b9c4b210bfccd7c830b98e249dc24eaa.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31

CS 716 Advanced Computer Networks By Dr. Amir Qayyum 1

Lecture No. 41 2

Message Integrity Protocols • Digital signature using RSA – Special case of a message integrity where the code can only have been generated by one participant – Compute signature with private key and verify with public key 3

Message Integrity Protocols • Keyed MD 5 – Sender: m + MD 5 (m + k) + E(E(k, rcv-pub), private) – Receiver • recovers random key using the sender’s public key • applies MD 5 to the concatenation of this random key message 4

Message Integrity Protocols • MD 5 with RSA signature – Sender: m + E(MD 5(m), private) – Receiver • Decrypts signature with sender’s public key • Compares result with MD 5 checksum sent with message 5
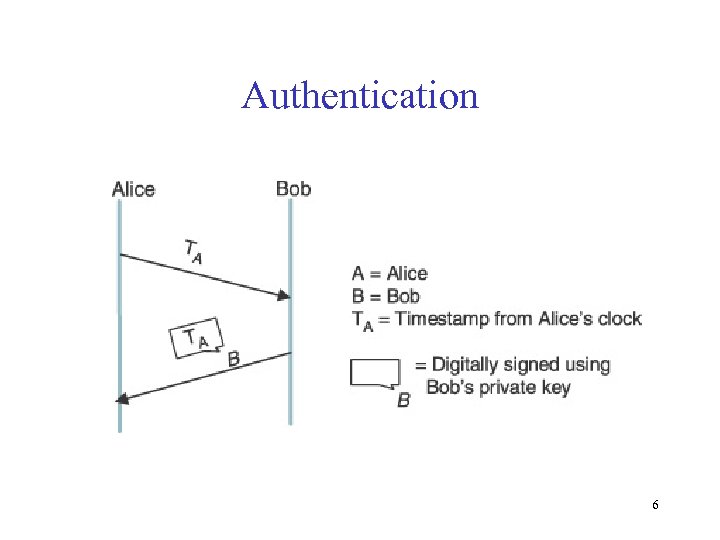
Authentication 6
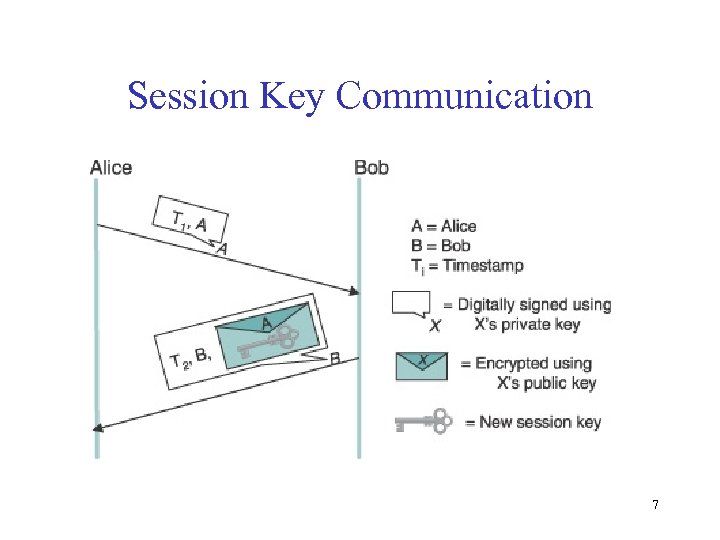
Session Key Communication 7
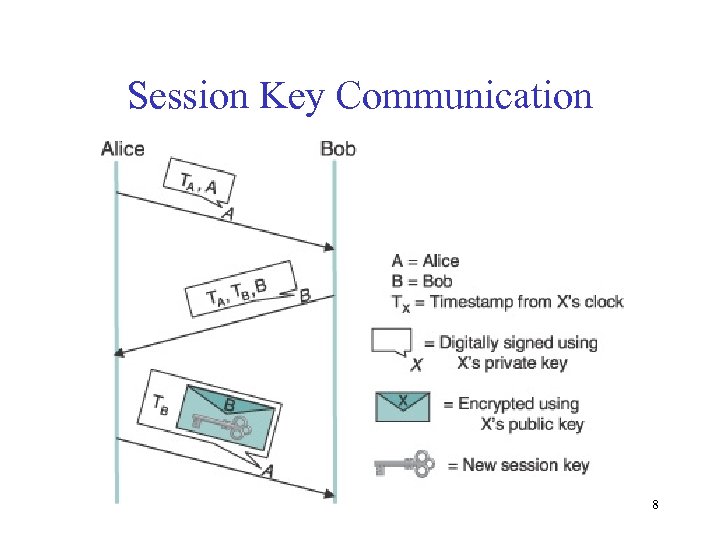
Session Key Communication 8
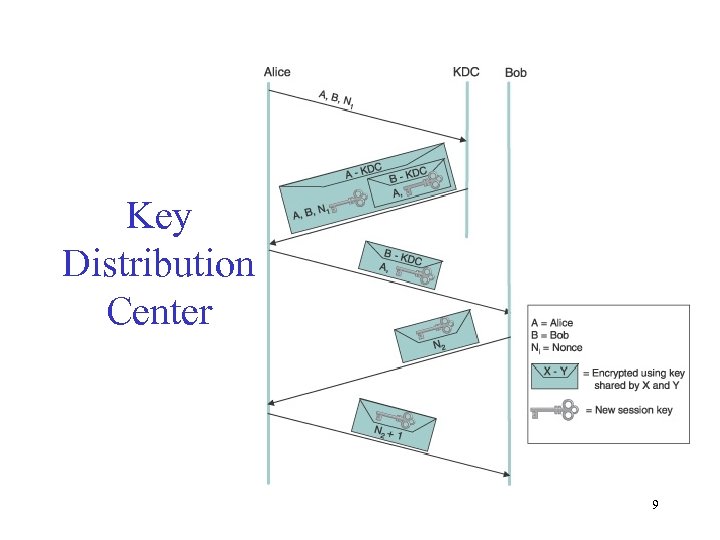
Key Distribution Center 9
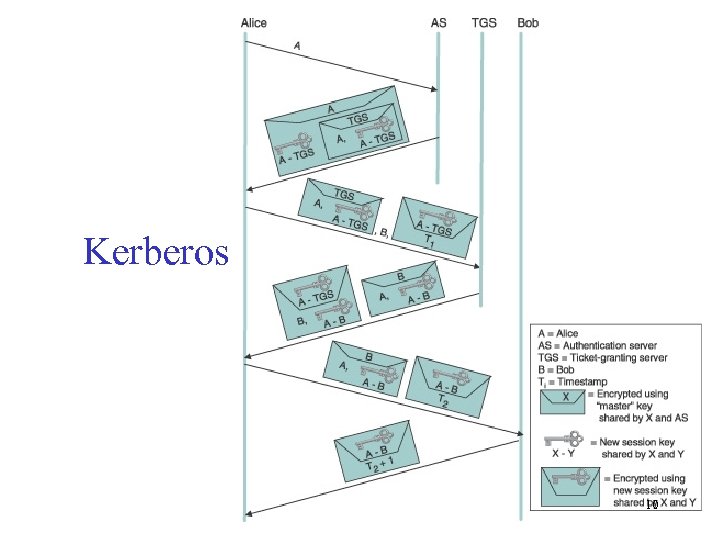
Kerberos 10
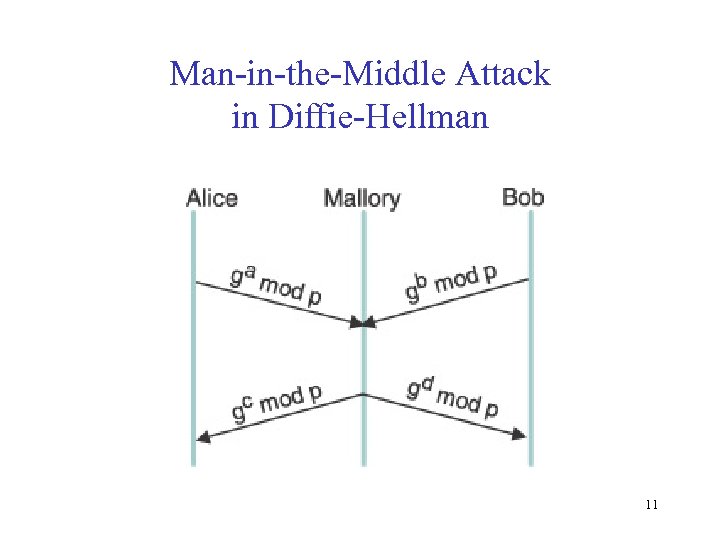
Man-in-the-Middle Attack in Diffie-Hellman 11

