9faa2f5016252b507dca8fe2716e368b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

CUAHSI Water. One. Flow Web Services By Tim Whiteaker CE 394 K. 2 Hydrology 1 February 2007

Outline • • What are Web Services What is Water. One. Flow What is Water. ML How do we use HIS Analyst to access Water. One. Flow
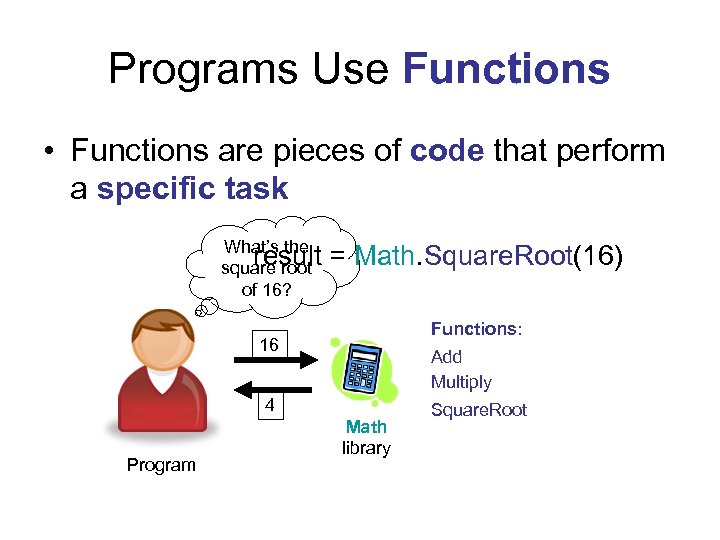
Programs Use Functions • Functions are pieces of code that perform a specific task What’s the result square root of 16? = Math. Square. Root(16) Functions: 16 Add Multiply 4 Program Math library Square. Root
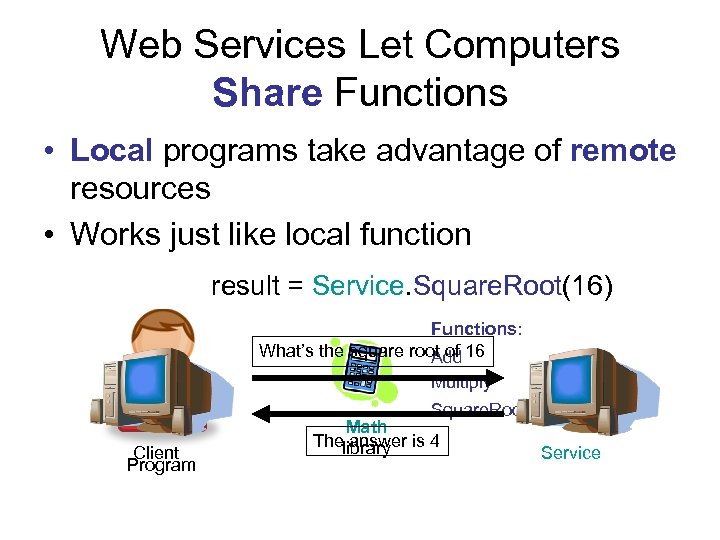
Web Services Let Computers Share Functions • Local programs take advantage of remote resources • Works just like local function result = Service. Square. Root(16) Functions: What’s the square root of 16 Add Multiply Square. Root Client Program Math Thelibrary is 4 answer Service

How Do Web Services Work • SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) is a protocol for exchanging messages over a network • WSDL (Web Services Description Language) is a language for describing what a web service can do
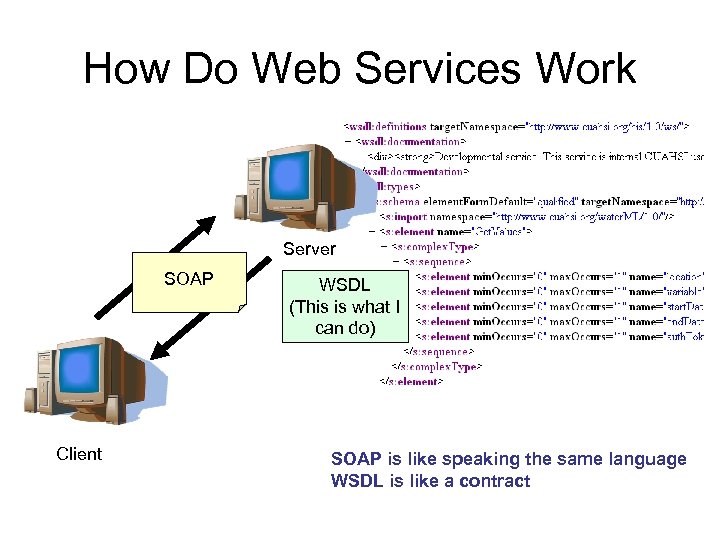
How Do Web Services Work Server SOAP Client WSDL (This is what I can do) SOAP is like speaking the same language WSDL is like a contract

