a385830fb7c6734e9f258f253b65ff8e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina
CSCE 515: Computer Network Programming Wenyuan Xu Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of South Carolina
 Course Goal: n Understand the basic principles of computer networks Network basic ¨ Basic design principles in network protocols ¨ Internet protocols ¨ Wireless network protocols ¨ n Study the programming aspects of computer networks Socket programming ¨ Inter-process communication ¨ n Understand how network research is done How to determine what is important ¨ What are the trend ¨ CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Course Goal: n Understand the basic principles of computer networks Network basic ¨ Basic design principles in network protocols ¨ Internet protocols ¨ Wireless network protocols ¨ n Study the programming aspects of computer networks Socket programming ¨ Inter-process communication ¨ n Understand how network research is done How to determine what is important ¨ What are the trend ¨ CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Administrative n Course website: ¨ http: //www. cse. sc. edu/~wyxu/515 Fall 08/csce 515. html n Announcements n Homework Assignments n Lecture Notes n Links to required/recommended readings n How to reach me: ¨ Email: wyxu@cse. sc. edu ¨ Office Hours: MW 4: 00 pm-5: 00 pm or by appointment ¨ Office: SWGN 3 A 54 n Prerequisites: CSCE 311 Operating Systems CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Administrative n Course website: ¨ http: //www. cse. sc. edu/~wyxu/515 Fall 08/csce 515. html n Announcements n Homework Assignments n Lecture Notes n Links to required/recommended readings n How to reach me: ¨ Email: wyxu@cse. sc. edu ¨ Office Hours: MW 4: 00 pm-5: 00 pm or by appointment ¨ Office: SWGN 3 A 54 n Prerequisites: CSCE 311 Operating Systems CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Textbook n Required: ¨ n Unix Network Programming, The Sockets Networking API, Volumes 1, by W Richard Stevens, Bill Fenner, Andrew M. Rudoff, published by Addison-Wesley (UNP) Optional: ¨ ¨ n TCP/IP Illustrated Volumes 1, by W. Richard Stevens, published by Addison-Wesley, 1994 (TI). Java Network Programming, by Merlin Hughes, Michael Shoffner, Derek Hamner, Maria Winslow, Conrad Hughes, published Manning Publications Mailing list: ¨ CSCE 515 -001@lists. cse. sc. edu CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Textbook n Required: ¨ n Unix Network Programming, The Sockets Networking API, Volumes 1, by W Richard Stevens, Bill Fenner, Andrew M. Rudoff, published by Addison-Wesley (UNP) Optional: ¨ ¨ n TCP/IP Illustrated Volumes 1, by W. Richard Stevens, published by Addison-Wesley, 1994 (TI). Java Network Programming, by Merlin Hughes, Michael Shoffner, Derek Hamner, Maria Winslow, Conrad Hughes, published Manning Publications Mailing list: ¨ CSCE 515 -001@lists. cse. sc. edu CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Tentative topics OSI and TCP/IP Network models n TCP/IP n Socket programming n The Internet and Internet protocol n Web programming n Other network programming n CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Tentative topics OSI and TCP/IP Network models n TCP/IP n Socket programming n The Internet and Internet protocol n Web programming n Other network programming n CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Grading n 0% Homework (1 -2) ¨ Q&A n 50% Computer Projects (4 – three in C, one in Java) n 20% Midterm n 30% Final: closed book, and comprehensive. n Grading scale: n n n n A : 90 — 100 B+ : 87 — 89 B : 80 — 86 C+ : 77 — 79 C : 70 — 76 D : 60 — 69 F <= 59 CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Grading n 0% Homework (1 -2) ¨ Q&A n 50% Computer Projects (4 – three in C, one in Java) n 20% Midterm n 30% Final: closed book, and comprehensive. n Grading scale: n n n n A : 90 — 100 B+ : 87 — 89 B : 80 — 86 C+ : 77 — 79 C : 70 — 76 D : 60 — 69 F <= 59 CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Homework & projects n Programming Environments ¨ Unix workstation lab. : n n n n 1 D 39 (Sun + Linux) 1 D 45 (Linux) All students should have an account on Computer Science and Engineering Department Unix workstations All grading will be done on CSE Linux! Submission should be via Drop Box Make sure you understand how to submit (practice first)! Directions for submission will be posted on the course home page with the first assignment. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Homework & projects n Programming Environments ¨ Unix workstation lab. : n n n n 1 D 39 (Sun + Linux) 1 D 45 (Linux) All students should have an account on Computer Science and Engineering Department Unix workstations All grading will be done on CSE Linux! Submission should be via Drop Box Make sure you understand how to submit (practice first)! Directions for submission will be posted on the course home page with the first assignment. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Project grading n n It is expected that everyone is a good programmer Comment your code! Your code should be readable, structured! 25% of the grade depends on the quality of the code. ¨ ¨ ¨ Is the code easy to understand? Is it easy to make a small change of the functionality? Can code handle unexpected input, exceptions? n Programs must come with a makefile n Java programs must come with a shell script that starts them: ¨ ¨ Sets CLASSPATH to the right value Remember that I will try your programs in a directory with a different name than you! CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Project grading n n It is expected that everyone is a good programmer Comment your code! Your code should be readable, structured! 25% of the grade depends on the quality of the code. ¨ ¨ ¨ Is the code easy to understand? Is it easy to make a small change of the functionality? Can code handle unexpected input, exceptions? n Programs must come with a makefile n Java programs must come with a shell script that starts them: ¨ ¨ Sets CLASSPATH to the right value Remember that I will try your programs in a directory with a different name than you! CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Project grading n n 25% of the grade depends on documentation Documentations must contain: Your name and student number ¨ How to use your programs ¨ Which program does what, which parameters are needed, screenshots ¨ A description of your program’s design ¨ n Documentations must not contain: Your code in words ¨ “After spending the whole weekend and today at my girlfriend’s house trying to solve the exercises for the Network Programming course which are due today, I must confess that I did not succeed in solving them all”. ¨ CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Project grading n n 25% of the grade depends on documentation Documentations must contain: Your name and student number ¨ How to use your programs ¨ Which program does what, which parameters are needed, screenshots ¨ A description of your program’s design ¨ n Documentations must not contain: Your code in words ¨ “After spending the whole weekend and today at my girlfriend’s house trying to solve the exercises for the Network Programming course which are due today, I must confess that I did not succeed in solving them all”. ¨ CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Grading n Horner code: ¨ All submitted work should be yours! ¨ NO sharing of code ¨ Do not copy code from Internet ¨ Discussion is encouraged CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Grading n Horner code: ¨ All submitted work should be yours! ¨ NO sharing of code ¨ Do not copy code from Internet ¨ Discussion is encouraged CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Email Policies n Make sure you put your course (CSCE 515) in the subject of the message. n Remember that it is not my emergency if you need help at the last minute. I may check my messages in time to help you make a deadline, but this may not necessarily be the case. n Ask specific question instead of general question. ¨ ¨ n Bad example: “I don’t know why it does not work? ” In general, I will answer quick questions sooner than one that will take a long time to answer In general I will monitor and respond to email during office hours, but in-person students will take precedence. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Email Policies n Make sure you put your course (CSCE 515) in the subject of the message. n Remember that it is not my emergency if you need help at the last minute. I may check my messages in time to help you make a deadline, but this may not necessarily be the case. n Ask specific question instead of general question. ¨ ¨ n Bad example: “I don’t know why it does not work? ” In general, I will answer quick questions sooner than one that will take a long time to answer In general I will monitor and respond to email during office hours, but in-person students will take precedence. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Your Best Strategy n Come to every lecture n Read articles related to network protocols and network programming n Do not wait till last minute to prepare for exam or work on project n Enjoy the fun! CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Your Best Strategy n Come to every lecture n Read articles related to network protocols and network programming n Do not wait till last minute to prepare for exam or work on project n Enjoy the fun! CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Lectures need your help! n Ask questions n Correct Wenyuan! *Extra credit! n Make suggestions! n Read something interesting and relevant to this course? Announce it in class! CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Lectures need your help! n Ask questions n Correct Wenyuan! *Extra credit! n Make suggestions! n Read something interesting and relevant to this course? Announce it in class! CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Introduction
Introduction
 What is network? n n The term network can refer to any interconnected group or system. A computer network is composed of multiple computers connected together using a telecommunication system. n “…communication system for connecting end-systems” n End-systems a. k. a. “hosts” ¨ ¨ ¨ n Interconnection may be any medium capable of communicating information: ¨ ¨ n PCs, workstations dedicated computers network components Copper wire Lasers (optical fiber) Radio /Satellite link Cable (coax) Example: Ethernet. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
