24f36856ae4a4a13711c789663e39462.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 54

CSFB Product Control Process Reengineering RFP Proposal March 4 th, 2005

25 Broadway New York, NY 10004 212 618 4000 March 4, 2005 CONFIDENTIAL Ms. XYZ New York, Dear Ms xyzy: Thank you for the opportunity to propose on CSFB’s Product Control Process Reengineering RFP. The attached document outlines our understanding of the project requirements and our approach, as well as the project team resources and professional arrangements. We understand the importance of this initiative to CSFB through our work with ISIS and other functions, and believe that Deloitte is uniquely qualified to assist. We look forward to discussing our response with you further and to working with you on this critical initiative. If you have any questions or would like to discuss this proposal further please do not hesitate to contact the undersigned. We would welcome an opportunity to arrange for a meeting with members of the proposed team upon your request. The undersigned, being persons duly authorized to represent the Supplier, states that this Request for Proposal has been read and understood, and that the Supplier agrees to be bound by the terms and conditions contained within this RFP and proposal. The individuals whose signatures follow represent and certify that they have the authority to represent and act on the behalf of Deloitte Consulting LLP, 25 Broadway, New York, NY 10004 “Company”. They recognize for themselves and for Company that the information contained therein the RFP, including Appendices, is CONFIDENTIAL and was released to Company to enable a response to the RFP. Company shall not disclose such RFP information – or the fact that Company has been asked to submit a proposal – to a third party for any reason. Without limiting the foregoing, Company is not authorized, without CSFB’s prior written consent, to publicize the fact that they are a potential Supplier to CSFB for PC Business Process Reengineering. The individuals recognize for themselves and for Company that at the request of CSFB, the RFP and any copies thereof, either hard copy or electronic copy, shall immediately be returned to CSFB. The individual also represents and certifies that the Proposal, including cost structures, was developed independently and with no collaboration of any other provider of firms and with no purpose of restricting competition. The RFP to which this Proposal relates has been read and its requested terms, except as indicated herein this Proposal, will be accepted should Deloitte Consulting LLP be selected as the provider of such Services to Credit Suisse First Boston LLC. Company certifies that such Proposal shall remain in effect for 90 days from Proposal due date. Kindest regards, Adam Broun Principal Ken Landis Principal

CSFB has initiated an assessment to identify opportunities to maximize the operational efficiency of the Product Control area. This initiative is critical to achieve cost and resource efficiencies, increase capacity and manage risk more effectively for the firm. Based on preliminary assessments, it is CSFB’s opinion that a significant opportunity exists to rationalize Product Control processes, resulting not only in cost savings from reduced headcount, the simplification of processes, and the retirement of outdated or redundant applications, but also in “best practice” business processes, which will facilitate new business initiatives, improve internal client service, and create a more rigorous control environment. CSFB plans to engage a partner to assist and collaborate on this reengineering assessment. The critical aspects in conducting the assessment are to determine the current business process flows, document key processes, identify opportunities to reengineer processes and recommend a migration plan to capture those opportunities. In addition during this phase, the team will identify minimum levels of acceptable efficiency and control with the aim of providing a potential “menu” of reengineering alternatives. This document details Deloitte’s response to your request for proposal. Our proposed approach and assessment framework targets your specific needs and incorporates relevant insights from our experience in capital markets, accounting and regulatory advisory and large scale reengineering efforts: § Significant experience working with leading investment banks addressing complex business, operational, and technology challenges and opportunities § Recognized advisory and implementation experience as a strategic partner on a number of prominent reengineering efforts § § In-depth product knowledge to accelerate and drive a targeted and realistic assessment aligned with your strategic goals Access to relevant industry benchmarks on product and process costs Ability to apply best of breed tools and processes (i. e, lean, six sigma, etc) Experience in developing innovative solutions that can simultaneously deliver operational efficiency and provide for a sustainable growth platform § Combined expertise in accounting, control, risk and regulatory policies, practices and standards

Table Of Contents I. Executive Summary II. Introduction & Marketplace Perspectives III. Our Approach IV. “Test Driving” the Approach V. Team Structure, Profiles & Fees VI. Qualifications & References VII. Available Tools VIII. Appendices IX. Required attachments: § Supplier_Assessment_Questionnaire. doc § CSFB_Master_Agreement. doc 3

I. Executive Summary
Executive Summary § Based on our industry experience and knowledge of CSFB we believe there is an opportunity to reduce the Product Control run rate by approximately 5%-12% per annum ($9 -$21 MM), within the scope defined, by reengineering the primary functions within the department. Significant additional savings might be possible with end-to-end changes in the operating and technology model across the trade cycle § To identify and achieve these benefits we will examine and utilize the following levers: - Policy/control adjustments - Redesigning processes - People effectiveness - Organization re-design - Selected system/technology enhancements § Reengineering can deliver the additional benefits of enhanced control, risk management and the ability to support increased trade volumes and new products – a critical consideration for support of CSFB’s business strategy § To extend this analysis across all products/functions and develop the business case, implementation roadmap and migration plan we propose a twelve week diagnostic with product aligned workstreams § The diagnostic would be conducted by a dedicated Deloitte team with extensive Product Control and reengineering experience. This team would be split between London and New York and supported by a number of product and subject matter specialists with deep product accounting experience § The middle office cost driver and process mapping work conducted within the ISIS transparency initiative would be the starting point of our analysis, along with other pre-existing documentation and analysis (e. g. , Sarbanes-Oxley process documentation) § We measure our success on this engagement by CSFB’s success: in identifying measurable, sustainable 2006 cost savings without compromising risk or client service 5

II. Introduction & Marketplace Perspectives
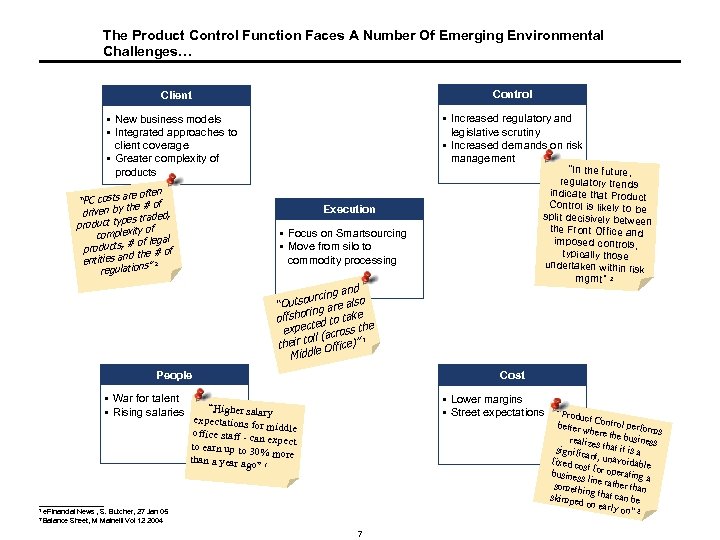
The Product Control Function Faces A Number Of Emerging Environmental Challenges… Client Control § New business models § Integrated approaches to client coverage § Greater complexity of products § Increased regulatory and legislative scrutiny § Increased demands on risk management are often “PC costs e # of th driven by , pes traded product ty ity of complex # of legal products, d the # of entities an ns” 2 regulatio “In the future, regulatory trends indicate that Product Control is likely to be split decisively betwee n the Front Office and imposed controls, typically those undertaken within risk mgmt” 2 Execution § Focus on Smartsourcing § Move from silo to commodity processing nd cing a utsour are also “O ring offsho ed to take t expec (across the 1 toll their e Office)” l Midd People § War for talent § Rising salaries 1 Cost § Lower margins § Street expectations “Higher salary expectations fo r middle office staff - ca n expect to earn up to 30 %m than a year ago” 1 ore e. Financial News , S. Butcher, 27 Jan 05 Sheet, M Mainelli Vol 12 2004 2 Balance 7 “Produc t. C better w ontrol perform s here the busines realizes s that it is signific a an fixed co t, unavoidable st busines for operating a s line ra the someth ing that r than can be skimpe d on ea rly on” 2
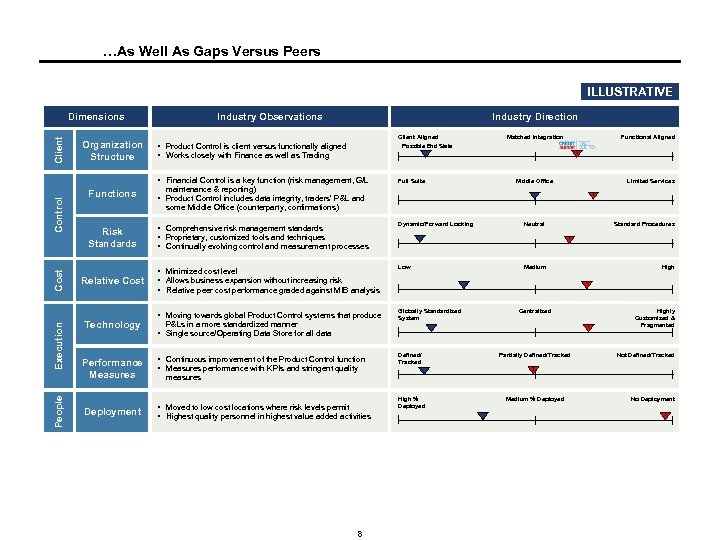
…As Well As Gaps Versus Peers ILLUSTRATIVE Client Dimensions Organization Structure Industry Observations Industry Direction Client Aligned Possible End State § Product Control is client versus functionally aligned § Works closely with Finance as well as Trading Control Cost Execution Functional Aligned ? § Financial Control is a key function (risk management, G/L People Matched Integration Full Suite Functions Risk Standards § Comprehensive risk management standards § Proprietary, customized tools and techniques § Continually evolving control and measurement processes Dynamic/Forward Looking § Minimized cost level § Allows business expansion without increasing risk § Relative peer cost performance graded against MIB analysis Low § Moving towards global Product Control systems that produce Globally Standardized System Middle Office Limited Services maintenance & reporting) § Product Control includes data integrity, traders’ P&L and some Middle Office (counterparty, confirmations) Relative Cost Technology P&Ls in a more standardized manner § Single source/Operating Data Store for all data ? Neutral Standard Procedures ? Medium High ? Centralized ? Performance Measures § Continuous improvement of the Product Control function § Measures performance with KPIs and stringent quality Deployment § Moved to low cost locations where risk levels permit § Highest quality personnel in highest value added activities Defined/ Tracked Partially Defined/Tracked Highly Customized & Fragmented Not Defined/Tracked ? measures 8 High % Deployed Medium % Deployed No Deployment ?
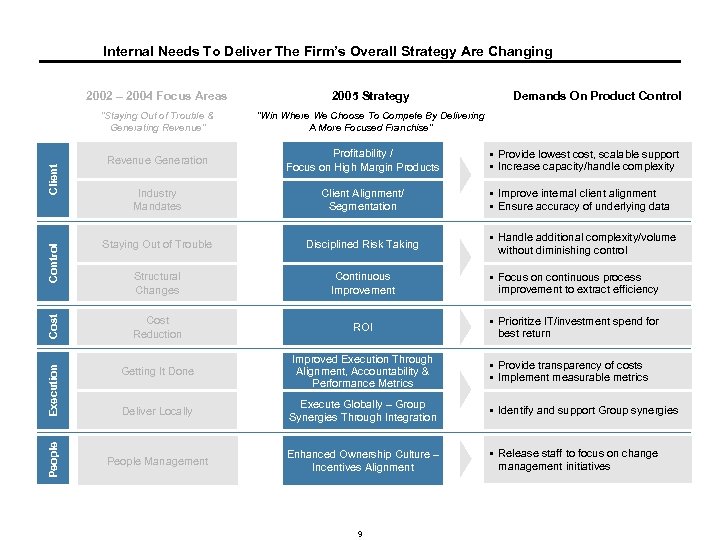
Internal Needs To Deliver The Firm’s Overall Strategy Are Changing “Staying Out of Trouble & Generating Revenue” Demands On Product Control “Win Where We Choose To Compete By Delivering A More Focused Franchise” § Provide lowest cost, scalable support § Increase capacity/handle complexity Profitability / Focus on High Margin Products Industry Mandates Client Alignment/ Segmentation Staying Out of Trouble Disciplined Risk Taking Structural Changes Continuous Improvement § Focus on continuous process improvement to extract efficiency Cost Reduction ROI § Prioritize IT/investment spend for best return Getting It Done Improved Execution Through Alignment, Accountability & Performance Metrics Deliver Locally Execute Globally – Group Synergies Through Integration § Identify and support Group synergies People Management Enhanced Ownership Culture – Incentives Alignment § Release staff to focus on change management initiatives People Control Client Revenue Generation Cost 2005 Strategy Execution 2002 – 2004 Focus Areas 9 § Improve internal client alignment § Ensure accuracy of underlying data § Handle additional complexity/volume without diminishing control § Provide transparency of costs § Implement measurable metrics