CUAHSI Web Services (Water. One. FLow) • Standard mechanism for flow of hydrologic data between hydrologic data servers (databases) and users. • Provides data access to – – – USGS NWIS EPA STORET NCEP North American Model (NAM) NASA MODIS Daymet NWS ASOS http: //water. sdsc. edu/water. One. Flow/
Water Data Web Sites
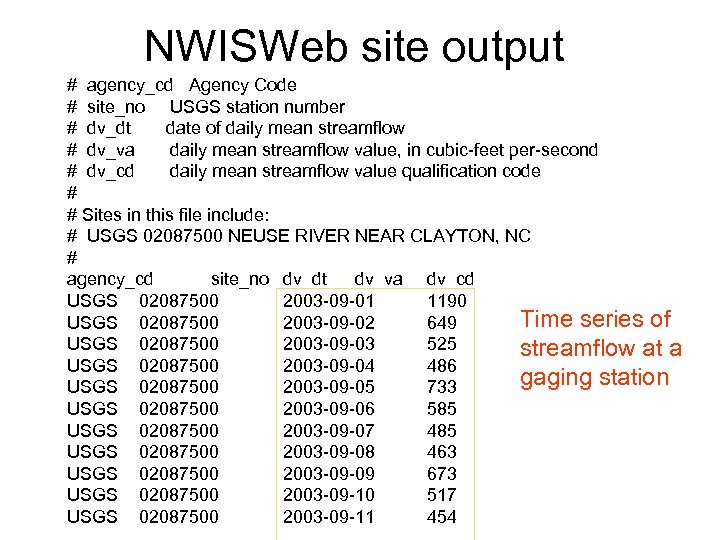
NWISWeb site output # agency_cd Agency Code # site_no USGS station number # dv_dt date of daily mean streamflow # dv_va daily mean streamflow value, in cubic-feet per-second # dv_cd daily mean streamflow value qualification code # # Sites in this file include: # USGS 02087500 NEUSE RIVER NEAR CLAYTON, NC # agency_cd site_no dv_dt dv_va dv_cd USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -01 1190 Time series of USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -02 649 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -03 525 streamflow at a USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -04 486 gaging station USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -05 733 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -06 585 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -07 485 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -08 463 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -09 673 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -10 517 USGS 02087500 2003 -09 -11 454
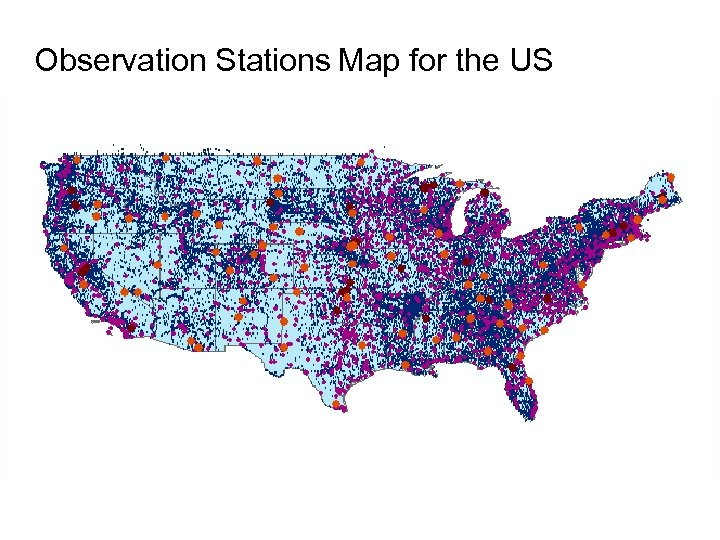
Observation Stations Map for the US Ameriflux Towers (NASA & DOE) NOAA Automated Surface Observing System USGS National Water Information System NOAA Climate Reference Network
Water. One. Flow • Consistent Query Format • Consistent Data Format

Water. One. Flow Methods • (Almost) the same for all networks • Methods – Get. Site. Info – Give me info about a site – Get. Variable. Info – Give me info about a variable – Get. Values – Give me a time series for a variable at a site

