a44b40f42e2de5f1456a8489e0380697.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 CTC-275 Construction Methods Intro & Earthwork
CTC-275 Construction Methods Intro & Earthwork
 Get SUNYIT email account
Get SUNYIT email account
 • Many different ways to build same building • How many ways can you build a ham and cheese sandwich? • Types of ham, bread, cheese, toppings
• Many different ways to build same building • How many ways can you build a ham and cheese sandwich? • Types of ham, bread, cheese, toppings
 • Construction methods change when – Materials change • Why thatch roofs? • Why teepees and long houses? • How important where nails to building – Equipment changes • Horses to steam engines to today • Erie Canal was dug with shovels and rock sleds • Steam engines were stationary with belts going from pulleys to the engine
• Construction methods change when – Materials change • Why thatch roofs? • Why teepees and long houses? • How important where nails to building – Equipment changes • Horses to steam engines to today • Erie Canal was dug with shovels and rock sleds • Steam engines were stationary with belts going from pulleys to the engine
 House Construction • What materials can be used to build a house and what equipment is required – Wood – hammers, saws, drills, squares • Can also use engineered wood • What has happened to lumber in last 100 years? – Concrete – either cast in place, precast, or shotcrete • Can be above ground or below – – – Steel Stone Brick Adobe – only need forms Haybales
House Construction • What materials can be used to build a house and what equipment is required – Wood – hammers, saws, drills, squares • Can also use engineered wood • What has happened to lumber in last 100 years? – Concrete – either cast in place, precast, or shotcrete • Can be above ground or below – – – Steel Stone Brick Adobe – only need forms Haybales
 House Construction • Wooden houses can be constructed using three methods – 1. Balloon Framing – 2. Platform Frame – 3. Modular – assembly line
House Construction • Wooden houses can be constructed using three methods – 1. Balloon Framing – 2. Platform Frame – 3. Modular – assembly line
 Questions • What made skyscrapers possible? • How old is concrete and who first used it • How old are nails?
Questions • What made skyscrapers possible? • How old is concrete and who first used it • How old are nails?
 Construction Order • There is an order to all projects – What activities get done first – What activities need to be done in a specific order – What activities can be done at any point in time
Construction Order • There is an order to all projects – What activities get done first – What activities need to be done in a specific order – What activities can be done at any point in time
 Construction Order – Above ground Swimming pools • Remove topsoil & level area 3’ larger that pool diameter • Rake soil to remove rocks and roots • Layout bottom track • Dump sand inside pool area • Level track • Layout wall parts • Roll wall and put on J channel and top rail • Bolt wall, attach skimmer
Construction Order – Above ground Swimming pools • Remove topsoil & level area 3’ larger that pool diameter • Rake soil to remove rocks and roots • Layout bottom track • Dump sand inside pool area • Level track • Layout wall parts • Roll wall and put on J channel and top rail • Bolt wall, attach skimmer
 Construction Order – Swimming pools • • • Spread sand inside pool wall – rake & tamp Attach wall uprights Attach liner to J channel Use vacuum to suck liner to wall Plumb sand filter & pump together w/ skimmer & return line • Attach top coping • Add water • Cut out skimmer and return
Construction Order – Swimming pools • • • Spread sand inside pool wall – rake & tamp Attach wall uprights Attach liner to J channel Use vacuum to suck liner to wall Plumb sand filter & pump together w/ skimmer & return line • Attach top coping • Add water • Cut out skimmer and return
