 CT advances • Recent advances in CT are quickly incorporated into PET/CT • Manufacturers are now able to install PET/CT with 128 slices • The lower cost of SPECT means that “high-end” CT is rarely installed in SPECT-CT
CT advances • Recent advances in CT are quickly incorporated into PET/CT • Manufacturers are now able to install PET/CT with 128 slices • The lower cost of SPECT means that “high-end” CT is rarely installed in SPECT-CT
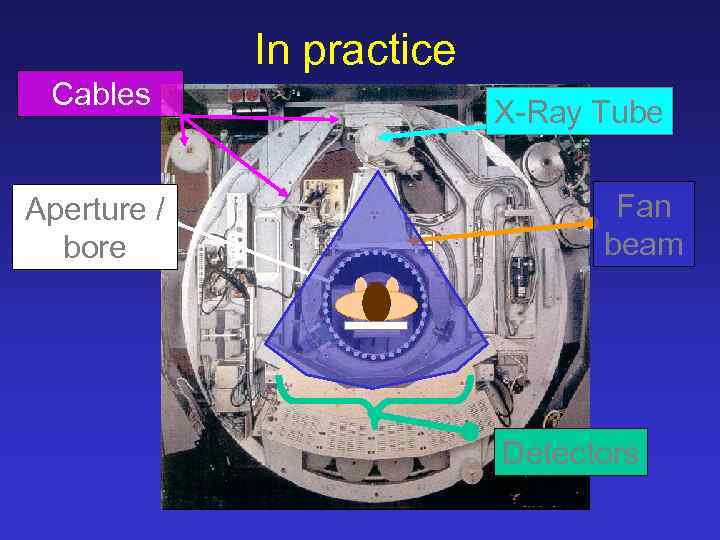 In practice Cables Aperture / bore X-Ray Tube Fan beam Detectors
In practice Cables Aperture / bore X-Ray Tube Fan beam Detectors
 Fast gantry rotation ~ 0. 33 second rotation Courtesy Im. PACT
Fast gantry rotation ~ 0. 33 second rotation Courtesy Im. PACT
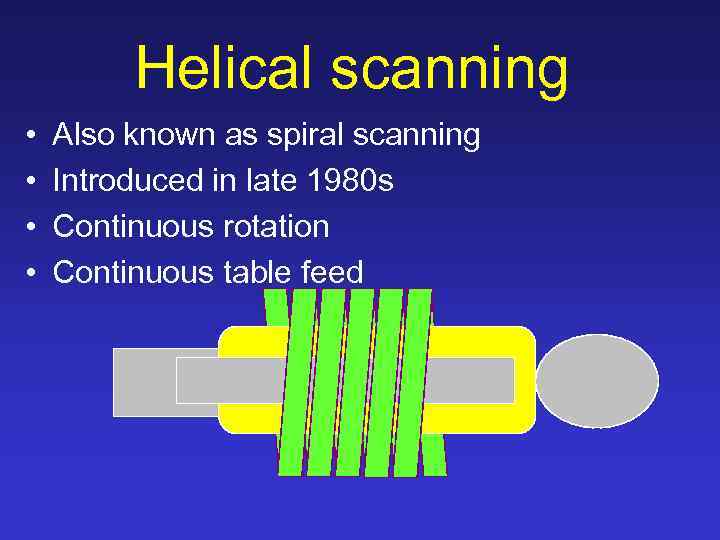 Helical scanning • • Also known as spiral scanning Introduced in late 1980 s Continuous rotation Continuous table feed
Helical scanning • • Also known as spiral scanning Introduced in late 1980 s Continuous rotation Continuous table feed
 Helical MSCT
Helical MSCT
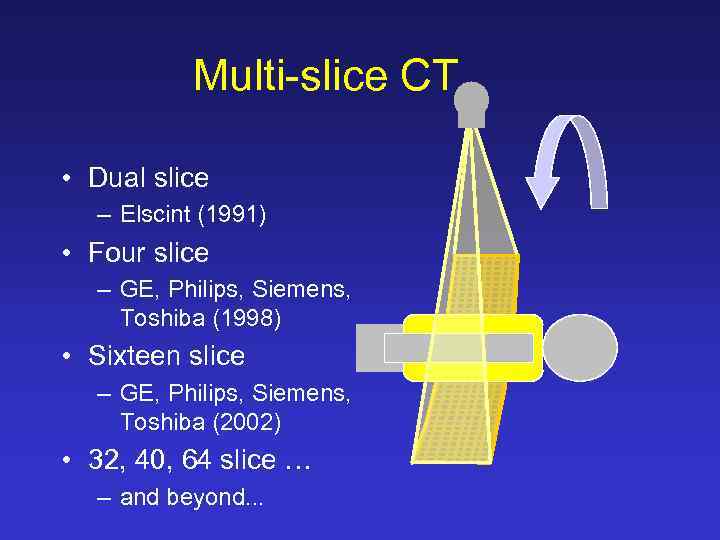 Multi-slice CT • Dual slice – Elscint (1991) • Four slice – GE, Philips, Siemens, Toshiba (1998) • Sixteen slice – GE, Philips, Siemens, Toshiba (2002) • 32, 40, 64 slice … – and beyond. . .
