e5ff56ce2caec4549206651487a7383a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 15
 CSCC 40 Analysis and Design of Information Systems These lecture slides are provided for the personal use of students taking CSCC 40 in the Fall term of 2007 at the University of Toronto. Copying for purposes other than this use, and all forms of distribution are expressly prohibited. Some slides are adapted from the course textbook: Object-Oriented Systems Analysis and Design Using UML. 3 rd ed. Bennett, Mc. Robb, Farmer. Mc. Graw-Hill. 2002. The following sources of information are also recommended • Project Management Institute • Association of Computing Machinery • IEEE Computer Society University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 1
CSCC 40 Analysis and Design of Information Systems These lecture slides are provided for the personal use of students taking CSCC 40 in the Fall term of 2007 at the University of Toronto. Copying for purposes other than this use, and all forms of distribution are expressly prohibited. Some slides are adapted from the course textbook: Object-Oriented Systems Analysis and Design Using UML. 3 rd ed. Bennett, Mc. Robb, Farmer. Mc. Graw-Hill. 2002. The following sources of information are also recommended • Project Management Institute • Association of Computing Machinery • IEEE Computer Society University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 1
 ACM computing curricula 2001 software engineering processes requirements and specifications design validation delivery of systems evolution project management tools and environments component-based computing formal methods these topics are covered in reliability CSCC 40 and CSCD 08 University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 2
ACM computing curricula 2001 software engineering processes requirements and specifications design validation delivery of systems evolution project management tools and environments component-based computing formal methods these topics are covered in reliability CSCC 40 and CSCD 08 University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 2
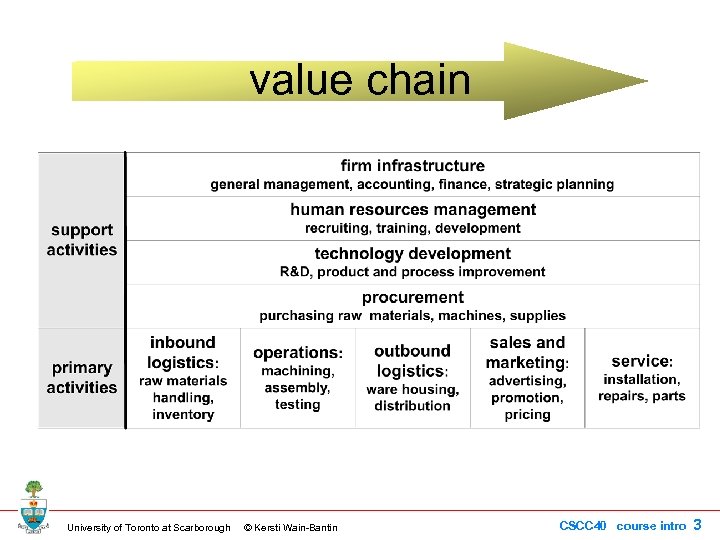 value chain University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 3
value chain University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 3
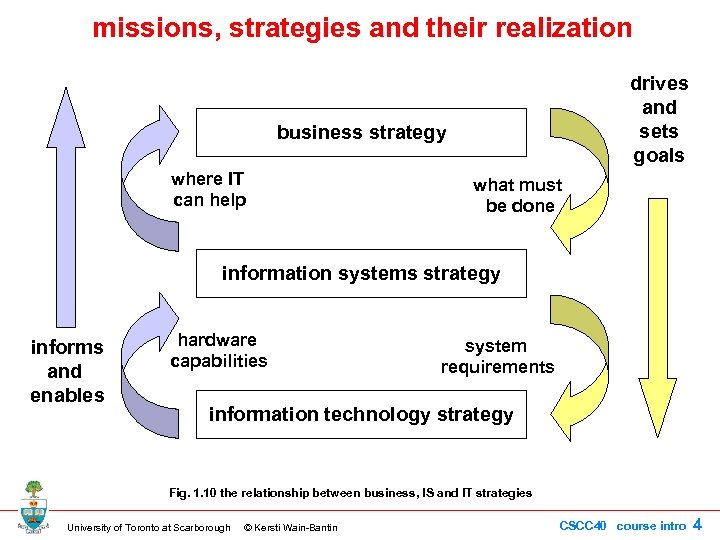 missions, strategies and their realization drives and sets goals business strategy where IT can help what must be done information systems strategy informs and enables hardware capabilities system requirements information technology strategy Fig. 1. 10 the relationship between business, IS and IT strategies University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 4