Get. Site. Info • Input • Output – Network name and site code – Authorization token – Site name – Site location – Variables measured at the site • Variable code • Period of record where response = service. Get. Site. Info("NWIS: 08158000", "")
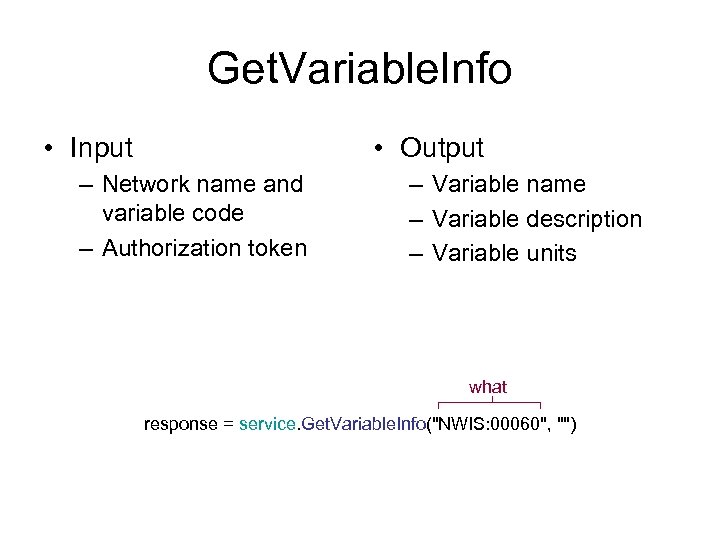
Get. Variable. Info • Input • Output – Network name and variable code – Authorization token – Variable name – Variable description – Variable units what response = service. Get. Variable. Info("NWIS: 00060", "")

Get. Values • Input • Output – Network name and location (e. g. , site code) – Network name and variable code – Start datetime – End datetime – Authorization token – Site info – Variable info – Time series where what response = service. Get. Values("NWIS: 08158000", "NWIS: 00060", _ "2006 -12 -31 T 01: 00", "2006 -12 -31 T 08: 00", "") when

The “Where” in Get. Values • Works for sites, or geographic locations • Network. Name: Site. Code – NWIS: 08158000 • GEOM: POINT(Longitude Latitude) – GEOM: POINT(-113 35) • GEOM: BOX(WLon SLat, ELon NLat) – GEOM: BOX(-108 45, -107 46)
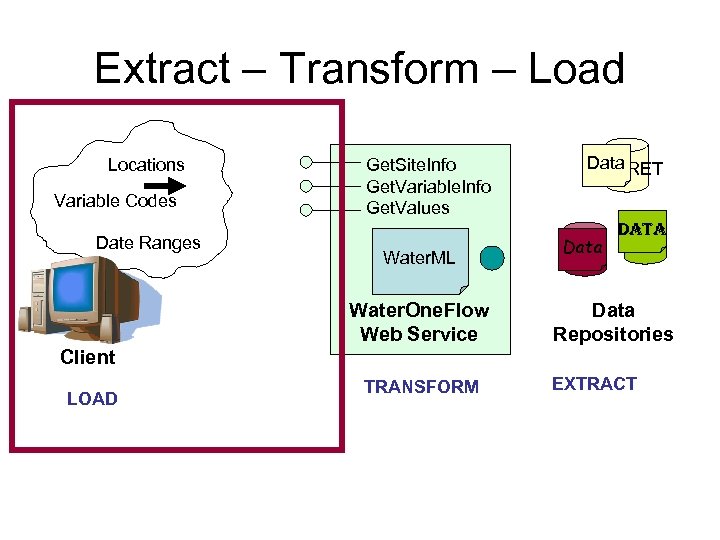
Extract – Transform – Load Locations Variable Codes Get. Site. Info Get. Variable. Info Get. Values Data STORET Water. ML Water. One. Flow Web Service Date Ranges Data NAM NWIS Data Repositories Client LOAD TRANSFORM EXTRACT

