c1a7df301988df06c612f5dd8463e3f4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Cu 2 O deposition Process Rhodia Kermel
Cu 2 O deposition Process Rhodia Kermel
 Summary • Concept presentation • Technical requirements • Process description • Advantages Rhodia Kermel 2
Summary • Concept presentation • Technical requirements • Process description • Advantages Rhodia Kermel 2
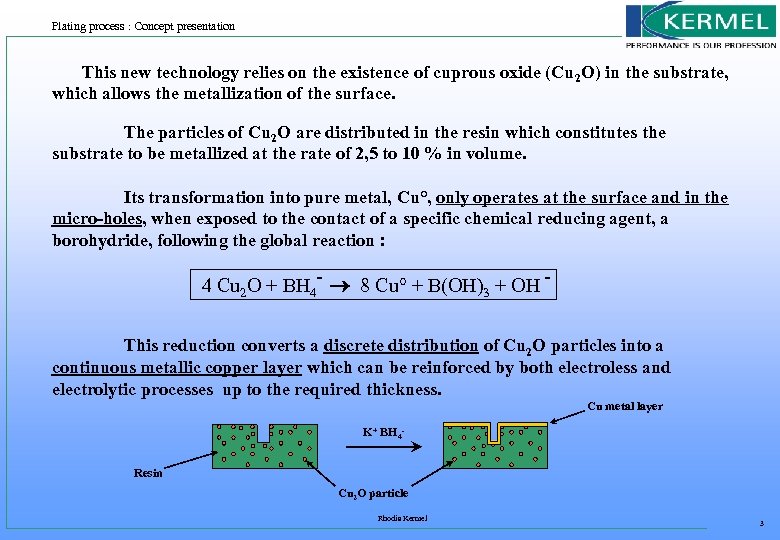 Plating process : Concept presentation This new technology relies on the existence of cuprous oxide (Cu 2 O) in the substrate, which allows the metallization of the surface. The particles of Cu 2 O are distributed in the resin which constitutes the substrate to be metallized at the rate of 2, 5 to 10 % in volume. Its transformation into pure metal, Cu°, only operates at the surface and in the micro-holes, when exposed to the contact of a specific chemical reducing agent, a borohydride, following the global reaction : 4 Cu 2 O + BH 4 - 8 Cu° + B(OH)3 + OH This reduction converts a discrete distribution of Cu 2 O particles into a continuous metallic copper layer which can be reinforced by both electroless and electrolytic processes up to the required thickness. Cu metal layer K+ BH 4 Resin Cu 2 O particle Rhodia Kermel 3
Plating process : Concept presentation This new technology relies on the existence of cuprous oxide (Cu 2 O) in the substrate, which allows the metallization of the surface. The particles of Cu 2 O are distributed in the resin which constitutes the substrate to be metallized at the rate of 2, 5 to 10 % in volume. Its transformation into pure metal, Cu°, only operates at the surface and in the micro-holes, when exposed to the contact of a specific chemical reducing agent, a borohydride, following the global reaction : 4 Cu 2 O + BH 4 - 8 Cu° + B(OH)3 + OH This reduction converts a discrete distribution of Cu 2 O particles into a continuous metallic copper layer which can be reinforced by both electroless and electrolytic processes up to the required thickness. Cu metal layer K+ BH 4 Resin Cu 2 O particle Rhodia Kermel 3
 Plating process : Concept presentation Products and operation for the process application : l l Cu 2 O particles : - pulverulent powder, can be refined, dispersed within the polymeric matrix, - cheap and usual product, - several suppliers. Chemical treatment before the reduction to remove the superficial layer of the matrix : - to achieve high level of peel strength (see photo 1 next page), - to metallize simultaneously holes and surfaces (see photo 2 next page). Reducing agent : mainly potassium or sodium borohydride - usual (several suppliers) and low cost (much cheaper than palladium), - easy to handle (not hazardous, in an aqueous form), - easy to use : at first sight, borohydride solution can be substituted to palladium batch in the standard process line. Optimization to fit the wanted requirement: - concentration, size and dispersion of Cu 2 O particles, - chemical treatment before reducing, - reduction’s parameters. Rhodia Kermel 4