missions, strategies and their realization drives and sets goals business strategy where IT can help what must be done information systems strategy informs and enables hardware capabilities system requirements information technology strategy Fig. 1. 10 the relationship between business, IS and IT strategies University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 4
 all systems (manual and/or automated) have these characteristics system boundary inputs what the system does control feed-forward outputs feedback how the system is controlled University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 5
all systems (manual and/or automated) have these characteristics system boundary inputs what the system does control feed-forward outputs feedback how the system is controlled University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 5
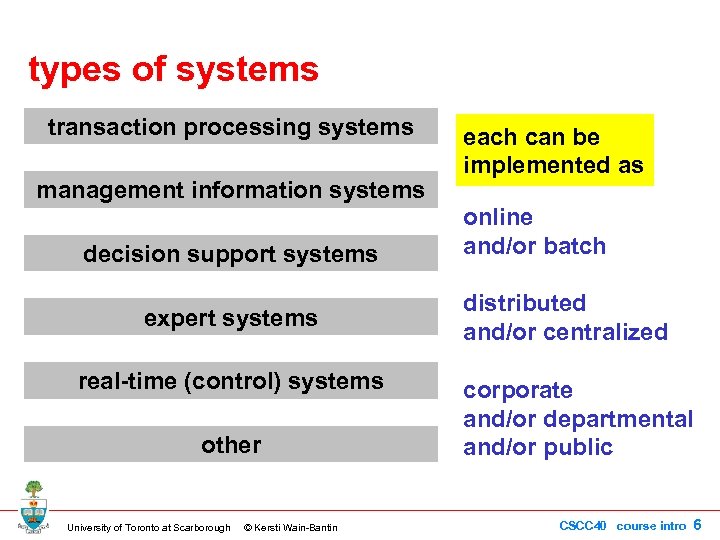 types of systems transaction processing systems management information systems decision support systems expert systems real-time (control) systems other University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin each can be implemented as online and/or batch distributed and/or centralized corporate and/or departmental and/or public CSCC 40 course intro 6
types of systems transaction processing systems management information systems decision support systems expert systems real-time (control) systems other University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin each can be implemented as online and/or batch distributed and/or centralized corporate and/or departmental and/or public CSCC 40 course intro 6
 the three perspectives technological hardware, networks, databases, CASE tools. . . social how do individuals and organizations use information, how are they affected by technology… professional practices and standards, policies, quality practices. . . University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 7
the three perspectives technological hardware, networks, databases, CASE tools. . . social how do individuals and organizations use information, how are they affected by technology… professional practices and standards, policies, quality practices. . . University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 7
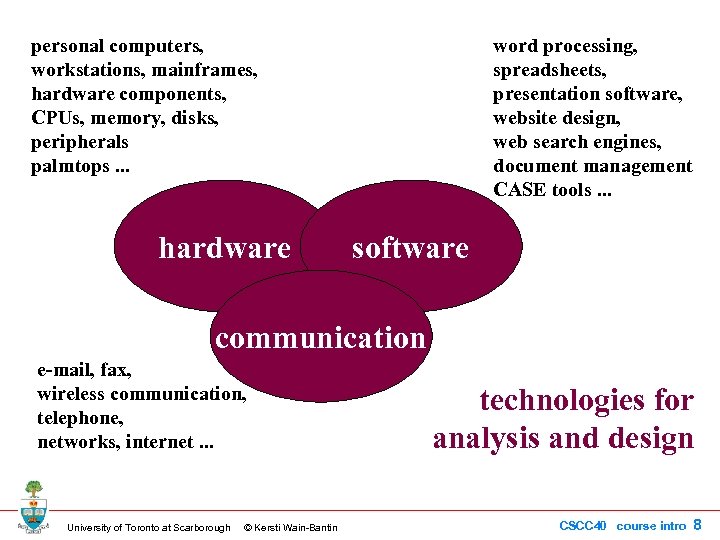 personal computers, workstations, mainframes, hardware components, CPUs, memory, disks, peripherals palmtops. . . hardware word processing, spreadsheets, presentation software, website design, web search engines, document management CASE tools. . . software communication e-mail, fax, wireless communication, telephone, networks, internet. . . University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin technologies for analysis and design CSCC 40 course intro 8