Water. ML – The Output of Water. One. Flow • Standardized for all data sources • Formats – Object – XML (for programs that can’t handle objects) • Defined in XML
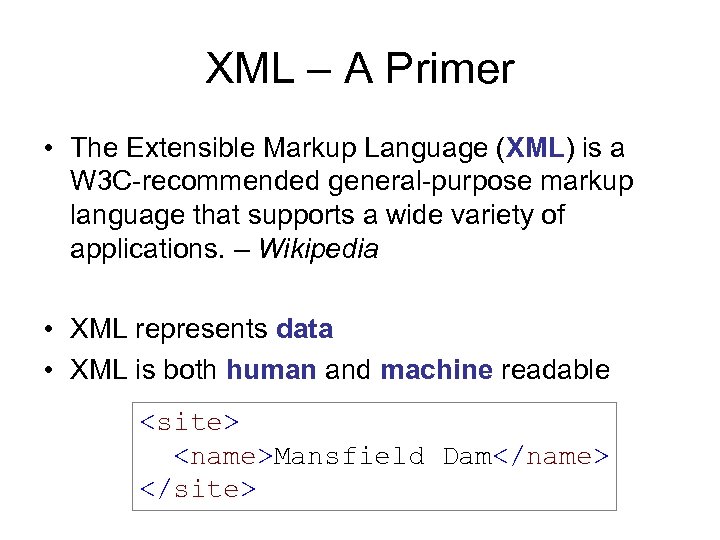
XML – A Primer • The Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a W 3 C-recommended general-purpose markup language that supports a wide variety of applications. – Wikipedia • XML represents data • XML is both human and machine readable <site> <name>Mansfield Dam</name> </site>
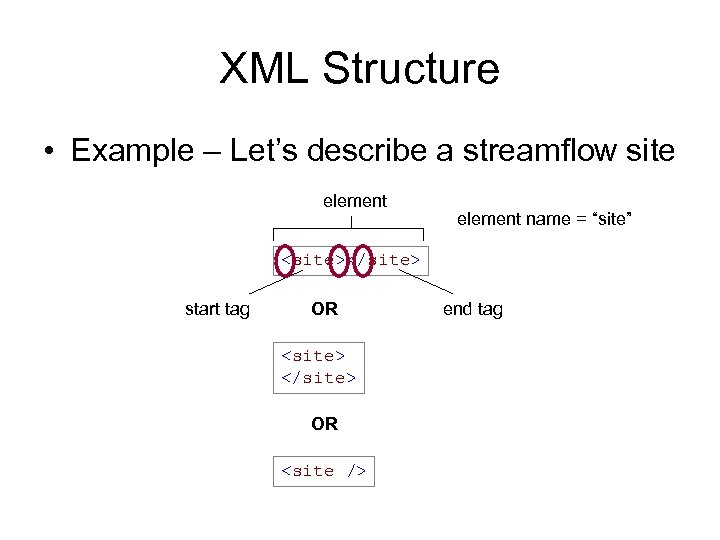
XML Structure • Example – Let’s describe a streamflow site element name = “site” <site></site> start tag OR <site> </site> OR <site /> end tag
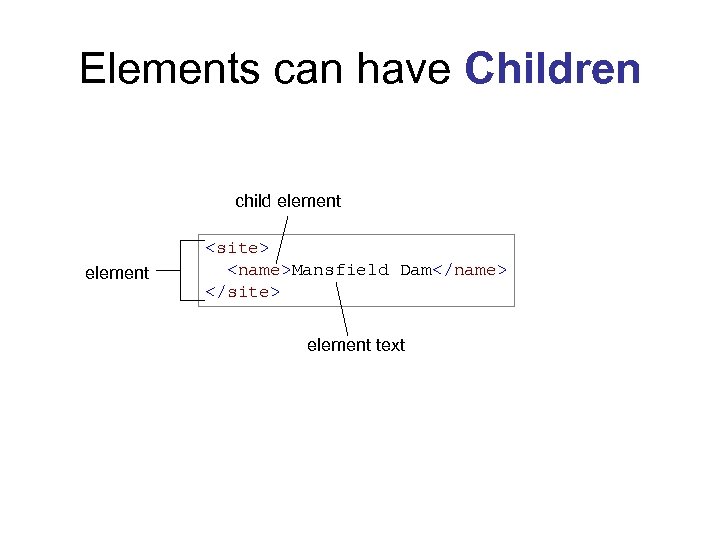
Elements can have Children child element <site> <name>Mansfield Dam</name> </site> element text

Elements can have Attributes <site> <name>Mansfield Dam</name> <site. Code network=“NWIS”>08154510</site. Code> </site> attribute name attribute value

XML Nesting <site> <name>Mansfield Dam</name> <site. Code network=“NWIS”>08154510</site. Code> <location> <latitude>30. 39</latitude> <longitude>97. 91</longitude> </location> </site>