Multi-slice CT • Dual slice – Elscint (1991) • Four slice – GE, Philips, Siemens, Toshiba (1998) • Sixteen slice – GE, Philips, Siemens, Toshiba (2002) • 32, 40, 64 slice … – and beyond. . .
 Larger detector arrays • 128/256 row scanners – Allow whole organ coverage in single rotation 256 row detector (256 x 0. 5) = 128 mm Z - axis Aquilion 64 detector Detector mock-ups courtesy of Toshiba
Larger detector arrays • 128/256 row scanners – Allow whole organ coverage in single rotation 256 row detector (256 x 0. 5) = 128 mm Z - axis Aquilion 64 detector Detector mock-ups courtesy of Toshiba
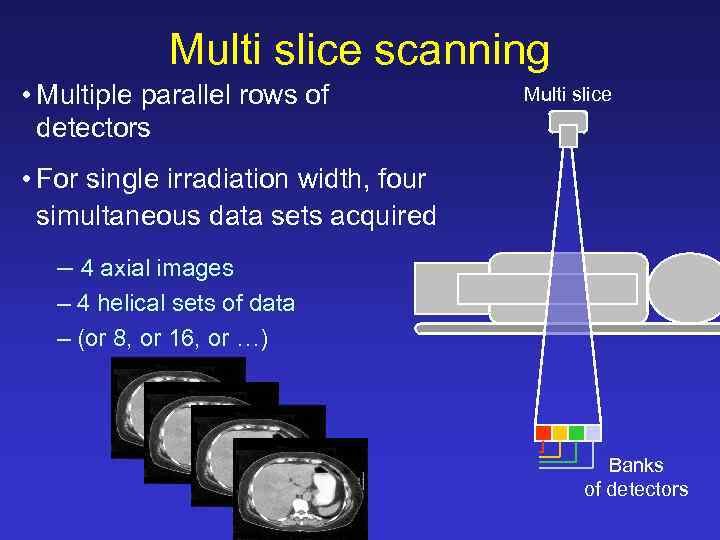 Multi slice scanning • Multiple parallel rows of detectors Multi slice • For single irradiation width, four simultaneous data sets acquired – 4 axial images – 4 helical sets of data – (or 8, or 16, or …) Banks of detectors
Multi slice scanning • Multiple parallel rows of detectors Multi slice • For single irradiation width, four simultaneous data sets acquired – 4 axial images – 4 helical sets of data – (or 8, or 16, or …) Banks of detectors
 QC for SPECT/CT or PET/CT • Routine checks (noise, CT number accuracy) • Geometrical alignment of SPECT & CT/PET images • Check of accuracy of correction – – head and body sized water phantoms – Is the CT attenuation correct? Homogeneous phantom – AC Emission values constant across the phantom?
