMILY Power-oriented culture EIFFEL TOWER Rule-oriented culture Hierarchy
4/Guided missile culture Equity Fulfillment-oriented Project-oriented culture INCUBATOR GUIDED MISSILE Person Emphasis Task Emphasis FAMILY Power-oriented culture EIFFEL TOWER Rule-oriented culture Hierarchy
 4/ Guided missile culture • • • Project-oriented culture Egalitarian and task-oriented Specific relationships Problem centered way of thinking People are seen as experts Management by objectives
4/ Guided missile culture • • • Project-oriented culture Egalitarian and task-oriented Specific relationships Problem centered way of thinking People are seen as experts Management by objectives
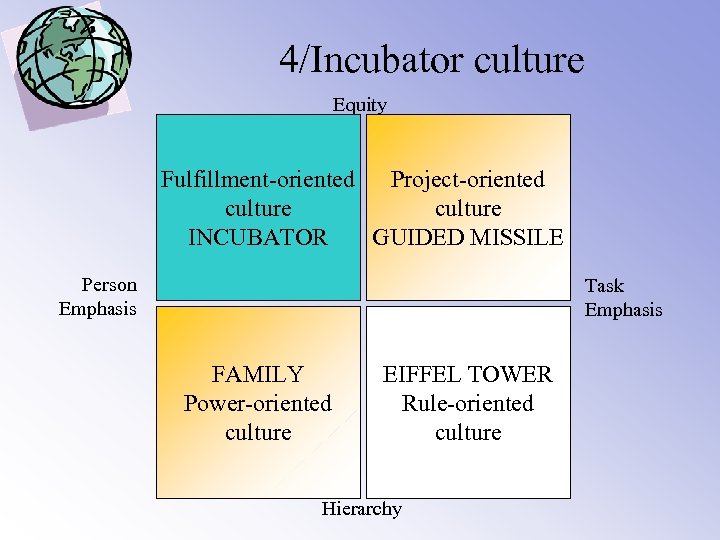 4/Incubator culture Equity Fulfillment-oriented Project-oriented culture INCUBATOR GUIDED MISSILE Person Emphasis Task Emphasis FAMILY Power-oriented culture EIFFEL TOWER Rule-oriented culture Hierarchy
4/Incubator culture Equity Fulfillment-oriented Project-oriented culture INCUBATOR GUIDED MISSILE Person Emphasis Task Emphasis FAMILY Power-oriented culture EIFFEL TOWER Rule-oriented culture Hierarchy
 4/ Incubator culture • • Self-fulfilment oriented culture No structure Diffuse relationships Thinking is process-oriented and creative People are seen as co-creators Change is improvised Management by enthusiasm
4/ Incubator culture • • Self-fulfilment oriented culture No structure Diffuse relationships Thinking is process-oriented and creative People are seen as co-creators Change is improvised Management by enthusiasm
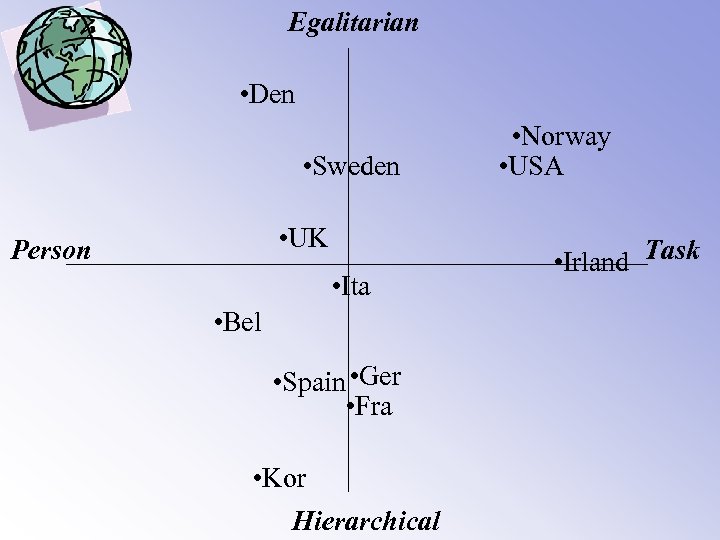 Egalitarian • Den • Sweden • UK Person • Ita • Bel • Spain • Ger • Fra • Kor Hierarchical • Norway • USA • Irland Task
Egalitarian • Den • Sweden • UK Person • Ita • Bel • Spain • Ger • Fra • Kor Hierarchical • Norway • USA • Irland Task
 Managing Cultural Differences Process Reconciliation Resolve cultural differences Respect Appreciate cultural differences Recognition Increase awareness of one’s own cultural perception Time