Plating process : Concept presentation Products and operation for the process application : l l Cu 2 O particles : - pulverulent powder, can be refined, dispersed within the polymeric matrix, - cheap and usual product, - several suppliers. Chemical treatment before the reduction to remove the superficial layer of the matrix : - to achieve high level of peel strength (see photo 1 next page), - to metallize simultaneously holes and surfaces (see photo 2 next page). Reducing agent : mainly potassium or sodium borohydride - usual (several suppliers) and low cost (much cheaper than palladium), - easy to handle (not hazardous, in an aqueous form), - easy to use : at first sight, borohydride solution can be substituted to palladium batch in the standard process line. Optimization to fit the wanted requirement: - concentration, size and dispersion of Cu 2 O particles, - chemical treatment before reducing, - reduction’s parameters. Rhodia Kermel 4
 Plating process : Concept presentation Photo 1 : Interface between the substrate and the copper obtained after a chemical treatment Photo 2 : Very good peel strength continuity for the metal layer in surface and holes thanks to reduced Cu 2 O particles Rhodia Kermel 5
Plating process : Concept presentation Photo 1 : Interface between the substrate and the copper obtained after a chemical treatment Photo 2 : Very good peel strength continuity for the metal layer in surface and holes thanks to reduced Cu 2 O particles Rhodia Kermel 5
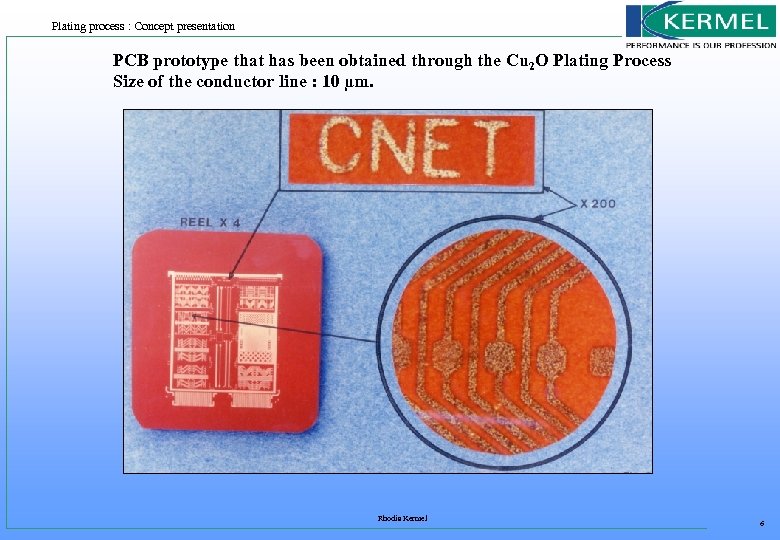 Plating process : Concept presentation PCB prototype that has been obtained through the Cu 2 O Plating Process Size of the conductor line : 10 µm. Rhodia Kermel 6
Plating process : Concept presentation PCB prototype that has been obtained through the Cu 2 O Plating Process Size of the conductor line : 10 µm. Rhodia Kermel 6
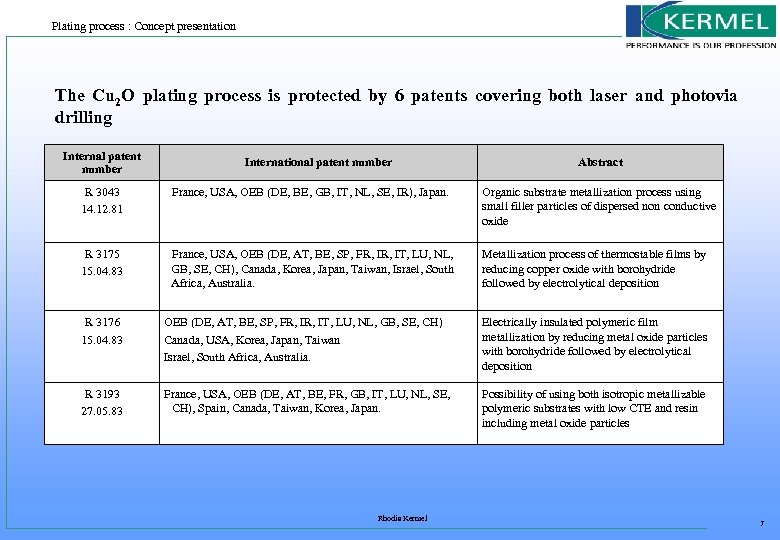 Plating process : Concept presentation The Cu 2 O plating process is protected by 6 patents covering both laser and photovia drilling Internal patent number International patent number Abstract R 3043 14. 12. 81 France, USA, OEB (DE, BE, GB, IT, NL, SE, IR), Japan. Organic substrate metallization process using small filler particles of dispersed non conductive oxide R 3175 15. 04. 83 France, USA, OEB (DE, AT, BE, SP, FR, IT, LU, NL, GB, SE, CH), Canada, Korea, Japan, Taiwan, Israel, South Africa, Australia. Metallization process of thermostable films by reducing copper oxide with borohydride followed by electrolytical deposition R 3176 15. 04. 83 OEB (DE, AT, BE, SP, FR, IT, LU, NL, GB, SE, CH) Canada, USA, Korea, Japan, Taiwan Israel, South Africa, Australia. Electrically insulated polymeric film metallization by reducing metal oxide particles with borohydride followed by electrolytical deposition R 3193 27. 05. 83 France, USA, OEB (DE, AT, BE, FR, GB, IT, LU, NL, SE, CH), Spain, Canada, Taiwan, Korea, Japan. Possibility of using both isotropic metallizable polymeric substrates with low CTE and resin including metal oxide particles Rhodia Kermel 7