QC for SPECT/CT or PET/CT • Routine checks (noise, CT number accuracy) • Geometrical alignment of SPECT & CT/PET images • Check of accuracy of correction – – head and body sized water phantoms – Is the CT attenuation correct? Homogeneous phantom – AC Emission values constant across the phantom?
 Image noise Scanner’s water phantom • • • CT 01 Measured daily – weekly 40 % of phantom diameter Standard deviation Central slice Noise image
Image noise Scanner’s water phantom • • • CT 01 Measured daily – weekly 40 % of phantom diameter Standard deviation Central slice Noise image
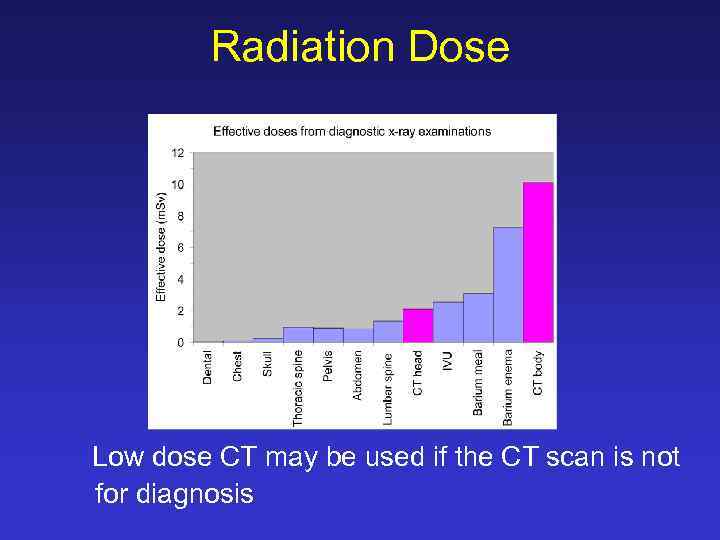 Radiation Dose Low dose CT may be used if the CT scan is not for diagnosis
Radiation Dose Low dose CT may be used if the CT scan is not for diagnosis
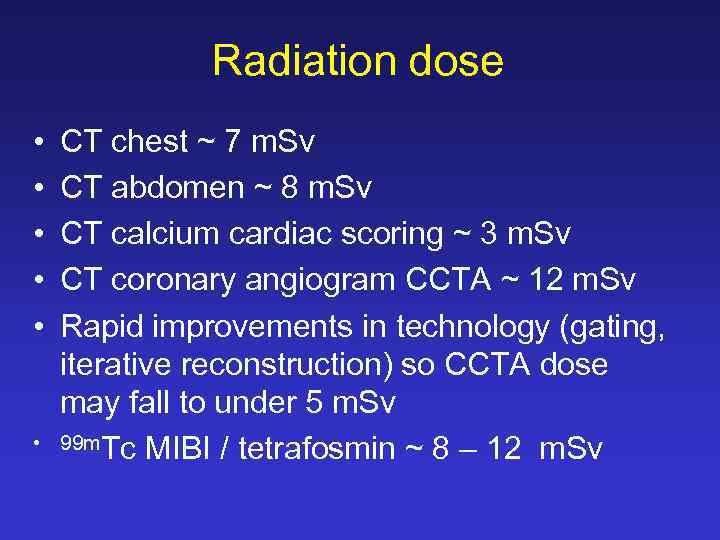 Radiation dose • • • CT chest ~ 7 m. Sv CT abdomen ~ 8 m. Sv CT calcium cardiac scoring ~ 3 m. Sv CT coronary angiogram CCTA ~ 12 m. Sv Rapid improvements in technology (gating, iterative reconstruction) so CCTA dose may fall to under 5 m. Sv 99 m. Tc MIBI / tetrafosmin ~ 8 – 12 m. Sv