What is network? n n The term network can refer to any interconnected group or system. A computer network is composed of multiple computers connected together using a telecommunication system. n “…communication system for connecting end-systems” n End-systems a. k. a. “hosts” ¨ ¨ ¨ n Interconnection may be any medium capable of communicating information: ¨ ¨ n PCs, workstations dedicated computers network components Copper wire Lasers (optical fiber) Radio /Satellite link Cable (coax) Example: Ethernet. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Why network? n Sharing resources ¨ n Resources become available regardless of the user’s physical location (server based, peer 2 peer) Load Sharing/utilization Jobs processed on least crowed machine ¨ Resource can be shared ¨ n High reliability ¨ n Alternative source of supply (multiple copies) Computer as a communication tools CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Why network? n Sharing resources ¨ n Resources become available regardless of the user’s physical location (server based, peer 2 peer) Load Sharing/utilization Jobs processed on least crowed machine ¨ Resource can be shared ¨ n High reliability ¨ n Alternative source of supply (multiple copies) Computer as a communication tools CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Wide variety of types of networks n Circuit switched ¨ dedicated circuit per call ¨ performance (guaranteed) ¨ call setup required ¨ telephone system n Packet switched: ¨ data sent thru net in discrete “chunks” ¨ user A, B packets share network resources ¨ resources used as needed ¨ store and forward: packets move one hop at a time ¨ The Internet (TCP/IP) CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Wide variety of types of networks n Circuit switched ¨ dedicated circuit per call ¨ performance (guaranteed) ¨ call setup required ¨ telephone system n Packet switched: ¨ data sent thru net in discrete “chunks” ¨ user A, B packets share network resources ¨ resources used as needed ¨ store and forward: packets move one hop at a time ¨ The Internet (TCP/IP) CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
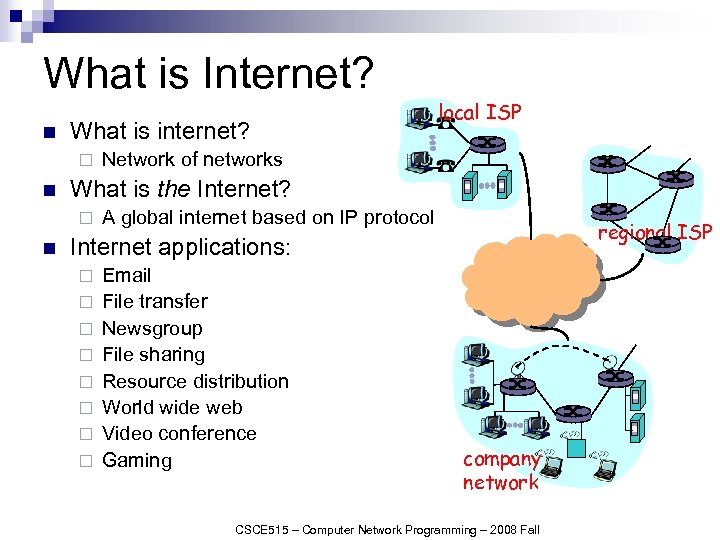 What is Internet? n What is internet? ¨ n Network of networks What is the Internet? ¨ n local ISP A global internet based on IP protocol regional ISP Internet applications: ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ Email File transfer Newsgroup File sharing Resource distribution World wide web Video conference Gaming company network CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
What is Internet? n What is internet? ¨ n Network of networks What is the Internet? ¨ n local ISP A global internet based on IP protocol regional ISP Internet applications: ¨ ¨ ¨ ¨ Email File transfer Newsgroup File sharing Resource distribution World wide web Video conference Gaming company network CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Emerging networks n Embedded networks n Every physical object is connected ¨ ¨ n n Open/close your garage via network Know which milk can is about to expire Sensor networks Physical space is instrumented and connected Detect presence of people in a room and set temperature