dacad55d18f892bb661a86c025e89bdb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 CT & MRI – What is Expected from the Radiological Technologists Dr. Harsha Dissanayake MBBS, M. Phil, MD(Radiology) Dip. Neurovascular Diseases (France) Consultant Radiologist & Senior Lecturer Faculty of Medical Sciences University of Sri Jayewardenepura
CT & MRI – What is Expected from the Radiological Technologists Dr. Harsha Dissanayake MBBS, M. Phil, MD(Radiology) Dip. Neurovascular Diseases (France) Consultant Radiologist & Senior Lecturer Faculty of Medical Sciences University of Sri Jayewardenepura
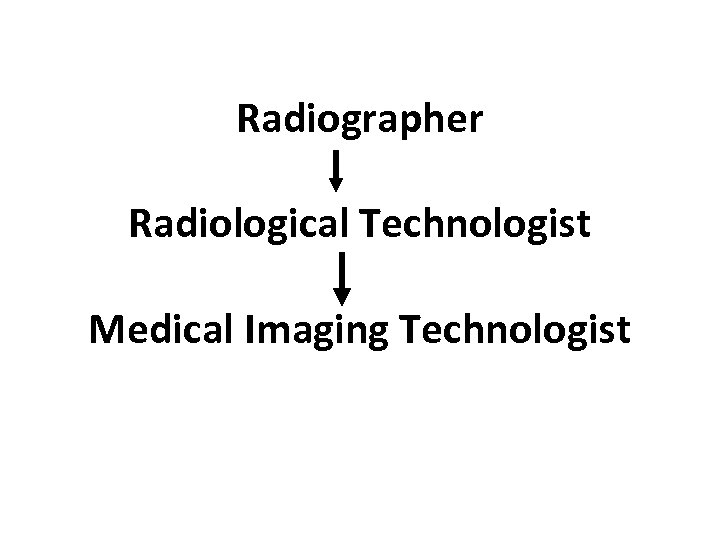 Radiographer Radiological Technologist Medical Imaging Technologist
Radiographer Radiological Technologist Medical Imaging Technologist
 Who is a Radiological Technologist? • a trained health care professional • who performs medical imaging by • producing high quality images which is useful to diagnose and treat injury or disease. • patient’s diagnosis and treatment is often dependent on the images produced. • He is an important member of the Health care team.
Who is a Radiological Technologist? • a trained health care professional • who performs medical imaging by • producing high quality images which is useful to diagnose and treat injury or disease. • patient’s diagnosis and treatment is often dependent on the images produced. • He is an important member of the Health care team.
 Health Care Professional • undertakes a specialized set of tasks • enjoys considerable work autonomy • engaged in creative and intellectually challenging work • Patients place a great deal of trust in them • strict codes of conduct • Ethical and moral obligations
Health Care Professional • undertakes a specialized set of tasks • enjoys considerable work autonomy • engaged in creative and intellectually challenging work • Patients place a great deal of trust in them • strict codes of conduct • Ethical and moral obligations
 What should be the goal – when encountered with a patient • To generate the best possible, • Highest quality, • Appropriate images – which will be used to arrive at the diagnosis / or to treat.
What should be the goal – when encountered with a patient • To generate the best possible, • Highest quality, • Appropriate images – which will be used to arrive at the diagnosis / or to treat.
 How to achieve this goal ? • Asses the patient’s problem – get the information • Analyze • Set the goal clear • Formulate a plan to achieve the goal • Workout the plan performing the tasks • Self evaluate your images – “Is this the best possible images that I can generate? ”
How to achieve this goal ? • Asses the patient’s problem – get the information • Analyze • Set the goal clear • Formulate a plan to achieve the goal • Workout the plan performing the tasks • Self evaluate your images – “Is this the best possible images that I can generate? ”
 Quality control of the procedure • Inferior quality images / study – Area of interest inadequately covered / all sequences not included ………. etc May lead to – Inaccurate interpretation / wrong diagnosis – Repeated exposure – Radiation hazards to the patient / self / staff – Additional cost – Additional time
Quality control of the procedure • Inferior quality images / study – Area of interest inadequately covered / all sequences not included ………. etc May lead to – Inaccurate interpretation / wrong diagnosis – Repeated exposure – Radiation hazards to the patient / self / staff – Additional cost – Additional time
 Competency ? • expertise and knowledge of patient handling • physics, anatomy, physiology and radiology to assess patients • develop optimal radiologic techniques to plan and evaluate – resulting radiographic images. • Should be able to spot “what is not normal” – pathology • Radiation Protection • Quality Control
Competency ? • expertise and knowledge of patient handling • physics, anatomy, physiology and radiology to assess patients • develop optimal radiologic techniques to plan and evaluate – resulting radiographic images. • Should be able to spot “what is not normal” – pathology • Radiation Protection • Quality Control
 How the competency is gained? • High school Diploma – Certificate course • University Degree BSc in Diagnostic Radiography/Diagnostic Imaging – 3 yrs • Can specialize in-house or through a university course as a postgraduate in CT, MRI, Nuclear Medicine …. . with opportunities to gain an MSc in their field.