personal computers, workstations, mainframes, hardware components, CPUs, memory, disks, peripherals palmtops. . . hardware word processing, spreadsheets, presentation software, website design, web search engines, document management CASE tools. . . software communication e-mail, fax, wireless communication, telephone, networks, internet. . . University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin technologies for analysis and design CSCC 40 course intro 8
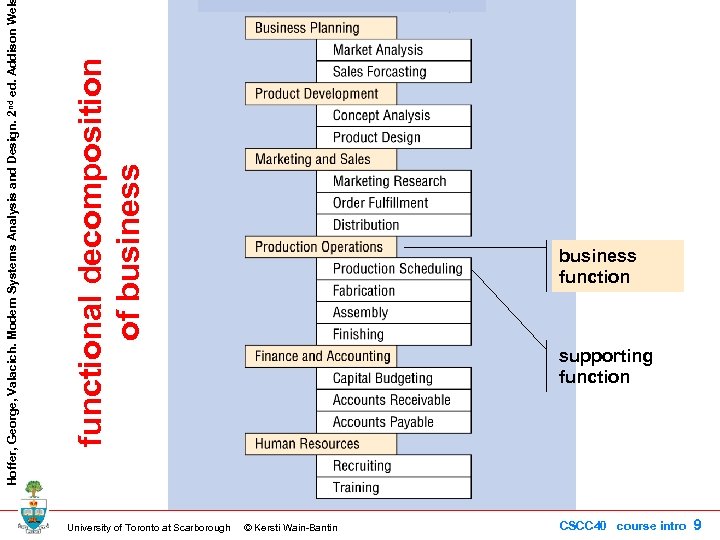 University of Toronto at Scarborough functional decomposition of business Hoffer, George, Valacich. Modern Systems Analysis and Design. 2 nd ed. Addison Wel business function supporting function © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 9
University of Toronto at Scarborough functional decomposition of business Hoffer, George, Valacich. Modern Systems Analysis and Design. 2 nd ed. Addison Wel business function supporting function © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 9
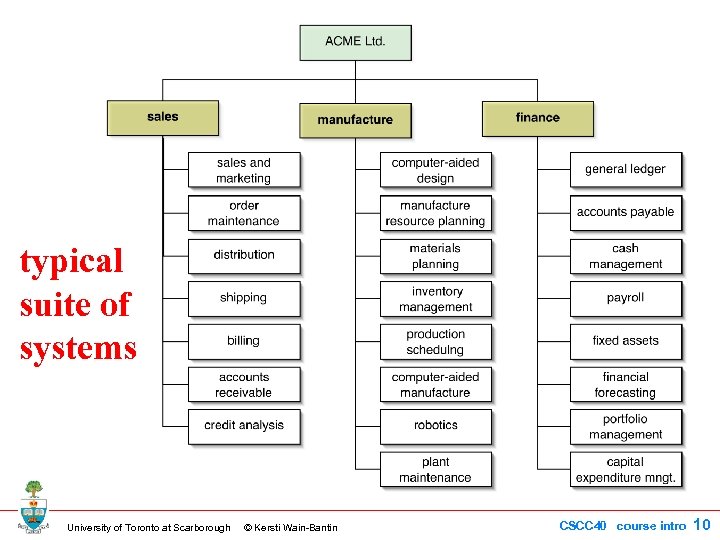 typical suite of systems University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 10
typical suite of systems University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 10
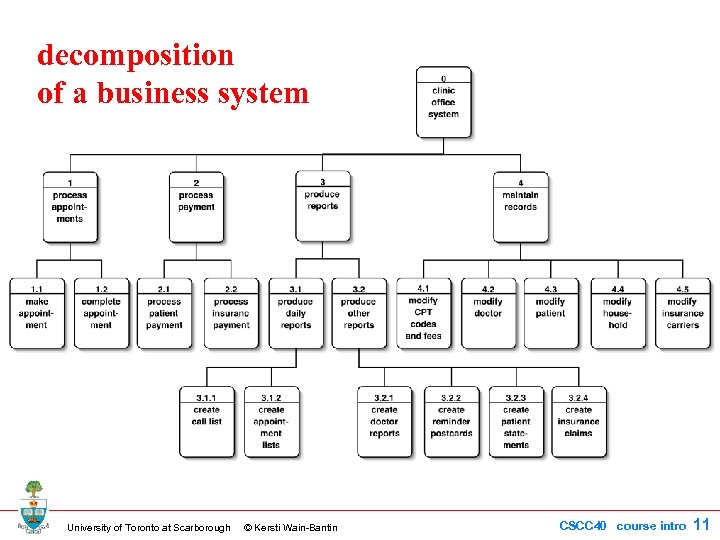 decomposition of a business system University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 11
decomposition of a business system University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 11
 conceptual complexity ! Where does one system end, and another start? If a system is a subjective view of reality, then who’s view do we work with? How do we cope when: • the system is too large to be understood by any one person? • technology is changing all the time? • user requirements are changing all the time? • new development tools and techniques and methodologies are constantly needed? University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 12
conceptual complexity ! Where does one system end, and another start? If a system is a subjective view of reality, then who’s view do we work with? How do we cope when: • the system is too large to be understood by any one person? • technology is changing all the time? • user requirements are changing all the time? • new development tools and techniques and methodologies are constantly needed? University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 12
 we have coping strategies ! methodologies: waterfall, prototype, extreme. . . time-tested techniques for: verification, validation, estimating. . . abstraction and decomposition modeling methods: structured, object-oriented. . . tools for: project control, design control, configuration management. . . University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 13