Key Distribution • Certificate – Special type of digitally signed document: “I certify that the public key in this document belongs to the entity named in this document, signed X. ” – The name of the entity being certified – The public key of the entity – The name of the certification authority – A digital signature 12

Key Distribution • Certification Authority (CA) – Administrative entity that issues certificates – Useful only to someone that already holds the CA’s public key. 13
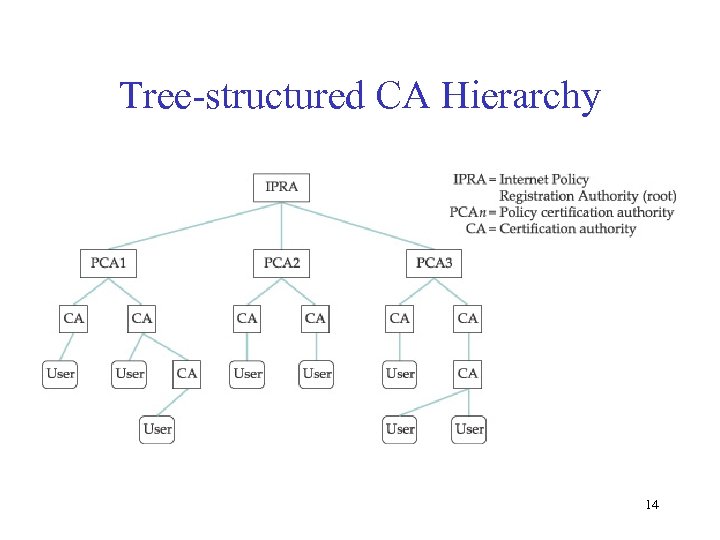
Tree-structured CA Hierarchy 14

Key Distribution (cont) • Chain of Trust – If X certifies that a certain public key belongs to Y, and