6afbf413874cc725a0d88c99b78700b7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 67
 Cultural Patterns and Processes
Cultural Patterns and Processes


 MMMMM… the Mc. Arabia • Three falafel balls, made from ground chickpeas and fava beans, fried in canola oil and served on Iraqi pita bread with tahini and chopped salad.
MMMMM… the Mc. Arabia • Three falafel balls, made from ground chickpeas and fava beans, fried in canola oil and served on Iraqi pita bread with tahini and chopped salad.
 Or maybe…POUTINE! • french fries, layered with cheese curds and smothered beneath brown gravy. Cheese curds are the solid parts of sour milk.
Or maybe…POUTINE! • french fries, layered with cheese curds and smothered beneath brown gravy. Cheese curds are the solid parts of sour milk.
 How about authentic Hawaiian food? • Spam is so popular in Hawaii it has been dubbed "The Hawaiian Steak, " so it is no surprise that Mc. Donald's put the meat in their Deluxe Breakfast. Eggs, rice, hashbrowns, spam and toast.
How about authentic Hawaiian food? • Spam is so popular in Hawaii it has been dubbed "The Hawaiian Steak, " so it is no surprise that Mc. Donald's put the meat in their Deluxe Breakfast. Eggs, rice, hashbrowns, spam and toast.
 Ole! Gazpacho
Ole! Gazpacho
 Cultural geography • The study of people’s lifestyles, their creations, and their relationships to the earth and the supernatural
Cultural geography • The study of people’s lifestyles, their creations, and their relationships to the earth and the supernatural
 Key questions • How do geographers define culture? • How do geographers look at spatial and place aspects of culture in the form of language, religion, race, ethnicity, and gender? • How are cultural patterns represented at different scales, from local to global? • How do cultural traits move through space and time? • What are key aspects to the geography of language and religion? • How does culture shape human-environment relationships? • How is culture expressed in landscapes, and how do different landscapes reflect different cultural identities?
Key questions • How do geographers define culture? • How do geographers look at spatial and place aspects of culture in the form of language, religion, race, ethnicity, and gender? • How are cultural patterns represented at different scales, from local to global? • How do cultural traits move through space and time? • What are key aspects to the geography of language and religion? • How does culture shape human-environment relationships? • How is culture expressed in landscapes, and how do different landscapes reflect different cultural identities?
 Basics of Culture • Material components of Culture Vs. Nonmaterial components of Culture • Cultural geography – Looks at how and why culture is expressed in different ways in different places • Cultural Landscape-CARL SAUER – The built environment – The physical implications of human culture
Basics of Culture • Material components of Culture Vs. Nonmaterial components of Culture • Cultural geography – Looks at how and why culture is expressed in different ways in different places • Cultural Landscape-CARL SAUER – The built environment – The physical implications of human culture
 Sequent occupance • The succession of cultures leaving their mark in a shared space or territory • Ex. Romans, Saxons, Vikings, and others who conquered England over a 3000 year period • CULTURAL ECOLOGY – Human-environment interaction
