a7e006f81e9acf00d1bab2ee5af81edb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

CTC 475 Review ¡ BTCF to ATCF

CTC 475 Estimating and Inflation

Objectives Know a few ways to estimate prices ¡ Know how to account for inflation ¡ Know the difference between actual and real dollars ¡

Estimating Cash Flows Should be an organized approach ¡ Work breakdown structure (tasks, subtasks) ¡ Cost and Revenue (life-cycle)
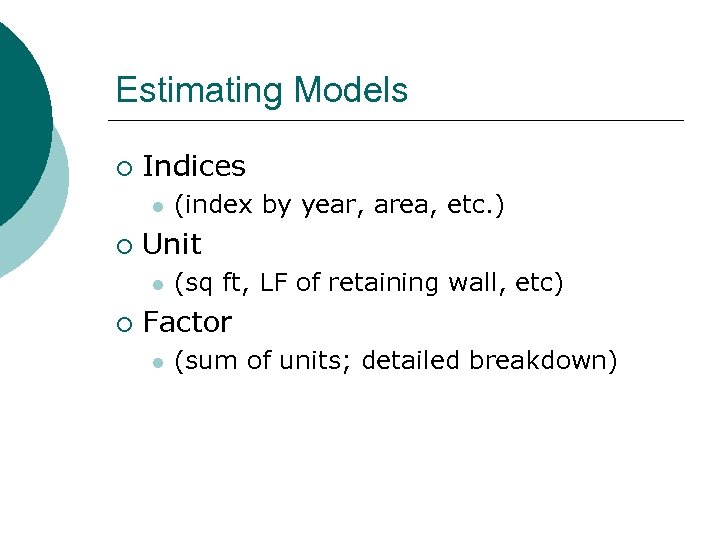
Estimating Models ¡ Indices l ¡ Unit l ¡ (index by year, area, etc. ) (sq ft, LF of retaining wall, etc) Factor l (sum of units; detailed breakdown)

Index Example Index for New York City is 1. 26 ¡ Construction costs are 26% higher than upstate NY ¡

Unit Technique House approximately 2000 sq ft ¡ Price approximately $55/sq ft ¡ Estimated Price=$110, 000 ¡

Factor Technique-More detailed 2 x 4 ¡ Faucets ¡ Lights ¡ Plywood ¡ Shingles ¡ Etc. ¡
Other ideas Bottom-up estimating ¡ Top down estimating (design to cost) ¡ Value Engineering-get input in design process for better design at lower cost ¡

Inflation ¡ ¡ ¡ Prices change over time Inflation-an increase in the average price paid for goods and services Can affect economic comparison of alternatives

Deflation ¡ ¡ Deflation—prices decrease over time Inflation is much more common than deflation
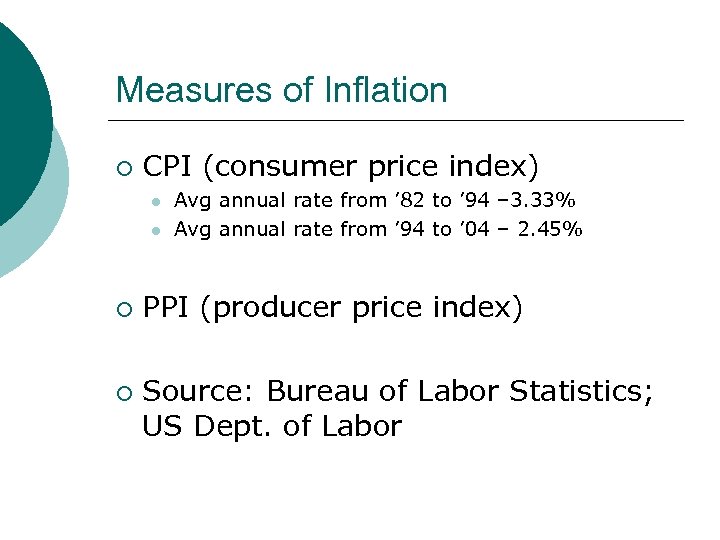
Measures of Inflation ¡ CPI (consumer price index) l l ¡ ¡ Avg annual rate from ’ 82 to ’ 94 – 3. 33% Avg annual rate from ’ 94 to ’ 04 – 2. 45% PPI (producer price index) Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics; US Dept. of Labor

Actual Dollars (A$) 1. 2. The # of dollars associated w/ a cash flow as of the time it occurs Other names: l l Nominal Current Then-current Inflated $