 Construction Order • Buildings: • • • Clear site Foundation work Framing & Siding Roofing Windows and Doors Siding Electrical - rough Plumbing - rough Insulation Wall finishes
Construction Order • Buildings: • • • Clear site Foundation work Framing & Siding Roofing Windows and Doors Siding Electrical - rough Plumbing - rough Insulation Wall finishes
 Construction Order • Buildings: • • • Foundation slab HVAC Ceilings Electrical – finish Plumbing – finish Paint/wall coverings Flooring Landscaping Pavement
Construction Order • Buildings: • • • Foundation slab HVAC Ceilings Electrical – finish Plumbing – finish Paint/wall coverings Flooring Landscaping Pavement
 Construction Order • How far along do you need to be before starting next activity? • On a house – probably one at a time • On a 1 floor bldg – probably 1 activity at a time but depends on size • Skyscraper – 1 activity per floor
Construction Order • How far along do you need to be before starting next activity? • On a house – probably one at a time • On a 1 floor bldg – probably 1 activity at a time but depends on size • Skyscraper – 1 activity per floor
 Construction Order • Highways • • • Centerline survey Clearing Bridge work Centerline survey Earthwork to get to bottom of subbase elevation Centerline survey Subbase placement Centerline survey Base placement
Construction Order • Highways • • • Centerline survey Clearing Bridge work Centerline survey Earthwork to get to bottom of subbase elevation Centerline survey Subbase placement Centerline survey Base placement
 Construction Order • Highways • • • Centerline survey Drainage Utilities (lights etc) Pavement base course Pavement wearing course Side slope grading Guard rail Lights and signs Pavement Markings
Construction Order • Highways • • • Centerline survey Drainage Utilities (lights etc) Pavement base course Pavement wearing course Side slope grading Guard rail Lights and signs Pavement Markings
 Construction Order • Move from one end of project to the other with each activity • Have multiple activities happening at any time • Surveying is a full time activity
Construction Order • Move from one end of project to the other with each activity • Have multiple activities happening at any time • Surveying is a full time activity
 Start at beginning • Earthwork – Moving rock or soil from one location to another – Processing it to meet location, elevation, density moisture content, etc – Efficient earthwork requires: accurate estimating of work quantities and conditions, proper equipment, competent job mangement
Start at beginning • Earthwork – Moving rock or soil from one location to another – Processing it to meet location, elevation, density moisture content, etc – Efficient earthwork requires: accurate estimating of work quantities and conditions, proper equipment, competent job mangement
 Equip Selection • Proper equipment has major impact on efficiency and profitablility • Can equipment perform required work • Also look at profitablility, other uses for equipment, return on investment, availability of parts and services, effect of downtime on other construction equip
Equip Selection • Proper equipment has major impact on efficiency and profitablility • Can equipment perform required work • Also look at profitablility, other uses for equipment, return on investment, availability of parts and services, effect of downtime on other construction equip
 Equipment planning • Need to plan to effectively use equipment • Production of equipment – Production = Volume per cycle/cycles per hour – Cycles per hour is based on efficiency of equip • Swing angle and elevation to truck bed • Soil hardness and Soil type • Room to manuever
Equipment planning • Need to plan to effectively use equipment • Production of equipment – Production = Volume per cycle/cycles per hour – Cycles per hour is based on efficiency of equip • Swing angle and elevation to truck bed • Soil hardness and Soil type • Room to manuever