How the competency is gained? • High school Diploma – Certificate course • University Degree BSc in Diagnostic Radiography/Diagnostic Imaging – 3 yrs • Can specialize in-house or through a university course as a postgraduate in CT, MRI, Nuclear Medicine …. . with opportunities to gain an MSc in their field.
 CT & MRI – What is Expected from the Radiological Technologists • Before / During / After the procedure • Check the identity and the requested investigation • Check the consent • explaining the procedure • ensure that the patent has had the correct preparation • Keep the emergency tray ready
CT & MRI – What is Expected from the Radiological Technologists • Before / During / After the procedure • Check the identity and the requested investigation • Check the consent • explaining the procedure • ensure that the patent has had the correct preparation • Keep the emergency tray ready
 • clothing, ensure that there are no metal objects that may interfere • Check the clinical details – if inadequate make a note of the patents problem & relevant details. Get previous imaging Ix reports/films • If the requested investigation is not clear / inappropriate, always discuss with the referring clinician • Check the patients data sheet / questionnaire – whether it is appropriately filled • Are there any contraindications / Allergies?
• clothing, ensure that there are no metal objects that may interfere • Check the clinical details – if inadequate make a note of the patents problem & relevant details. Get previous imaging Ix reports/films • If the requested investigation is not clear / inappropriate, always discuss with the referring clinician • Check the patients data sheet / questionnaire – whether it is appropriately filled • Are there any contraindications / Allergies?
 During the scanning • Radiation dose • All medical radiation exposures must be justified and the radiation levels optimized • Radiation to the patient (in diagnostic studies), staff and the general public are to be kept As Low As Reasonably Achievable (the ALARA principle)
During the scanning • Radiation dose • All medical radiation exposures must be justified and the radiation levels optimized • Radiation to the patient (in diagnostic studies), staff and the general public are to be kept As Low As Reasonably Achievable (the ALARA principle)
 Protocols • Protocols are mere guidelines. • Has to modify according to the individual patients problem – when ever necessary • Timing of the procedure • Whether to give contrast or not • Timing of the contrast injection • Arterial / venous / late phases • Oral /rectal contrast • MRI – additional sequences - ? Haemorrage / Calcification / stroke ……. .
Protocols • Protocols are mere guidelines. • Has to modify according to the individual patients problem – when ever necessary • Timing of the procedure • Whether to give contrast or not • Timing of the contrast injection • Arterial / venous / late phases • Oral /rectal contrast • MRI – additional sequences - ? Haemorrage / Calcification / stroke ……. .
 Example 1 • 60 yrs • Male • Haematuria • Ix. – CT KUB
Example 1 • 60 yrs • Male • Haematuria • Ix. – CT KUB
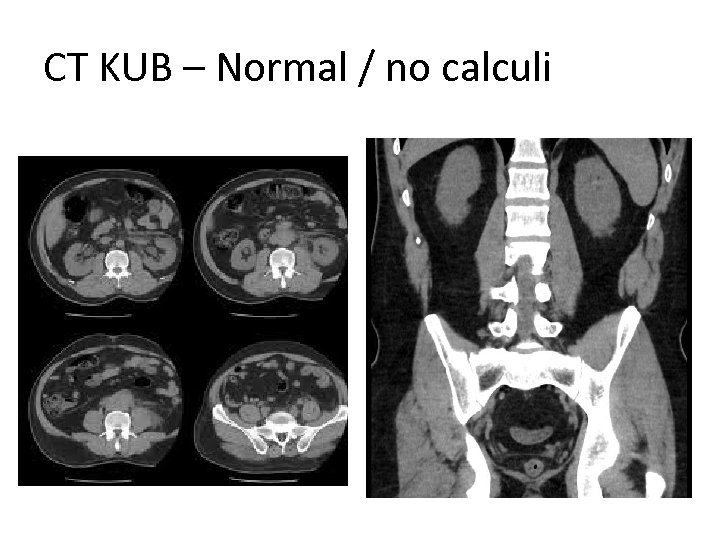 CT KUB – Normal / no calculi
CT KUB – Normal / no calculi
 • Are you happy?
• Are you happy?