Water. ML • XML for describing water data • Defined at http: //water. sdsc. edu/water. One. Flow/documentation/schema/ • Water. One. Flow returns data in Water. ML format
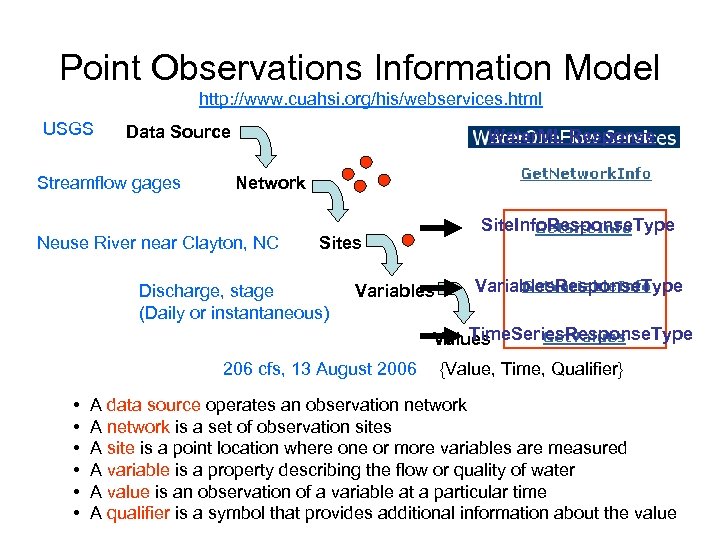
Point Observations Information Model http: //www. cuahsi. org/his/webservices. html USGS Data Source Streamflow gages Water. ML Response Network Neuse River near Clayton, NC Site. Info. Response. Type Sites Discharge, stage (Daily or instantaneous) Variables. Response. Type Time. Series. Response. Type Values 206 cfs, 13 August 2006 • • • {Value, Time, Qualifier} A data source operates an observation network A network is a set of observation sites A site is a point location where one or more variables are measured A variable is a property describing the flow or quality of water A value is an observation of a variable at a particular time A qualifier is a symbol that provides additional information about the value
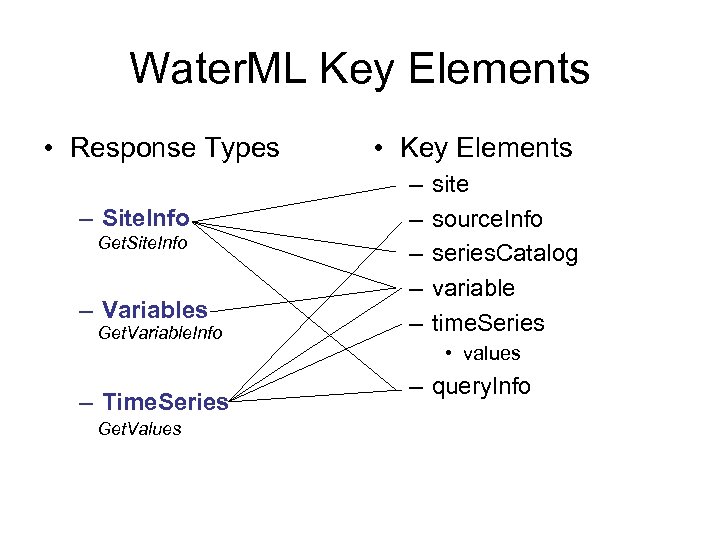
Water. ML Key Elements • Response Types – Site. Info Get. Site. Info – Variables Get. Variable. Info – Time. Series Get. Values • Key Elements – – – site source. Info series. Catalog variable time. Series • values – query. Info

Site. Info. Response. Type • Namespaces • query. Info • site Network Sites Variables

query. Info • Parameters sent to service • URLs called (if external resource)
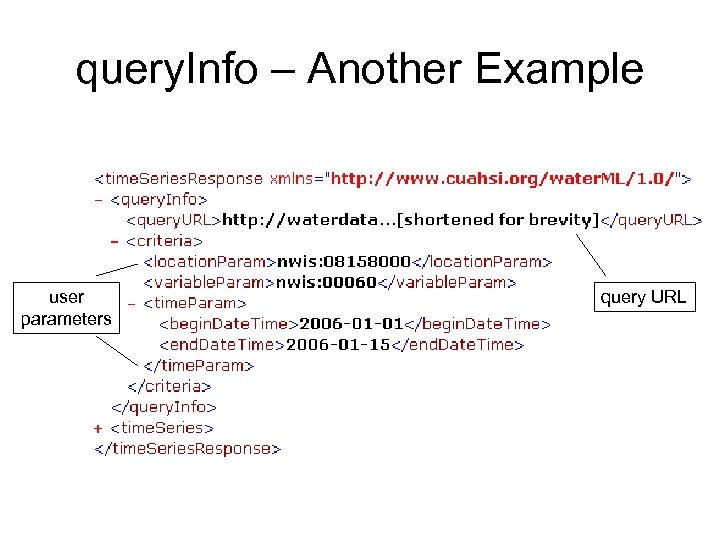
query. Info – Another Example user parameters query URL
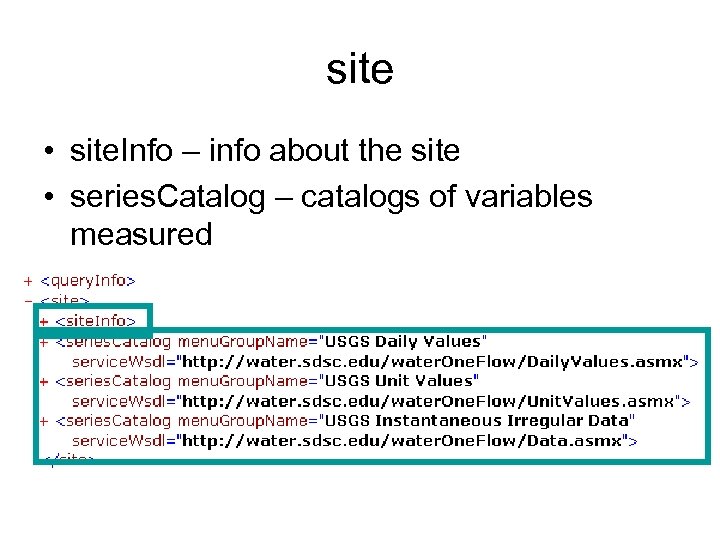
site • site. Info – info about the site • series. Catalog – catalogs of variables measured