Y certifies that another public key belongs to Z, then there exists a chain of certificates from X to Z – Someone that wants to verify Z’s public key has to know X’s public key and follow the chain • Certificate Revocation List 15

PGP Message Integrity and Authentication Sender identity and message integrity confirmed if checksums match Calculate MD 5 checksum over message contents Calculate MD 5 checksum on received message and compare against received value Sign checksum using RSA with sender‘s private key Decrypt signed checksum with sender‘s private key Transmitted message 16
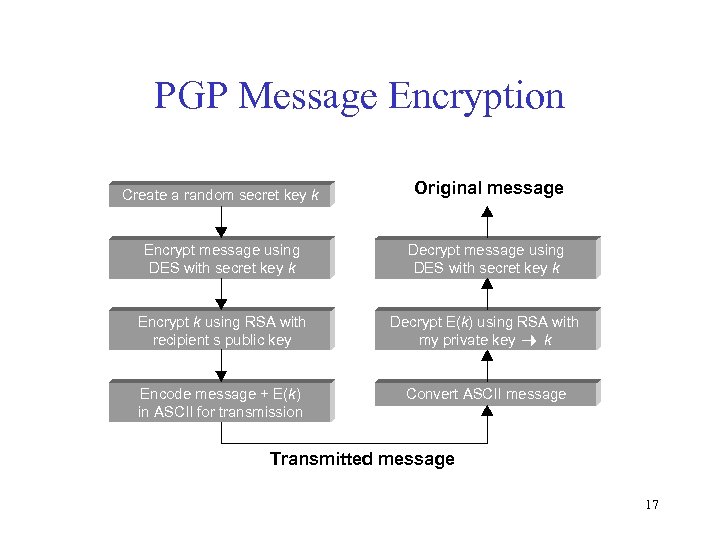