Product Control Needs To Change To Deliver The Firm’s Evolving Strategy While Simultaneously Supporting Growth And Efficiency Initiatives Product Control must absorb increased volume and additional complexity… Supporting Growth Higher PC Impact § ABS § Build out Equity Prop § § § § § capabilities within cross divisional prop group Build out Prime Services Cash Equities – Plan ’ 06 CDO CMBS Commodities Build Out Credit Derivatives Desk-based Positioning Derivatives – Plan ’ 06 Emerging Markets Equity Syndication Desk FID Strategic Book GFX Growth in Asia, Japan and Australia High Yield Insurance Structuring Interest Rate Products Rebuild Derivatives Residential Mortgages Vertical Integration Strategy Tax Structuring Lower PC Impact Higher PC Impact § Capture Derivatives § Alignment of Equity § § § § § Research/Sector Focus Cash Equities Execution Platform Client Segmentation – Europe Client Segmentation - US European Secondary Credit Trading Extend Trading Analyst Function FID Syndication Desk Global Top Account Strategy Increase integration of FID Business Lines Migrate HOLT small-cap coverage to sectors Options – Automated Market Making § § § Productivity Establish Integration Derivatives Structuring Finance Control Efficiency Improvement GAD Transparency ISIS MO & Coverage Model ISIS Tactical Efficiency Capture ISIS Transparency Mortgage Change Program New Capital Markets Structure Product Control Improvement Unified FID/Equity Proprietary Group Vertical Integration of FIG Lower PC Impact § § § § § Cross-CSG Synergies Data Centers Finance Deployment GTI Transparency IPO 7 & AD 07 Efficiency Programs ISIS Singapore Migration IT Phase 2 Deployment IT Tactical Cost Reduction Non-IT Purchasing Spend Phase 1 Deployment (ISIS & IT) Reducing Cost/ Increasing Efficiency …while reducing cost without compromising risk or degrading control 10
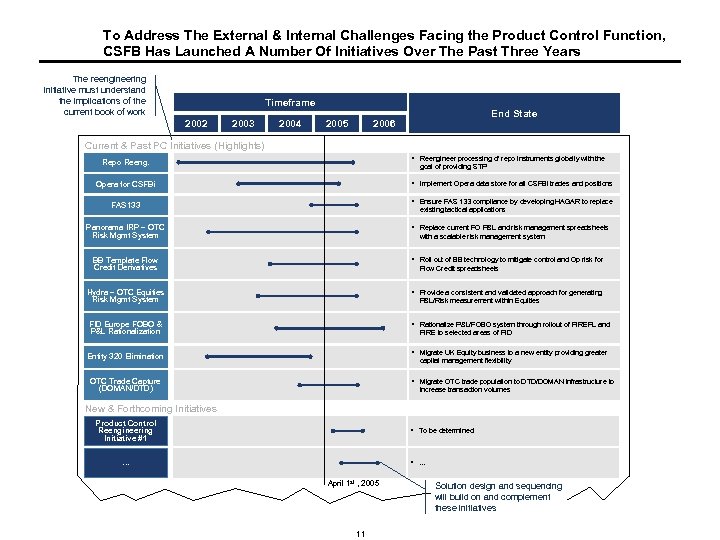
To Address The External & Internal Challenges Facing the Product Control Function, CSFB Has Launched A Number Of Initiatives Over The Past Three Years The reengineering initiative must understand the implications of the current book of work Timeframe 2002 2003 2004 2005 End State 2006 Current & Past PC Initiatives (Highlights) § Reengineer processing of repo instruments globally with the Repo Reeng. goal of providing STP Opera for CSFBi § Implement Opera data store for all CSFBi trades and positions FAS 133 § Ensure FAS 133 compliance by developing HAGAR to replace Panorama IRP – OTC Risk Mgmt System § Replace current FO P&L and risk management spreadsheets existing tactical applications with a scalable risk management system BB Template Flow Credit Derivatives § Roll out of BB technology to mitigate control and Op risk for Hydra – OTC Equities Risk Mgmt System § Provide a consistent and validated approach for generating FID Europe FOBO & P&L Rationalization § Rationalize P&L/FOBO system through rollout of FIREPL and Entity 320 Elimination § Migrate UK Equity business to a new entity providing greater Flow Credit spreadsheets P&L/Risk measurement within Equities FIRE to selected areas of FID capital management flexibility OTC Trade Capture (DOMAN/DTD) § Migrate OTC trade population to DTD/DOMAN infrastructure to increase transaction volumes New & Forthcoming Initiatives Product Control Reengineering Initiative #1 § To be determined … § … April 1 st , 2005 11 Solution design and sequencing will build on and complement these initiatives
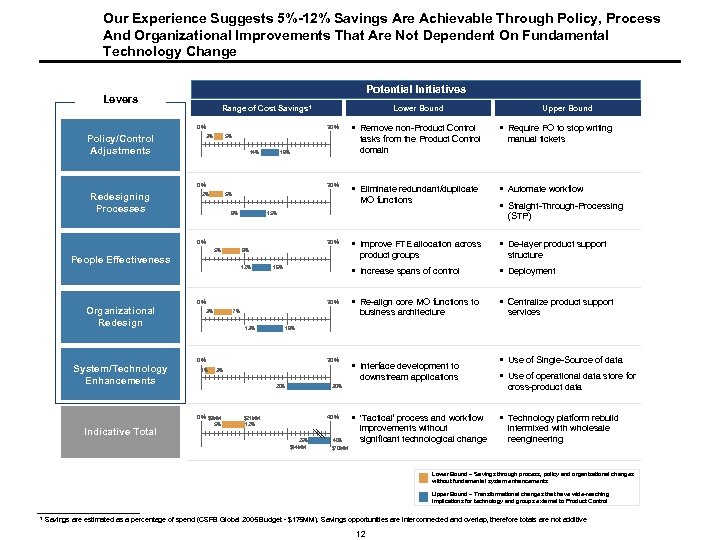
Our Experience Suggests 5%-12% Savings Are Achievable Through Policy, Process And Organizational Improvements That Are Not Dependent On Fundamental Technology Change Potential Initiatives Levers Range of Cost Savings 1 0% Policy/Control Adjustments 30% 3% 5% 14% 30% 2% 5% 9% 12% System/Technology Enhancements 16% 30% Indicative Total § De-layer product support § Deployment § Re-align core MO functions to § Centralize product support services 19% 30% 3% § Interface development to downstream applications 20% 5% § Automate workflow structure business architecture 7% 0% $9 MM manual tickets § Increase spans of control 0% 1% § Improve FTE allocation across product groups 0% 13% § Require FO to stop writing (STP) 9% People Effectiveness Upper Bound § Straight-Through-Processing 15% 30% 5% 3% § Eliminate redundant/duplicate MO functions 0% Organizational Redesign § Remove non-Product Control tasks from the Product Control domain 18% 0% Redesigning Processes Lower Bound 30% 40% $21 MM 12% 25% $44 MM 40% $70 MM § ‘Tactical’ process and workflow improvements without significant technological change § Use of Single-Source of data § Use of operational data store for cross-product data § Technology platform rebuild intermixed with wholesale reengineering Lower Bound – Savings through process, policy and organizational changes without fundamental system enhancements Upper Bound – Transformational changes that have wide-reaching implications for technology and groups external to Product Control 1 Savings are estimated as a percentage of spend (CSFB Global 2005 Budget - $175 MM). Savings opportunities are interconnected and overlap, therefore totals are not additive 12
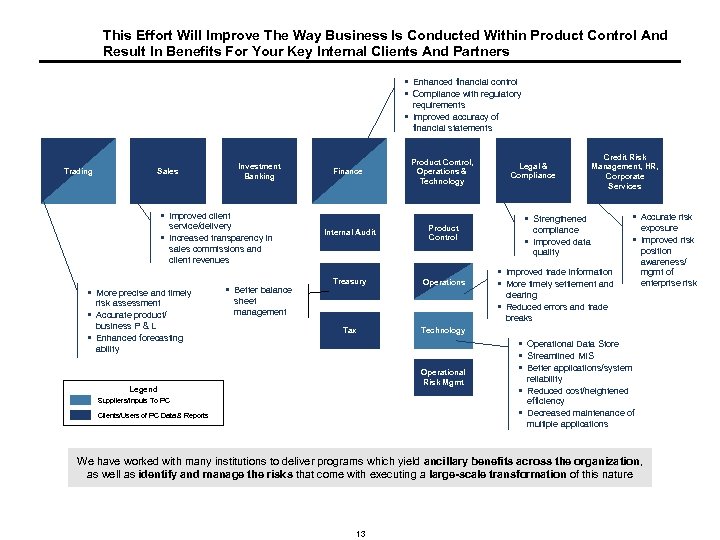
This Effort Will Improve The Way Business Is Conducted Within Product Control And Result In Benefits For Your Key Internal Clients And Partners § Enhanced financial control § Compliance with regulatory requirements § Improved accuracy of financial statements Trading Investment Banking Sales Finance Product Control, Operations & Technology Internal Audit Product Control § Improved client service/delivery § Increased transparency in sales commissions and client revenues § More precise and timely risk assessment § Accurate product/ business P & L § Enhanced forecasting ability § Better balance Treasury Operations Legal & Compliance Credit Risk Management, HR, Corporate Services § Strengthened § Accurate risk compliance § Improved data quality § Improved risk exposure § Improved trade information § More timely settlement and position awareness/ mgmt of enterprise risk clearing sheet management § Reduced errors and trade breaks Tax Technology Operational Risk Mgmt Legend § Operational Data Store § Streamlined MIS § Better applications/system reliability § Reduced cost/heightened efficiency Suppliers/Inputs To PC § Decreased maintenance of Clients/Users of PC Data & Reports multiple applications We have worked with many institutions to deliver programs which yield ancillary benefits across the organization, as well as identify and manage the risks that come with executing a large-scale transformation of this nature 13