Sequent occupance • The succession of cultures leaving their mark in a shared space or territory • Ex. Romans, Saxons, Vikings, and others who conquered England over a 3000 year period • CULTURAL ECOLOGY – Human-environment interaction
 Human-environment interactions • Environmental determinism – Environment determines all • Possibilism – Environment sets limits • And CULTURAL DETERMINISM – Environment does not set limits…WE set the restrictions on ourselves
Human-environment interactions • Environmental determinism – Environment determines all • Possibilism – Environment sets limits • And CULTURAL DETERMINISM – Environment does not set limits…WE set the restrictions on ourselves
 The Jigsaw of Culture • Cultural traits – A single attribute of a culture • Ex. Bowing to show respect • Cultural Complex – The combination of all culture traits creates a unique set of traits – Like a recipe – Ex. All the things Americans do makes us American… no other culture has THAT unique combination
The Jigsaw of Culture • Cultural traits – A single attribute of a culture • Ex. Bowing to show respect • Cultural Complex – The combination of all culture traits creates a unique set of traits – Like a recipe – Ex. All the things Americans do makes us American… no other culture has THAT unique combination
 Cont… • Culture systems – When complexes share traits the complexes can merge – Ex. People in N. Germany has a different accent but they combine with the rest of Germany to form the German cultural system
Cont… • Culture systems – When complexes share traits the complexes can merge – Ex. People in N. Germany has a different accent but they combine with the rest of Germany to form the German cultural system
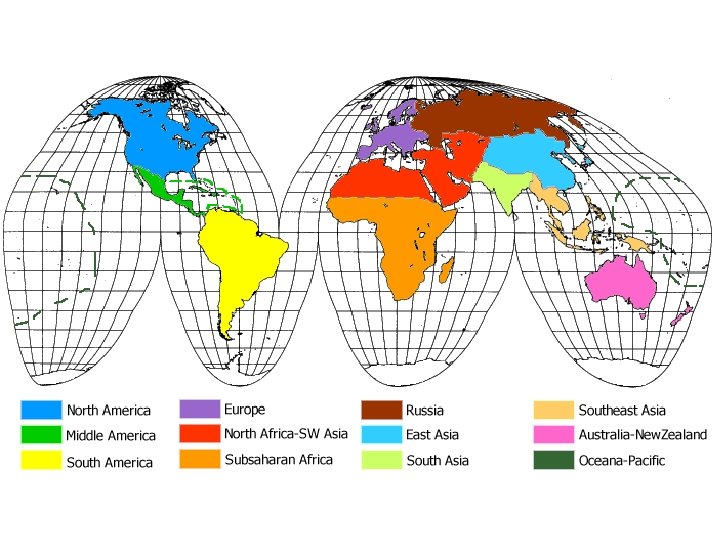
 Cultural Regions and Realms • Cultural regions – Drawn around people with similarities in their cultural systems • Regional Identity – Emotional attachment to the group of people and places associated with a particular culture region – Leads to… • Perceptual Regions (vernacular regions) – Defined by peoples emotions and feelings about an area rather than objective regions
Cultural Regions and Realms • Cultural regions – Drawn around people with similarities in their cultural systems • Regional Identity – Emotional attachment to the group of people and places associated with a particular culture region – Leads to… • Perceptual Regions (vernacular regions) – Defined by peoples emotions and feelings about an area rather than objective regions
 Cultural Realm • Merging together of culture regions
Cultural Realm • Merging together of culture regions
 Cultural Diffusion • The spread of people’s culture across space • Spatial diffusions – The spread of any phenomenon across space – Ex. Disease – Two types… expansion and relocation
Cultural Diffusion • The spread of people’s culture across space • Spatial diffusions – The spread of any phenomenon across space – Ex. Disease – Two types… expansion and relocation
 Expansion Diffusion • The cultural component spreads outward to new places while remaining strong in the home hearth – Ex. Islam spreading from Saudi Arabian hearth
Expansion Diffusion • The cultural component spreads outward to new places while remaining strong in the home hearth – Ex. Islam spreading from Saudi Arabian hearth
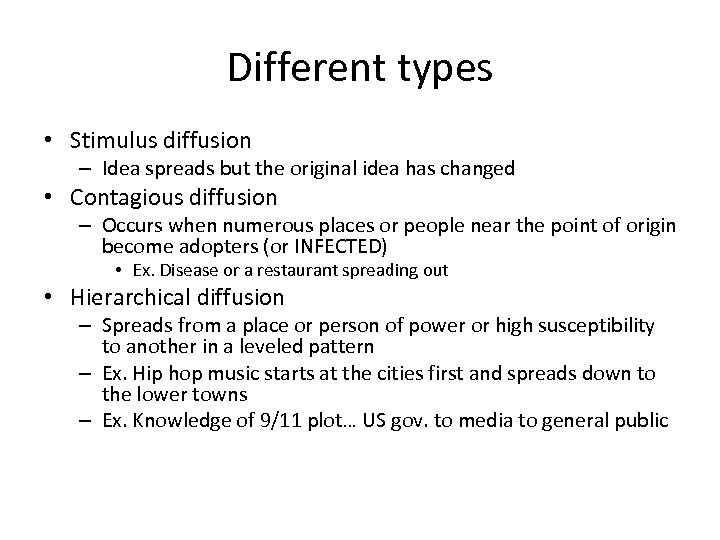 Different types • Stimulus diffusion – Idea spreads but the original idea has changed • Contagious diffusion – Occurs when numerous places or people near the point of origin become adopters (or INFECTED) • Ex. Disease or a restaurant spreading out • Hierarchical diffusion – Spreads from a place or person of power or high susceptibility to another in a leveled pattern – Ex. Hip hop music starts at the cities first and spreads down to the lower towns – Ex. Knowledge of 9/11 plot… US gov. to media to general public