Managing Cultural Differences Process Reconciliation Resolve cultural differences Respect Appreciate cultural differences Recognition Increase awareness of one’s own cultural perception Time
 CASE Cultural Transformation at NUMMI
CASE Cultural Transformation at NUMMI
 NUMMI • Joint venture between Generals Motors and Toyota • US and Japanese culture needed mixed up • In order to get success, some differences needed to be reconciliated
NUMMI • Joint venture between Generals Motors and Toyota • US and Japanese culture needed mixed up • In order to get success, some differences needed to be reconciliated
 Cultural Reconciliation Universalist Particularist • Obligation to report problems in order to improve system • Differences of opinion are accepted and valued • Flexibility of work rules • Tolerant atmosphere
Cultural Reconciliation Universalist Particularist • Obligation to report problems in order to improve system • Differences of opinion are accepted and valued • Flexibility of work rules • Tolerant atmosphere
 Cultural Reconciliation Individualist Communitarist • Employment security • Participative decision making • Plant collective discipline • Managers closer to employees in order to give them support • Creation of open offices, communal cafetaria • Flat wage structure
Cultural Reconciliation Individualist Communitarist • Employment security • Participative decision making • Plant collective discipline • Managers closer to employees in order to give them support • Creation of open offices, communal cafetaria • Flat wage structure
 Cultural Reconciliation Specific Diffuse • More than a workplace • Focus on quality and process rather than quantity • Building-trust first in order to achieve results
Cultural Reconciliation Specific Diffuse • More than a workplace • Focus on quality and process rather than quantity • Building-trust first in order to achieve results