we have coping strategies ! methodologies: waterfall, prototype, extreme. . . time-tested techniques for: verification, validation, estimating. . . abstraction and decomposition modeling methods: structured, object-oriented. . . tools for: project control, design control, configuration management. . . University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 13
 what we want to avoid / prevent. . . from end user’s perspective. . . What system? I haven’t seen a new system. (vaporware) It might work, but it’s dreadful to use. (lots of reasons) It’s pretty, but does it do anything useful? (not an improvement) from client’s perspective. . . If I’d known the real price, I’d never have agreed. It’s no use delivering it now –we needed it last April. OK, so it works, but the installation was such a mess, my staff will never trust it. I didn’t want it in the first place. Everything’s changed now –we need a completely different system. University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 14
what we want to avoid / prevent. . . from end user’s perspective. . . What system? I haven’t seen a new system. (vaporware) It might work, but it’s dreadful to use. (lots of reasons) It’s pretty, but does it do anything useful? (not an improvement) from client’s perspective. . . If I’d known the real price, I’d never have agreed. It’s no use delivering it now –we needed it last April. OK, so it works, but the installation was such a mess, my staff will never trust it. I didn’t want it in the first place. Everything’s changed now –we need a completely different system. University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 14
 what we want to avoid / prevent. . . from the developer’s perspective. . . We built what they said they wanted. There wasn’t enough time to do it any better. Don’t blame me –I’ve never done O-O analysis before. How can I fix it –I don’t know how it’s supposed to work. We said it was impossible, but no-one listened. The system’s fine –the users are the problem. University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 15
what we want to avoid / prevent. . . from the developer’s perspective. . . We built what they said they wanted. There wasn’t enough time to do it any better. Don’t blame me –I’ve never done O-O analysis before. How can I fix it –I don’t know how it’s supposed to work. We said it was impossible, but no-one listened. The system’s fine –the users are the problem. University of Toronto at Scarborough © Kersti Wain-Bantin CSCC 40 course intro 15