Different types • Stimulus diffusion – Idea spreads but the original idea has changed • Contagious diffusion – Occurs when numerous places or people near the point of origin become adopters (or INFECTED) • Ex. Disease or a restaurant spreading out • Hierarchical diffusion – Spreads from a place or person of power or high susceptibility to another in a leveled pattern – Ex. Hip hop music starts at the cities first and spreads down to the lower towns – Ex. Knowledge of 9/11 plot… US gov. to media to general public
 Relocation diffusion • Involves the actual movement of the original adopters from their hearth to a new place • Ex. Movement of Russian capital from St. Petersburg to Moscow • Ex. HIV/AIDS spread by movement • Migrant diffusion – Innovation spreads but only lasts a brief time – Ex. The flu
Relocation diffusion • Involves the actual movement of the original adopters from their hearth to a new place • Ex. Movement of Russian capital from St. Petersburg to Moscow • Ex. HIV/AIDS spread by movement • Migrant diffusion – Innovation spreads but only lasts a brief time – Ex. The flu
 Mixie • They can be combined – Ex. The flu – Ex. HIV/AIDS
Mixie • They can be combined – Ex. The flu – Ex. HIV/AIDS
 Culture • Cultural Convergence – The process of two cultures blending and becoming more alike • Acculturation – A weaker culture adopts a more dominant culture’s traits – May lead to… • Assimilation – Complete erase of the weaker culture
Culture • Cultural Convergence – The process of two cultures blending and becoming more alike • Acculturation – A weaker culture adopts a more dominant culture’s traits – May lead to… • Assimilation – Complete erase of the weaker culture
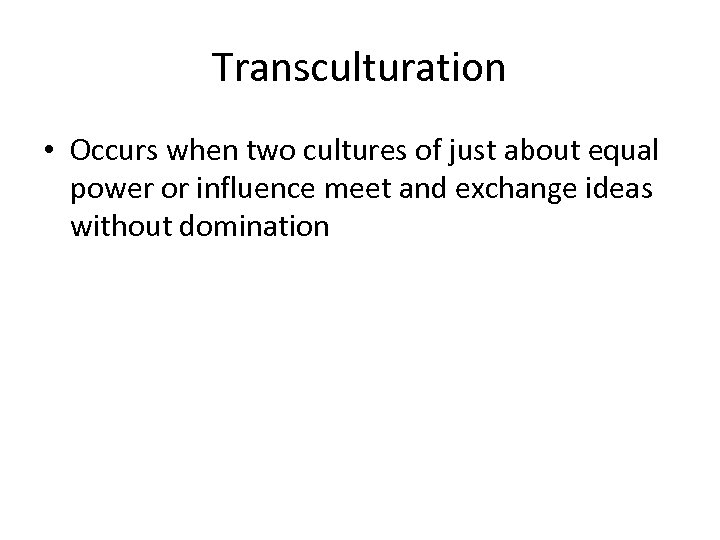 Transculturation • Occurs when two cultures of just about equal power or influence meet and exchange ideas without domination
Transculturation • Occurs when two cultures of just about equal power or influence meet and exchange ideas without domination
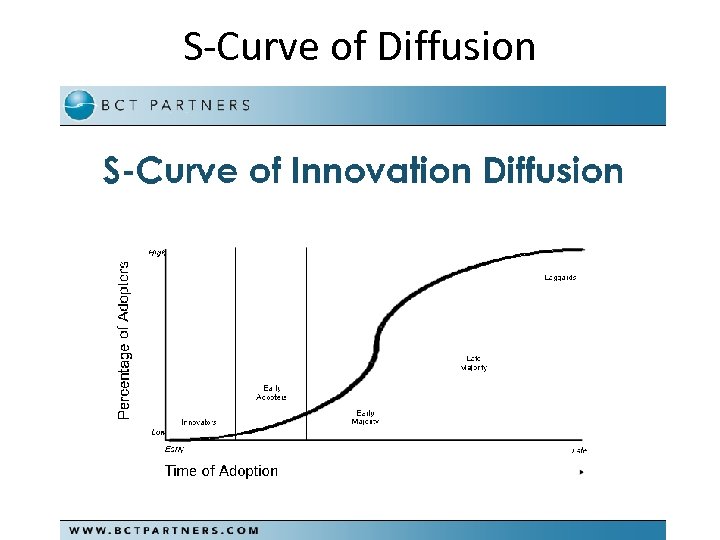 S-Curve of Diffusion
S-Curve of Diffusion
 Cultural hearth • Where innovations in a culture begin • INDEPENDENT INNOVATION – Originate without knowledge of similar innovations – Ex. Agricultural innovation in E. Asia and Mesopotamia
Cultural hearth • Where innovations in a culture begin • INDEPENDENT INNOVATION – Originate without knowledge of similar innovations – Ex. Agricultural innovation in E. Asia and Mesopotamia
 Religion
Religion
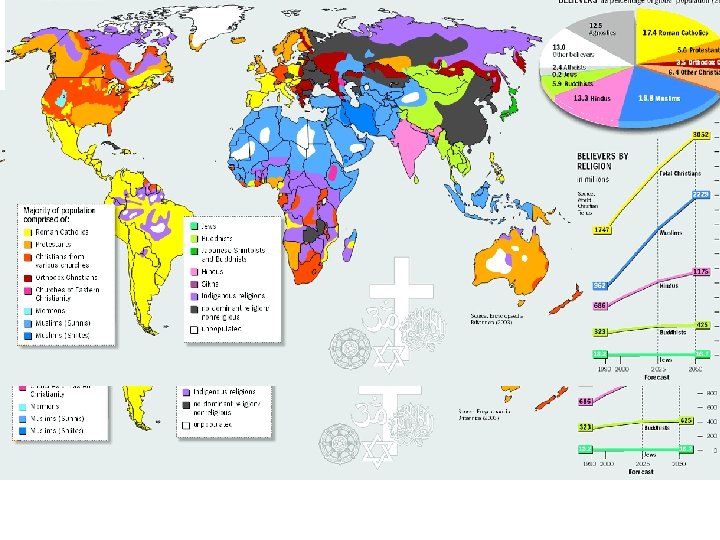
 Religion • A set of beliefs and activities that are created to help human celebrate and understand their place in the world – Can be MONOTHEISTIC or POLYTHEISTIC • Universalizing Religions – Universal appeal • Ethnic Religions – Attempt to appeal to only one group
Religion • A set of beliefs and activities that are created to help human celebrate and understand their place in the world – Can be MONOTHEISTIC or POLYTHEISTIC • Universalizing Religions – Universal appeal • Ethnic Religions – Attempt to appeal to only one group
 Universalizing Religions • Branches => Denominations => sects
Universalizing Religions • Branches => Denominations => sects