Plating process : Concept presentation The Cu 2 O plating process is protected by 6 patents covering both laser and photovia drilling Internal patent number International patent number Abstract R 3043 14. 12. 81 France, USA, OEB (DE, BE, GB, IT, NL, SE, IR), Japan. Organic substrate metallization process using small filler particles of dispersed non conductive oxide R 3175 15. 04. 83 France, USA, OEB (DE, AT, BE, SP, FR, IT, LU, NL, GB, SE, CH), Canada, Korea, Japan, Taiwan, Israel, South Africa, Australia. Metallization process of thermostable films by reducing copper oxide with borohydride followed by electrolytical deposition R 3176 15. 04. 83 OEB (DE, AT, BE, SP, FR, IT, LU, NL, GB, SE, CH) Canada, USA, Korea, Japan, Taiwan Israel, South Africa, Australia. Electrically insulated polymeric film metallization by reducing metal oxide particles with borohydride followed by electrolytical deposition R 3193 27. 05. 83 France, USA, OEB (DE, AT, BE, FR, GB, IT, LU, NL, SE, CH), Spain, Canada, Taiwan, Korea, Japan. Possibility of using both isotropic metallizable polymeric substrates with low CTE and resin including metal oxide particles Rhodia Kermel 7
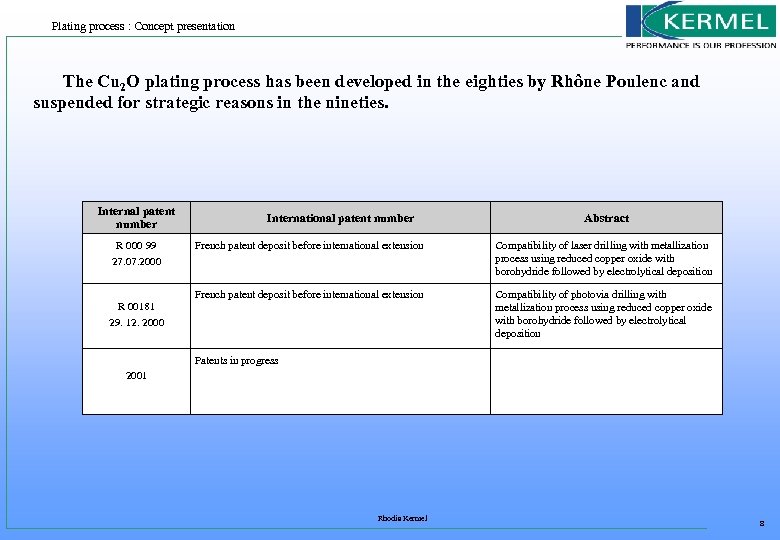 Plating process : Concept presentation The Cu 2 O plating process has been developed in the eighties by Rhône Poulenc and suspended for strategic reasons in the nineties. Internal patent number R 000 99 27. 07. 2000 International patent number Abstract French patent deposit before international extension Compatibility of laser drilling with metallization process using reduced copper oxide with borohydride followed by electrolytical deposition French patent deposit before international extension Compatibility of photovia drilling with metallization process using reduced copper oxide with borohydride followed by electrolytical deposition R 00181 29. 12. 2000 Patents in progress 2001 Rhodia Kermel 8
Plating process : Concept presentation The Cu 2 O plating process has been developed in the eighties by Rhône Poulenc and suspended for strategic reasons in the nineties. Internal patent number R 000 99 27. 07. 2000 International patent number Abstract French patent deposit before international extension Compatibility of laser drilling with metallization process using reduced copper oxide with borohydride followed by electrolytical deposition French patent deposit before international extension Compatibility of photovia drilling with metallization process using reduced copper oxide with borohydride followed by electrolytical deposition R 00181 29. 12. 2000 Patents in progress 2001 Rhodia Kermel 8
 • Concept presentation • Technical requirements • Process description • Advantages Rhodia Kermel 9
• Concept presentation • Technical requirements • Process description • Advantages Rhodia Kermel 9