 Equipment planning • Cost per production unit = equip cost per working hour/equip production per hour • Table 2 -1 show efficiencies
Equipment planning • Cost per production unit = equip cost per working hour/equip production per hour • Table 2 -1 show efficiencies
 Soil And Rock • General Soil Characteristics • Trafficability – ability of soil to support weight of vehicles under repeated traffic – Controls traffic on unimproved access roads – Also gives measure of how earthmoving equip will operate – Primarily function of moisture conditions and soil type • Loadability – how difficult to excavate and haul a soil – Granular – high – Compact cohesive - low
Soil And Rock • General Soil Characteristics • Trafficability – ability of soil to support weight of vehicles under repeated traffic – Controls traffic on unimproved access roads – Also gives measure of how earthmoving equip will operate – Primarily function of moisture conditions and soil type • Loadability – how difficult to excavate and haul a soil – Granular – high – Compact cohesive - low
 Soil And Rock • Unit Soil Weight – Pounds /cy – Depends on soil type, moisture content, degree of compaction – Relation between soil weight and bearing capacity • So soil weight is used as a measure of compaction • Soil weight is also a factor in hauling
Soil And Rock • Unit Soil Weight – Pounds /cy – Depends on soil type, moisture content, degree of compaction – Relation between soil weight and bearing capacity • So soil weight is used as a measure of compaction • Soil weight is also a factor in hauling
 Soil And Rock • Moisture Content(%) = (moist wt – dry wt)/dry wt X 100 • Soil sample 120# • Dry weight 100# • MC = (120 -100)/100 X 100 = 20%
Soil And Rock • Moisture Content(%) = (moist wt – dry wt)/dry wt X 100 • Soil sample 120# • Dry weight 100# • MC = (120 -100)/100 X 100 = 20%
 Soil ID • • Boulders Cobbles – over 3” diameter Gravel 1/4” – 3” diameter Sand 0. 7 mm (200 sieve) – ¼” diameter Silt 0. 002 – 0. 7 mm Clay less than 0. 002 mm Organic Matter decaying organic matter Soils classified using these types
Soil ID • • Boulders Cobbles – over 3” diameter Gravel 1/4” – 3” diameter Sand 0. 7 mm (200 sieve) – ¼” diameter Silt 0. 002 – 0. 7 mm Clay less than 0. 002 mm Organic Matter decaying organic matter Soils classified using these types
 Soil Classification Systems • Unified System – All material 3’’+ removed – Separates soils into two main groups- Fine grained and coarse grained – Table 2 -2, Figure 2 -1 • AASHTO System – – 7 classes of soil Based on suitability of soil for subgrade Table 2 -3 Table 2 -4
Soil Classification Systems • Unified System – All material 3’’+ removed – Separates soils into two main groups- Fine grained and coarse grained – Table 2 -2, Figure 2 -1 • AASHTO System – – 7 classes of soil Based on suitability of soil for subgrade Table 2 -3 Table 2 -4
 Soil Volume Change Characteristics • Soil Conditions – Bank – material in natural state before disturbance – Bank cubic yard – Loose – material that has been excavated or loaded loose cubic yard – Compacted – material after compaction compacted cubic yard
Soil Volume Change Characteristics • Soil Conditions – Bank – material in natural state before disturbance – Bank cubic yard – Loose – material that has been excavated or loaded loose cubic yard – Compacted – material after compaction compacted cubic yard
 Soil Volume Change Characteristics • Swell – Soil increases in volume when it is excavated • Soil grains are loosened and air fills voids • So 1 unit of soil in bank is smaller than the soil once it is excavated • Swell(%) = ((weight/bank vol)/(weight/loose vol)1)X 100 • Soil wt = 2800#/cy in bank • Soil wt = 2000#/cy loose • Swell = ((2800/2000)-1)X 100 = 40%
