848f6d6a59412bc4c3ca7cf469e1684d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
 CSCI 125 & 161 / ENGR 144 Lecture 2 Martin van Bommel
CSCI 125 & 161 / ENGR 144 Lecture 2 Martin van Bommel
 Hardware vs Software • Hardware - physical components you can see and touch – e. g. processor, keyboard, disk drive • Software - instructions for hardware – e. g. operating system, compiler, word processor
Hardware vs Software • Hardware - physical components you can see and touch – e. g. processor, keyboard, disk drive • Software - instructions for hardware – e. g. operating system, compiler, word processor
 Software Development • Early computers - complex coding schemes – machine language - 0’s and 1’s • Later on - introduction of system software – assembly language - mnemonics for operations – assembly program assembler machine lang • Even later - compilers created – high-level languages (HLL) - natural language – HLL program compiler machine language
Software Development • Early computers - complex coding schemes – machine language - 0’s and 1’s • Later on - introduction of system software – assembly language - mnemonics for operations – assembly program assembler machine lang • Even later - compilers created – high-level languages (HLL) - natural language – HLL program compiler machine language
 High Level Languages • • • 1957 - John Backus - FORTRAN 1958, 60, 64 - ALGOL, COBOL, BASIC 1970 - US Dept. of Defence - Ada 1971 - Nicklaus Wirth - Pascal 1972 - Dennis Ritchie - C 1977 - Nicklaus Wirth - Modula-2 1983 – Bjarne Stroustrup – C++ (C with class) 1989 - ANSI C adopted 1998 – ANSI C++ adopted
High Level Languages • • • 1957 - John Backus - FORTRAN 1958, 60, 64 - ALGOL, COBOL, BASIC 1970 - US Dept. of Defence - Ada 1971 - Nicklaus Wirth - Pascal 1972 - Dennis Ritchie - C 1977 - Nicklaus Wirth - Modula-2 1983 – Bjarne Stroustrup – C++ (C with class) 1989 - ANSI C adopted 1998 – ANSI C++ adopted
 Computer Components • CPU - Central Processing Unit – controls operation of entire systems – performs arithmetic and logic operations – stores and retrieves instructions and data contains • ALU - Arithmetic-Logic Unit • Control Unit
Computer Components • CPU - Central Processing Unit – controls operation of entire systems – performs arithmetic and logic operations – stores and retrieves instructions and data contains • ALU - Arithmetic-Logic Unit • Control Unit
 Components (con’t) • Main memory (internal or primary memory) – RAM - Random Access Memory – stores instructions and data temporarily • Secondary memory (external or auxiliary) – magnetic disk (hard disk or floppy), tape – CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, Flash drive, etc. • Peripherals - used for Input/Output – keyboard, printer, monitor, etc.
Components (con’t) • Main memory (internal or primary memory) – RAM - Random Access Memory – stores instructions and data temporarily • Secondary memory (external or auxiliary) – magnetic disk (hard disk or floppy), tape – CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, Flash drive, etc. • Peripherals - used for Input/Output – keyboard, printer, monitor, etc.