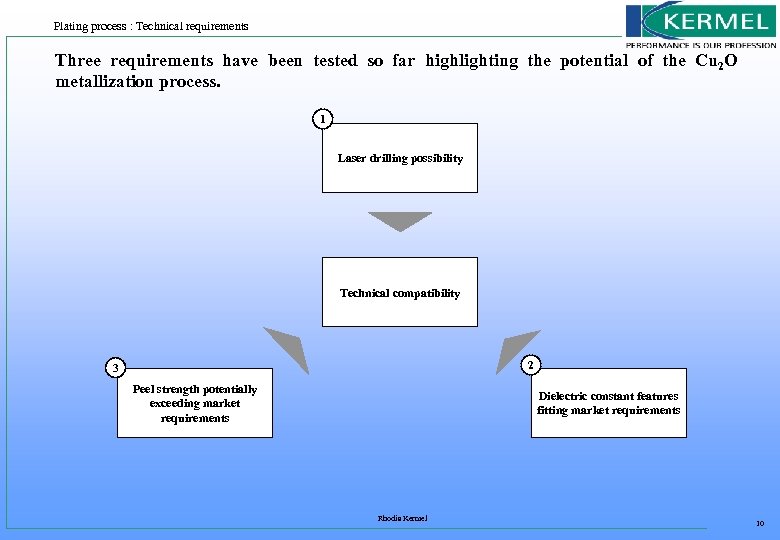 Plating process : Technical requirements Three requirements have been tested so far highlighting the potential of the Cu 2 O metallization process. 1 Laser drilling possibility Technical compatibility 2 3 Peel strength potentially exceeding market requirements Dielectric constant features fitting market requirements Rhodia Kermel 10
Plating process : Technical requirements Three requirements have been tested so far highlighting the potential of the Cu 2 O metallization process. 1 Laser drilling possibility Technical compatibility 2 3 Peel strength potentially exceeding market requirements Dielectric constant features fitting market requirements Rhodia Kermel 10
 Plating process : Technical requirements Cu 2 O particles do not hinder the laser drilling quality. Non optimized laser drilling tests for Epoxy + Cu 2 O weight concentration: 60 % in volume: 10 % Source: Delta Electronic services Rhodia Kermel 11
Plating process : Technical requirements Cu 2 O particles do not hinder the laser drilling quality. Non optimized laser drilling tests for Epoxy + Cu 2 O weight concentration: 60 % in volume: 10 % Source: Delta Electronic services Rhodia Kermel 11
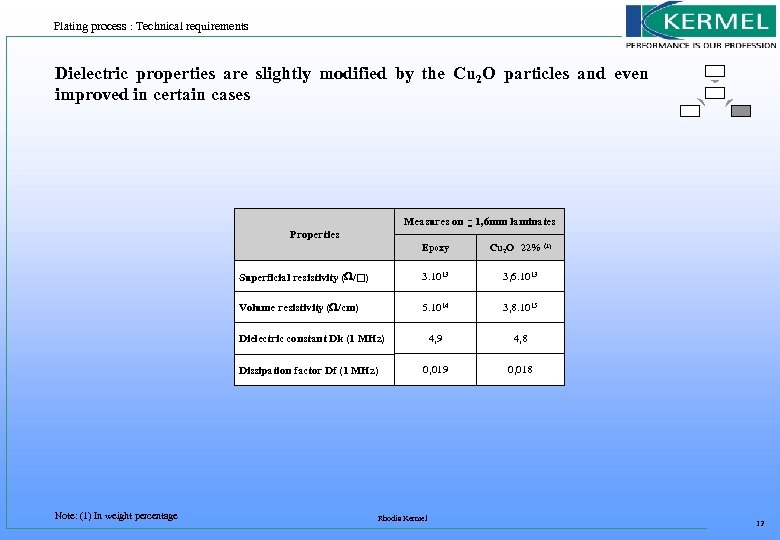 Plating process : Technical requirements Dielectric properties are slightly modified by the Cu 2 O particles and even improved in certain cases Measures on ~ 1, 6 mm laminates Properties Epoxy Cu 2 O 22% (1) Superficial resistivity ( / ) 3. 1013 3, 6. 1013 Volume resistivity ( /cm) 5. 1014 3, 8. 1015 4, 9 4, 8 0, 019 0, 018 Dielectric constant Dk (1 MHz) Dissipation factor Df (1 MHz) Note: (1) In weight percentage Rhodia Kermel 12
Plating process : Technical requirements Dielectric properties are slightly modified by the Cu 2 O particles and even improved in certain cases Measures on ~ 1, 6 mm laminates Properties Epoxy Cu 2 O 22% (1) Superficial resistivity ( / ) 3. 1013 3, 6. 1013 Volume resistivity ( /cm) 5. 1014 3, 8. 1015 4, 9 4, 8 0, 019 0, 018 Dielectric constant Dk (1 MHz) Dissipation factor Df (1 MHz) Note: (1) In weight percentage Rhodia Kermel 12
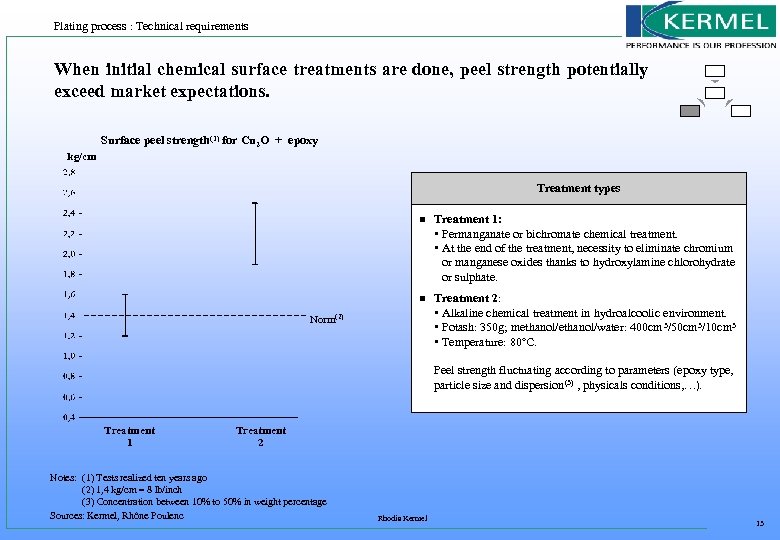 Plating process : Technical requirements When initial chemical surface treatments are done, peel strength potentially exceed market expectations. Surface peel strength(1) for Cu 2 O + epoxy kg/cm Treatment types n Treatment 1: • Permanganate or bichromate chemical treatment. • At the end of the treatment, necessity to eliminate chromium or manganese oxides thanks to hydroxylamine chlorohydrate or sulphate. n Treatment 2: • Alkaline chemical treatment in hydroalcoolic environment. • Potash: 350 g; methanol/water: 400 cm 3/50 cm 3/10 cm 3 • Temperature: 80°C. Norm(2) Peel strength fluctuating according to parameters (epoxy type, particle size and dispersion (3) , physicals conditions, …). Treatment 1 Treatment 2 Notes: (1) Tests realized ten years ago (2) 1, 4 kg/cm = 8 lb/inch (3) Concentration between 10% to 50% in weight percentage Sources: Kermel, Rhône Poulenc Rhodia Kermel 13