Soil Volume Change Characteristics • Swell – Soil increases in volume when it is excavated • Soil grains are loosened and air fills voids • So 1 unit of soil in bank is smaller than the soil once it is excavated • Swell(%) = ((weight/bank vol)/(weight/loose vol)1)X 100 • Soil wt = 2800#/cy in bank • Soil wt = 2000#/cy loose • Swell = ((2800/2000)-1)X 100 = 40%
 Soil Volume Change Characteristics • Shrinkage – Soil decreases in volume when it is compacted • Air is forced out of soil • So 1 unit of soil compacted is smaller than the soil in the bank or once it is excavated • Shrinkage(%) = (1 -(weight/bank vol)/(weight/compacted vol))X 100 • Soil wt = 2800#/cy in bank • Soil wt = 3500#/cy compacted • Shrinkage = (1 -(2800/3500))X 100 = 20%
Soil Volume Change Characteristics • Shrinkage – Soil decreases in volume when it is compacted • Air is forced out of soil • So 1 unit of soil compacted is smaller than the soil in the bank or once it is excavated • Shrinkage(%) = (1 -(weight/bank vol)/(weight/compacted vol))X 100 • Soil wt = 2800#/cy in bank • Soil wt = 3500#/cy compacted • Shrinkage = (1 -(2800/3500))X 100 = 20%
 Soil Volume Change Characteristics • Load and Shrinkage Factors – Need a common unit of measure for earthwork (get rid of calculations ) – Can use any of the three measures • Called pay measure in contract • Load factor = 1/(1+swell) – How many BCY can fit on a truck – LCY *Load Factor = BCY • Shrinkage factor = 1 - shrinkage • How many BCY needed for CCY • BCY * Shrinkage factor = CCY
Soil Volume Change Characteristics • Load and Shrinkage Factors – Need a common unit of measure for earthwork (get rid of calculations ) – Can use any of the three measures • Called pay measure in contract • Load factor = 1/(1+swell) – How many BCY can fit on a truck – LCY *Load Factor = BCY • Shrinkage factor = 1 - shrinkage • How many BCY needed for CCY • BCY * Shrinkage factor = CCY
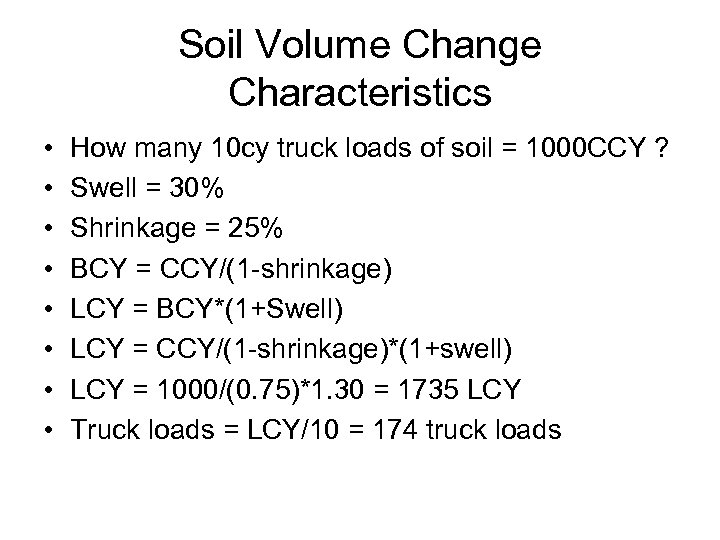 Soil Volume Change Characteristics • • How many 10 cy truck loads of soil = 1000 CCY ? Swell = 30% Shrinkage = 25% BCY = CCY/(1 -shrinkage) LCY = BCY*(1+Swell) LCY = CCY/(1 -shrinkage)*(1+swell) LCY = 1000/(0. 75)*1. 30 = 1735 LCY Truck loads = LCY/10 = 174 truck loads
Soil Volume Change Characteristics • • How many 10 cy truck loads of soil = 1000 CCY ? Swell = 30% Shrinkage = 25% BCY = CCY/(1 -shrinkage) LCY = BCY*(1+Swell) LCY = CCY/(1 -shrinkage)*(1+swell) LCY = 1000/(0. 75)*1. 30 = 1735 LCY Truck loads = LCY/10 = 174 truck loads
 Spoil Banks • Material removed from excavation – Longer than wide – spoil bank – triangular x section – Conical – spoil pile – To determine the size of the bank or pile need swell and angle of repose for soil – Angle of repose = angle that soil on side of bank naturally form • Varies with moisture content and type • Table 2 -6
Spoil Banks • Material removed from excavation – Longer than wide – spoil bank – triangular x section – Conical – spoil pile – To determine the size of the bank or pile need swell and angle of repose for soil – Angle of repose = angle that soil on side of bank naturally form • Varies with moisture content and type • Table 2 -6
 Spoil Banks • Spoil bank – Vol = X sect area x length – B = (4 V/(lx tan R))^1. 2 – H = (B x tan R)/2 – B – base width – H height – L length – R angle of repose – V volume
Spoil Banks • Spoil bank – Vol = X sect area x length – B = (4 V/(lx tan R))^1. 2 – H = (B x tan R)/2 – B – base width – H height – L length – R angle of repose – V volume
 Spoil Banks • Spoil pile – Vol = 1/3 p(D/2)^2 X H – D = (7. 64 V/tan R)^1/3 – H = D/2 x tan R – D – diameter of base – H height – R angle of repose – V volume
Spoil Banks • Spoil pile – Vol = 1/3 p(D/2)^2 X H – D = (7. 64 V/tan R)^1/3 – H = D/2 x tan R – D – diameter of base – H height – R angle of repose – V volume
 – How long would a spoil bank for 40000 cy be if it was 100’ wide? Angle of repose = 30 deg – How high can a spoil pile 50’ in diameter be if the angle of repose = 35 deg? • How many cy can it hold?