III. Our Approach
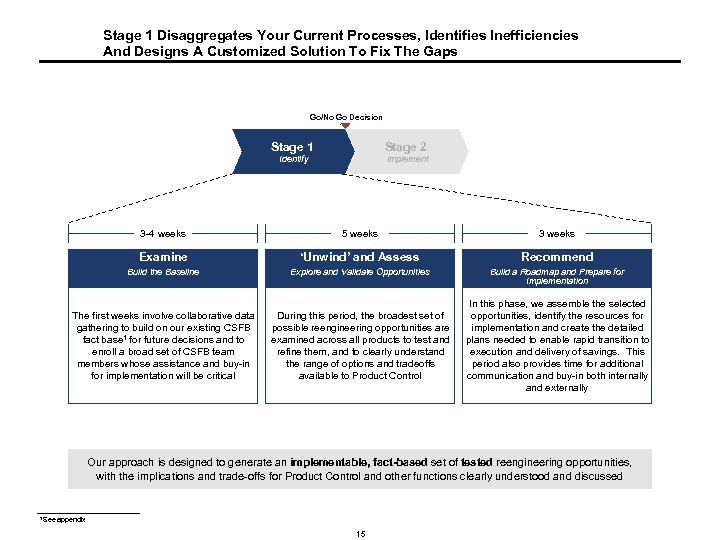
Stage 1 Disaggregates Your Current Processes, Identifies Inefficiencies And Designs A Customized Solution To Fix The Gaps Go/No Go Decision Stage 1 3 -4 weeks Stage 2 Identify Implement 5 weeks 3 weeks Examine ‘Unwind’ and Assess Recommend Build the Baseline Explore and Validate Opportunities Build a Roadmap and Prepare for Implementation The first weeks involve collaborative data gathering to build on our existing CSFB fact base 1 for future decisions and to enroll a broad set of CSFB team members whose assistance and buy-in for implementation will be critical During this period, the broadest set of possible reengineering opportunities are examined across all products to test and refine them, and to clearly understand the range of options and tradeoffs available to Product Control In this phase, we assemble the selected opportunities, identify the resources for implementation and create the detailed plans needed to enable rapid transition to execution and delivery of savings. This period also provides time for additional communication and buy-in both internally and externally Our approach is designed to generate an implementable, fact-based set of tested reengineering opportunities, with the implications and trade-offs for Product Control and other functions clearly understood and discussed 1 See appendix 15
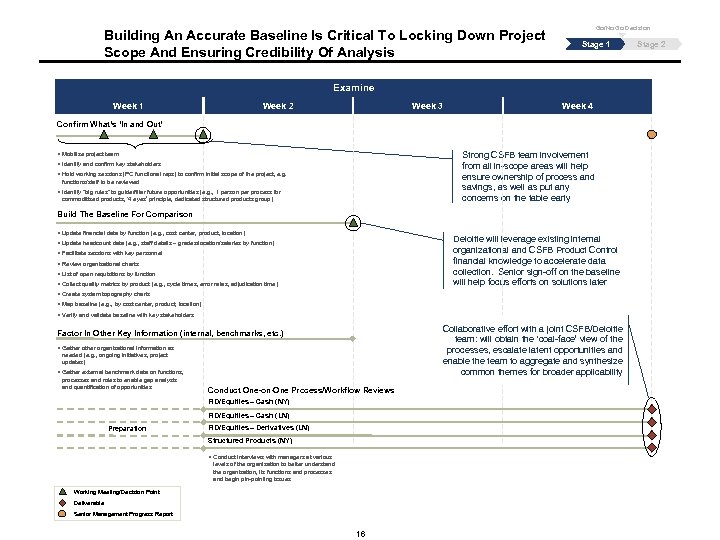
Building An Accurate Baseline Is Critical To Locking Down Project Scope And Ensuring Credibility Of Analysis Go/No Go Decision Stage 1 Examine Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Confirm What’s ‘In and Out’ Strong CSFB team involvement from all in-scope areas will help ensure ownership of process and savings, as well as put any concerns on the table early § Mobilize project team § Identify and confirm key stakeholders § Hold working sessions (PC functional reps) to confirm initial scope of the project, e. g. functions/staff to be reviewed § Identify “big rules” to guide/filter future opportunities (e. g. , 1 person per process for commoditized products, ‘ 4 eyes’ principle, dedicated structured products group) Build The Baseline For Comparison § Update financial data by function (e. g. , cost center, product, location) Deloitte will leverage existing internal organizational and CSFB Product Control financial knowledge to accelerate data collection. Senior sign-off on the baseline will help focus efforts on solutions later § Update headcount data (e. g. , staff details – grades/location/salaries by function) § Facilitate sessions with key personnel § Review organizational charts § List of open requisitions by function § Collect quality metrics by product (e. g. , cycle times, error rates, adjudication time) § Create system topography charts § Map baseline (e. g. , by cost center, product, location) § Verify and validate baseline with key stakeholders Collaborative effort with a joint CSFB/Deloitte team: will obtain the ‘coal-face’ view of the processes, escalatent opportunities and enable the team to aggregate and synthesize common themes for broader applicability Factor In Other Key Information (internal, benchmarks, etc. ) § Gather organizational information as needed (e. g. , ongoing initiatives, project updates) § Gather external benchmark data on functions, processes and roles to enable gap analysis and quantification of opportunities Conduct One-on-One Process/Workflow Reviews FID/Equities – Cash (NY) FID/Equities – Cash (LN) Preparation FID/Equities – Derivatives (LN) Structured Products (NY) § Conduct interviews with managers at various levels of the organization to better understand the organization, its functions and processes and begin pin-pointing issues Working Meeting/Decision Point Deliverable Senior Management Progress Report 16 Stage 2
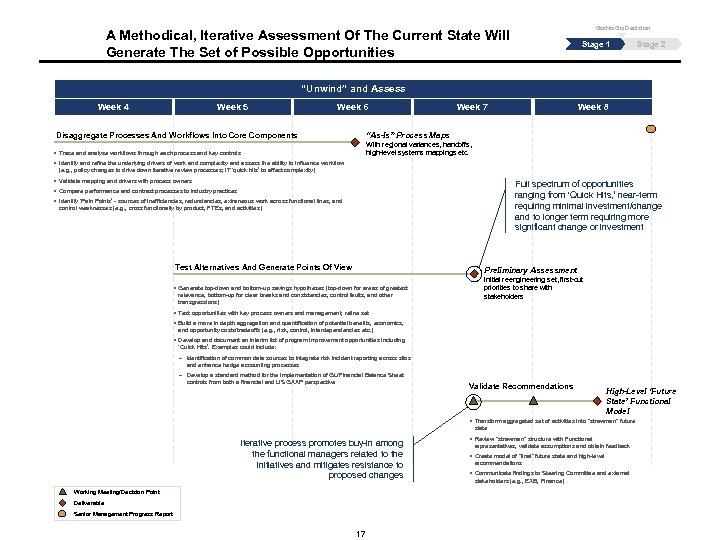
Go/No Go Decision A Methodical, Iterative Assessment Of The Current State Will Generate The Set of Possible Opportunities Stage 1 Stage 2 “Unwind” and Assess Week 4 Week 5 Week 6 Disaggregate Processes And Workflows Into Core Components Week 7 Week 8 “As-Is” Process Maps With regional variances, handoffs, high-level systems mappings etc. § Trace and analyze workflows through each process and key controls § Identify and refine the underlying drivers of work and complexity and assess the ability to influence workflow (e. g. , policy changes to drive down iterative review processes; IT ‘quick hits’ to affect complexity) § Validate mapping and drivers with process owners Full spectrum of opportunities ranging from ‘Quick Hits, ’ near-term requiring minimal investment/change and to longer term requiring more significant change or investment § Compare performance and contrast processes to industry practices § Identify ‘Pain Points’ - sources of inefficiencies, redundancies, extraneous work across functional lines, and control weaknesses (e. g. , cross functionally by product, FTEs, and activities) Test Alternatives And Generate Points Of View Preliminary Assessment § Generate top-down and bottom-up savings hypotheses (top-down for areas of greatest relevance, bottom-up for clear breaks and consistencies, control faults, and other transgressions) Initial reengineering set, first-cut priorities to share with stakeholders § Test opportunities with key process owners and management; refine set § Build a more in depth aggregation and quantification of potential benefits, economics, and opportunity costs/tradeoffs (e. g. , risk, control, interdependencies etc. ) § Develop and document an interim list of program improvement opportunities including ‘Quick Hits’. Examples could include: - Identification of common data sources to integrate risk incident reporting across silos and enhance hedge accounting processes - Develop a standard method for the implementation of GL/Financial Balance Sheet controls from both a financial and US GAAP perspective Validate Recommendations High-Level ‘Future State’ Functional Model § Transform aggregated set of activities into “strawman” future state Iterative process promotes buy-in among the functional managers related to the initiatives and mitigates resistance to proposed changes Working Meeting/Decision Point Deliverable Senior Management Progress Report 17 § Review “strawman” structure with Functional representatives, validate assumptions and obtain feedback § Create model of “final” future state and high-level recommendations § Communicate findings to Steering Committee and external stakeholders (e. g. , EXB, Finance)
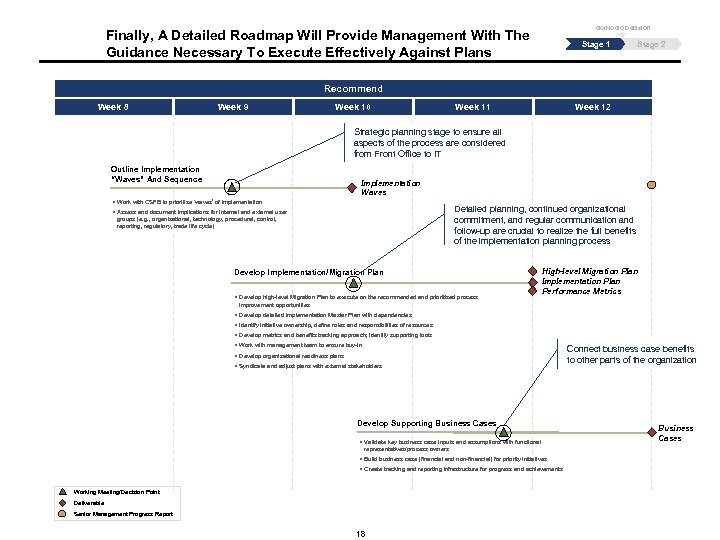
Go/No Go Decision Finally, A Detailed Roadmap Will Provide Management With The Guidance Necessary To Execute Effectively Against Plans Stage 1 Stage 2 Recommend Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 Week 11 Week 12 Strategic planning stage to ensure all aspects of the process are considered from Front Office to IT Outline Implementation “Waves” And Sequence Implementation Waves § Work with CSFB to prioritize ‘waves’ of implementation Detailed planning, continued organizational commitment, and regular communication and follow-up are crucial to realize the full benefits of the implementation planning process § Assess and document implications for internal and external user groups (e. g. , organizational, technology, procedural, control, reporting, regulatory, trade life cycle) Develop Implementation/Migration Plan § Develop high-level Migration Plan to execute on the recommended and prioritized process High-level Migration Plan Implementation Plan Performance Metrics improvement opportunities § Develop detailed Implementation Master Plan with dependencies § Identify initiative ownership, define roles and responsibilities of resources § Develop metrics and benefits tracking approach; identify supporting tools § Work with management team to ensure buy-in § Develop organizational readiness plans § Syndicate and adjust plans with external stakeholders Develop Supporting Business Cases § Validate key business case inputs and assumptions with functional representatives/process owners § Build business case (financial and non-financial) for priority initiatives § Create tracking and reporting infrastructure for progress and achievements Working Meeting/Decision Point Deliverable Senior Management Progress Report 18 Connect business case benefits to other parts of the organization Business Cases
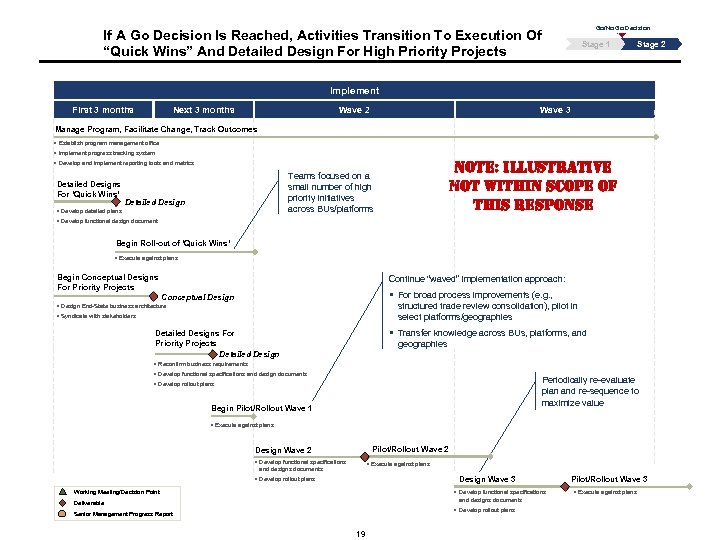
Go/No Go Decision If A Go Decision Is Reached, Activities Transition To Execution Of “Quick Wins” And Detailed Design For High Priority Projects Stage 1 Stage 2 Implement First 3 months Next 3 months Wave 2 Wave 3 Manage Program, Facilitate Change, Track Outcomes § Establish program management office § Implement progress tracking system NOTE: ILLUSTRATIVE NOT WITHIN SCOPE OF THIS RESPONSE § Develop and implement reporting tools and metrics Detailed Designs For ‘Quick Wins’ Teams focused on a small number of high priority initiatives across BUs/platforms Detailed Design § Develop detailed plans § Develop functional design document Begin Roll-out of ‘Quick Wins’ § Execute against plans Begin Conceptual Designs For Priority Projects Continue “waved” implementation approach: § For broad process improvements (e. g. , Conceptual Design structured trade review consolidation), pilot in select platforms/geographies § Design End-State business architecture § Syndicate with stakeholders § Transfer knowledge across BUs, platforms, and Detailed Designs For Priority Projects Detailed Design geographies § Reconfirm business requirements § Develop functional specifications and design documents Periodically re-evaluate plan and re-sequence to maximize value § Develop rollout plans Begin Pilot/Rollout Wave 1 § Execute against plans Pilot/Rollout Wave 2 Design Wave 2 § Develop functional specifications § Execute against plans and designs documents Design Wave 3 § Develop rollout plans Working Meeting/Decision Point § Develop functional specifications and designs documents Deliverable § Develop rollout plans Senior Management Progress Report 19 Pilot/Rollout Wave 3 § Execute against plans