Radiation dose • • • CT chest ~ 7 m. Sv CT abdomen ~ 8 m. Sv CT calcium cardiac scoring ~ 3 m. Sv CT coronary angiogram CCTA ~ 12 m. Sv Rapid improvements in technology (gating, iterative reconstruction) so CCTA dose may fall to under 5 m. Sv 99 m. Tc MIBI / tetrafosmin ~ 8 – 12 m. Sv
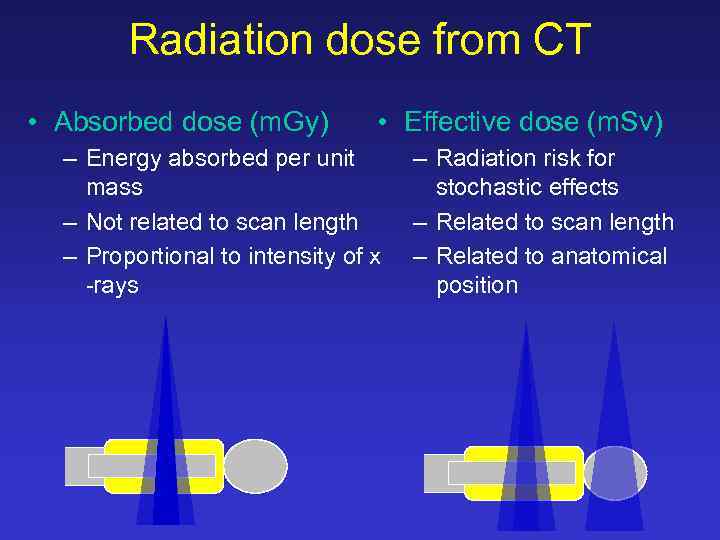 Radiation dose from CT • Absorbed dose (m. Gy) • Effective dose (m. Sv) – Energy absorbed per unit mass – Not related to scan length – Proportional to intensity of x -rays – Radiation risk for stochastic effects – Related to scan length – Related to anatomical position
Radiation dose from CT • Absorbed dose (m. Gy) • Effective dose (m. Sv) – Energy absorbed per unit mass – Not related to scan length – Proportional to intensity of x -rays – Radiation risk for stochastic effects – Related to scan length – Related to anatomical position
 Scan parameters affecting absorbed dose • Scan parameter settings: – Tube voltage (k. V) – Tube current (m. A) – Rotation time (s) – Helical pitch • …and to a lesser extent: – Focal spot size – Irradiated slice width