– How long would a spoil bank for 40000 cy be if it was 100’ wide? Angle of repose = 30 deg – How high can a spoil pile 50’ in diameter be if the angle of repose = 35 deg? • How many cy can it hold?
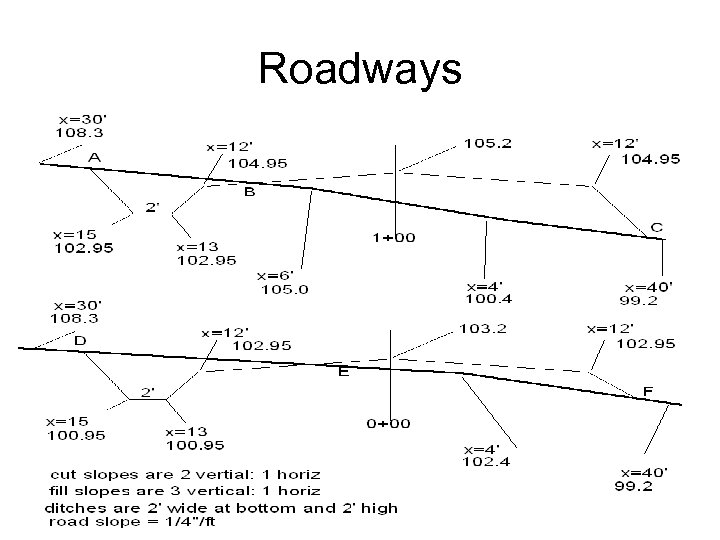
 Estimating earthwork • 3 types of excavations – Small pit – Trench – Large areas • Roadways – Find cut and fill using cross sections – Mass diagram
Estimating earthwork • 3 types of excavations – Small pit – Trench – Large areas • Roadways – Find cut and fill using cross sections – Mass diagram
 Roadways
Roadways
 Estimating earthwork • Pit Excavations – Area X average depth – Depending on size and ground may break into several geometric shapes to get volume – Give bank volume
Estimating earthwork • Pit Excavations – Area X average depth – Depending on size and ground may break into several geometric shapes to get volume – Give bank volume
 Estimating earthwork • Trench Excavations – V = x sectional area X length – Take x sections every 50 feet and compute volumes between x sections • When estimating don’t forget the angle of repose and OSHA
Estimating earthwork • Trench Excavations – V = x sectional area X length – Take x sections every 50 feet and compute volumes between x sections • When estimating don’t forget the angle of repose and OSHA
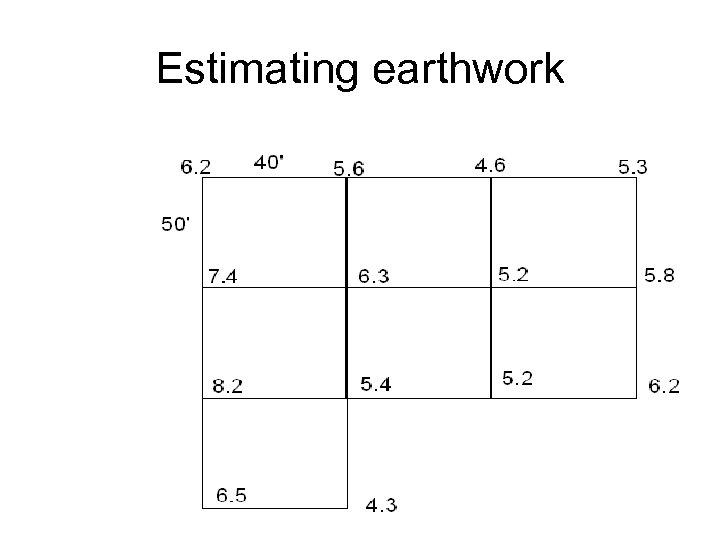
 Estimating earthwork • Large Areas – Use a grid to find volume – V = A*(average depth) – For a rectangle – V = (Lx. W)(h 1+h 2+h 3+h 4)/4(1/27) cy
Estimating earthwork • Large Areas – Use a grid to find volume – V = A*(average depth) – For a rectangle – V = (Lx. W)(h 1+h 2+h 3+h 4)/4(1/27) cy
 Estimating earthwork
Estimating earthwork