IV. “Test Driving” The Approach
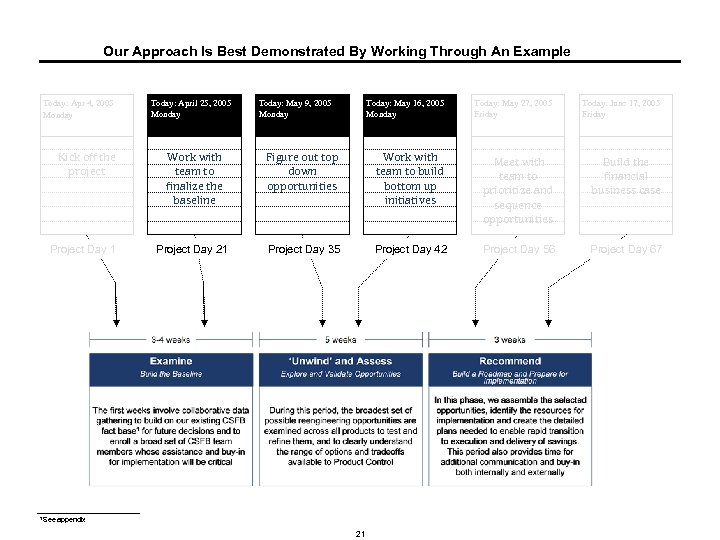
Our Approach Is Best Demonstrated By Working Through An Example Today: Apr 4, 2005 Monday Kick off the project Project Day 1 Today: April 25, 2005 Monday Today: May 9, 2005 Monday Today: May 16, 2005 Monday Today: May 27, 2005 Friday Today: June 17, 2005 Friday Work with team to finalize the baseline Figure out top down opportunities Work with team to build bottom up initiatives Meet with team to prioritize and sequence opportunities Build the financial business case Project Day 21 Project Day 35 Project Day 42 Project Day 56 Project Day 67 1 See appendix 21
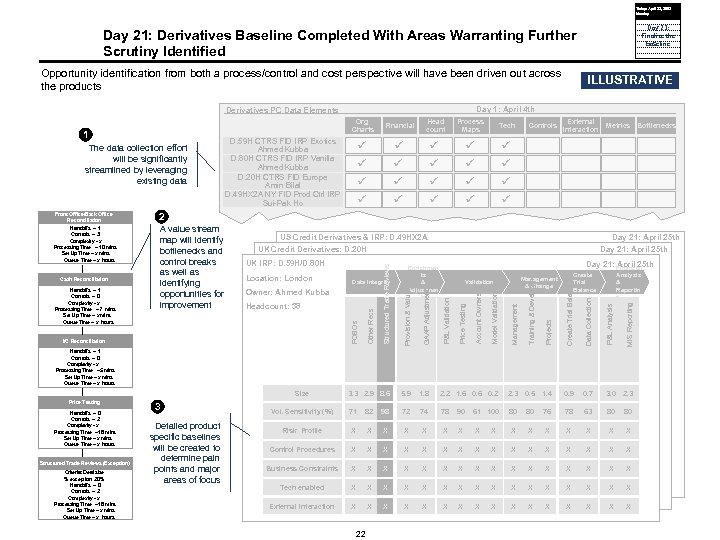
Today: April 25, 2005 Monday Day 21: Finalize the baseline Day 21: Derivatives Baseline Completed With Areas Warranting Further Scrutiny Identified Opportunity identification from both a process/control and cost perspective will have been driven out across the products Day 1: April 4 th Derivatives PC Data Elements Org Charts 1 The data collection effort will be significantly streamlined by leveraging existing data Process Maps Tech ü ü ü Controls External Interaction Metrics Bottlenecks 2 US Credit Derivatives & IRP: D. 49 HX 2 A UK Credit Derivatives: D. 20 H Location: London Model Validation Management Training & Development Projects Create Trial Balance Data Collection P&L Analysis MIS Reporting Day 21: Financial April 25 th GAAP Adjustments UK Location: London IRP: D. 59 H/D. 80 H Owner: Ahmed Kubba Day 21: April 25 th Provision & Valuations 3. 3 2. 9 8. 6 5. 9 1. 8 2. 2 1. 6 0. 2 2. 3 0. 5 1. 4 0. 9 0. 7 3. 0 2. 3 Vol. Sensitivity (%) 71 82 98 72 74 78 90 61 100 80 80 76 78 63 80 80 Risk Profile X X X X Control Procedures X X X X Business Constraints X X X X Tech enabled X X X X External Interaction X X X X Headcount: 38 I/C Reconcilliation Reconciliation Management & Change Validation Account Ownersip Data Integrity Price Testing Location: London Kubba Owner: Ahmed 38 Headcount: Kubba Enrichmen ts & Adjustmen ts P&L Validation A value stream map will identify bottlenecks and control breaks as well as identifying opportunities for improvement Structured Trade Reviews Handoffs – 1 Controls – 0 Complexity - x Processing Time – 7 mins Set Up Time – x mins Queue Time – x hours Financial Head count ü ü Other Recs Cash Reconciliation ü ü D. 59 H CTRS FID IRP Exotics Ahmed Kubba D. 80 H CTRS FID IRP Vanilla Ahmed Kubba D. 20 H CTRS FID Europe Amin Bilal D. 49 HX 2 A NY FID Prod Ctrl IRP Sui-Pak Ho FOBOs Front Office/Back Office Reconciliation Handoffs – 1 Controls – 3 Complexity - x Processing Time – 10 mins Set Up Time – x mins Queue Time – x hours Queue Time ILLUSTRATIVE Analysis & Reportin g Create Trial Balance Handoffs – 1 Controls – 0 Complexity - x Processing Time – 5 mins Set Up Time – x mins Queue Time – x hours Size Price Testing Handoffs – 0 Controls – 2 Complexity - x Processing Time – 18 mins Set Up Time – x mins Queue Time – x hours Structured Trade Reviews (Exception) Price Testing Structured Trade Review (Exception) Criteria: Deal size % exception: 20% Handoffs – 0 Controls – 2 Complexity - x Processing Time – 18 mins Set Up Time – x mins Queue Time – x hours 3 Detailed product specific baselines will be created to determine pain points and major areas of focus 22
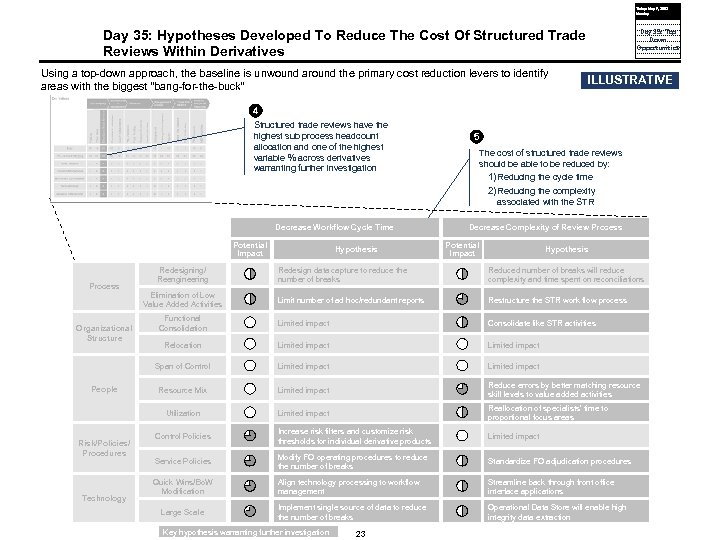
Today: May 9, 2005 Monday Day 35: Hypotheses Developed To Reduce The Cost Of Structured Trade Reviews Within Derivatives Using a top-down approach, the baseline is unwound around the primary cost reduction levers to identify areas with the biggest “bang-for-the-buck” Day 35: Top Down Opportunities ILLUSTRATIVE 4 Structured trade reviews have the highest sub process headcount allocation and one of the highest variable % across derivatives warranting further investigation 5 The cost of structured trade reviews should be able to be reduced by: 1) Reducing the cycle time 2) Reducing the complexity associated with the STR Decrease Workflow Cycle Time Potential Impact Hypothesis People Risk/Policies/ Procedures Technology Reduced number of breaks will reduce complexity and time spent on reconciliations Limit number of ad hoc/redundant reports Restructure the STR work flow process Functional Consolidation Limited impact Consolidate like STR activities Relocation Limited impact Resource Mix Limited impact Reduce errors by better matching resource skill levels to value added activities Utilization Organizational Structure Redesign data capture to reduce the number of breaks Span of Control Process Redesigning/ Reengineering Hypothesis Decrease Complexity of Review Process Limited impact Reallocation of specialists’ time to proportional focus areas Control Policies Increase risk filters and customize risk thresholds for individual derivative products Limited impact Service Policies Modify FO operating procedures to reduce the number of breaks Standardize FO adjudication procedures Quick Wins/Bo. W Modification Align technology processing to workflow management Streamline back through front office interface applications Implement single source of data to reduce the number of breaks Operational Data Store will enable high integrity data extraction Elimination of Low Value Added Activities Large Scale Key hypothesis warranting further investigation 23
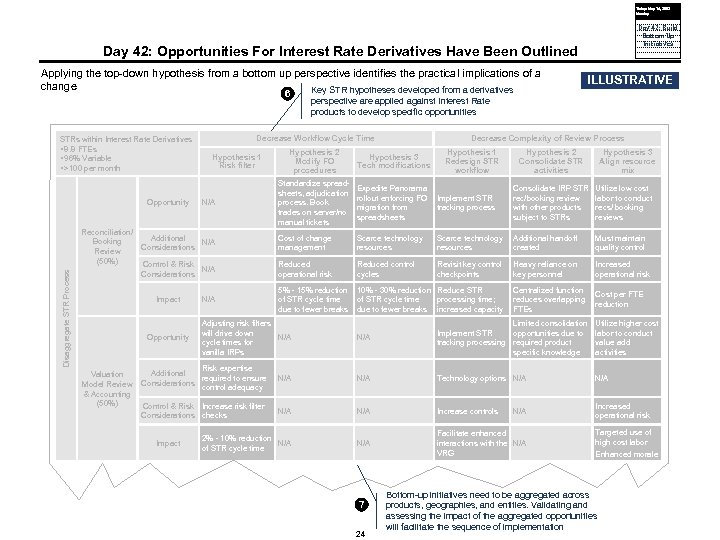
Today: May 16, 2005 Monday Day 42: Build Bottom Up Initiatives Day 42: Opportunities For Interest Rate Derivatives Have Been Outlined Applying the top-down hypothesis from a bottom up perspective identifies the practical implications of a change Key STR hypotheses developed from a derivatives 6 STRs within Interest Rate Derivatives § 8. 8 FTEs § 96% Variable § >100 per month Disaggregate STR Process Opportunity N/A Reconciliation/ Additional Booking N/A Considerations Review (50%) Control & Risk N/A Considerations Impact Opportunity N/A Hypothesis 2 Modify FO procedures Decrease Complexity of Review Process Hypothesis 3 Tech modifications Hypothesis 1 Redesign STR workflow Hypothesis 2 Consolidate STR activities Hypothesis 3 Align resource mix Standardize spreadsheets, adjudication process. Book trades on server/no manual tickets Expedite Panorama rollout enforcing FO Implement STR migration from tracking process spreadsheets Consolidate IRP STR rec/booking review with other products subject to STRs Utilize low cost labor to conduct recs/ booking reviews Cost of change management Scarce technology resources Additional handoff created Must maintain quality control Reduced operational risk Reduced control cycles Revisit key control checkpoints Heavy reliance on key personnel Increased operational risk Centralized function reduces overlapping FTEs Cost per FTE reduction 5% - 15% reduction 10% - 30% reduction Reduce STR of STR cycle time processing time; due to fewer breaks increased capacity Adjusting risk filters will drive down N/A cycle times for vanilla IRPs N/A Limited consolidation opportunities due to Implement STR tracking processing required product specific knowledge Utilize higher cost labor to conduct value add activities N/A Technology options N/A N/A Increase controls Increased operational risk 2% - 10% reduction N/A of STR cycle time N/A Facilitate enhanced interactions with the N/A VRG Risk expertise Additional Valuation required to ensure Model Review Considerations control adequacy & Accounting (50%) Control & Risk Increase risk filter Considerations checks Impact perspective are applied against Interest Rate products to develop specific opportunities Decrease Workflow Cycle Time Hypothesis 1 Risk filter ILLUSTRATIVE 7 24 N/A Targeted use of high cost labor Enhanced morale Bottom-up initiatives need to be aggregated across products, geographies, and entities. Validating and assessing the impact of the aggregated opportunities will facilitate the sequence of implementation
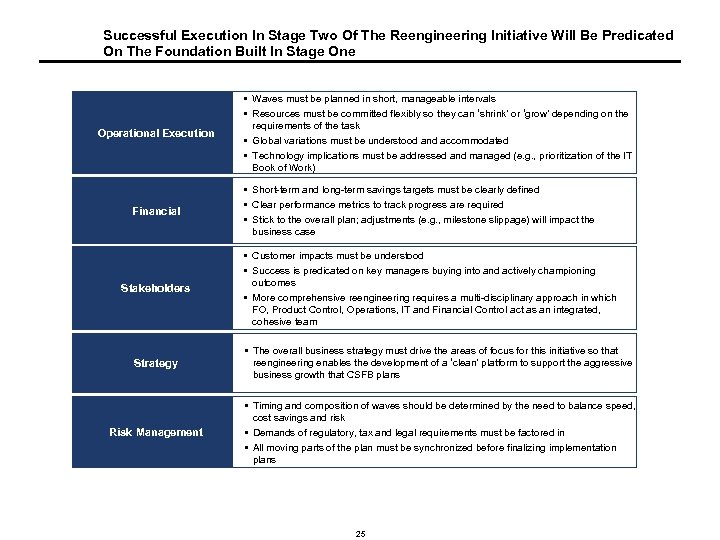
Successful Execution In Stage Two Of The Reengineering Initiative Will Be Predicated On The Foundation Built In Stage One Operational Execution Financial Stakeholders § Waves must be planned in short, manageable intervals § Resources must be committed flexibly so they can ‘shrink’ or ‘grow’ depending on the requirements of the task § Global variations must be understood and accommodated § Technology implications must be addressed and managed (e. g. , prioritization of the IT Book of Work) § Short-term and long-term savings targets must be clearly defined § Clear performance metrics to track progress are required § Stick to the overall plan; adjustments (e. g. , milestone slippage) will impact the business case § Customer impacts must be understood § Success is predicated on key managers buying into and actively championing outcomes § More comprehensive reengineering requires a multi-disciplinary approach in which FO, Product Control, Operations, IT and Financial Control act as an integrated, cohesive team Strategy § The overall business strategy must drive the areas of focus for this initiative so that reengineering enables the development of a ‘clean’ platform to support the aggressive business growth that CSFB plans Risk Management § Timing and composition of waves should be determined by the need to balance speed, cost savings and risk § Demands of regulatory, tax and legal requirements must be factored in § All moving parts of the plan must be synchronized before finalizing implementation plans 25

