ec05cb7772efd857cf4422f537b2354f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19
CSC Muon Trigger On Detector Components B. Paul Padley Rice University June, 2002 US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 1
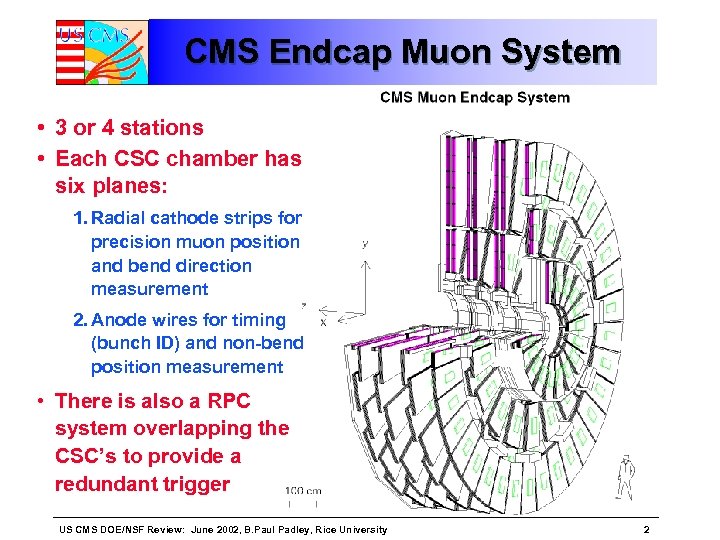
CMS Endcap Muon System • 3 or 4 stations • Each CSC chamber has six planes: 1. Radial cathode strips for precision muon position and bend direction measurement 2. Anode wires for timing (bunch ID) and non-bend position measurement • There is also a RPC system overlapping the CSC’s to provide a redundant trigger US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 2
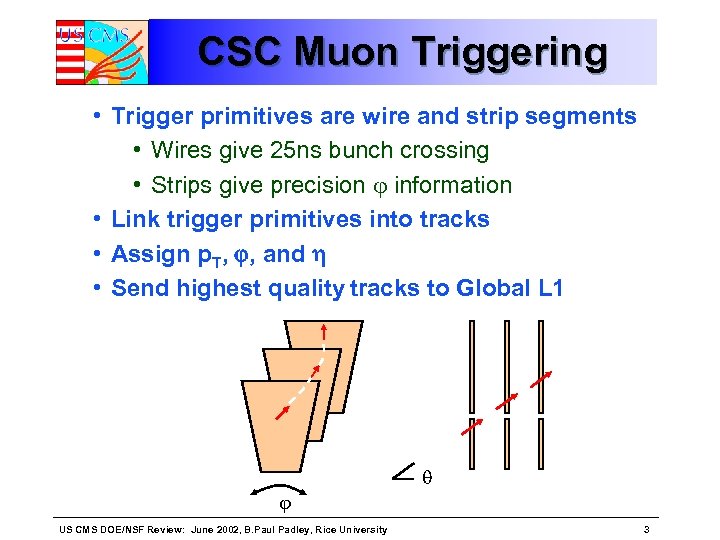
CSC Muon Triggering • Trigger primitives are wire and strip segments • Wires give 25 ns bunch crossing • Strips give precision information • Link trigger primitives into tracks • Assign p. T, , and • Send highest quality tracks to Global L 1 US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 3
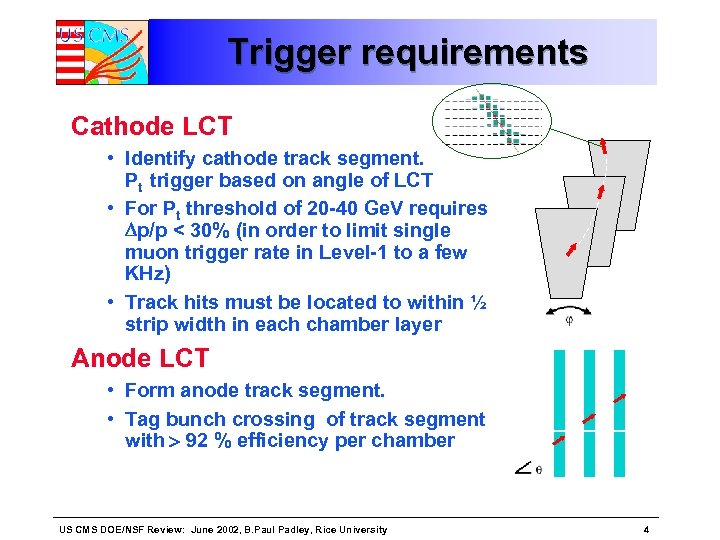