accordingly ¨ Know exactly how many cars on Route 26 ¨ n n Disposable networks One time use network ¨ Disaster recovery, smart dust CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Emerging networks n Embedded networks n Every physical object is connected ¨ ¨ n n Open/close your garage via network Know which milk can is about to expire Sensor networks Physical space is instrumented and connected Detect presence of people in a room and set temperature accordingly ¨ Know exactly how many cars on Route 26 ¨ n n Disposable networks One time use network ¨ Disaster recovery, smart dust CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Characteristics Lots of them (density) n Cheap unreliable elements n Run on batteries n Location becomes a key attribute n Information sensing around users n CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Characteristics Lots of them (density) n Cheap unreliable elements n Run on batteries n Location becomes a key attribute n Information sensing around users n CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Some terms LAN n WAN n MAN n CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Some terms LAN n WAN n MAN n CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 LAN - Local Area Network n connects computers that are physically close together ( < 1 mile). ¨ high speed ¨ multi-access n Technologies: ¨ Ethernet 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps ¨ Token Ring 16 Mbps ¨ FDDI 100 Mbps CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
LAN - Local Area Network n connects computers that are physically close together ( < 1 mile). ¨ high speed ¨ multi-access n Technologies: ¨ Ethernet 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps ¨ Token Ring 16 Mbps ¨ FDDI 100 Mbps CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 WAN - Wide Area Network n connects computers that are physically far apart. “long-haul network”. ¨ typically slower than a LAN. ¨ typically less reliable than a LAN. ¨ point-to-point n Technologies: ¨ telephone lines ¨ Satellite communications CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
WAN - Wide Area Network n connects computers that are physically far apart. “long-haul network”. ¨ typically slower than a LAN. ¨ typically less reliable than a LAN. ¨ point-to-point n Technologies: ¨ telephone lines ¨ Satellite communications CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 MAN - Metropolitan Area Network n Larger than a LAN and smaller than a WAN - example: campus-wide network - multi-access network n Technologies: ¨ coaxial cable ¨ microwave CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
MAN - Metropolitan Area Network n Larger than a LAN and smaller than a WAN - example: campus-wide network - multi-access network n Technologies: ¨ coaxial cable ¨ microwave CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Network Protocols
Network Protocols
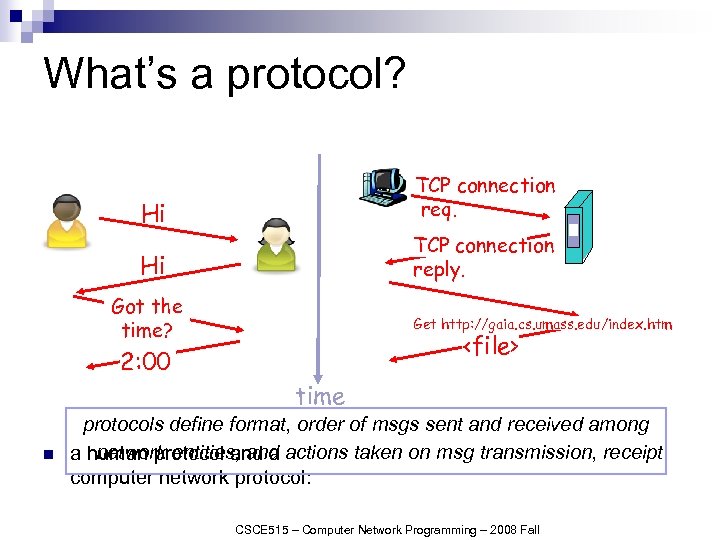 What’s a protocol? Hi TCP connection req. Hi TCP connection reply. Got the time? Get http: //gaia. cs. umass. edu/index. htm
What’s a protocol? Hi TCP connection req. Hi TCP connection reply. Got the time? Get http: //gaia. cs. umass. edu/index. htm