V. Team Structure, Profiles and Fees
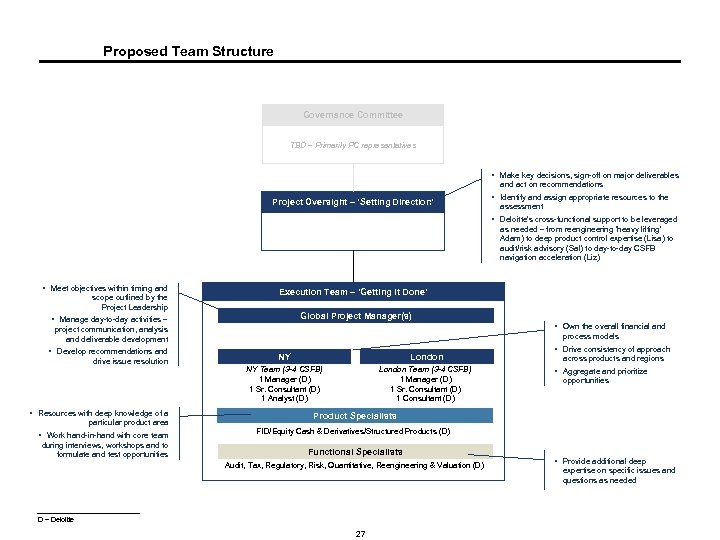
Proposed Team Structure Governance Committee TBD – Primarily PC representatives § Make key decisions, sign-off on major deliverables and act on recommendations Project Oversight – ‘Setting Direction’ § Identify and assign appropriate resources to the assessment § Deloitte’s cross-functional support to be leveraged as needed – from reengineering ‘heavy lifting’ Adam) to deep product control expertise (Lisa) to audit/risk advisory (Sal) to day-to-day CSFB navigation acceleration (Liz) § Meet objectives within timing and scope outlined by the Project Leadership Execution Team – ‘Getting It Done’ Global Project Manager(s) § Manage day-to-day activities – § Own the overall financial and project communication, analysis and deliverable development § Develop recommendations and drive issue resolution § Resources with deep knowledge of a particular product area process models NY London NY Team (3 -4 CSFB) 1 Manager (D) 1 Sr. Consultant (D) 1 Analyst (D) London Team (3 -4 CSFB) 1 Manager (D) 1 Sr. Consultant (D) 1 Consultant (D) § Drive consistency of approach across products and regions § Aggregate and prioritize opportunities Product Specialists § Work hand-in-hand with core team FID/Equity Cash & Derivatives/Structured Products (D) during interviews, workshops and to formulate and test opportunities Functional Specialists Audit, Tax, Regulatory, Risk, Quantitative, Reengineering & Valuation (D) D – Deloitte 27 § Provide additional deep expertise on specific issues and questions as needed
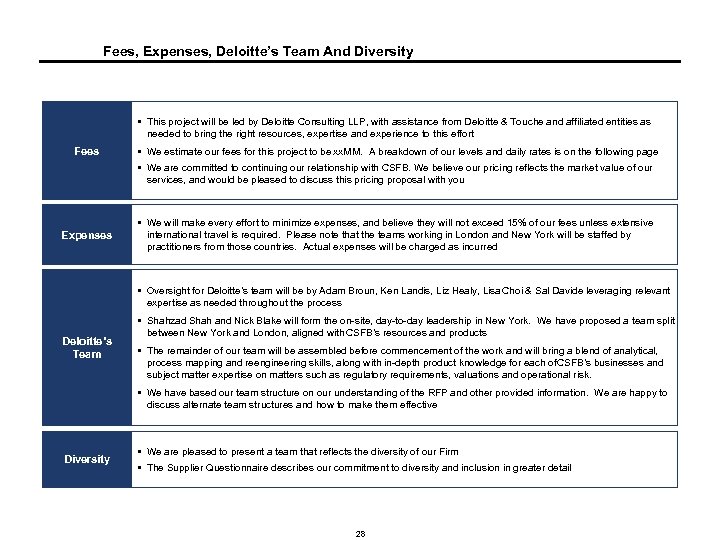
Fees, Expenses, Deloitte’s Team And Diversity § This project will be led by Deloitte Consulting LLP, with assistance from Deloitte & Touche and affiliated entities as needed to bring the right resources, expertise and experience to this effort Fees § We estimate our fees for this project to be xx. MM. A breakdown of our levels and daily rates is on the following page § We are committed to continuing our relationship with CSFB. We believe our pricing reflects the market value of our services, and would be pleased to discuss this pricing proposal with you § We will make every effort to minimize expenses, and believe they will not exceed 15% of our fees unless extensive Expenses international travel is required. Please note that the teams working in London and New York will be staffed by practitioners from those countries. Actual expenses will be charged as incurred § Oversight for Deloitte’s team will be by Adam Broun, Ken Landis, Liz Healy, Lisa Choi & Sal Davide leveraging relevant expertise as needed throughout the process § Shahzad Shah and Nick Blake will form the on-site, day-to-day leadership in New York. We have proposed a team split Deloitte’s Team between New York and London, aligned with CSFB’s resources and products § The remainder of our team will be assembled before commencement of the work and will bring a blend of analytical, process mapping and reengineering skills, along with in-depth product knowledge for each of SFB’s businesses and C subject matter expertise on matters such as regulatory requirements, valuations and operational risk. § We have based our team structure on our understanding of the RFP and other provided information. We are happy to discuss alternate team structures and how to make them effective Diversity § We are pleased to present a team that reflects the diversity of our Firm § The Supplier Questionnaire describes our commitment to diversity and inclusion in greater detail 28
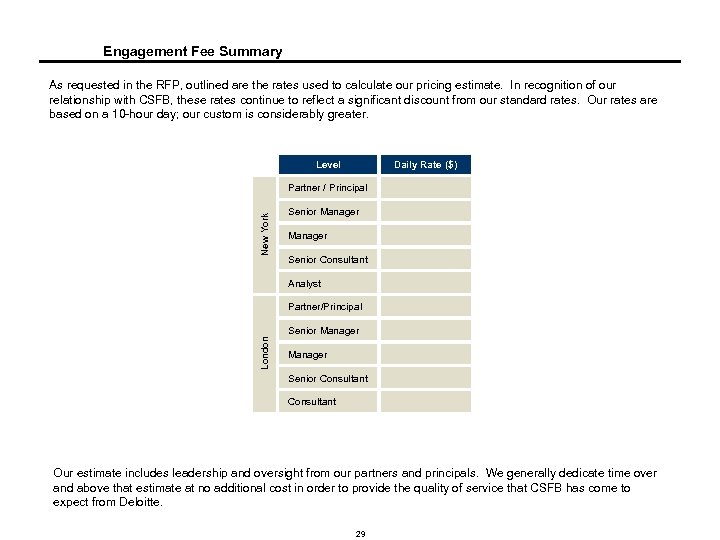
Engagement Fee Summary As requested in the RFP, outlined are the rates used to calculate our pricing estimate. In recognition of our relationship with CSFB, these rates continue to reflect a significant discount from our standard rates. Our rates are based on a 10 -hour day; our custom is considerably greater. Level Daily Rate ($) New York Partner / Principal Senior Manager Senior Consultant Analyst Partner/Principal London Senior Manager Senior Consultant Our estimate includes leadership and oversight from our partners and principals. We generally dedicate time over and above that estimate at no additional cost in order to provide the quality of service that CSFB has come to expect from Deloitte. 29

