e33233f8a2503e29767030cd51bd45e7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

CS 723 - Probability and Stochastic Processes

Lecture No. 11

In Previous Lectures Discussion of discrete random variables and their associated concepts Thorough analysis of gambling games like chuck-a-luck and prize bonds Jointly random variables and their joint distribution function PMF and CDF Marginal distributions of two random variables from joint distributions Independence of two random variables

Conditional Distribution The probabilities or random variables change due to additional information The collection of conditional probability values give conditional PMF/CDF Conditioning can be on any event
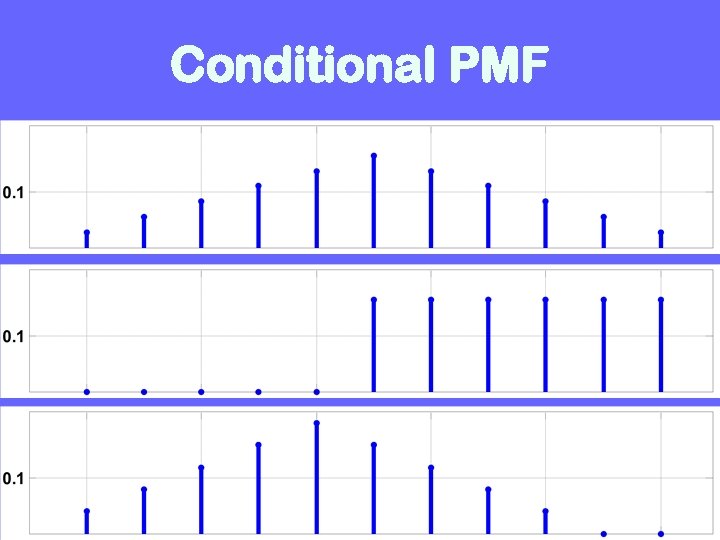
Conditional PMF

Expected Value Average value of the random variable from a large collection of outcomes Example: a class with 100 students In general, E(X) = ∑ xi Pr(X=xi) = ∑ xi pi Chuck-a-luck is an unfair game because the expected value is -0. 0787 Prize bonds have a expected value of 24. 4 for 1500 rupee prize bonds Are prize bonds a fair game? No!

Expected Value Expected value of Bernoulli distribution B(N, p) is Np Expected number of customers going into a restaurant in 10 minutes was 24 Expected value of Poisson distribution is always λ The value of λ chosen for Poisson approximation was 24
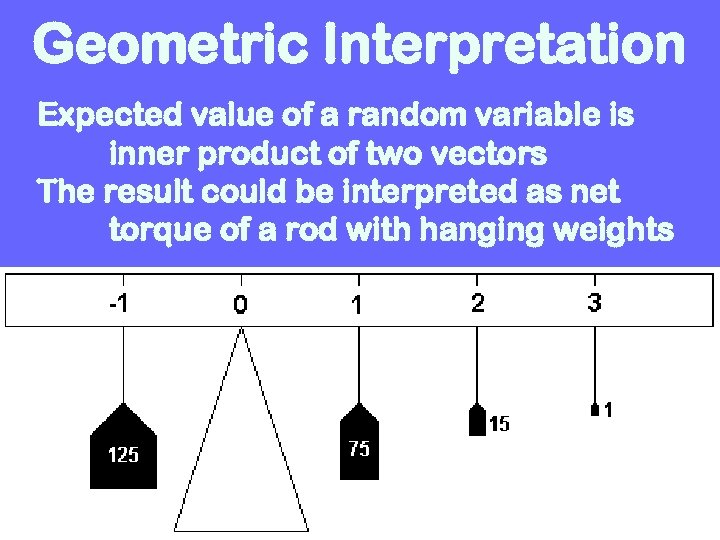
Geometric Interpretation Expected value of a random variable is inner product of two vectors The result could be interpreted as net torque of a rod with hanging weights
Transformation of RV’s Random variable maps outcome to point on real line Other mappings can be introduced before assignment of probabilities Additional mappings can involve one random variable R→R, two random variables R 2 → R, or more RV’s Examples: Z 1 = X+Y , Z 2 = |X-Y| Y = 2 X , Y = X – 3 , Y = 2 X + 3 Y
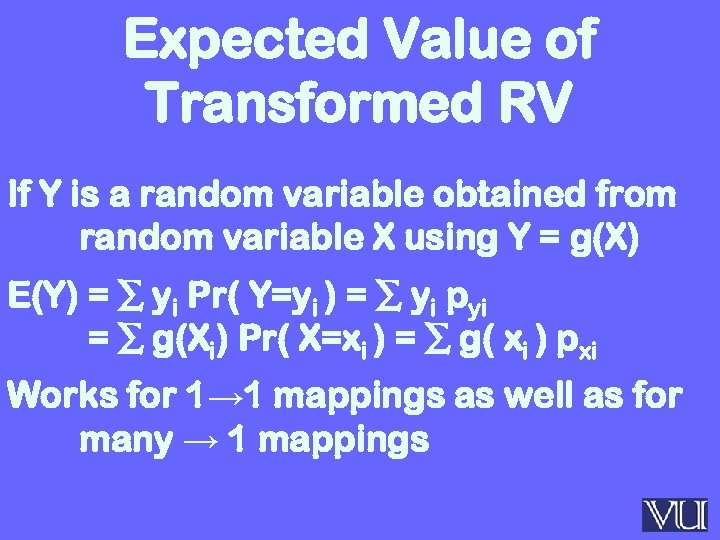
Expected Value of Transformed RV If Y is a random variable obtained from random variable X using Y = g(X) E(Y) = ∑ yi Pr( Y=yi ) = ∑ yi pyi = ∑ g(Xi) Pr( X=xi ) = ∑ g( xi ) pxi Works for 1→ 1 mappings as well as for many → 1 mappings

Expectation of Y=g(X) Gambling game of chuck-a-luck run by a benevolent gambling house You don’t loose your bet and get a chance to win 4, 3, or 2 dollars. Transformed RV is Y = X+1 E(Y) = (75*2 + 15*3 + 1*4)/216 = 0. 92 For prize bonds with inflation effect Y = X – 30 and E(Y) = E(X) – 30 = -5. 56 E(X+a) = E(X) + a & E(b. X) = b. E(X)

Moments Expected values of transformed RV’s of the kind Y = Xp and Y = (X – m)p The first type are simple moments and second type are central moments Expected value of Y = (X – m)2 is called variance of random variable X
e33233f8a2503e29767030cd51bd45e7.ppt