 Internal Representation • Each unit of memory a two-state device – off or on, 0 or 1 – represent in Binary, two Binary Digits (bits) • Organized into groups of 8 bits - bytes – represents single keyboard character • Larger grouping of 16 or 32 bits - word – represents single integer value – identified by address for access
Internal Representation • Each unit of memory a two-state device – off or on, 0 or 1 – represent in Binary, two Binary Digits (bits) • Organized into groups of 8 bits - bytes – represents single keyboard character • Larger grouping of 16 or 32 bits - word – represents single integer value – identified by address for access
 Memory Sizes • Kilobyte (K) = 210 = 1, 024 bytes • Megabyte (Mb) = 220 = 1, 048, 576 bytes • Gigabyte (Gb) = 230 = 1, 073, 741, 824 bytes
Memory Sizes • Kilobyte (K) = 210 = 1, 024 bytes • Megabyte (Mb) = 220 = 1, 048, 576 bytes • Gigabyte (Gb) = 230 = 1, 073, 741, 824 bytes
 SI Memory Sizes • System International – Convention • Kilobyte = 103 bytes = one thousand bytes • Megabyte = 106 bytes = one million bytes • Gigabyte = 109 bytes = one billion bytes • Kibibyte (K) = 210 = 1, 024 bytes • Mebibyte (Mb) = 220 = 1, 048, 576 bytes • Gibibyte (Gb) = 230 = 1, 073, 741, 824 bytes
SI Memory Sizes • System International – Convention • Kilobyte = 103 bytes = one thousand bytes • Megabyte = 106 bytes = one million bytes • Gigabyte = 109 bytes = one billion bytes • Kibibyte (K) = 210 = 1, 024 bytes • Mebibyte (Mb) = 220 = 1, 048, 576 bytes • Gibibyte (Gb) = 230 = 1, 073, 741, 824 bytes
 Decimal Number Systems • Base 10 • Digits - 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 • e. g. 34210 = = 3 x 102 + 4 x 101 + 2 x 100 = 3 x 100 + 4 x 10 + 2 x 1 = 300 + 40 +2
Decimal Number Systems • Base 10 • Digits - 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 • e. g. 34210 = = 3 x 102 + 4 x 101 + 2 x 100 = 3 x 100 + 4 x 10 + 2 x 1 = 300 + 40 +2
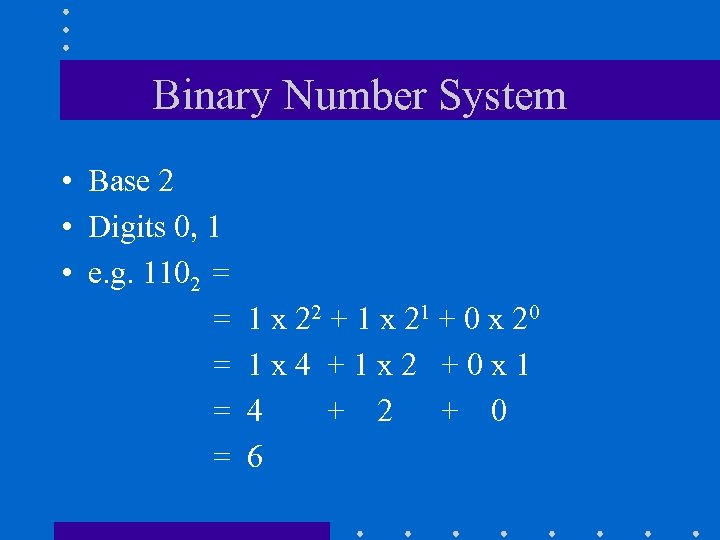 Binary Number System • Base 2 • Digits 0, 1 • e. g. 1102 = = = 1 x 22 + 1 x 21 + 0 x 20 1 x 4 +1 x 2 +0 x 1 4 + 2 + 0 6