Trigger requirements Cathode LCT • Identify cathode track segment. Pt trigger based on angle of LCT • For Pt threshold of 20 -40 Ge. V requires Dp/p < 30% (in order to limit single muon trigger rate in Level-1 to a few KHz) • Track hits must be located to within ½ strip width in each chamber layer Anode LCT • Form anode track segment. • Tag bunch crossing of track segment with > 92 % efficiency per chamber US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 4

EMU “Trigger” Cards Anode LCT Card (ALCT) • • Sits on Chamber Receives Anode Front End Board discriminator signals Finds eta coordinate of two best track stubs and quality Sends to Trigger Motherboard (TMB) • Receives ALCT info • Receives Cathode Front End Board discriminator Signals • Finds location, bend angle and quality of two best cathode track stubs • Correlates Anode and Cathode LCT’s • Sends to Port Card (MPC) US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 5
EMU “Trigger” Cards Cont’d EMU Clock and Control Board (CCB) • Receives Clock and Control signals (such as L 1 accept, reset…) from Trigger Timing and Control system • Redistributes these signals on the custom backplane. RPC Interface Module (RIM) • Transition module that receives RPC trigger information • Could be used in TMB to eliminate ghosts (if they are a problem). US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 6
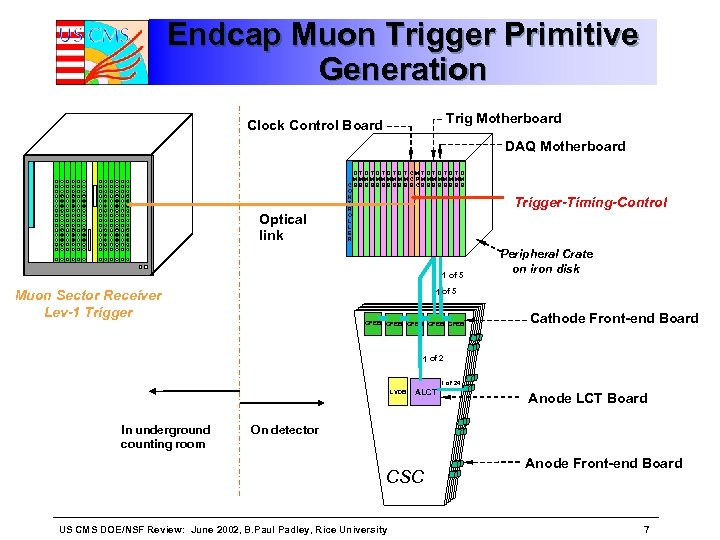
Endcap Muon Trigger Primitive Generation Trig Motherboard Clock Control Board DAQ Motherboard Optical link D TD T D T CMT D T D MM M MM C P M MM M C BB BBB BB BCB BB B O N T R O L L E R 1 of 5 Trigger-Timing-Control Peripheral Crate on iron disk 1 of 5 Muon Sector Receiver Lev-1 Trigger CFEB CFEB Cathode Front-end Board 1 of 24 LVDB In underground counting room ALCT Anode LCT Board On detector CSC US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University Anode Front-end Board 7
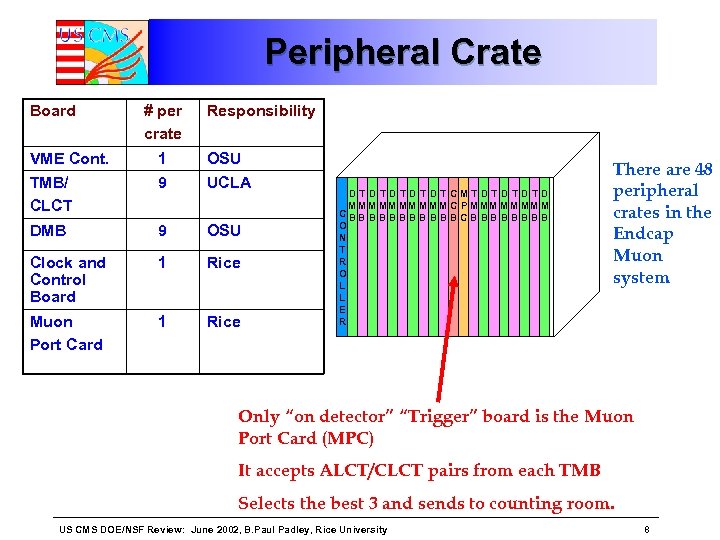
Peripheral Crate Board # per crate Responsibility VME Cont. 1 OSU TMB/ CLCT 9 UCLA DMB 9 OSU Clock and Control Board 1 Rice Muon Port Card 1 Rice D TD T D T CMT DT D T D M MM M M C P M MM M M CBB B CB BB B O N T R O L L E R There are 48 peripheral crates in the Endcap Muon system Only “on detector” “Trigger” board is the Muon Port Card (MPC) It accepts ALCT/CLCT pairs from each TMB Selects the best 3 and sends to counting room. US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 8