VI. Qualifications & References
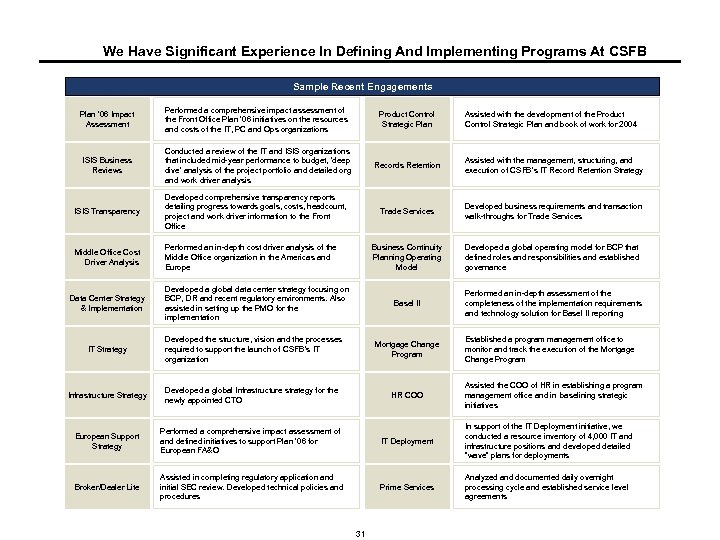
We Have Significant Experience In Defining And Implementing Programs At CSFB Sample Recent Engagements Plan ’ 06 Impact Assessment Performed a comprehensive impact assessment of the Front Office Plan ’ 06 initiatives on the resources and costs of the IT, PC and Ops organizations Product Control Strategic Plan ISIS Business Reviews Conducted a review of the IT and ISIS organizations that included mid-year performance to budget, ‘deep dive’ analysis of the project portfolio and detailed org and work driver analysis Records Retention Assisted with the management, structuring, and execution of CSFB’s IT Record Retention Strategy ISIS Transparency Developed comprehensive transparency reports detailing progress towards goals, costs, headcount, project and work driver information to the Front Office Trade Services Developed business requirements and transaction walk-throughs for Trade Services Middle Office Cost Driver Analysis Performed an in-depth cost driver analysis of the Middle Office organization in the Americas and Europe Business Continuity Planning Operating Model Developed a global operating model for BCP that defined roles and responsibilities and established governance Basel II Performed an in-depth assessment of the completeness of the implementation requirements and technology solution for Basel II reporting Data Center Strategy & Implementation Developed a global data center strategy focusing on BCP, DR and recent regulatory environments. Also assisted in setting up the PMO for the implementation Assisted with the development of the Product Control Strategic Plan and book of work for 2004 IT Strategy Developed the structure, vision and the processes required to support the launch of CSFB’s IT organization Mortgage Change Program Infrastructure Strategy Developed a global Infrastructure strategy for the newly appointed CTO HR COO European Support Strategy Performed a comprehensive impact assessment of and defined initiatives to support Plan ’ 06 for European FA&O IT Deployment In support of the IT Deployment initiative, we conducted a resource inventory of 4, 000 IT and infrastructure positions and developed detailed “wave” plans for deployments Broker/Dealer Lite Assisted in completing regulatory application and initial SEC review. Developed technical policies and procedures Prime Services Analyzed and documented daily overnight processing cycle and established service level agreements 31 Established a program management office to monitor and track the execution of the Mortgage Change Program Assisted the COO of HR in establishing a program management office and in baselining strategic initiatives
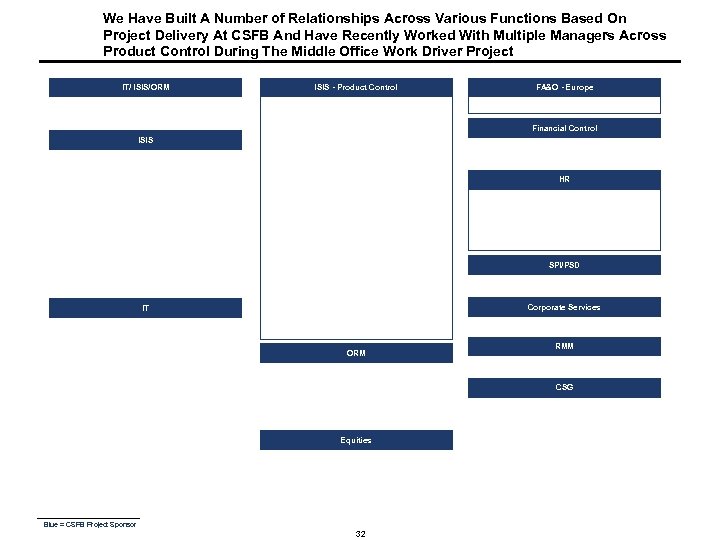
We Have Built A Number of Relationships Across Various Functions Based On Project Delivery At CSFB And Have Recently Worked With Multiple Managers Across Product Control During The Middle Office Work Driver Project IT/ ISIS/ORM ISIS - Product Control FA&O - Europe Financial Control ISIS HR SPI/PSD Corporate Services IT ORM RMM CSG Equities Blue = CSFB Project Sponsor 32
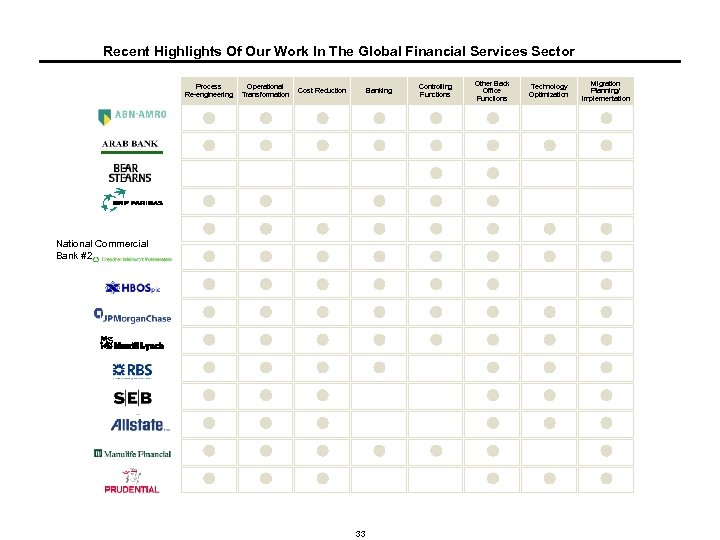
Recent Highlights Of Our Work In The Global Financial Services Sector Process Re-engineering Operational Transformation Cost Reduction Banking National Commercial Bank #2 33 Controlling Functions Other Back Office Functions Technology Optimization Migration Planning/ Implementation
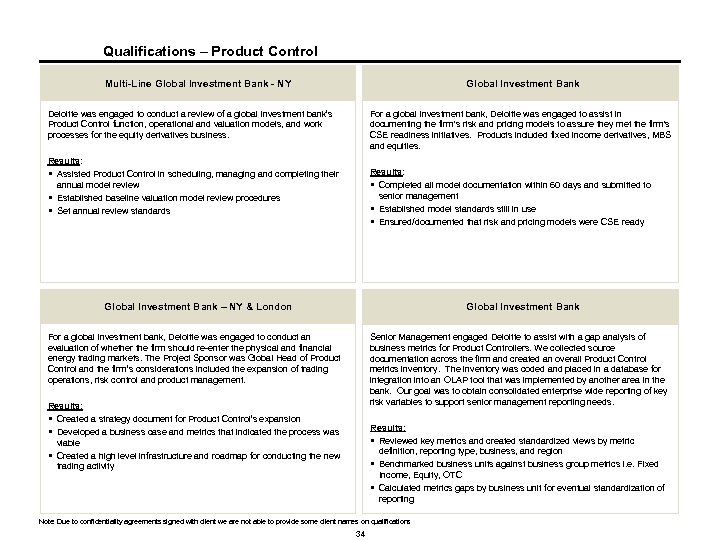
Qualifications – Product Control Multi-Line Global Investment Bank - NY Global Investment Bank Deloitte was engaged to conduct a review of a global investment bank’s Product Control function, operational and valuation models, and work processes for the equity derivatives business. For a global investment bank, Deloitte was engaged to assist in documenting the firm's risk and pricing models to assure they met the firm's CSE readiness initiatives. Products included fixed income derivatives, MBS and equities. Results: § Assisted Product Control in scheduling, managing and completing their annual model review § Established baseline valuation model review procedures § Set annual review standards Results: § Completed all model documentation within 60 days and submitted to senior management § Established model standards still in use § Ensured/documented that risk and pricing models were CSE ready Global Investment Bank – NY & London Global Investment Bank For a global investment bank, Deloitte was engaged to conduct an evaluation of whether the firm should re-enter the physical and financial energy trading markets. The Project Sponsor was Global Head of Product Control and the firm’s considerations included the expansion of trading operations, risk control and product management. Senior Management engaged Deloitte to assist with a gap analysis of business metrics for Product Controllers. We collected source documentation across the firm and created an overall Product Control metrics inventory. The inventory was coded and placed in a database for integration into an OLAP tool that was implemented by another area in the bank. Our goal was to obtain consolidated enterprise wide reporting of key risk variables to support senior management reporting needs. Results: § Created a strategy document for Product Control’s expansion § Developed a business case and metrics that indicated the process was viable § Created a high level infrastructure and roadmap for conducting the new trading activity Results: § Reviewed key metrics and created standardized views by metric definition, reporting type, business, and region § Benchmarked business units against business group metrics i. e. Fixed Income, Equity, OTC § Calculated metrics gaps by business unit for eventual standardization of reporting Note: Due to confidentiality agreements signed with client we are not able to provide some client names on qualifications 34
Qualifications – Process Improvement & Cost Reduction Deloitte was engaged to redesign and improve IT and Operational functions. This included: the replacement of outdated legacy systems; elimination of duplication and unnecessary reconciliation and manual processes; and automation of information reporting. Deloitte was engaged to design and implement a strategic cost reduction initiative to remove 350 m Yen from the cost base of the operations function. A 5 step approach to the design was used, capturing current operating model and process, base-lining and developing performance metrics. We were then engaged in iterative re-design of process and organization. Results: § Reengineered infrastructure and processes from settlement systems to General Ledger § Consolidated functions and processes from multiple accounting streams to one integrated system utilizing SAP enabled re-engineering § Restructured the role of finance to encompass business support and analysis rather than solely reporting of historic information Results: § Streamlined and re-engineered processes (segregating simple/complex tasks, reducing rework and managing waste in linear processes) § Introduced performance management techniques across the organization (people, process and systems performance management) § The joint client/practitioner team re-designed the operations group in just under 12 weeks enabling the implementation team to deliver against the new operating model and processes in 14 weeks Deloitte undertook a significant cost reduction exercise for overall operations, seeking to reduce the cost base by around £ 175 m and reduce the workforce by up to 25%. Deloitte worked closely with the client in a highly collaborative manner to rapidly identify and deliver tactical/quick win results. Deloitte was engaged to redesign and improve IT and operational functions which included enabling enterprise-wide shared services, enterprise-wide management information strategies, and improved cost identification, cash management, reporting and procurement. Our work resulted in significant cost reductions. Results: § Savings of £ 177 m delivered within 12 months: - IT Services £ 80 m - Procurement: £ 21 m - Support Services: £ 49 m - Customer Services: £ 27 m § All savings externally audited – final audited result was £ 201 M Results: § Completely reengineered the finance function including cash management, procurement and sourcing, general accounting, cost management, and reporting and analysis § Measurable recurring annual benefits were estimated to be over 100 % of the total project cost 35
Qualifications – Process Improvement & Systems Implementations Deloitte was engaged to assist senior management in the reengineering of BNP-Paribas Capital Market activities. This involved implementing a new back office system to manage derivatives in a centralized manner. Deloitte implemented a new treasury and derivatives system: § Merrill Lynch bank - Deloitte conducted a front-to-back implementation for the treasury activity products including bonds, money markets, loans, swaps, CDs, commercial paper and repos Results: Focusing on the reengineering of Back Office processes resulted in: § Integration of all derivatives products in Murex § Integration of Murex Back Office into the BNP-BFI environment (Accounting, Risk, FO systems. . . ) § Reengineering and redefining back office processes and procedures § Creating a new front-to-back office organization § Rollout: Defined the go live strategy and migration plan. Successfully managed the migration into Murex G 2000 § Merrill Lynch - Deloitte provided implementation assistance for a Summit system installation to provide front-to-back office support for emerging market bond trading and foreign exchange business globally Results: § Provided full program and project stream management § Designed business processes, developed and executed acceptance tests and implemented plan (including validation of FX module newly added by Summit for Merrill) § Set-up accounting and testing Global US Investment Bank Supranational Bank As part of a strategic project, Deloitte provided assistance for selection and development of a global multi-entity derivatives trading system capable of supporting all major types of derivatives. Deloitte was appointed to implement a new front to back office organization plus accounting solution for treasury, fixed income and derivatives (IRD, CD) activities. The large-scale project covered virtually all departments of the bank over an 18 month period, and involved a significant level of process reengineering. Results: § Phase I - strategy feasibility study which considered high level business systems architecture, detailed business case, application architecture, detailed development and migration planning, detailed functional design, business process redesign and sizing and analysis of technical options § Phase II - detailed evaluation of various risk management software packages to assess their functionality against the requirements identified in phase I. This focused on information technology issues, including leading edge analysis of the use of the Sybase database product § Phase III - provided implementation assistance, detailed design and architecture planning Results: § Provided program and project stream management; defined user requirements and enhancements to the software; designed a new target organizational structure and redefined transaction processes § Configured and integrated SUMMIT and SAP; built interfaces to the existing data warehouse and risk applications; conducted testing and user training Note: Due to confidentiality agreements signed with client we are not able to provide some client names on qualifications 36
Qualifications – Operating Model Transformations Global Investment Bank Deloitte was engaged by ABN Amro to design a global operating model to combine FX and Money Markets. Key objectives included reducing cost, enhancing transparency, driving consistency of attributable activities and adding mission critical capabilities. Our work helped define a global operating model and standardized set of global processes. Deloitte was engaged to set up the Umbrella PMO for the equities and fixed income Operating Model Transformation Program. Priorities included short -term focus on optimizing cost reduction and improving internal controls and a medium-term focus on service improvements (both internal and external). The Program was responsible for generating a minimum of € 212 million savings by the end of 2005. Results: § Increased efficiency with centralized desk management and more consistent pricing § Increased central control and reduced operational risk (simplified the current operating model, provided greater transparency for local trading activities) § Reduced cost of operational infrastructure (centralized operational systems and back office) § Provided for costs avoidance and increased flexibility to take advantage of future market opportunities Results: § Refocused equities and fixed income to create a robust, competitive and cost-effective platform § Defined mapping rules to determine interim location of functions in the operating model § Devised business architecture principles underpinning the operating model § Conducted functional mapping of the operating model including a FTE analysis to support the design effort § Repositioned the group to take advantage of future growth Deloitte was engaged to develop a complete operating model re-design for a major banking division. The new model was designed to facilitate the migration of the division to a new operating platform and several internal functions to new locations. Deloitte collaborated closely with client management to prioritize actions, make decisions and resolve major issues Deloitte was engaged to develop a Target Operating Model to lead reintegration of credit cards businesses into to the group in combination with lending as part of a new Consumer Finance division. Analyzed the two prevailing operating models for loans (Bank of Scotland Direct and Halifax loans) and credit cards and created a financially viable model. Facilitated workshops with key participants so consolidation opportunities could be identified and quantified. In a validation phase, we investigated all identified opportunities. Working in teams with the client, we developed business cases and a high level implementation plan. Results: § The Target Operating Model became the focal point of all change, in particular the complex re-organization of processes, functional responsibilities and costs over several sites § The TOM enabled all involved to clearly understand the blueprint for the future, and for management to clearly see how the cost imperatives would be met through the re-organization Results: § Identified consolidation opportunities of £ 21 m § £ 20 m in cost reduction was subsequently realized Note: Due to confidentiality agreements signed with client we are not able to provide some client names on qualifications 37