Binary Number System • Base 2 • Digits 0, 1 • e. g. 1102 = = = 1 x 22 + 1 x 21 + 0 x 20 1 x 4 +1 x 2 +0 x 1 4 + 2 + 0 6
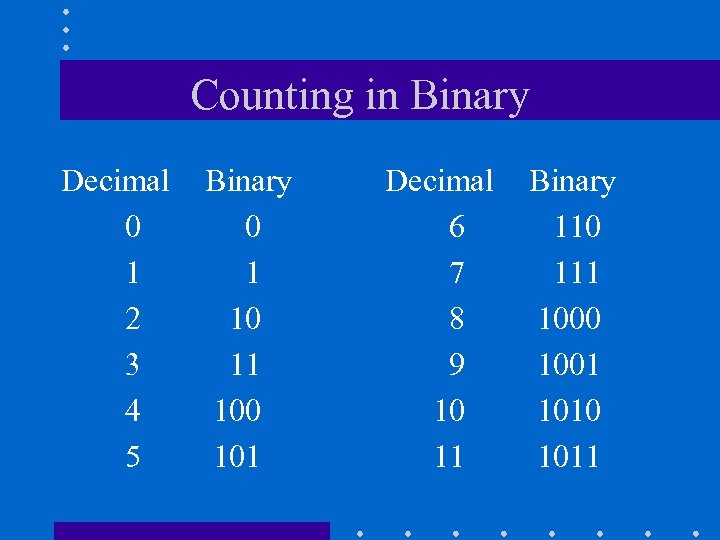 Counting in Binary Decimal 0 1 2 3 4 5 Binary 0 1 10 11 100 101 Decimal 6 7 8 9 10 11 Binary 110 111 1000 1001 1010 1011
Counting in Binary Decimal 0 1 2 3 4 5 Binary 0 1 10 11 100 101 Decimal 6 7 8 9 10 11 Binary 110 111 1000 1001 1010 1011
 Character Representation • • 1 byte = 8 bits = 1 character? 256 possible codes with 8 bits Assign a character to each code Common assignment – ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange – defines first 128
Character Representation • • 1 byte = 8 bits = 1 character? 256 possible codes with 8 bits Assign a character to each code Common assignment – ASCII - American Standard Code for Information Interchange – defines first 128
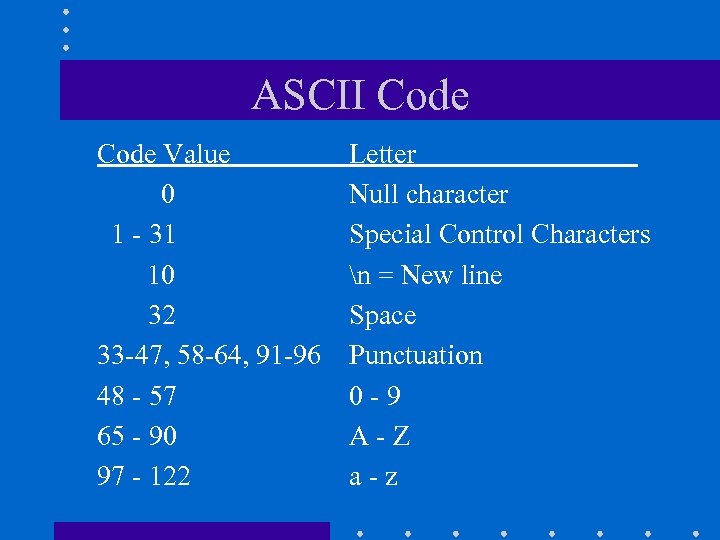 ASCII Code Value 0 1 - 31 10 32 33 -47, 58 -64, 91 -96 48 - 57 65 - 90 97 - 122 Letter Null character Special Control Characters n = New line Space Punctuation 0 -9 A-Z a-z
ASCII Code Value 0 1 - 31 10 32 33 -47, 58 -64, 91 -96 48 - 57 65 - 90 97 - 122 Letter Null character Special Control Characters n = New line Space Punctuation 0 -9 A-Z a-z
 Interesting ASCII Choice? • Digits 0 through 9 seem strange? Digit Dec Hex 0 48 30 1 49 31 … … … 9 57 39
Interesting ASCII Choice? • Digits 0 through 9 seem strange? Digit Dec Hex 0 48 30 1 49 31 … … … 9 57 39
 Unicode • International language coding standard • Superset of ASCII • Various codes defined to use upper 128 bits for symbols and other languages
Unicode • International language coding standard • Superset of ASCII • Various codes defined to use upper 128 bits for symbols and other languages
 16 bits? • • • Two characters? One integer? Part of a floating point? Machine language instruction? Memory address? • Depends on application!
16 bits? • • • Two characters? One integer? Part of a floating point? Machine language instruction? Memory address? • Depends on application!