site. Info • Name • Site Code • Location
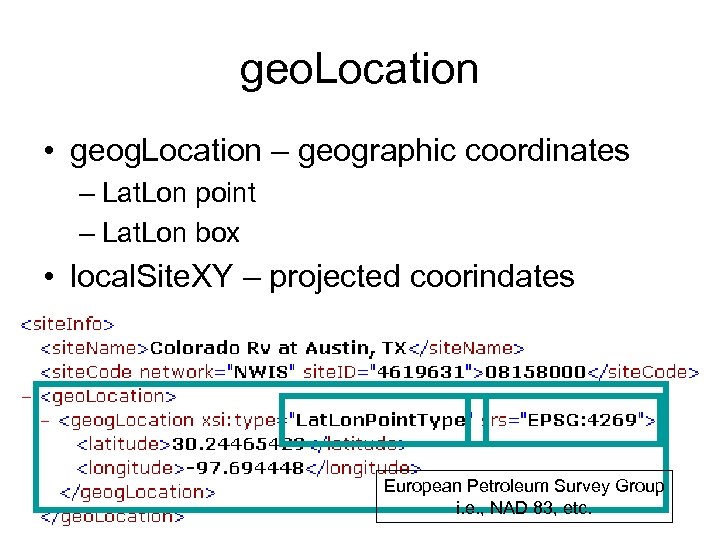
geo. Location • geog. Location – geographic coordinates – Lat. Lon point – Lat. Lon box • local. Site. XY – projected coorindates European Petroleum Survey Group i. e. , NAD 83, etc.
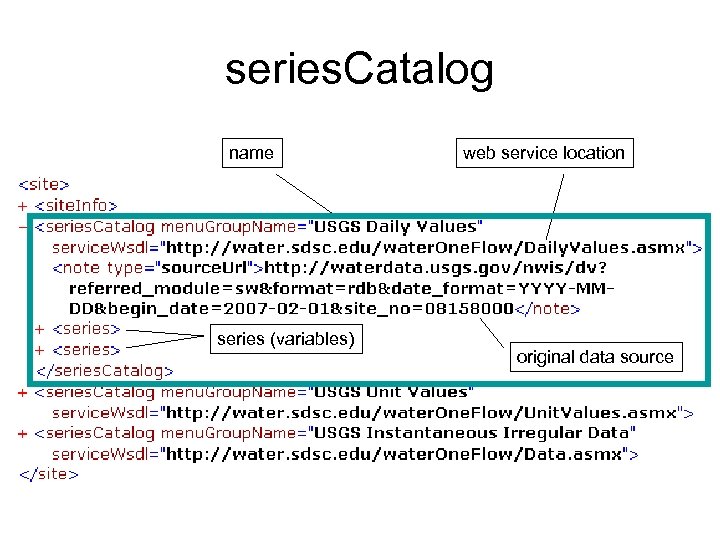
series. Catalog name series (variables) web service location original data source

series • variable – what is measured • value. Count – how many measurements • variable. Time. Interval – when is it measured

variable • variable. Code – global identifier • variable. Name Sites • units Variables Values

variable. Time. Interval • Time. Interval. Type – date range • Time. Single. Type – single measurement • Time. Period. Real. Time. Type – last n days

ISO Time • International Organization for Standardization • 1998 -03 -01 T 14: 30: 00 = March 1, 1998, at 2: 30 in the afternoon
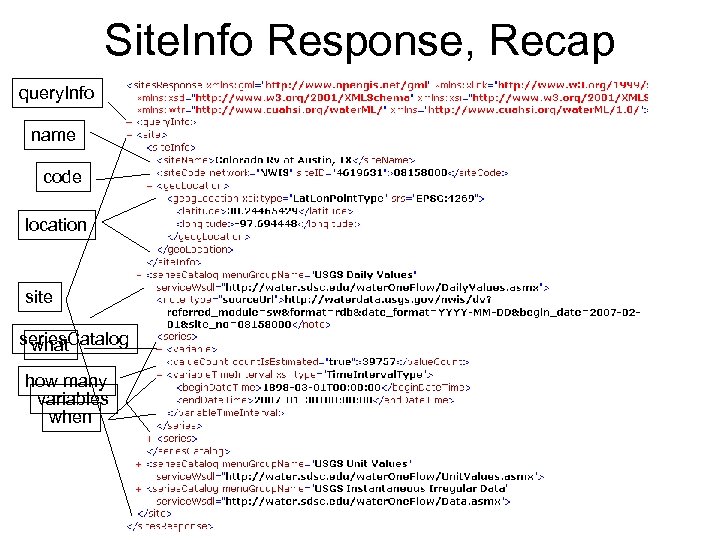
Site. Info Response, Recap query. Info name code location site series. Catalog what how many variables when

Variables. Response. Type • variable – same as in series element • Code, name, units Sites Variables Values

Additional variable Children • variable. Description • value. Type (enumeration) – Field Observation – Sample – Model Simulation Result – Derived Value • general. Category – e. g. , “water quality” • sample. Medium – e. g. , “water column” -- Many are optional