Plating process : Technical requirements When initial chemical surface treatments are done, peel strength potentially exceed market expectations. Surface peel strength(1) for Cu 2 O + epoxy kg/cm Treatment types n Treatment 1: • Permanganate or bichromate chemical treatment. • At the end of the treatment, necessity to eliminate chromium or manganese oxides thanks to hydroxylamine chlorohydrate or sulphate. n Treatment 2: • Alkaline chemical treatment in hydroalcoolic environment. • Potash: 350 g; methanol/water: 400 cm 3/50 cm 3/10 cm 3 • Temperature: 80°C. Norm(2) Peel strength fluctuating according to parameters (epoxy type, particle size and dispersion (3) , physicals conditions, …). Treatment 1 Treatment 2 Notes: (1) Tests realized ten years ago (2) 1, 4 kg/cm = 8 lb/inch (3) Concentration between 10% to 50% in weight percentage Sources: Kermel, Rhône Poulenc Rhodia Kermel 13
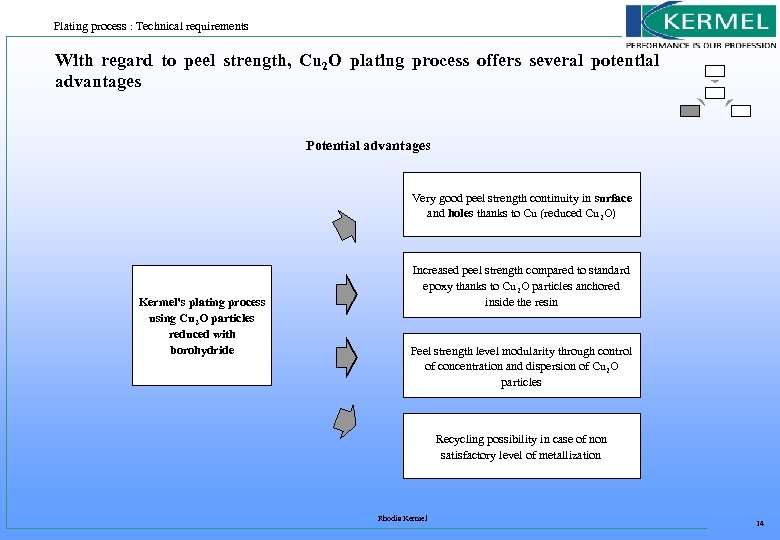 Plating process : Technical requirements With regard to peel strength, Cu 2 O plating process offers several potential advantages Potential advantages Very good peel strength continuity in surface and holes thanks to Cu (reduced Cu 2 O) Kermel's plating process using Cu 2 O particles reduced with borohydride Increased peel strength compared to standard epoxy thanks to Cu 2 O particles anchored inside the resin Peel strength level modularity through control of concentration and dispersion of Cu 2 O particles Recycling possibility in case of non satisfactory level of metallization Rhodia Kermel 14
Plating process : Technical requirements With regard to peel strength, Cu 2 O plating process offers several potential advantages Potential advantages Very good peel strength continuity in surface and holes thanks to Cu (reduced Cu 2 O) Kermel's plating process using Cu 2 O particles reduced with borohydride Increased peel strength compared to standard epoxy thanks to Cu 2 O particles anchored inside the resin Peel strength level modularity through control of concentration and dispersion of Cu 2 O particles Recycling possibility in case of non satisfactory level of metallization Rhodia Kermel 14
 • Concept presentation • Technical requirements • Process description • Advantages Rhodia Kermel 15
• Concept presentation • Technical requirements • Process description • Advantages Rhodia Kermel 15
 Plating process : Description At first sight, in the SBU layer production process, minor changes should occur in major PCB makers production lines to implement the Cu 2 O metallization concept. Changes occur principally in 2 steps : - drilling when compared to RCC (see step 4 of the process chart), - electroless plating with a substitution of the palladium by the borohydride reduction bath (see step 5). With the Cu 2 O metallization concept, the number of the process steps is : - 25% less than RCC technology, - the same than liquid technology. SBU layer simplified production steps with CO 2 laser drilling and with different elaborated materials is presented in the 4 next slides. Rhodia Kermel 16