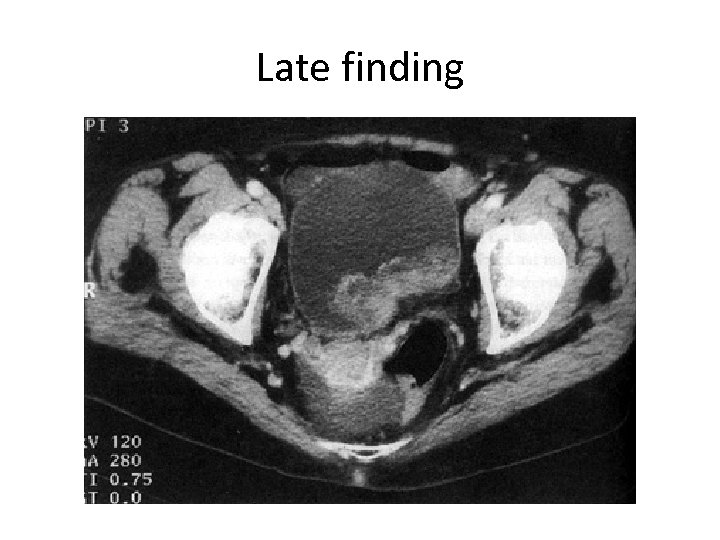 Late finding
Late finding
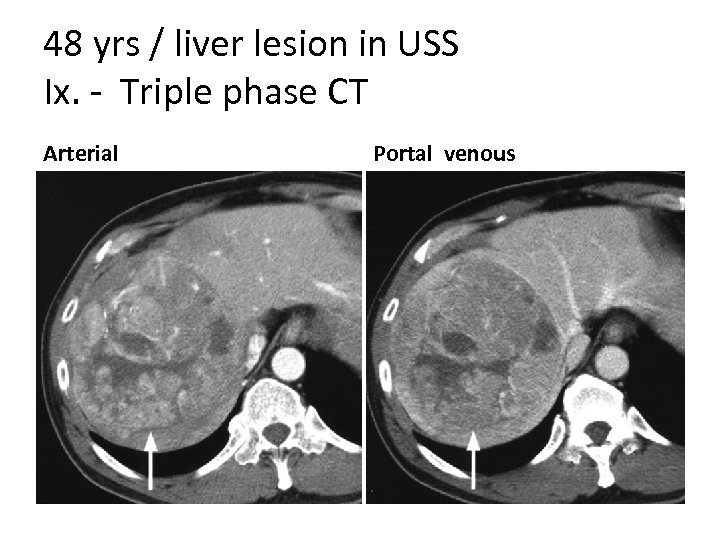 48 yrs / liver lesion in USS Ix. - Triple phase CT Arterial Portal venous
48 yrs / liver lesion in USS Ix. - Triple phase CT Arterial Portal venous
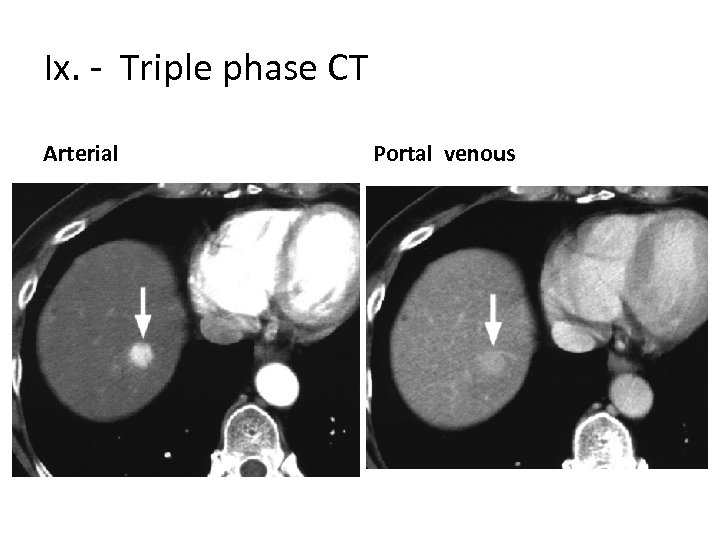 Ix. - Triple phase CT Arterial Portal venous
Ix. - Triple phase CT Arterial Portal venous
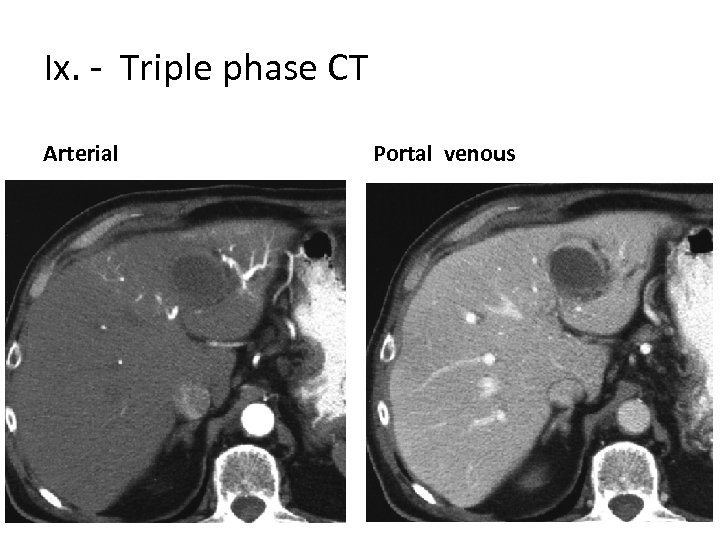 Ix. - Triple phase CT Arterial Portal venous
Ix. - Triple phase CT Arterial Portal venous