Qualifications – Bank Wide Integration/Design The bank proposed a global re-organization of its current operating structure. Deloitte was engaged to define an operating model for each client -facing business line, support and control function. Design of the new structure included: a review and assessment of existing Arab Bank strategy; process and organization; modelling of generic best practices in operations; assessment of key business issues; and the presentation of action alternatives for further discussion. Deloitte was engaged after the merger to assist in the integration of diverse business practices and technology infrastructures, including Capital Markets, and to provide PMO and resources to support integration activity. Results: Deloitte deployed an experienced team to assist JP Morgan Chase in various parts of the merger, focusing on: § Synergies identification: prioritization of integration of high value activities § Merger risk management: identification and quantification of potential risks § PMO: managed the creation and issuance of deliverables and overall project communication. Used PMO net to escalate key issues Results: § Created a high-level transition roadmap, capturing major risks and obstacles associated with implementation of Head Office Charters § Presented a newly defined mission statement to align the activities of each business line/ function § Defined and refined new regional responsibilities and intra-organisational relationships 38

Clients Who Are Willing To Share Their Experiences Previous clients of Deloitte are available to speak to CSFB Evaluation Committee Members to provide insights into their reengineering experience Managing Director Business Management – Global Markets National Commercial Bank #1 UK, SENIOR MANAGING DIRECTOR § Project(s): Various Transformation Programs § Project Role: Person. . t served as the project sponsor and was a member of the project’s steering committee § Project(s): Deloitte & Touche is the independent auditor § Project Role: Person. . served as the senior business unit controller for Equities § Project(s): Reengineering Front To Back & Systems Implementation § Project Role: Person. . served as the BNP Paribas project sponsor and was a member of the project’s steering committee Managing Director FRANCE If you wish to speak to any of these references, please contact Adam Broun, +1 781 354 3231, abroun@deloitte. com who will be pleased to arrange a conversation 39

VII. Available Tools
Sample Tools – Process & Initiatives Prioritization Industry. Print Prior. ITTM § Is a collection of Industry specific, enterprise wide process models that incorporate best practices for key business and support functions § Industry. Print is used to: – Jump start projects by providing a starting point for as -is and to-be modelling – Integrate industry best practices, to inform process redesign and reveal performance improvement opportunities § Is a highly flexible tool that enables teams to define their own prioritization criteria and unique weightings to each project to profile their risk/value tradeoff and thereby facilitate sequencing § Applying the prioritization criteria to each project yields a user-friendly view of the Risk/Value relationship, rendering the low risk, “quick win” projects readily visible Information Space Maps Cause & Effect Analysis Comparison of information space maps demonstrates a reduction in the complexity of the information exchange by analyzing the key components of the process under review. § Information Space Map benefits include: • Reduction in information handoffs Fishbone analysis, used to force teams to focus beyond symptoms to root causes. Provides a structure to cause identification effort, and balanced list of ideas. Utilized once the problem is identified to determine the cause. • Reduction in organizations involved • Reduction in systems used Map. ITTM § Provides ability to view the impact project portfolios have on enterprise improvement levers 41
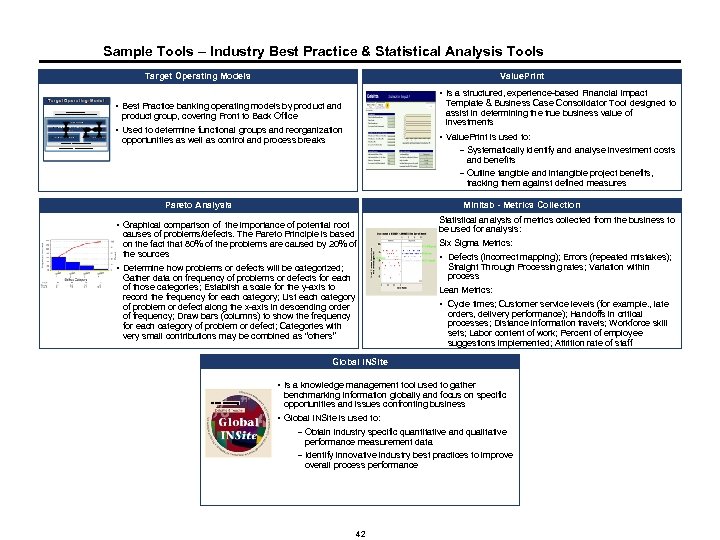
Sample Tools – Industry Best Practice & Statistical Analysis Tools Target Operating Models Value. Print § § Used to determine functional groups and reorganization opportunities as well as control and process breaks Is a structured, experience-based Financial Impact Template & Business Case Consolidator Tool designed to assist in determining the true business value of investments Value. Print is used to: – Systematically identify and analyse investment costs and benefits – Outline tangible and intangible project benefits, tracking them against defined measures Best Practice banking operating models by product and product group, covering Front to Back Office Pareto Analysis Minitab - Metrics Collection § Graphical comparison of the importance of potential root causes of problems/defects. The Pareto Principle is based on the fact that 80% of the problems are caused by 20% of the sources § Determine how problems or defects will be categorized; Gather data on frequency of problems or defects for each of those categories; Establish a scale for the y-axis to record the frequency for each category; List each category of problem or defect along the x-axis in descending order of frequency; Draw bars (columns) to show the frequency for each category of problem or defect; Categories with very small contributions may be combined as “others” Statistical analysis of metrics collected from the business to be used for analysis: Six Sigma Metrics: Defects (incorrect mapping); Errors (repeated mistakes); Straight Through Processing rates; Variation within process Lean Metrics: § § Cycle times; Customer service levels (for example. , late orders, delivery performance); Handoffs in critical processes; Distance information travels; Workforce skill sets; Labor content of work; Percent of employee suggestions implemented; Attrition rate of staff Global INSite § Is a knowledge management tool used to gather benchmarking information globally and focus on specific opportunities and issues confronting business § Global INSite is used to: – Obtain industry specific quantitative and qualitative performance measurement data – Identify innovative industry best practices to improve overall process performance Deloitte Consulting 42