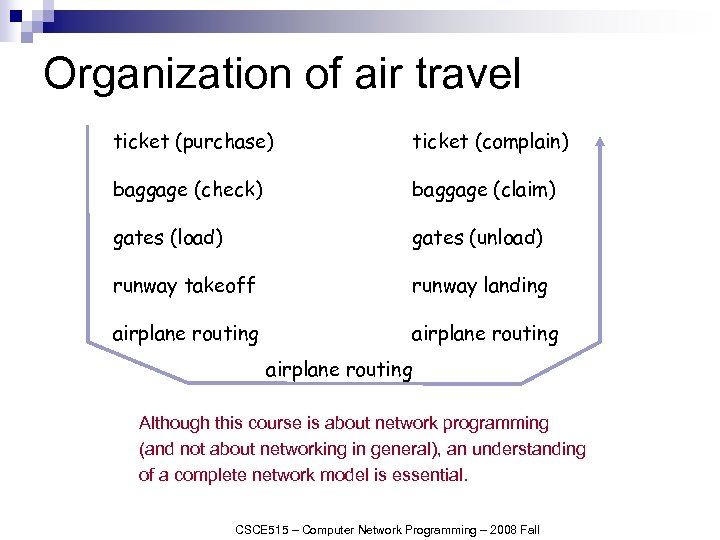 Organization of air travel ticket (purchase) ticket (complain) baggage (check) baggage (claim) gates (load) gates (unload) runway takeoff runway landing airplane routing Although this course is about network programming (and not about networking in general), an understanding of a complete network model is essential. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Organization of air travel ticket (purchase) ticket (complain) baggage (check) baggage (claim) gates (load) gates (unload) runway takeoff runway landing airplane routing Although this course is about network programming (and not about networking in general), an understanding of a complete network model is essential. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
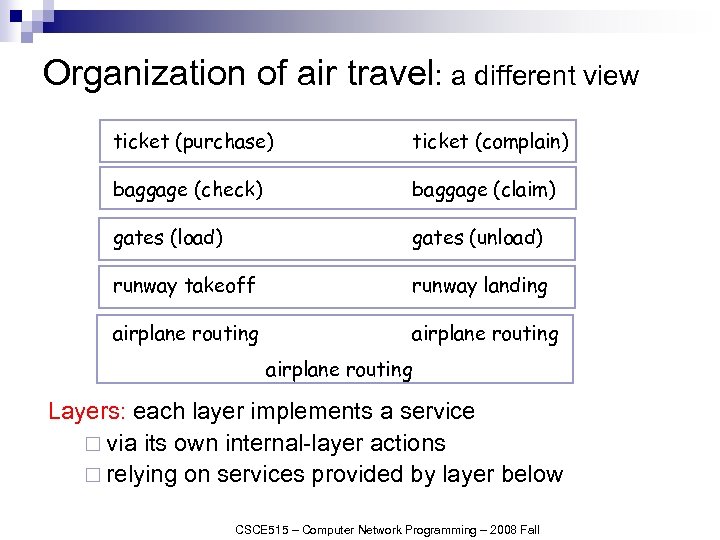 Organization of air travel: a different view ticket (purchase) ticket (complain) baggage (check) baggage (claim) gates (load) gates (unload) runway takeoff runway landing airplane routing Layers: each layer implements a service ¨ via its own internal-layer actions ¨ relying on services provided by layer below CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Organization of air travel: a different view ticket (purchase) ticket (complain) baggage (check) baggage (claim) gates (load) gates (unload) runway takeoff runway landing airplane routing Layers: each layer implements a service ¨ via its own internal-layer actions ¨ relying on services provided by layer below CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
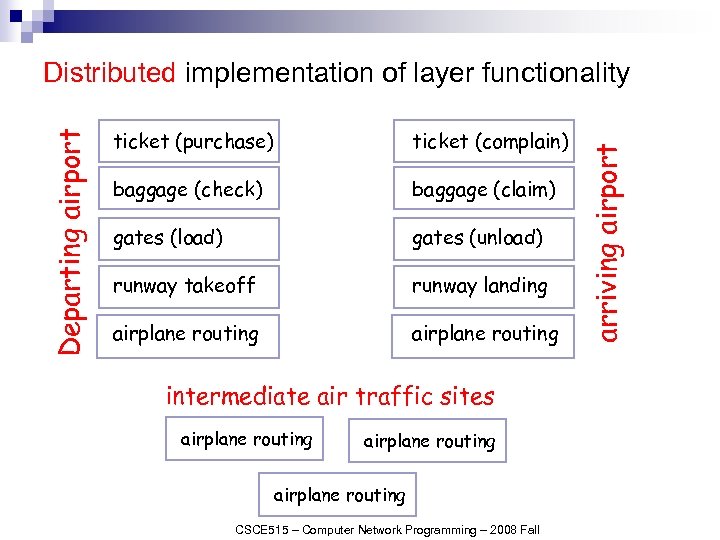 ticket (purchase) ticket (complain) baggage (check) baggage (claim) gates (load) gates (unload) runway takeoff runway landing airplane routing intermediate air traffic sites airplane routing CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall arriving airport Departing airport Distributed implementation of layer functionality
ticket (purchase) ticket (complain) baggage (check) baggage (claim) gates (load) gates (unload) runway takeoff runway landing airplane routing intermediate air traffic sites airplane routing CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall arriving airport Departing airport Distributed implementation of layer functionality
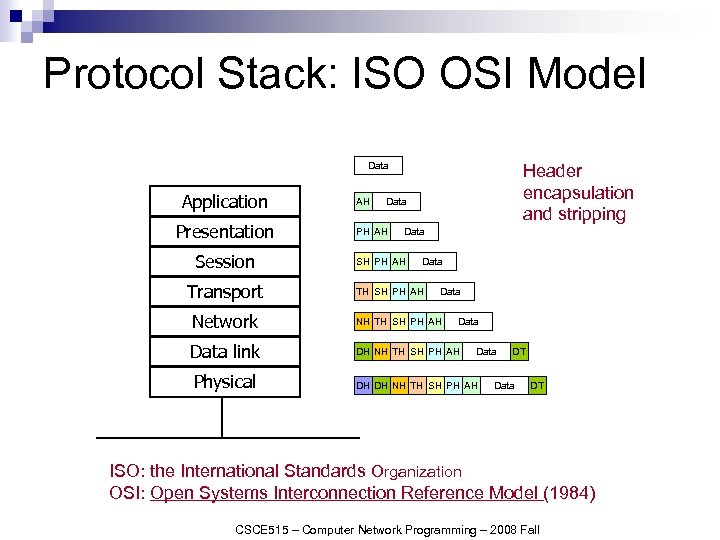 Protocol Stack: ISO OSI Model Data Application Presentation Session Transport AH Header encapsulation and stripping Data PH AH Data SH PH AH Data TH SH PH AH Data Network NH TH SH PH AH Data link DH NH TH SH PH AH Physical Data DH DH NH TH SH PH AH DT Data DT ISO: the International Standards Organization OSI: Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model (1984) CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Protocol Stack: ISO OSI Model Data Application Presentation Session Transport AH Header encapsulation and stripping Data PH AH Data SH PH AH Data TH SH PH AH Data Network NH TH SH PH AH Data link DH NH TH SH PH AH Physical Data DH DH NH TH SH PH AH DT Data DT ISO: the International Standards Organization OSI: Open Systems Interconnection Reference Model (1984) CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
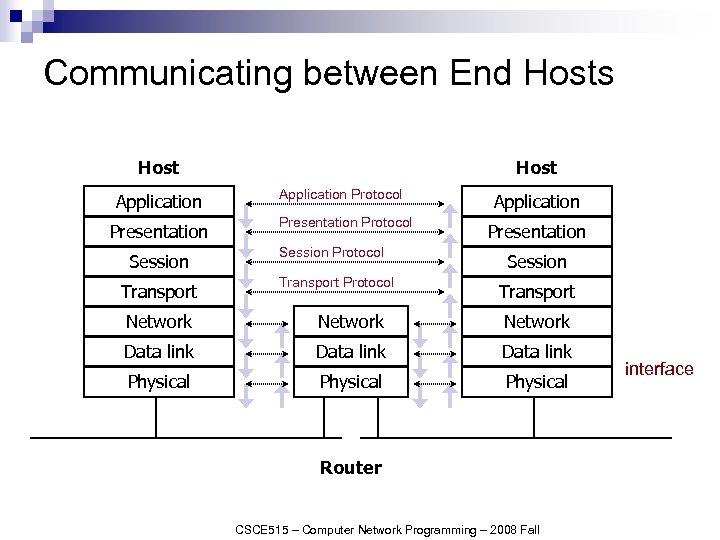 Communicating between End Hosts Host Application Presentation Session Transport Host Application Protocol Presentation Protocol Session Protocol Transport Protocol Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data link Physical Router CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall interface
Communicating between End Hosts Host Application Presentation Session Transport Host Application Protocol Presentation Protocol Session Protocol Transport Protocol Application Presentation Session Transport Network Data link Physical Router CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall interface