 Cultural Reconciliation Achievement Ascription • Past achievement has no importance • More respect for the status of the superior
Cultural Reconciliation Achievement Ascription • Past achievement has no importance • More respect for the status of the superior
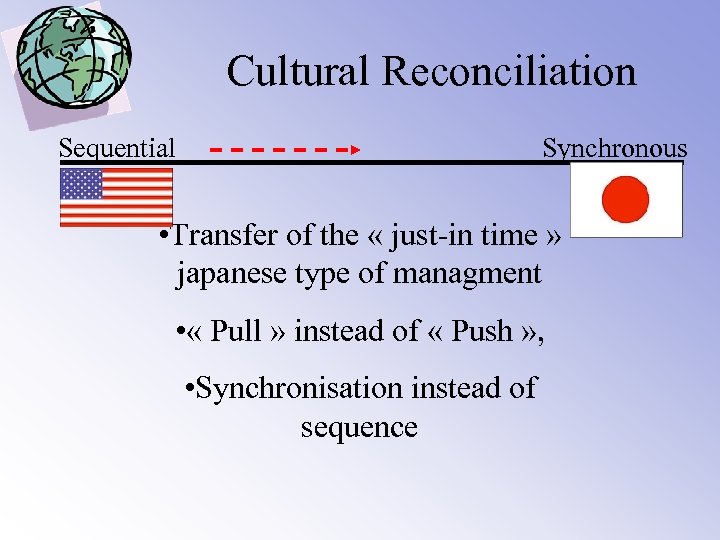 Cultural Reconciliation Sequential Synchronous • Transfer of the « just-in time » japanese type of managment • « Pull » instead of « Push » , • Synchronisation instead of sequence
Cultural Reconciliation Sequential Synchronous • Transfer of the « just-in time » japanese type of managment • « Pull » instead of « Push » , • Synchronisation instead of sequence
 Cultural Reconciliation Inner-directed Outer-directed • Flexibility • Looking for the problem instead of someone responsible
Cultural Reconciliation Inner-directed Outer-directed • Flexibility • Looking for the problem instead of someone responsible
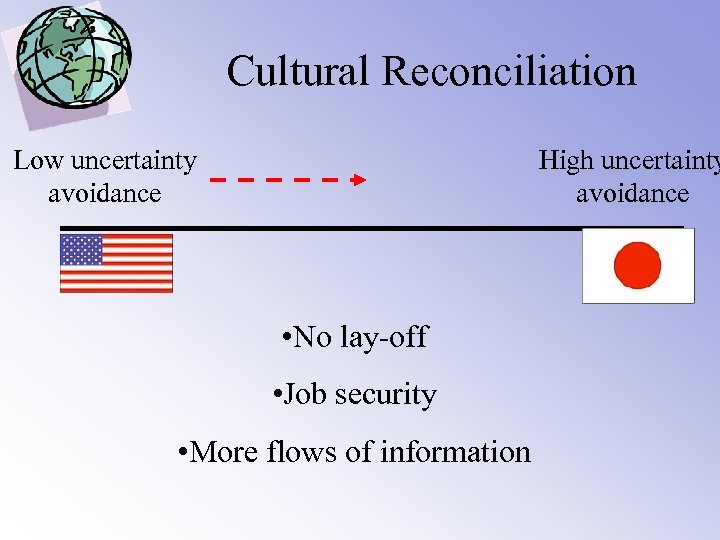 Cultural Reconciliation Low uncertainty avoidance High uncertainty avoidance • No lay-off • Job security • More flows of information
Cultural Reconciliation Low uncertainty avoidance High uncertainty avoidance • No lay-off • Job security • More flows of information
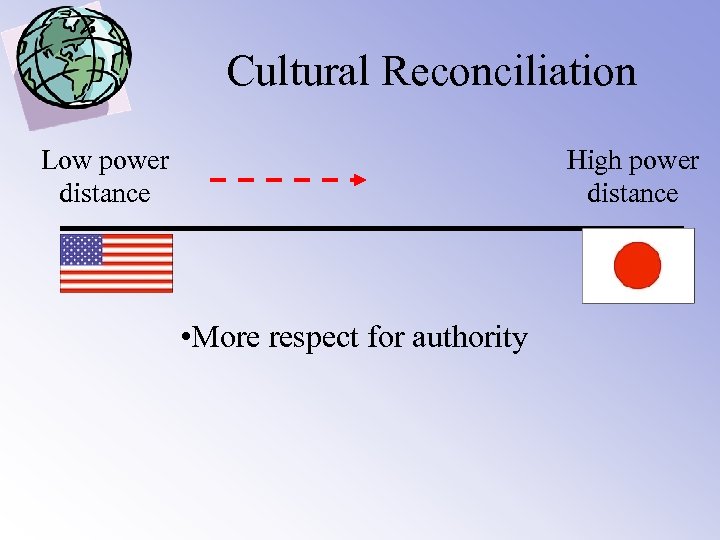 Cultural Reconciliation Low power distance High power distance • More respect for authority
Cultural Reconciliation Low power distance High power distance • More respect for authority
 NUMMI: Conclusion • Alone, Americans are much stronger than Japanese • In group the Japanese are much stronger than the Americans • Mix of two cultures can be beneficial for everybody • If you join two cultures and you can capture the positive points of both, you can get extraordinary results
NUMMI: Conclusion • Alone, Americans are much stronger than Japanese • In group the Japanese are much stronger than the Americans • Mix of two cultures can be beneficial for everybody • If you join two cultures and you can capture the positive points of both, you can get extraordinary results