 Buddhism • World’s 1 st universalizing religion • Founded in India near INDO-GANGETIC Hearth (Indus/Ganges rivers) • Founded by Prince Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha) who was born in 644 BCE • Diffusion: Spread throughout India then China, Korea, Japan, Tibet, Mongolia, and SE Asia along Silk Road • 350 million worldwide • Branches: Theraveda and Mahayana
Buddhism • World’s 1 st universalizing religion • Founded in India near INDO-GANGETIC Hearth (Indus/Ganges rivers) • Founded by Prince Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha) who was born in 644 BCE • Diffusion: Spread throughout India then China, Korea, Japan, Tibet, Mongolia, and SE Asia along Silk Road • 350 million worldwide • Branches: Theraveda and Mahayana
 Branches • Theravada – Monastic (monks and nuns) – 55% • Mahayana – Find salvation through meditation and prayer • Lamaism (in Tibet) – Combines monatiscism with local dieties and demons – The Dalai Lama is a proponent – China has tried to suppress this branch including EXILE of the Dalai Lama • Zen – In Japan
Branches • Theravada – Monastic (monks and nuns) – 55% • Mahayana – Find salvation through meditation and prayer • Lamaism (in Tibet) – Combines monatiscism with local dieties and demons – The Dalai Lama is a proponent – China has tried to suppress this branch including EXILE of the Dalai Lama • Zen – In Japan
 Cultural landscape of Buddhism • Pagoda – Derived from ancient burial mound shapes • Bodhi tree • Many pilgrimages
Cultural landscape of Buddhism • Pagoda – Derived from ancient burial mound shapes • Bodhi tree • Many pilgrimages
 Christianity • • • 600 years after Buddhism Offshoot of Judaism Originated in Semitic Hearth (Israel) Monotheistic Holy book: the Bible
Christianity • • • 600 years after Buddhism Offshoot of Judaism Originated in Semitic Hearth (Israel) Monotheistic Holy book: the Bible
 Cont… Diffusion • Largest number of adherents (2 billion) • Spread out especially through the Roman Empire • Nearly 90% in the W. Hemisphere are Christian
Cont… Diffusion • Largest number of adherents (2 billion) • Spread out especially through the Roman Empire • Nearly 90% in the W. Hemisphere are Christian
 Cont… Branches • Roman Catholic – Largest (830 million) – Hierarchical • Protestant – Broken into denominations – Baptist, Methodist, Pentecostal, and Lutheran – 503 million • Eastern Orthodox – – Formed during the Great Schism of 1054 14 separate churches Largest is Russian Orthodox 192 million (roots in Constantinople
Cont… Branches • Roman Catholic – Largest (830 million) – Hierarchical • Protestant – Broken into denominations – Baptist, Methodist, Pentecostal, and Lutheran – 503 million • Eastern Orthodox – – Formed during the Great Schism of 1054 14 separate churches Largest is Russian Orthodox 192 million (roots in Constantinople
 Cont… Cultural landscape • Roman Catholic • Protestant Church • Eastern Orthodox
Cont… Cultural landscape • Roman Catholic • Protestant Church • Eastern Orthodox
 Islam • • 600 CE 1. 2 billion worldwide Muhammad Diffused Globally from Saudi Arabia Mecca and Medina Monotheistic Holy Book: Koran/Quran Two Branches: Sunni and Shiite
Islam • • 600 CE 1. 2 billion worldwide Muhammad Diffused Globally from Saudi Arabia Mecca and Medina Monotheistic Holy Book: Koran/Quran Two Branches: Sunni and Shiite
 Cont… Branches • Sunni – 85% • Shiite – 15% – Believe that only descendants Muhammad should be head of Islam – Iraq and Iran
Cont… Branches • Sunni – 85% • Shiite – 15% – Believe that only descendants Muhammad should be head of Islam – Iraq and Iran
 Cultural Landscape • The Mosque