PGP Message Encryption Create a random secret key k Original message Encrypt message using DES with secret key k Decrypt message using DES with secret key k Encrypt k using RSA with recipient s public key Decrypt E(k) using RSA with my private key k Encode message + E(k) in ASCII for transmission Convert ASCII message Transmitted message 17
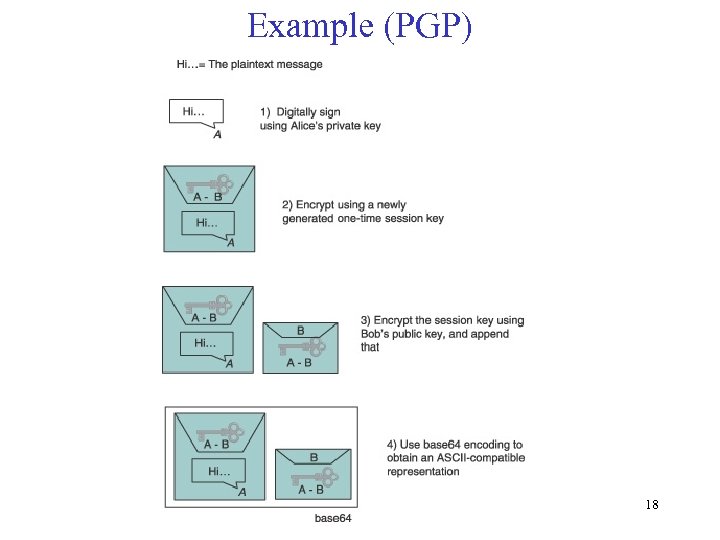
Example (PGP) 18
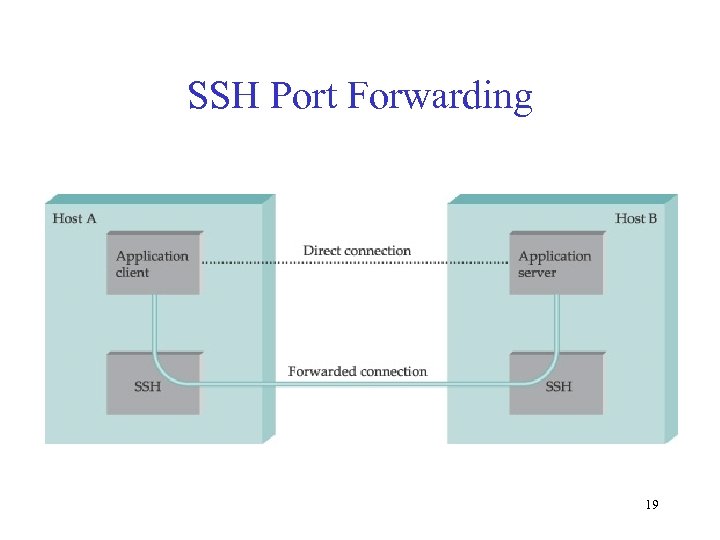
SSH Port Forwarding 19
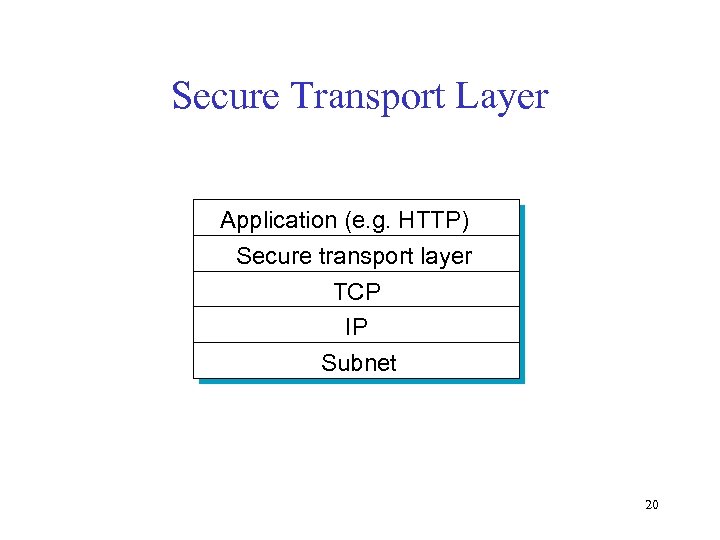
Secure Transport Layer Application (e. g. HTTP) Secure transport layer TCP IP Subnet 20