Time. Series. Response. Type • query. Info • time. Series – source. Info – “where” – variable – “what” – values Sites Variables Values
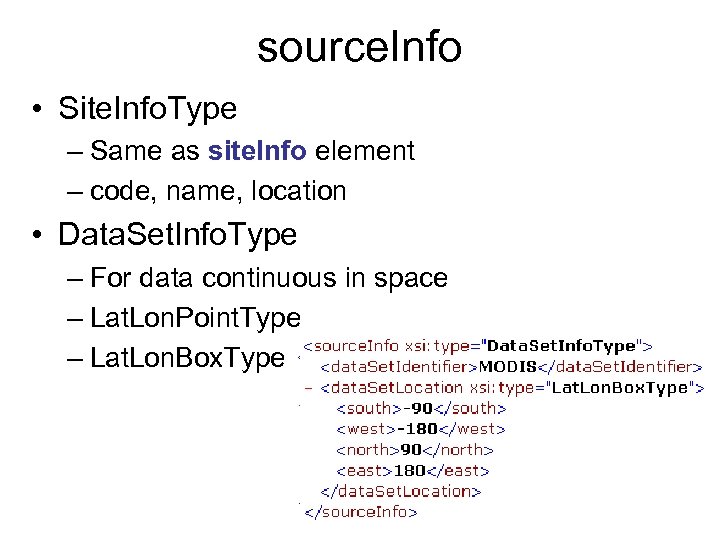
source. Info • Site. Info. Type – Same as site. Info element – code, name, location • Data. Set. Info. Type – For data continuous in space – Lat. Lon. Point. Type – Lat. Lon. Box. Type

variable • Same as previous variable element • code, name, units, etc.

values • Each time series value recorded in value element • Timestamp, plus metadata for the value, recorded in element’s attributes qualifier ISO Time value
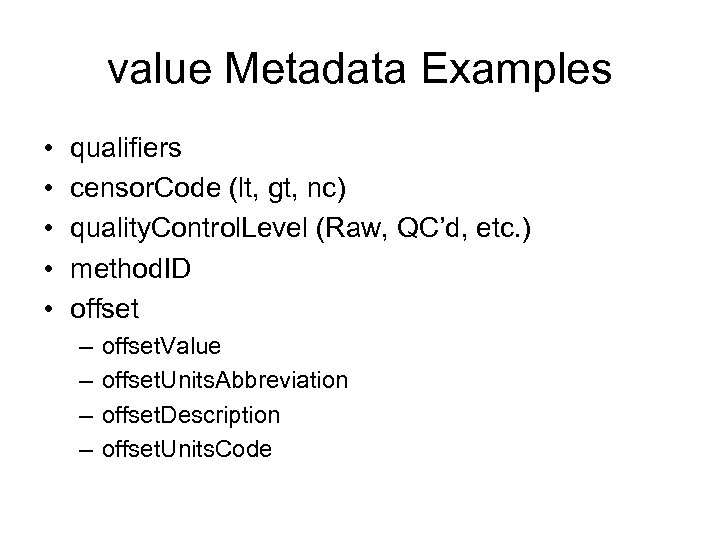
value Metadata Examples • • • qualifiers censor. Code (lt, gt, nc) quality. Control. Level (Raw, QC’d, etc. ) method. ID offset – – offset. Value offset. Units. Abbreviation offset. Description offset. Units. Code

Time. Series Response, Recap query. Info location variable values

Conclusions about Water. ML • Consistent Format • Includes lots of information • How do I use it? HIS Analyst

HIS Analyst • Desktop apps that use Water. One. Flow • Examples for various application environments • Hydro. Objects – for apps that aren’t web service enabled • Workbook available at: http: //www. cuahsi. org/his/docs/HIS-workbook-20061130. pdf

HIS Workbook • Ingesting NWIS Data into Excel • Ingesting STORET Data into Excel • Ingesting Weather and Streamflow Data into Arc. GIS • Plotting MODIS Data with Matlab • Ingesting NWIS Data using VB. Net • Ingesting NWIS Data Using Java