VIII. Appendices A: Middle Office Work Driver Approach B: Middle Office Work Diver Sample Output
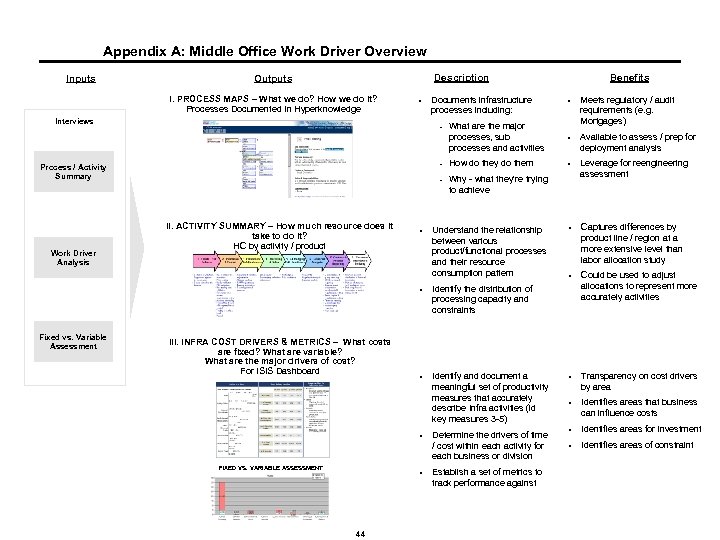
Appendix A: Middle Office Work Driver Overview Inputs Description Outputs I. PROCESS MAPS – What we do? How we do it? Processes Documented In Hyperknowledge Documents infrastructure processes including: § What are the major processes, sub processes and activities Meets regulatory / audit requirements (e. g. Mortgages) § Available to assess / prep for deployment analysis - How do they do them § - § Interviews Why - what they're trying to achieve Leverage for reengineering assessment § Captures differences by product line / region at a more extensive level than labor allocation study § Could be used to adjust allocations to represent more accurately activities § Transparency on cost drivers by area § Identifies areas that business can influence costs § Identifies areas for investment § Identifies areas of constraint - Process / Activity Summary II. ACTIVITY SUMMARY – How much resource does it take to do it? HC by activity / product Fixed vs. Variable Assessment III. INFRA COST DRIVERS & METRICS – What costs are fixed? What are variable? What are the major drivers of cost? For ISIS Dashboard § Understand the relationship between various product/functional processes and their resource consumption pattern § Work Driver Analysis Benefits Identify the distribution of processing capacity and constraints § Identify and document a meaningful set of productivity measures that accurately describe Infra activities (id key measures 3 -5) § FIXED VS. VARIABLE ASSESSMENT § 44 Determine the drivers of time / cost within each activity for each business or division Establish a set of metrics to track performance against
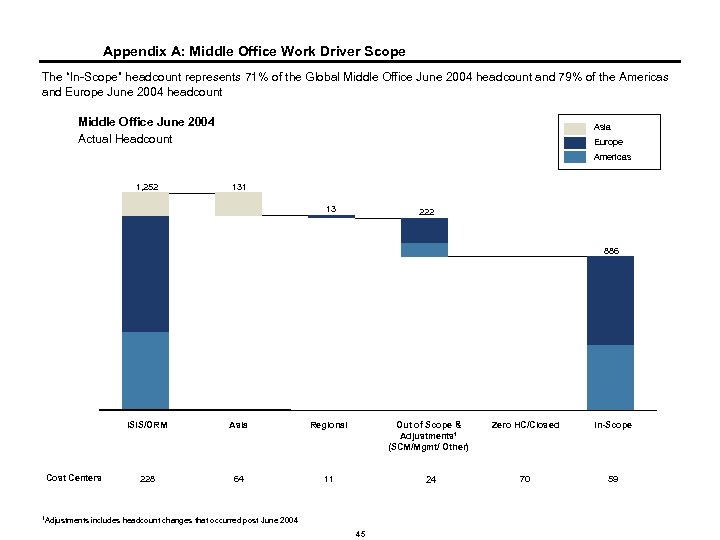
Appendix A: Middle Office Work Driver Scope The “In-Scope” headcount represents 71% of the Global Middle Office June 2004 headcount and 79% of the Americas and Europe June 2004 headcount Middle Office June 2004 Actual Headcount Asia Europe Americas 1, 252 131 131 13 222 145 77 886 665 509 456 377 ISIS/ORM Cost Centers Asia Regional Out of Scope & Adjustments 1 (SCM/Mgmt/ Other) Zero HC/Closed In-Scope 228 64 11 24 70 59 1 Adjustments includes headcount changes that occurred post June 2004 45
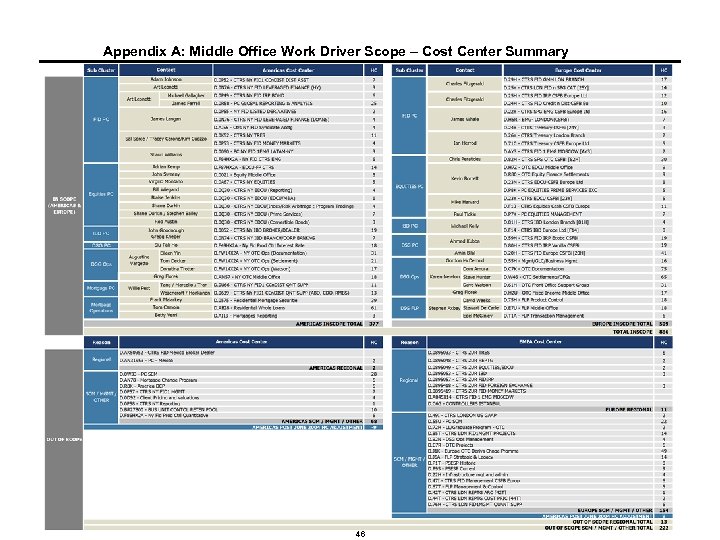
Appendix A: Middle Office Work Driver Scope – Cost Center Summary 46
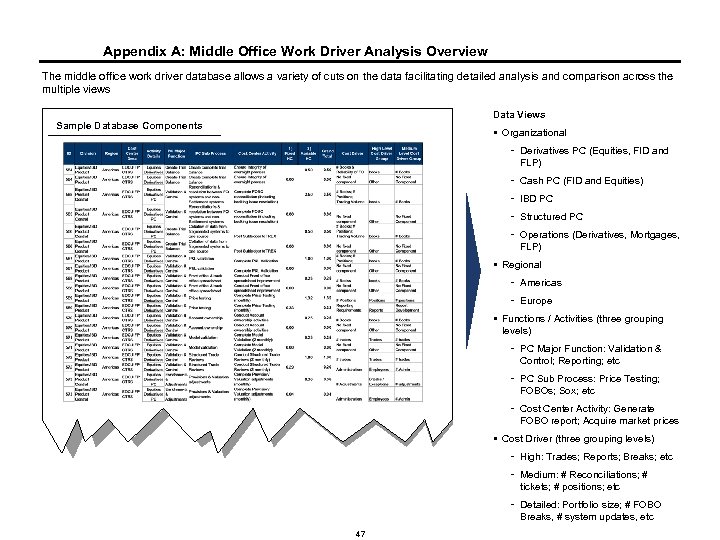
Appendix A: Middle Office Work Driver Analysis Overview The middle office work driver database allows a variety of cuts on the data facilitating detailed analysis and comparison across the multiple views Data Views Sample Database Components § Organizational - Derivatives PC (Equities, FID and FLP) - Cash PC (FID and Equities) - IBD PC - Structured PC - Operations (Derivatives, Mortgages, FLP) § Regional - Americas - Europe § Functions / Activities (three grouping levels) - PC Major Function: Validation & Control; Reporting; etc - PC Sub Process: Price Testing; FOBOs; Sox; etc - Cost Center Activity: Generate FOBO report; Acquire market prices § Cost Driver (three grouping levels) - High: Trades; Reports; Breaks; etc - Medium: # Reconciliations; # tickets; # positions; etc - Detailed: Portfolio size; # FOBO Breaks, # system updates, etc 47
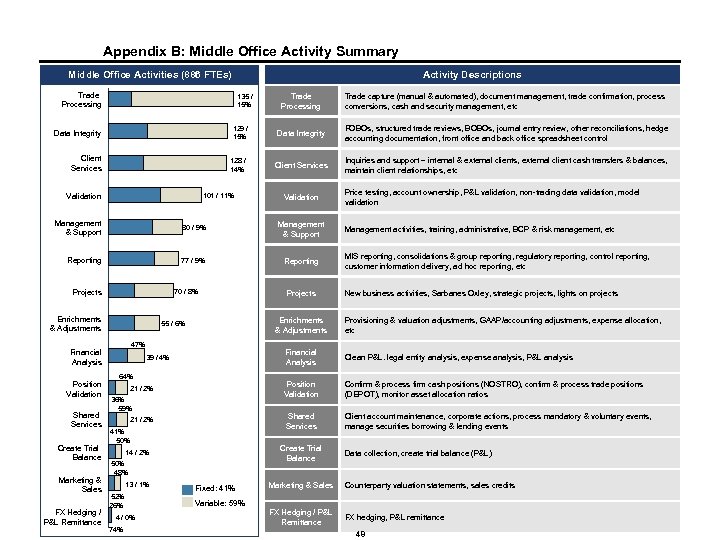
Appendix B: Middle Office Activity Summary Middle Office Activities (886 FTEs) Trade Processing Data Integrity Client Services 19% 55% Management & Support 59% 51% Financial Analysis Position Validation Shared Services Create Trial Balance Marketing & Sales FX Hedging / P&L Remittance 45% 41% 64% Enrichments & Adjustments 128 / 14% 70% Validation 39% 129 / 15% 68% 30% Projects 135 / 15% 81% 32% Reporting Activity Descriptions 36% 61% 49% 101 / 11% 70 / 8% Inquiries and support – internal & external clients, external client cash transfers & balances, maintain client relationships, etc Validation Projects Enrichments & Adjustments 55 / 6% Price testing, account ownership, P&L validation, non-trading data validation, model validation Management activities, training, administrative, BCP & risk management, etc MIS reporting, consolidations & group reporting, regulatory reporting, control reporting, customer information delivery, ad hoc reporting, etc New business activities, Sarbanes Oxley, strategic projects, lights on projects Provisioning & valuation adjustments, GAAP/accounting adjustments, expense allocation, etc Financial Analysis 41% 50% Confirm & process firm cash positions (NOSTRO), confirm & process trade positions (DEPOT), monitor asset allocation ratios Shared Services 21 / 2% Clean P&L. legal entity analysis, expense analysis, P&L analysis Position Validation 36% 59% Client account maintenance, corporate actions, process mandatory & voluntary events, manage securities borrowing & lending events Create Trial Balance 14 / 2% 50% 48% 74% Client Services Reporting 21 / 2% 4 / 0% FOBOs, structured trade reviews, BOBOs, journal entry review, other reconciliations, hedge accounting documentation, front office and back office spreadsheet control 77 / 9% 64% 13 / 1% Data Integrity Management & Support 39 / 4% 52% 26% Trade capture (manual & automated), document management, trade confirmation, process conversions, cash and security management, etc 80 / 9% 47% 53% Trade Processing Fixed: 41% Data collection, create trial balance (P&L) Marketing & Sales Counterparty valuation statements, sales credits FX Hedging / P&L Remittance FX hedging, P&L remittance Variable: 59% 48
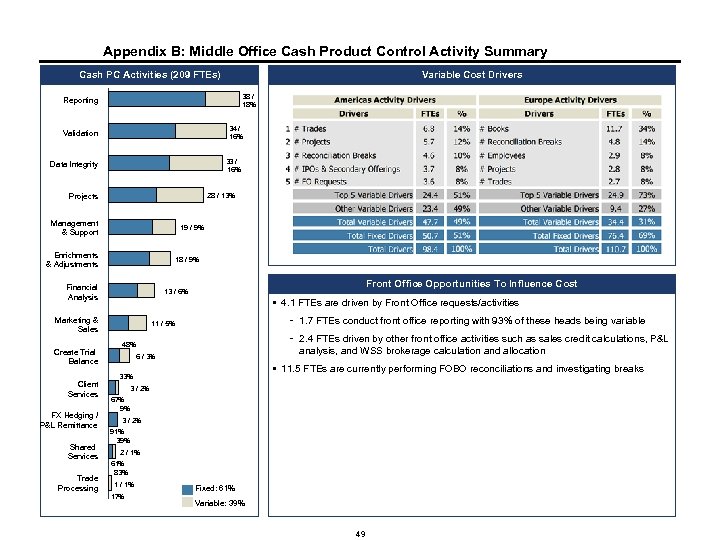
Appendix B: Middle Office Cash Product Control Activity Summary Cash PC Activities (209 FTEs) Reporting 74% Validation 26% 57% Data Integrity 53% Projects Management & Support 43% 47% 50% 65% Enrichments & Adjustments Financial Analysis Marketing & Sales Create Trial Balance Client Services FX Hedging / P&L Remittance Shared Services Trade Processing 50% 35% 67% 60% Variable Cost Drivers 38 / 18% 34 / 16% 33 / 16% 28 / 13% 19 / 9% 33% 18 / 9% 40% Front Office Opportunities To Influence Cost 13 / 6% § 4. 1 FTEs are driven by Front Office requests/activities - 1. 7 FTEs conduct front office reporting with 93% of these heads being variable 51% 49% 11 / 5% - 2. 4 FTEs driven by other front office activities such as sales credit calculations, P&L analysis, and WSS brokerage calculation and allocation 48% 52% 6 / 3% § 11. 5 FTEs are currently performing FOBO reconciliations and investigating breaks 33% 3 / 2% 67% 9% 3 / 2% 91% 39% 2 / 1% 61% 83% 1 / 1% 17% Fixed: 61% Variable: 39% 49
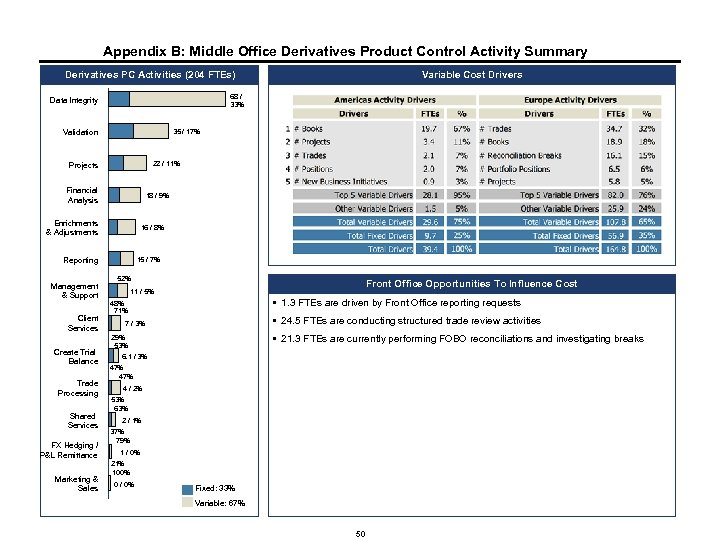
Appendix B: Middle Office Derivatives Product Control Activity Summary Derivatives PC Activities (204 FTEs) Data Integrity 18% Validation 41% Projects Financial Analysis Enrichments & Adjustments Reporting Management & Support Client Services Create Trial Balance Trade Processing Shared Services FX Hedging / P&L Remittance Marketing & Sales 68 / 33% 82% 59% 37% 63% Variable Cost Drivers 35 / 17% 22 / 11% 37% 63% 18 / 9% 33% 67% 16 / 8% 49% 51% 15 / 7% 52% Front Office Opportunities To Influence Cost 11 / 5% § 1. 3 FTEs are driven by Front Office reporting requests 48% 71% § 24. 5 FTEs are conducting structured trade review activities 7 / 3% § 21. 3 FTEs are currently performing FOBO reconciliations and investigating breaks 29% 53% 6. 1 / 3% 47% 4 / 2% 53% 63% 2 / 1% 37% 79% 1 / 0% 21% 100% 0 / 0% Fixed: 33% Variable: 67% 50
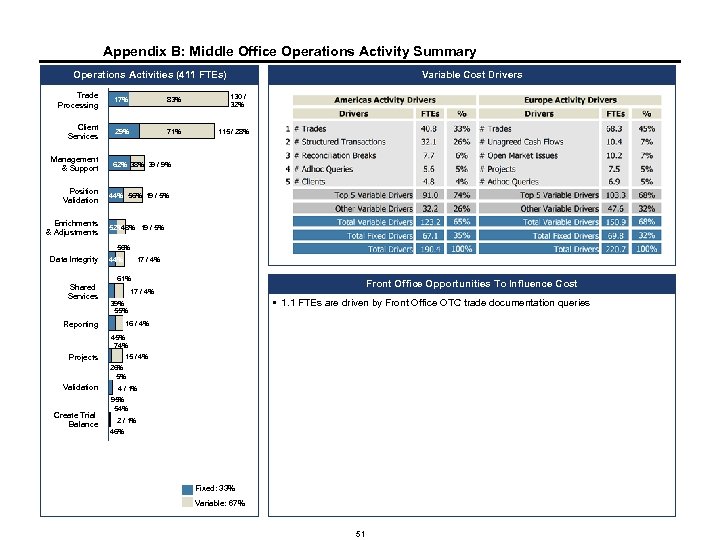
Appendix B: Middle Office Operations Activity Summary Operations Activities (411 FTEs) Trade Processing Client Services Variable Cost Drivers 17% 83% 130 / 32% 29% 71% 115 / 28% Management & Support 62% 38% 39 / 9% Position Validation 44% 56% 19 / 5% Enrichments & Adjustments 52% 48% 19 / 5% 56% Data Integrity Shared Services 44% 17 / 4% 61% Front Office Opportunities To Influence Cost 17 / 4% § 1. 1 FTEs are driven by Front Office OTC trade documentation queries 39% 55% Reporting 16 / 4% 45% 74% Projects 15 / 4% 26% 5% Validation Create Trial Balance 4 / 1% 95% 54% 2 / 1% 46% Fixed: 33% Variable: 67% 51

IX. Attachment 1: Supplier Assessment Questionnaire

IX. Attachment 2: CSFB Standard Agreement We are pleased to present our bid package for consideration. With regard to the contract terms and conditions proposed in the RFP, we are currently in the process of negotiating a Master Services Agreement ("MSA") with CSFB which terms and conditions will govern all of our services provided to CSFB. Our experience has indicated that almost without exception we have been able to reach agreement with each of our clients that has awarded us an engagement. In the vast majority of these cases, we have had some concerns over the proposed terms and conditions included in the request for proposal, however, in this case if we are awarded this engagement, we intend to negotiate in good faith with CSFB to reach an agreement on the MSA as expeditiously as possible. In this regard, we believe that the MSA as finally drafted and agreed will be appropriate for this engagement.
24f36856ae4a4a13711c789663e39462.ppt