CULTURAL ISSUES IN NEGOTIATIONS JAPAN












Япония Переговоры.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 CULTURAL ISSUES IN NEGOTIATIONS JAPAN
CULTURAL ISSUES IN NEGOTIATIONS JAPAN
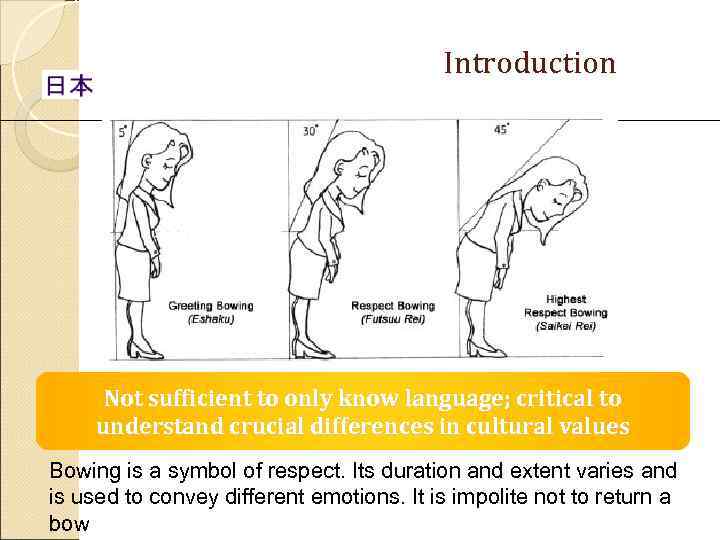
 Introduction Not sufficient to only know language; critical to understand crucial differences in cultural values Bowing is a symbol of respect. Its duration and extent varies and is used to convey different emotions. It is impolite not to return a bow
Introduction Not sufficient to only know language; critical to understand crucial differences in cultural values Bowing is a symbol of respect. Its duration and extent varies and is used to convey different emotions. It is impolite not to return a bow
 Business organization § Hierarchical and Bureaucratic § High degree of harmony and cooperation § Key focus on quality § Information oriented Focus on building long term relationships and emphasize on long term benefits
Business organization § Hierarchical and Bureaucratic § High degree of harmony and cooperation § Key focus on quality § Information oriented Focus on building long term relationships and emphasize on long term benefits
 Seniority system § Based on factors like age, sex, family name, occupation, physical features and birthplace § Titles are extremely important - signifies prestige and respect § Hierarchy legitimates the use of power Japanese will always examine relative positioning in negotiation
Seniority system § Based on factors like age, sex, family name, occupation, physical features and birthplace § Titles are extremely important - signifies prestige and respect § Hierarchy legitimates the use of power Japanese will always examine relative positioning in negotiation
 Decision making § Centralized § ‘Ringi’ system – all members involved in the process § Often slow – unwillingness to take risk and avoids on the spot decision making § Long term perspective Try to deal with higher ranks and in groups, factor in delays
Decision making § Centralized § ‘Ringi’ system – all members involved in the process § Often slow – unwillingness to take risk and avoids on the spot decision making § Long term perspective Try to deal with higher ranks and in groups, factor in delays
 Other aspects § Punctuality- always be on time § Indirectness critical in communication and avoid conflicts § Private people and uncomfortable with physical contact § Japanese less pressured by deadlines, slowdown as complications develop – threatened by stressful situations Avoid excessive assertiveness, may be viewed as aggressive
Other aspects § Punctuality- always be on time § Indirectness critical in communication and avoid conflicts § Private people and uncomfortable with physical contact § Japanese less pressured by deadlines, slowdown as complications develop – threatened by stressful situations Avoid excessive assertiveness, may be viewed as aggressive
 Pre-negotiation § Meet socially before beginning formal negotiation – avoiding social conversation may lead to bad impression § Establish and maintain harmony (Wa) – important aspect of Japanese social life § Exchange of business cards (Meishi) - use both hands, spend 20 -30 seconds on examining their card Emphasize on building trust and long term relationship
Pre-negotiation § Meet socially before beginning formal negotiation – avoiding social conversation may lead to bad impression § Establish and maintain harmony (Wa) – important aspect of Japanese social life § Exchange of business cards (Meishi) - use both hands, spend 20 -30 seconds on examining their card Emphasize on building trust and long term relationship
 Information exchange § Wait for counterpart’s signal before starting negotiation § Japanese are information oriented - offer detailed explanations before making actual proposal § Ensure to discuss long term generalized goals § Use informal channel of communication to get the true feeling of the Japanese Be patient and persistent and ready with information!!
Information exchange § Wait for counterpart’s signal before starting negotiation § Japanese are information oriented - offer detailed explanations before making actual proposal § Ensure to discuss long term generalized goals § Use informal channel of communication to get the true feeling of the Japanese Be patient and persistent and ready with information!!
 Persuasion § Patience and intelligence in collecting information without giving anything away is their style of negotiation § Avoidance strategies like non verbal expressions and silence used often – negotiator should not appear desperate § Avoid using aggressive tactics and threats. Negotiator asking for high price may destroy the trust built
Persuasion § Patience and intelligence in collecting information without giving anything away is their style of negotiation § Avoidance strategies like non verbal expressions and silence used often – negotiator should not appear desperate § Avoid using aggressive tactics and threats. Negotiator asking for high price may destroy the trust built
 Concession and agreement § Make the first proposal and receive counter proposal – focus on reciprocity § Japanese examine all issues simultaneously in a more holistic approach § Concessions are made only near the end of the talks and usually all at once – basic goal of long term mutual benefit § Customary to give the buyer a discount (called sabitsu) when agreement is reached - to demonstrate friendship and sincerity
Concession and agreement § Make the first proposal and receive counter proposal – focus on reciprocity § Japanese examine all issues simultaneously in a more holistic approach § Concessions are made only near the end of the talks and usually all at once – basic goal of long term mutual benefit § Customary to give the buyer a discount (called sabitsu) when agreement is reached - to demonstrate friendship and sincerity
 Post-negotiation § Fundamental approach is to emphasize the relationship being created § Specific items of a contract always open to renegotiation if the circumstances change § Signing manifested by ceremonial meetings and exchange of gifts Emphasize win-win situation and help increase the size of the pie
Post-negotiation § Fundamental approach is to emphasize the relationship being created § Specific items of a contract always open to renegotiation if the circumstances change § Signing manifested by ceremonial meetings and exchange of gifts Emphasize win-win situation and help increase the size of the pie
 nuances § Over 90% of the Japanese population buys a comic-magazine daily § Frogs are the symbol of good luck in Japan § Japanese drink tea with almost every meal § Heavy traffic – In Tokyo, a bicycle is usually faster than a car for most trips up to 50 minutes
nuances § Over 90% of the Japanese population buys a comic-magazine daily § Frogs are the symbol of good luck in Japan § Japanese drink tea with almost every meal § Heavy traffic – In Tokyo, a bicycle is usually faster than a car for most trips up to 50 minutes