Scan parameters affecting absorbed dose • Scan parameter settings: – Tube voltage (k. V) – Tube current (m. A) – Rotation time (s) – Helical pitch • …and to a lesser extent: – Focal spot size – Irradiated slice width
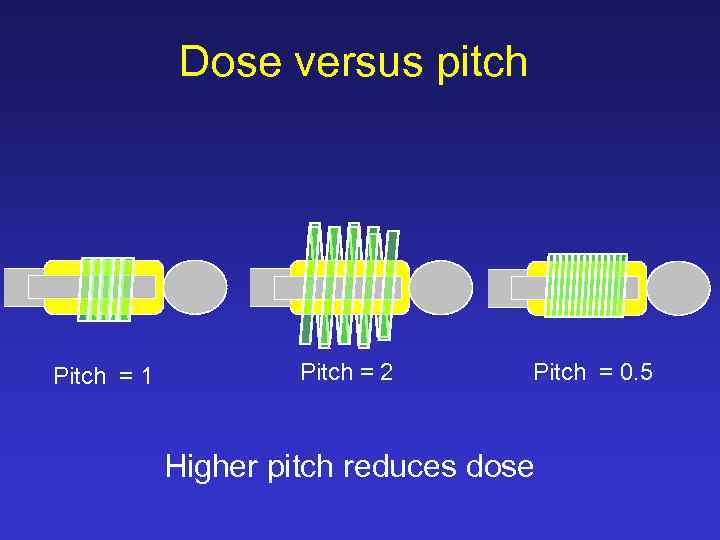 Dose versus pitch Pitch = 1 Pitch = 2 Pitch = 0. 5 Higher pitch reduces dose
Dose versus pitch Pitch = 1 Pitch = 2 Pitch = 0. 5 Higher pitch reduces dose
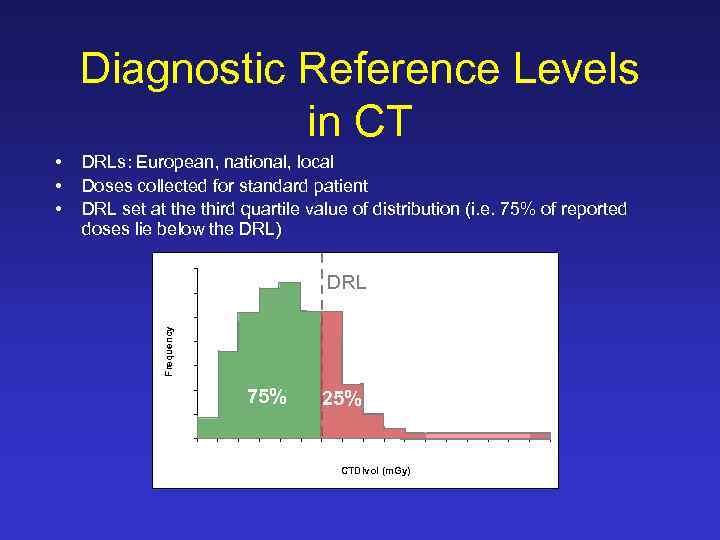 Diagnostic Reference Levels in CT DRLs: European, national, local Doses collected for standard patient DRL set at the third quartile value of distribution (i. e. 75% of reported doses lie below the DRL) 35 DRL 30 25 Frequency • • • 20 15 75% 10 25% 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 CTDIvol (m. Gy)
Diagnostic Reference Levels in CT DRLs: European, national, local Doses collected for standard patient DRL set at the third quartile value of distribution (i. e. 75% of reported doses lie below the DRL) 35 DRL 30 25 Frequency • • • 20 15 75% 10 25% 5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 CTDIvol (m. Gy)
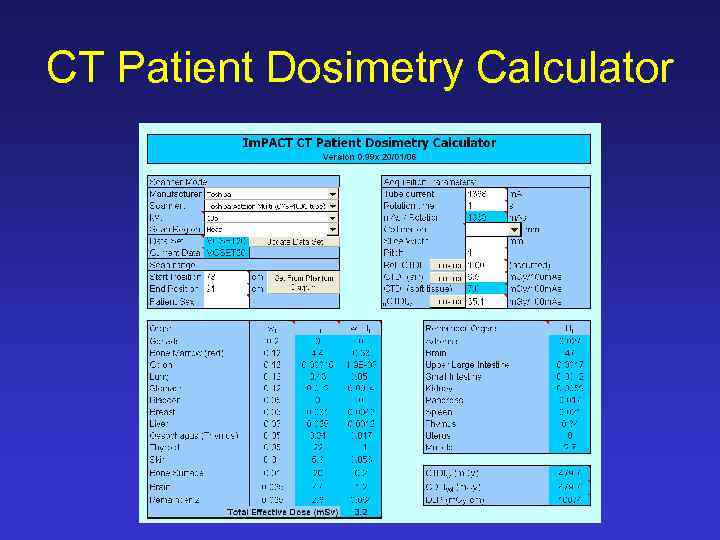 CT Patient Dosimetry Calculator
CT Patient Dosimetry Calculator