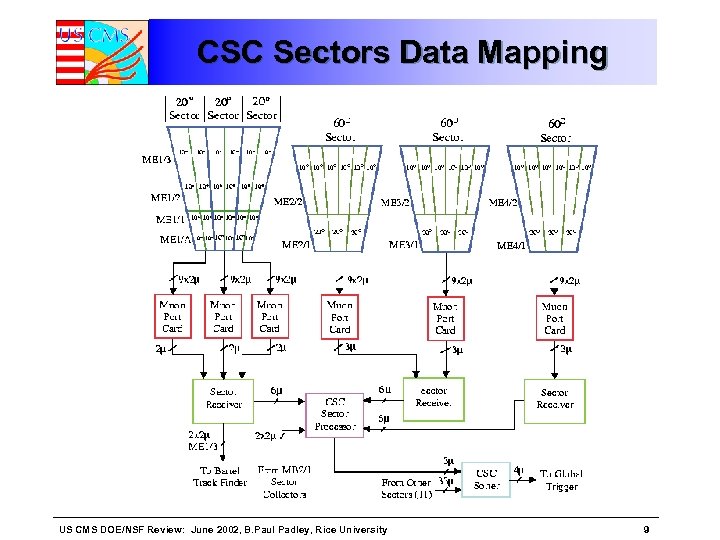
CSC Sectors Data Mapping US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 9
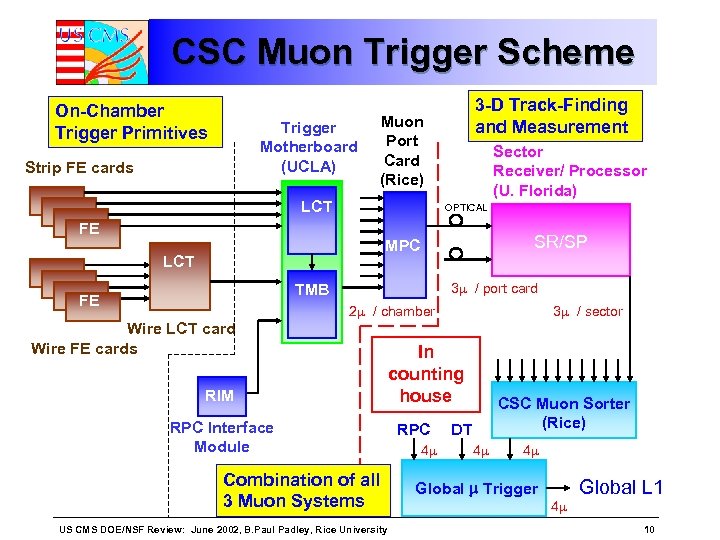
CSC Muon Trigger Scheme On-Chamber Trigger Primitives Trigger Motherboard (UCLA) Strip FE cards 3 -D Track-Finding and Measurement Muon Port Card (Rice) LCT Sector Receiver/ Processor (U. Florida) OPTICAL FE SR/SP MPC LCT 3 / port card TMB FE SP 2 / chamber Wire LCT card Wire FE cards RIM RPC Interface Module Combination of all 3 Muon Systems US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 3 / sector In counting house RPC 4 CSC Muon Sorter (Rice) DT 4 4 Global Trigger 4 Global L 1 10
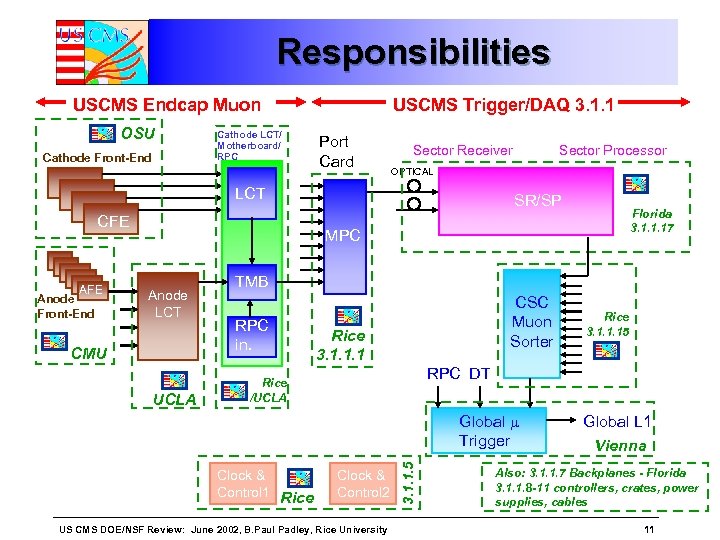
Responsibilities USCMS Endcap Muon OSU Cathode Front-End Cathode LCT/ Motherboard/ RPC USCMS Trigger/DAQ 3. 1. 1 Port Card Sector Receiver OPTICAL LCT CFE Anode Front-End Sector Processor SR/SP Florida 3. 1. 1. 17 MPC Anode LCT CMU UCLA TMB RPC in. CSC Muon Sorter Rice 3. 1. 1. 1 RPC DT Rice /UCLA Clock & Control 2 US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 3. 1. 1. 5 Global Trigger Clock & Control 1 Rice 3. 1. 1. 15 Global L 1 Vienna Also: 3. 1. 1. 7 Backplanes - Florida 3. 1. 1. 8 -11 controllers, crates, power supplies, cables 11