Real Dollars (R$) 1. 2. Dollars expressed in terms of the same purchasing power relative to a particular time Also called constant dollars
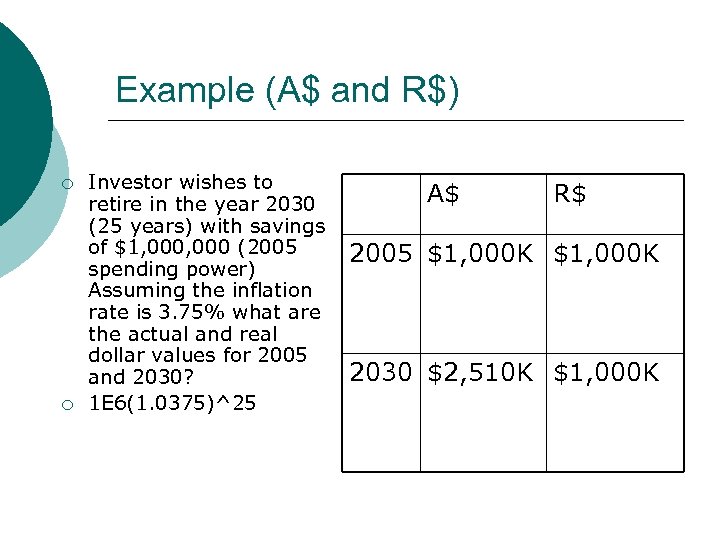
Example (A$ and R$) ¡ ¡ Investor wishes to retire in the year 2030 (25 years) with savings of $1, 000 (2005 spending power) Assuming the inflation rate is 3. 75% what are the actual and real dollar values for 2005 and 2030? 1 E 6(1. 0375)^25 A$ R$ 2005 $1, 000 K 2030 $2, 510 K $1, 000 K

Interest Rates ¡ Real interest rate (ir) l l l Rate paid for use of capital Doesn’t include inflation Also called inflation-free interest rate Inflation rate (f) ¡ Combined (market) interest rate (ic) ¡ Relationship between (f, ir, ic) ¡ l ic=ir+f+ir*f
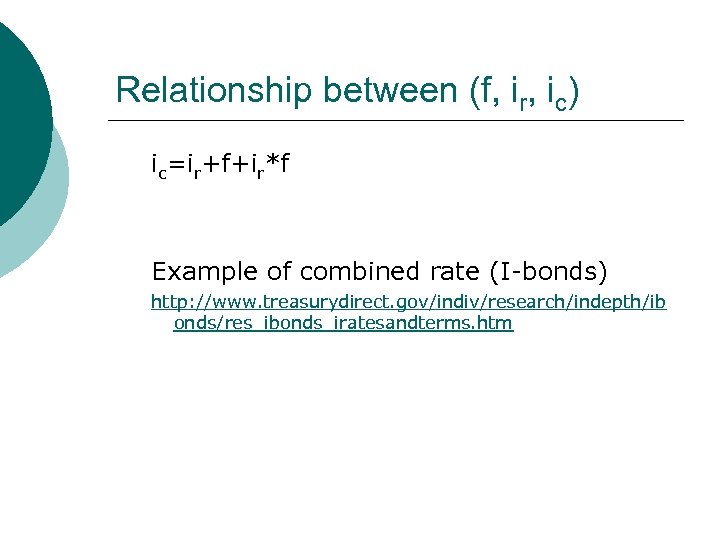
Relationship between (f, ir, ic) ic=ir+f+ir*f Example of combined rate (I-bonds) http: //www. treasurydirect. gov/indiv/research/indepth/ib onds/res_ibonds_iratesandterms. htm

Salary Purchasing Power Example 8 -1 from your book (pg 355 or 359) ¡ Salary data for 4 years (based on a 4% salary raise) is as follows: $45, 000 ¡ $46, 800 ¡ $48, 672 ¡ $50, 619 ¡
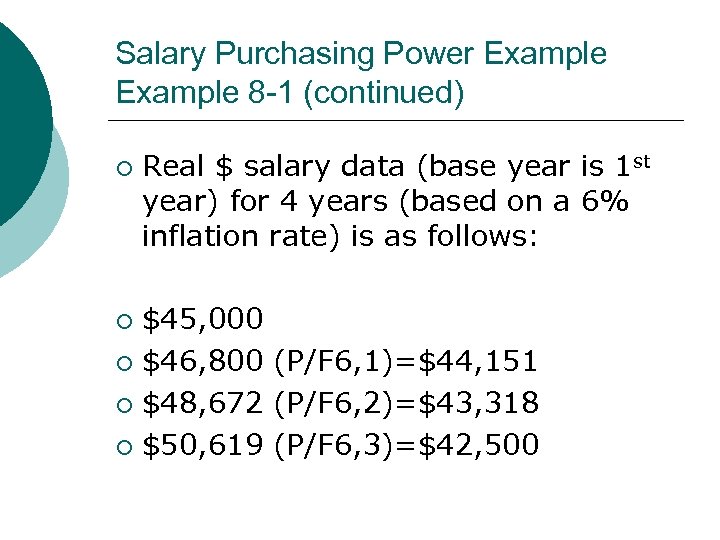
Salary Purchasing Power Example 8 -1 (continued) ¡ Real $ salary data (base year is 1 st year) for 4 years (based on a 6% inflation rate) is as follows: $45, 000 ¡ $46, 800 (P/F 6, 1)=$44, 151 ¡ $48, 672 (P/F 6, 2)=$43, 318 ¡ $50, 619 (P/F 6, 3)=$42, 500 ¡

Salary Increase Lesson?

Rules for Economic Analysis 2 Methods Express all cash flows in Actual $ and use the combined interest rate (ic)----accounts for inflation and use of capital OR ¡ Express all cash flows in terms of Real $ and use the real interest rate (ir)---doesn’t include inflation ¡

Using Actual Dollars ¡ ¡ Actual dollars change for some items (salaries, materials) Actual dollars don’t change for items fixed by contract (interest charges, lease fees, depreciation)
Next lecture ¡ Sensitivity Analyses ¡ Optimistic-Pessimistic ¡ Probabilistic
a7e006f81e9acf00d1bab2ee5af81edb.ppt