Plating process : Description At first sight, in the SBU layer production process, minor changes should occur in major PCB makers production lines to implement the Cu 2 O metallization concept. Changes occur principally in 2 steps : - drilling when compared to RCC (see step 4 of the process chart), - electroless plating with a substitution of the palladium by the borohydride reduction bath (see step 5). With the Cu 2 O metallization concept, the number of the process steps is : - 25% less than RCC technology, - the same than liquid technology. SBU layer simplified production steps with CO 2 laser drilling and with different elaborated materials is presented in the 4 next slides. Rhodia Kermel 16
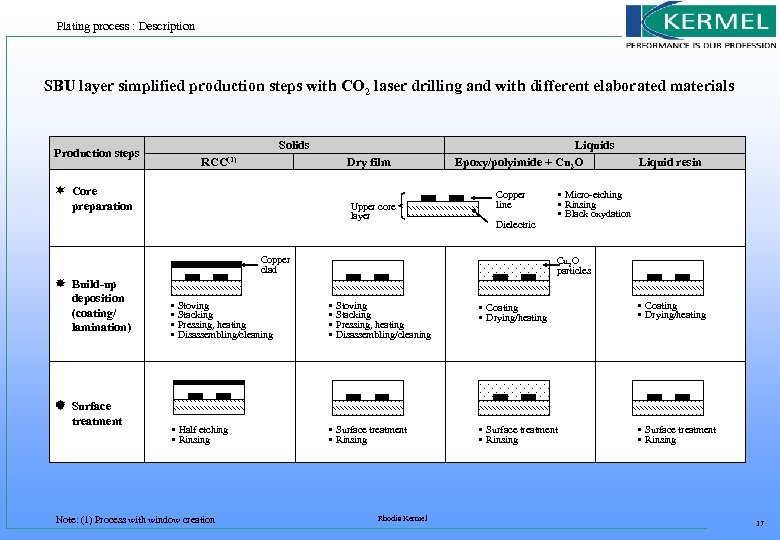 Plating process : Description SBU layer simplified production steps with CO 2 laser drilling and with different elaborated materials Solids Production steps RCC(1) Dry film Core preparation Upper core layer • • Stoving Stacking Pressing, heating Disassembling/cleaning Liquid resin • Micro-etching • Rinsing • Black oxydation Copper line Dielectric Copper clad Build-up deposition (coating/ lamination) Liquids Epoxy/polyimide + Cu 2 O particles • • Stoving Stacking Pressing, heating Disassembling/cleaning • Coating • Drying/heating • Surface treatment • Rinsing Surface treatment • Half etching • Rinsing Note: (1) Process with window creation • Surface treatment • Rinsing Rhodia Kermel 17
Plating process : Description SBU layer simplified production steps with CO 2 laser drilling and with different elaborated materials Solids Production steps RCC(1) Dry film Core preparation Upper core layer • • Stoving Stacking Pressing, heating Disassembling/cleaning Liquid resin • Micro-etching • Rinsing • Black oxydation Copper line Dielectric Copper clad Build-up deposition (coating/ lamination) Liquids Epoxy/polyimide + Cu 2 O particles • • Stoving Stacking Pressing, heating Disassembling/cleaning • Coating • Drying/heating • Surface treatment • Rinsing Surface treatment • Half etching • Rinsing Note: (1) Process with window creation • Surface treatment • Rinsing Rhodia Kermel 17
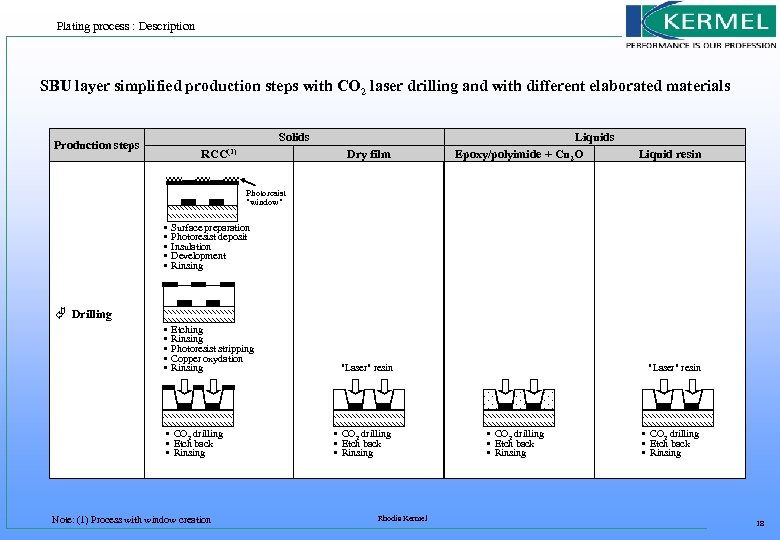 Plating process : Description SBU layer simplified production steps with CO 2 laser drilling and with different elaborated materials Solids Production steps RCC(1) Dry film Liquids Epoxy/polyimide + Cu 2 O Liquid resin Photoresist "window" • • • Surface preparation Photoresist deposit Insulation Development Rinsing • • • Etching Rinsing Photoresist stripping Copper oxydation Rinsing à Drilling • CO 2 drilling • Etch back • Rinsing Note: (1) Process with window creation "Laser" resin • CO 2 drilling • Etch back • Rinsing Rhodia Kermel "Laser" resin • CO 2 drilling • Etch back • Rinsing 18
Plating process : Description SBU layer simplified production steps with CO 2 laser drilling and with different elaborated materials Solids Production steps RCC(1) Dry film Liquids Epoxy/polyimide + Cu 2 O Liquid resin Photoresist "window" • • • Surface preparation Photoresist deposit Insulation Development Rinsing • • • Etching Rinsing Photoresist stripping Copper oxydation Rinsing à Drilling • CO 2 drilling • Etch back • Rinsing Note: (1) Process with window creation "Laser" resin • CO 2 drilling • Etch back • Rinsing Rhodia Kermel "Laser" resin • CO 2 drilling • Etch back • Rinsing 18