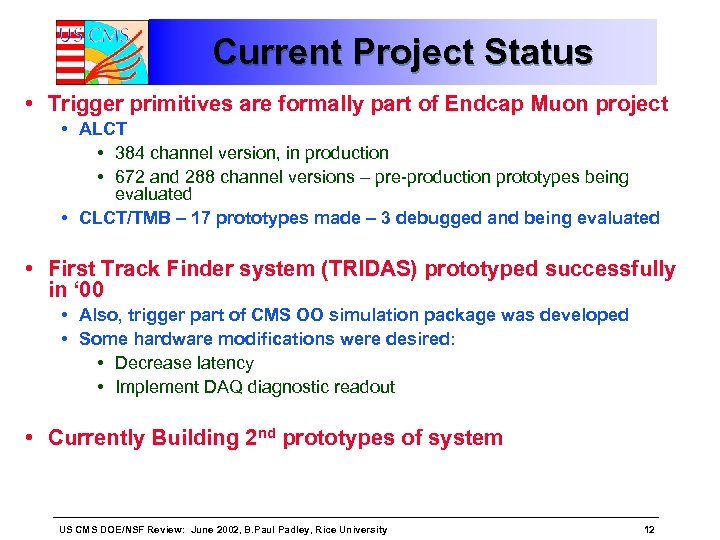
Current Project Status • Trigger primitives are formally part of Endcap Muon project • ALCT • 384 channel version, in production • 672 and 288 channel versions – pre-production prototypes being evaluated • CLCT/TMB – 17 prototypes made – 3 debugged and being evaluated • First Track Finder system (TRIDAS) prototyped successfully in ‘ 00 • Also, trigger part of CMS OO simulation package was developed • Some hardware modifications were desired: • Decrease latency • Implement DAQ diagnostic readout • Currently Building 2 nd prototypes of system US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 12
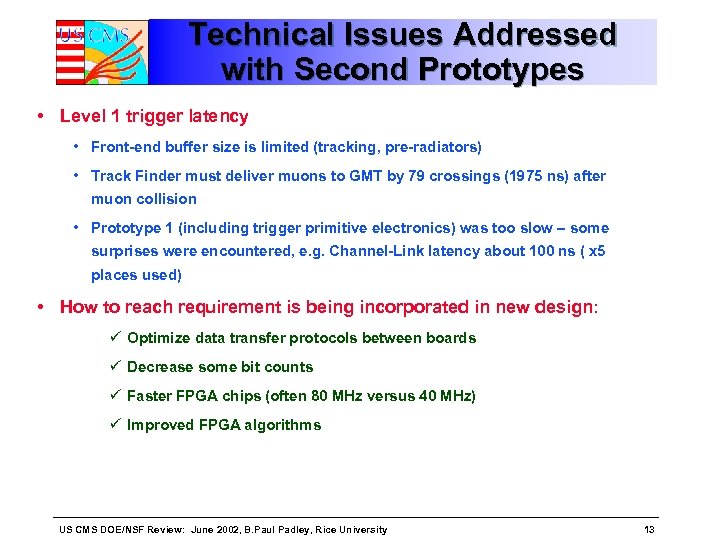
Technical Issues Addressed with Second Prototypes • Level 1 trigger latency • Front-end buffer size is limited (tracking, pre-radiators) • Track Finder must deliver muons to GMT by 79 crossings (1975 ns) after muon collision • Prototype 1 (including trigger primitive electronics) was too slow – some surprises were