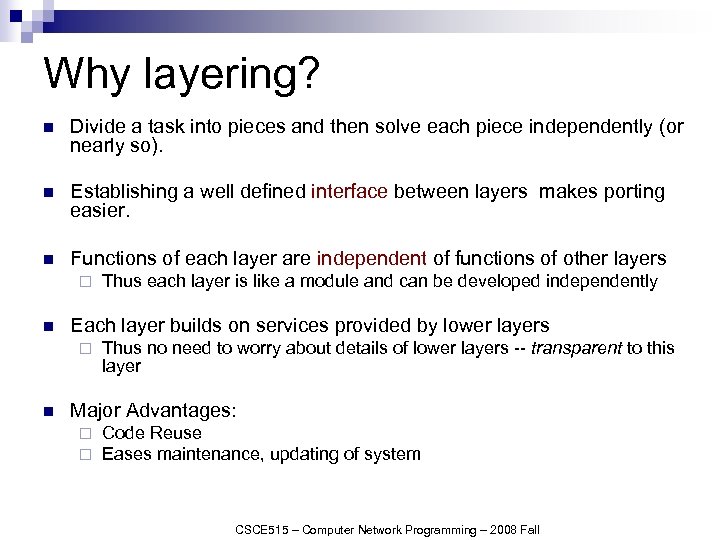 Why layering? n Divide a task into pieces and then solve each piece independently (or nearly so). n Establishing a well defined interface between layers makes porting easier. n Functions of each layer are independent of functions of other layers ¨ n Each layer builds on services provided by lower layers ¨ n Thus each layer is like a module and can be developed independently Thus no need to worry about details of lower layers -- transparent to this layer Major Advantages: ¨ ¨ Code Reuse Eases maintenance, updating of system CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Why layering? n Divide a task into pieces and then solve each piece independently (or nearly so). n Establishing a well defined interface between layers makes porting easier. n Functions of each layer are independent of functions of other layers ¨ n Each layer builds on services provided by lower layers ¨ n Thus each layer is like a module and can be developed independently Thus no need to worry about details of lower layers -- transparent to this layer Major Advantages: ¨ ¨ Code Reuse Eases maintenance, updating of system CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Programs & Processes n A program is an executable file. n A process or task is an instance of a program that is being executed. n A single program can generate multiple processes. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Programs & Processes n A program is an executable file. n A process or task is an instance of a program that is being executed. n A single program can generate multiple processes. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Client - Server n A server is a process - not a machine ! n A server waits for a request from a client. n A client is a process that sends a request to an existing server and (usually) waits for a reply. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Client - Server n A server is a process - not a machine ! n A server waits for a request from a client. n A client is a process that sends a request to an existing server and (usually) waits for a reply. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Client - Server Examples n Server returns the time-of-day. n Server returns a document. n Server prints a file for client. n Server does a disk read or write. n Server records a transaction. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Client - Server Examples n Server returns the time-of-day. n Server returns a document. n Server prints a file for client. n Server does a disk read or write. n Server records a transaction. CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Sample questions: n Difference? ¨ Subnet, a network, WAN ¨ Protocols vs. interface CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Sample questions: n Difference? ¨ Subnet, a network, WAN ¨ Protocols vs. interface CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
 Assignment & Next time n Reading: ¨ How NOT to go about a programming assignment ¨ TI Ch. 1 n Next Lecture: ¨ OSI model ¨ Data link layer CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall
Assignment & Next time n Reading: ¨ How NOT to go about a programming assignment ¨ TI Ch. 1 n Next Lecture: ¨ OSI model ¨ Data link layer CSCE 515 – Computer Network Programming – 2008 Fall