Cultural Landscape • The Mosque
 Cont… Misc… • 5 pillars • Pilgrimage to Mecca (holiest site) • Third holy site is Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem
Cont… Misc… • 5 pillars • Pilgrimage to Mecca (holiest site) • Third holy site is Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem
 Sikkhism • • • 22 million Syncretic religion Blend of Hindu and Islam Mainly in Punjab Region of India Monotheistic Holy book: Guru Granth Sahib
Sikkhism • • • 22 million Syncretic religion Blend of Hindu and Islam Mainly in Punjab Region of India Monotheistic Holy book: Guru Granth Sahib
 Ethnic Religion • Hinduism – Mainly in India – 900 million adherents • Predates Buddhism • Cultural landscape features Caste System • Judaism – Jewish diaspora – Holy book: Torah • Shintoism • Taoism • Shaminism – Any religion that follows a religious leader/healer/truth knower • Animism-belief that objects like trees, mountains, rivers have spirits in them
Ethnic Religion • Hinduism – Mainly in India – 900 million adherents • Predates Buddhism • Cultural landscape features Caste System • Judaism – Jewish diaspora – Holy book: Torah • Shintoism • Taoism • Shaminism – Any religion that follows a religious leader/healer/truth knower • Animism-belief that objects like trees, mountains, rivers have spirits in them
 Secularism and Theocracy • Secularism – Movement away from religion • Theocracy – Government run by religion – Ex. Former Taliban run Afghanistan – Ex. Iran
Secularism and Theocracy • Secularism – Movement away from religion • Theocracy – Government run by religion – Ex. Former Taliban run Afghanistan – Ex. Iran
 Religion and Conflict • Interfaith boundaries – China- Tibetan Buddhism and Atheism – Nigeria- Islam and Christianity – India- Hinduism and Sikkhism – India and Pakistan-Hinduism and Islam – Palestine- Judaism and Islam • Intrafaith boundaries – Iraq- Sunni and Shiite – USA- Christianity – N. Ireland- Protestants and Roman Catholics
Religion and Conflict • Interfaith boundaries – China- Tibetan Buddhism and Atheism – Nigeria- Islam and Christianity – India- Hinduism and Sikkhism – India and Pakistan-Hinduism and Islam – Palestine- Judaism and Islam • Intrafaith boundaries – Iraq- Sunni and Shiite – USA- Christianity – N. Ireland- Protestants and Roman Catholics
 Language
Language
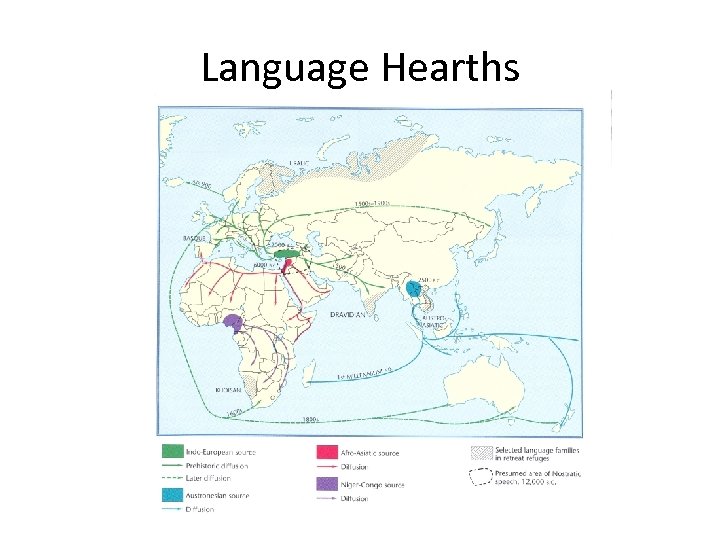
 Language • • Language Divergence Language replacement Language extinction Reverse reconstruction
Language • • Language Divergence Language replacement Language extinction Reverse reconstruction
 Language Hearths
Language Hearths
 Theories on hearth of Proto Indo European language • Conquest theory • Agricultural theory
Theories on hearth of Proto Indo European language • Conquest theory • Agricultural theory
 Monolingual and Multilingual • Can be centripetal or cetrifugal • Ex. Belgium – Dutch and French – Canada • French and English
Monolingual and Multilingual • Can be centripetal or cetrifugal • Ex. Belgium – Dutch and French – Canada • French and English
 Official and Standard Languages • Official • Standard – Acceptable forms
Official and Standard Languages • Official • Standard – Acceptable forms
 Others… • Lingua Franca – Facilitates trade • Pidgin – Simplified version • Becomes Creole/Creolized (once it is adopted) • Ex. French domination in the Caribbean…first pidgin French then became Creolized
Others… • Lingua Franca – Facilitates trade • Pidgin – Simplified version • Becomes Creole/Creolized (once it is adopted) • Ex. French domination in the Caribbean…first pidgin French then became Creolized