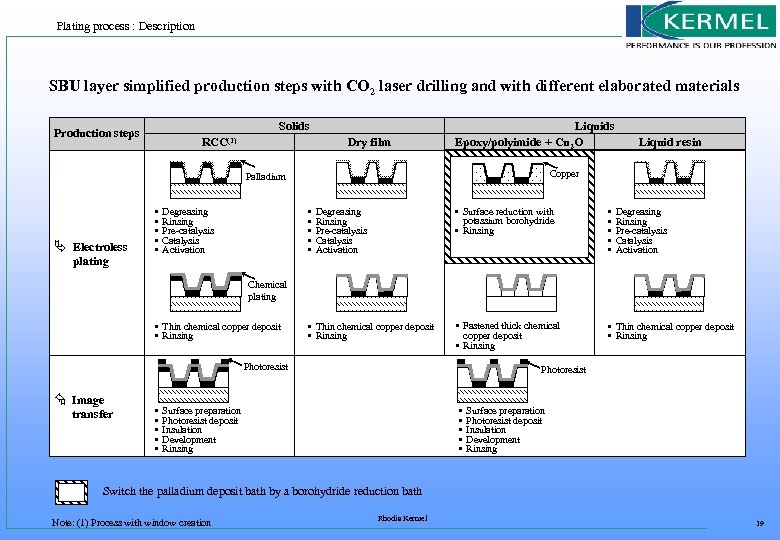 Plating process : Description SBU layer simplified production steps with CO 2 laser drilling and with different elaborated materials Solids Production steps RCC(1) Dry film Liquids Epoxy/polyimide + Cu 2 O Copper Palladium Ä Electroless plating • • • Degreasing Rinsing Pre-catalysis Catalysis Activation Liquid resin • Surface reduction with potassium borohydride • Rinsing Degreasing Rinsing Pre-catalysis Catalysis Activation • • • Fastened thick chemical copper deposit • Rinsing • Thin chemical copper deposit • Rinsing Degreasing Rinsing Pre-catalysis Catalysis Activation Chemical plating • Thin chemical copper deposit • Rinsing Photoresist Å Image transfer • • • Photoresist • • • Surface preparation Photoresist deposit Insulation Development Rinsing Switch the palladium deposit bath by a borohydride reduction bath Note: (1) Process with window creation Rhodia Kermel 19
Plating process : Description SBU layer simplified production steps with CO 2 laser drilling and with different elaborated materials Solids Production steps RCC(1) Dry film Liquids Epoxy/polyimide + Cu 2 O Copper Palladium Ä Electroless plating • • • Degreasing Rinsing Pre-catalysis Catalysis Activation Liquid resin • Surface reduction with potassium borohydride • Rinsing Degreasing Rinsing Pre-catalysis Catalysis Activation • • • Fastened thick chemical copper deposit • Rinsing • Thin chemical copper deposit • Rinsing Degreasing Rinsing Pre-catalysis Catalysis Activation Chemical plating • Thin chemical copper deposit • Rinsing Photoresist Å Image transfer • • • Photoresist • • • Surface preparation Photoresist deposit Insulation Development Rinsing Switch the palladium deposit bath by a borohydride reduction bath Note: (1) Process with window creation Rhodia Kermel 19
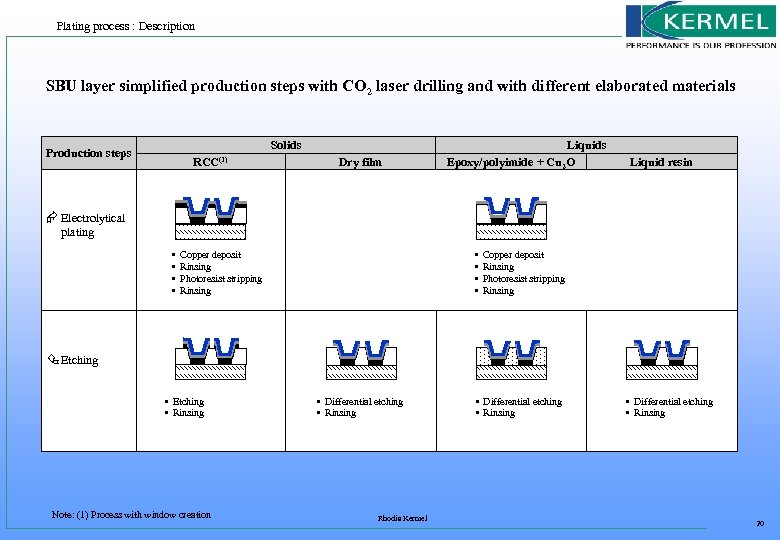 Plating process : Description SBU layer simplified production steps with CO 2 laser drilling and with different elaborated materials Solids Production steps RCC(1) Dry film Liquids Epoxy/polyimide + Cu 2 O Liquid resin Æ Electrolytical plating • • Copper deposit Rinsing Photoresist stripping Rinsing Ç Etching • Rinsing Note: (1) Process with window creation • Differential etching • Rinsing Rhodia Kermel • Differential etching • Rinsing 20
Plating process : Description SBU layer simplified production steps with CO 2 laser drilling and with different elaborated materials Solids Production steps RCC(1) Dry film Liquids Epoxy/polyimide + Cu 2 O Liquid resin Æ Electrolytical plating • • Copper deposit Rinsing Photoresist stripping Rinsing Ç Etching • Rinsing Note: (1) Process with window creation • Differential etching • Rinsing Rhodia Kermel • Differential etching • Rinsing 20
 • Concept presentation • Technical requirements • Process description • Advantages Rhodia Kermel 21