encountered, e. g. Channel-Link latency about 100 ns ( x 5 places used) • How to reach requirement is being incorporated in new design: ü Optimize data transfer protocols between boards ü Decrease some bit counts ü Faster FPGA chips (often 80 MHz versus 40 MHz) ü Improved FPGA algorithms US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 13
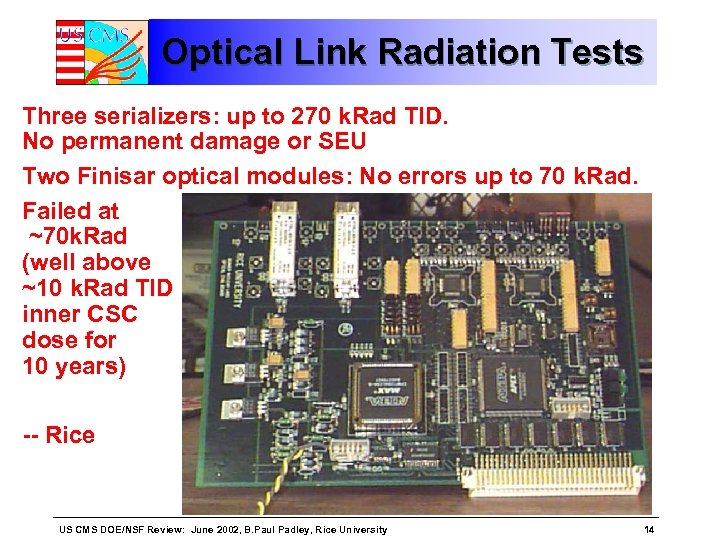
Optical Link Radiation Tests Three serializers: up to 270 k. Rad TID. No permanent damage or SEU Two Finisar optical modules: No errors up to 70 k. Rad. Failed at ~70 k. Rad (well above ~10 k. Rad TID inner CSC dose for 10 years) -- Rice US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 14
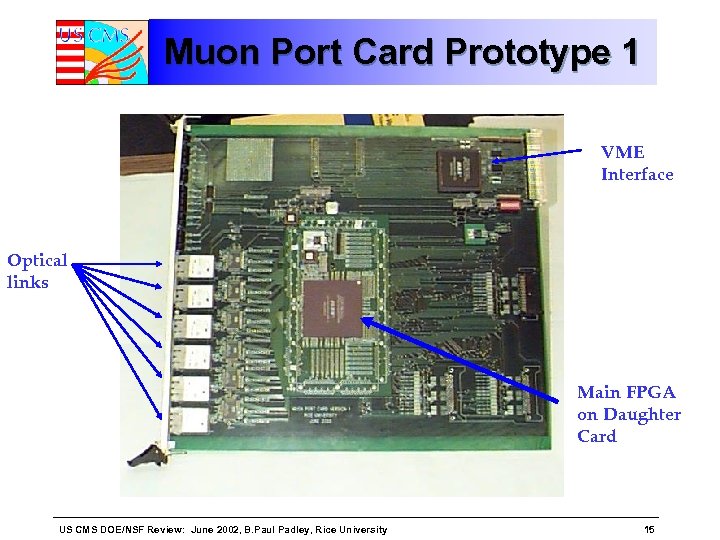
Muon Port Card Prototype 1 VME Interface Optical links Main FPGA on Daughter Card US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 15
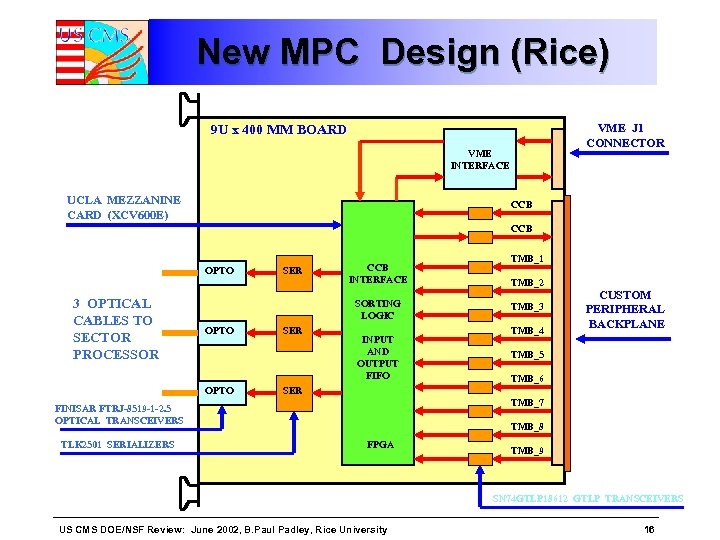
New MPC Design (Rice) VME J 1 CONNECTOR 9 U x 400 MM BOARD VME INTERFACE UCLA MEZZANINE CARD (XCV 600 E) CCB OPTO 3 OPTICAL CABLES TO SECTOR PROCESSOR SER CCB INTERFACE SORTING LOGIC OPTO SER INPUT AND OUTPUT FIFO TMB_2 TMB_3 TMB_4 CUSTOM PERIPHERAL BACKPLANE TMB_5 TMB_6 SER TMB_7 FINISAR FTRJ-8519 -1 -2. 