 Toponyms • Are Place names • Reflect cultural identity and impact the cultural landscape • May be controversial – Ex. India wanted to change Bombay to Mumbai (“Mumbai” relates to a Hindu god, this angered non-Hindus) • Can give historical clues – St. Petersburg (named by Peter the Great for his patron saint) – Can indicate the “dreams” of a place… • Paradise, CA • Hope, AK – Can reflect religion • “St. ” in N. New York and Quebec • Santa Barbara (reflects spanish/portugese language and catholic influence)
Toponyms • Are Place names • Reflect cultural identity and impact the cultural landscape • May be controversial – Ex. India wanted to change Bombay to Mumbai (“Mumbai” relates to a Hindu god, this angered non-Hindus) • Can give historical clues – St. Petersburg (named by Peter the Great for his patron saint) – Can indicate the “dreams” of a place… • Paradise, CA • Hope, AK – Can reflect religion • “St. ” in N. New York and Quebec • Santa Barbara (reflects spanish/portugese language and catholic influence)
 Ethnicity • Relates to sets of norms that people create to define their group through actual or perceived shared culture traits (language, religion, nationality) • Can be expressed in different ways – Territory • Albanians in Albania
Ethnicity • Relates to sets of norms that people create to define their group through actual or perceived shared culture traits (language, religion, nationality) • Can be expressed in different ways – Territory • Albanians in Albania
 Ethnic groups • Jews are spatially divided – Forced segregation in Nazi Germany • GHETTO- region in which an ethnic minority is forced to live by economic, legal, or gov pressures • ENCLAVE- place of minority concentration surrounded by unwelcoming groups • BARRIO- Spanish speaking ethnic neighborhood in a city
Ethnic groups • Jews are spatially divided – Forced segregation in Nazi Germany • GHETTO- region in which an ethnic minority is forced to live by economic, legal, or gov pressures • ENCLAVE- place of minority concentration surrounded by unwelcoming groups • BARRIO- Spanish speaking ethnic neighborhood in a city
 Race • Refers to a classification system of humans based on skin color and other genetic/physical characteristics • APARTHEID – Africa… particularly S. Africa – Separation of whites and blacks – What separates ethnicity and race? • More than just race
Race • Refers to a classification system of humans based on skin color and other genetic/physical characteristics • APARTHEID – Africa… particularly S. Africa – Separation of whites and blacks – What separates ethnicity and race? • More than just race
 Examples… • Puerto Ricans… include more than just a “Hispanic race”
Examples… • Puerto Ricans… include more than just a “Hispanic race”
 Social Distance • How “distant” two ethnicities are apart from each other but not in a spatial sense • Ethnocentrism – One group’s use of its cultural identity as the superior standard by which to judge others, often causes discriminatory behavior
Social Distance • How “distant” two ethnicities are apart from each other but not in a spatial sense • Ethnocentrism – One group’s use of its cultural identity as the superior standard by which to judge others, often causes discriminatory behavior