• Concept presentation • Technical requirements • Process description • Advantages Rhodia Kermel 21
 Plating process : Advantages This new plating process is : Easy to implement - Process gets simultaneously plated holes and surfaces. - Products are usually cost competitive and easy to handle (Cu 2 O and borohydride). - Number of process steps reduced. - Compatibility with liquid/film technologies. Reliable - Due to the high level of peel strength achieved. - Peel strength of plated copper increased in surface and in micro-via holes. Technologically advanced - Reliable access to additive/semi additive processes. - Reliable access to fine line. - The presence of Cu 2 O particles, compatible with the dielectric and CTE requirements, enhance thermal transfer of dielectric matrix. Economic - Reliability and more specifically of plated micro-holes. - Saving of labor because of less steps and operations. - Saving of investment because minimum changes in production lines for PCB makers. Rhodia Kermel 22
Plating process : Advantages This new plating process is : Easy to implement - Process gets simultaneously plated holes and surfaces. - Products are usually cost competitive and easy to handle (Cu 2 O and borohydride). - Number of process steps reduced. - Compatibility with liquid/film technologies. Reliable - Due to the high level of peel strength achieved. - Peel strength of plated copper increased in surface and in micro-via holes. Technologically advanced - Reliable access to additive/semi additive processes. - Reliable access to fine line. - The presence of Cu 2 O particles, compatible with the dielectric and CTE requirements, enhance thermal transfer of dielectric matrix. Economic - Reliability and more specifically of plated micro-holes. - Saving of labor because of less steps and operations. - Saving of investment because minimum changes in production lines for PCB makers. Rhodia Kermel 22
 Plating process : Conclusion As a conclusion, the Cu 2 O Plating Process is easy to implement, technologically advanced, and above all, reliable and economic. In that way, our innovative plating technology : • comes up to current specifications and even exceeds the market expectations, • answer potentially to the evolution in specifications, • is adaptable to most industrial processes. For more information, please contact : V. LORENTZ Marketing Department Tel : + 33 (0)3 89 20 47 44 Fax : + 33 (0)3 89 20 47 38 www. kermel. com Rhodia Kermel 23
Plating process : Conclusion As a conclusion, the Cu 2 O Plating Process is easy to implement, technologically advanced, and above all, reliable and economic. In that way, our innovative plating technology : • comes up to current specifications and even exceeds the market expectations, • answer potentially to the evolution in specifications, • is adaptable to most industrial processes. For more information, please contact : V. LORENTZ Marketing Department Tel : + 33 (0)3 89 20 47 44 Fax : + 33 (0)3 89 20 47 38 www. kermel. com Rhodia Kermel 23