Excel Demo
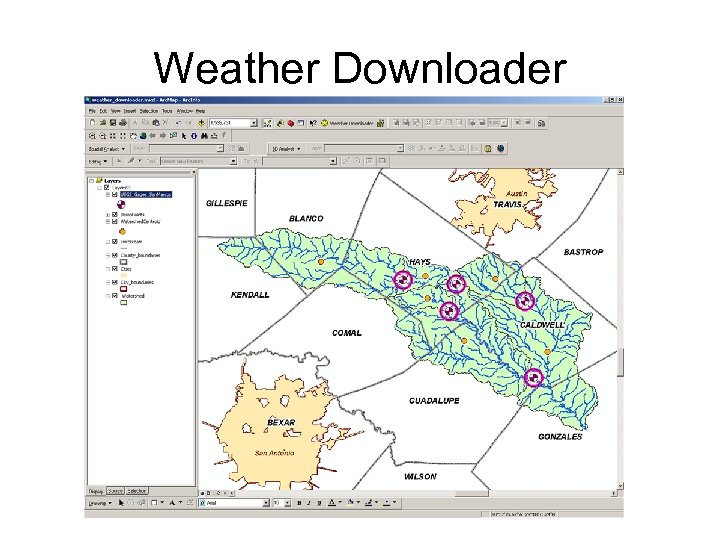
Weather Downloader
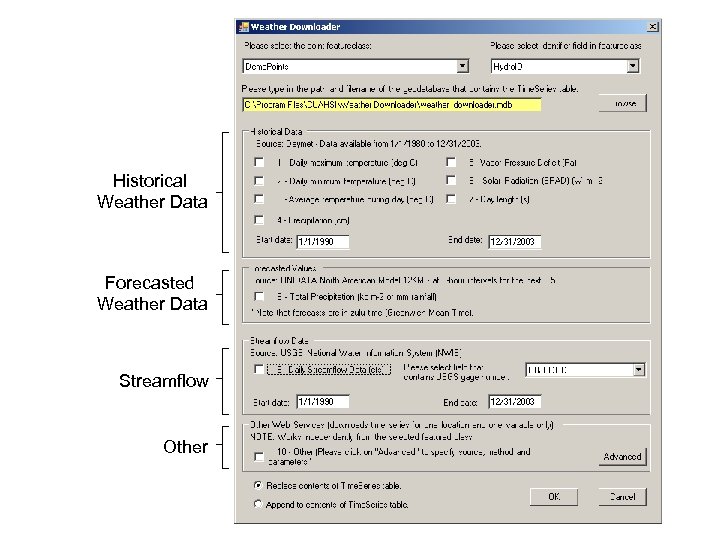
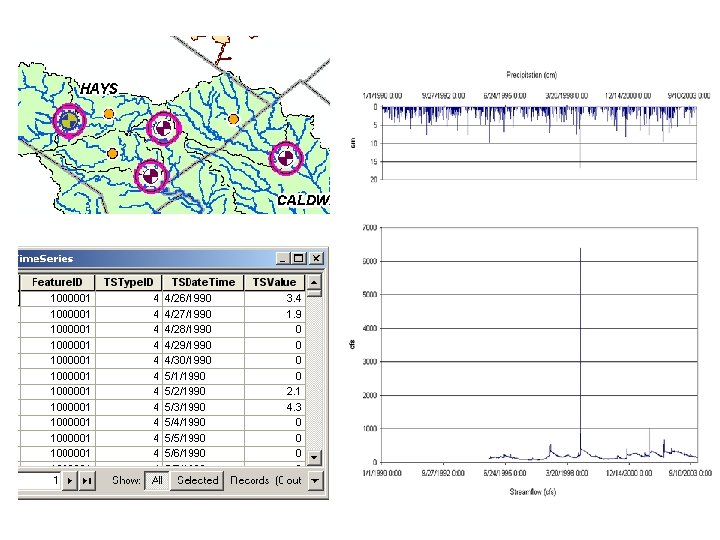
Historical Weather Data Forecasted Weather Data Streamflow Other
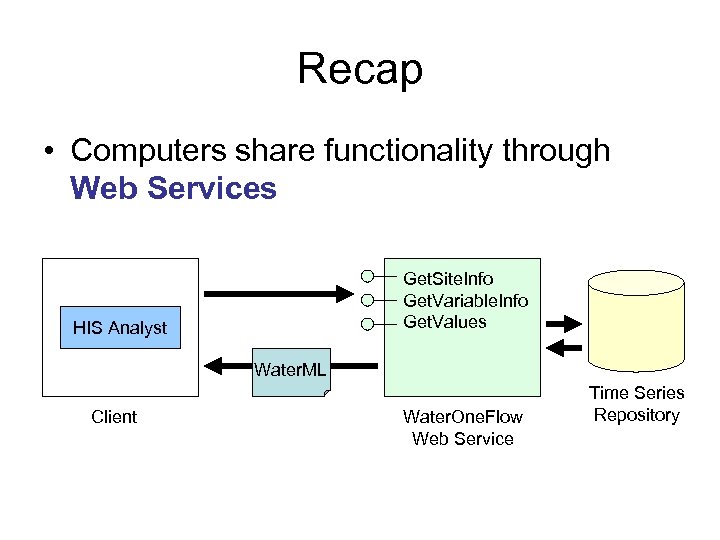
Recap • Computers share functionality through Web Services Get. Site. Info Get. Variable. Info Get. Values HIS Analyst Water. ML Client Water. One. Flow Web Service Time Series Repository
9faa2f5016252b507dca8fe2716e368b.ppt