5 OPTICAL TRANSCEIVERS TLK 2501 SERIALIZERS TMB_1 TMB_8 FPGA TMB_9 SN 74 GTLP 18612 GTLP TRANSCEIVERS US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 16
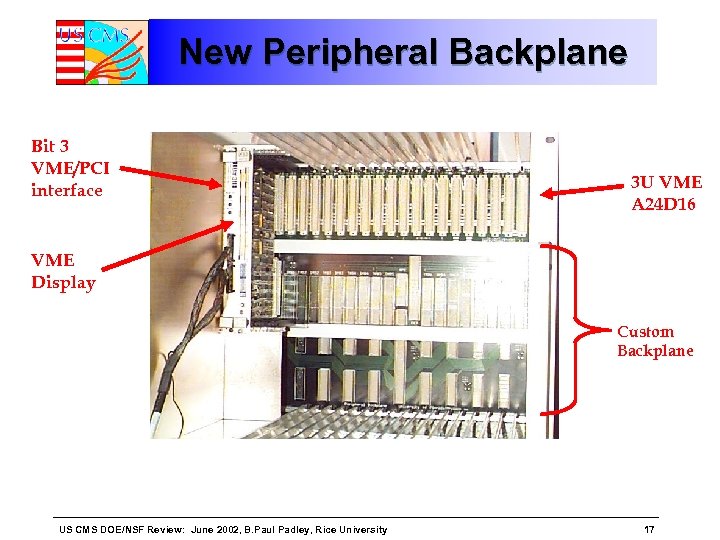
New Peripheral Backplane Bit 3 VME/PCI interface 3 U VME A 24 D 16 VME Display Custom Backplane US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 17
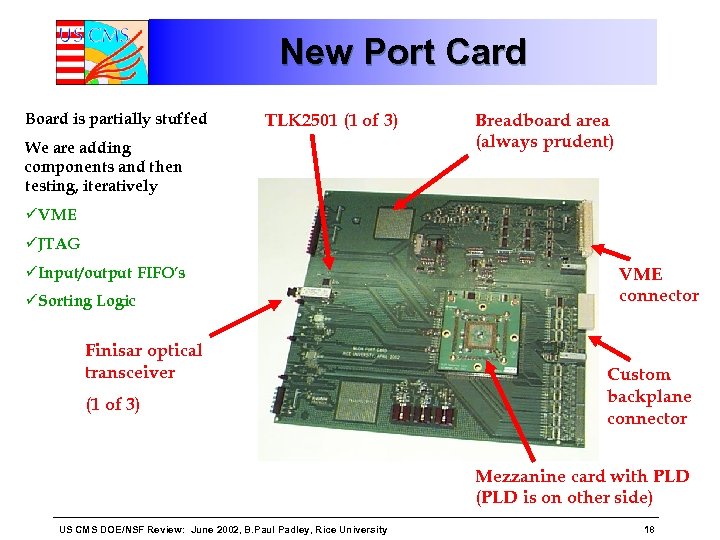
New Port Card Board is partially stuffed TLK 2501 (1 of 3) We are adding components and then testing, iteratively Breadboard area (always prudent) üVME üJTAG üInput/output FIFO’s üSorting Logic Finisar optical transceiver (1 of 3) VME connector Custom backplane connector Mezzanine card with PLD (PLD is on other side) US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 18

Personnel • Professors • Jay Hauser (UCLA), Paul Padley (Rice) • Postdocs • Martin Von der Mey (UCLA), TBA (Rice) • Students • Greg Pawloski (Rice) • Engineers • JK (UCLA), Mike Matveev (Rice), Ted Nussbaum (Rice) US CMS DOE/NSF Review: June 2002, B. Paul Padley, Rice University 19
ec05cb7772efd857cf4422f537b2354f.ppt