 Ethnic Conflict • Ethnic Cleansing – A process in which a racial or ethnic group attempt to expel from a territory another racial or ethnic group • Genocide – When a racial or ethnic group tries to kill another racial or ethnic group • Slobadan Milosevic (Serbian leader of former Yugoslavia) led genocide campaign against ethnic Albanians living in Kosovo (a region in Serbia) • Hitler • Sudan trying to eliminate ethnic groups in Darfur • Rwanda
Ethnic Conflict • Ethnic Cleansing – A process in which a racial or ethnic group attempt to expel from a territory another racial or ethnic group • Genocide – When a racial or ethnic group tries to kill another racial or ethnic group • Slobadan Milosevic (Serbian leader of former Yugoslavia) led genocide campaign against ethnic Albanians living in Kosovo (a region in Serbia) • Hitler • Sudan trying to eliminate ethnic groups in Darfur • Rwanda
 Gender • Men have more opportunities • Masculine and feminine are cultural traits • Men dominate economically, politically, and socially – Gender gap
Gender • Men have more opportunities • Masculine and feminine are cultural traits • Men dominate economically, politically, and socially – Gender gap
 Gender Problems • High maternal mortality rates – LDCs 100 -600 x more likely to die than women in MDCs • Female Infanticide – China – India and the DOWRY • Dowry Death in India – Failure to pay • Enfrancisement… right to vote • Longevity gap…women live longer
Gender Problems • High maternal mortality rates – LDCs 100 -600 x more likely to die than women in MDCs • Female Infanticide – China – India and the DOWRY • Dowry Death in India – Failure to pay • Enfrancisement… right to vote • Longevity gap…women live longer
 Folk and Pop culture • Folk culture – Limited in scope – Ex. Amish • Pop culture – Mass culture
Folk and Pop culture • Folk culture – Limited in scope – Ex. Amish • Pop culture – Mass culture
 Maladaptive Diffusion • Adoption of a diffusing trait that is impractical for a region or culture • Jeans in the summer
Maladaptive Diffusion • Adoption of a diffusing trait that is impractical for a region or culture • Jeans in the summer
 Cultural Imperialism • The invasion of a culture into another with the intent of dominating the invaded culture politically, economically, and/or socially • Ex. When Mc. Donald’s arrived in one African city protesters attacked the restaurant • Ex. Middle eastern culture resent the influx of western pop culture
Cultural Imperialism • The invasion of a culture into another with the intent of dominating the invaded culture politically, economically, and/or socially • Ex. When Mc. Donald’s arrived in one African city protesters attacked the restaurant • Ex. Middle eastern culture resent the influx of western pop culture
 Cultural Nationalism • The rise of anti cultural imperialism forces • The fight to resist cultural convergence and imperialism and remain distinct
Cultural Nationalism • The rise of anti cultural imperialism forces • The fight to resist cultural convergence and imperialism and remain distinct
 Cultural Homogeneity • Cultural sameness • Pop cultures threatens uniqueness
Cultural Homogeneity • Cultural sameness • Pop cultures threatens uniqueness
 Pop culture and Consumption • Many pop culture trends can lead to increase consumption and tax the natural resources and increase waste • Ex. Buy cars instead of public transportation… leads to more gas usage and more pollution • Ex. Plastic water bottles
Pop culture and Consumption • Many pop culture trends can lead to increase consumption and tax the natural resources and increase waste • Ex. Buy cars instead of public transportation… leads to more gas usage and more pollution • Ex. Plastic water bottles