![TLS Handshake Protocol Client Server Hello [C [Cer ertificate t. Ve ] rify] Keys TLS Handshake Protocol Client Server Hello [C [Cer ertificate t. Ve ] rify] Keys](https://present5.com/presentation/b9c4b210bfccd7c830b98e249dc24eaa/image-21.jpg)
TLS Handshake Protocol Client Server Hello [C [Cer ertificate t. Ve ] rify] Keys Finis hed Finis Data 21
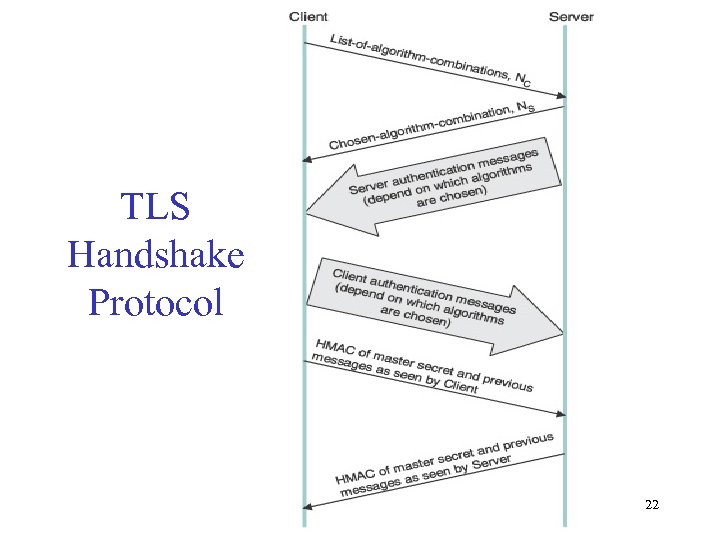
TLS Handshake Protocol 22
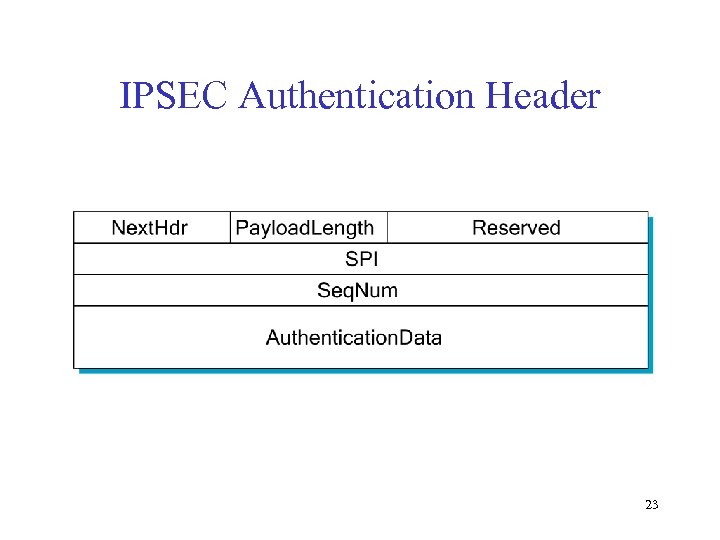
IPSEC Authentication Header 23
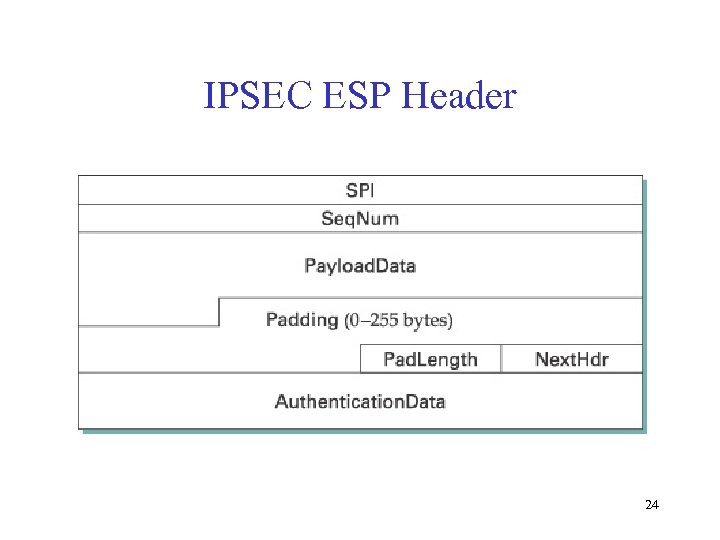
IPSEC ESP Header 24
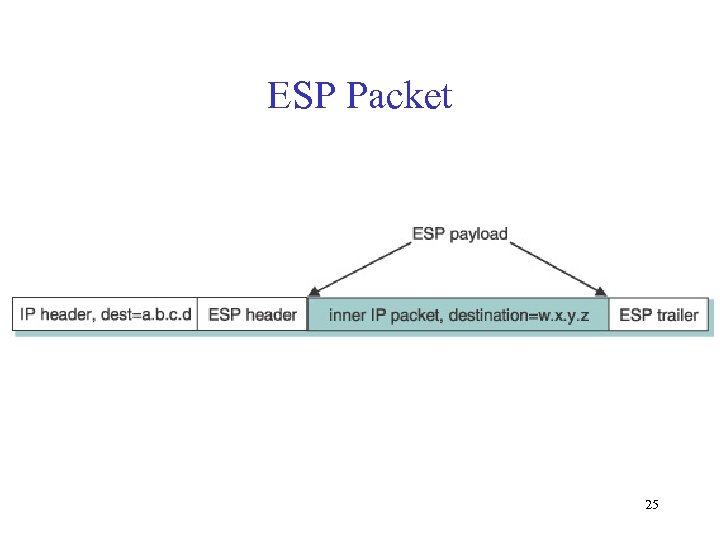
ESP Packet 25
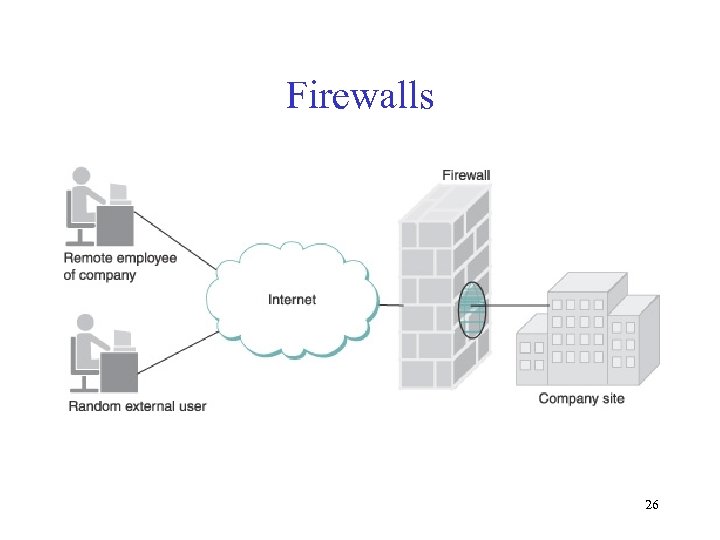
Firewalls 26
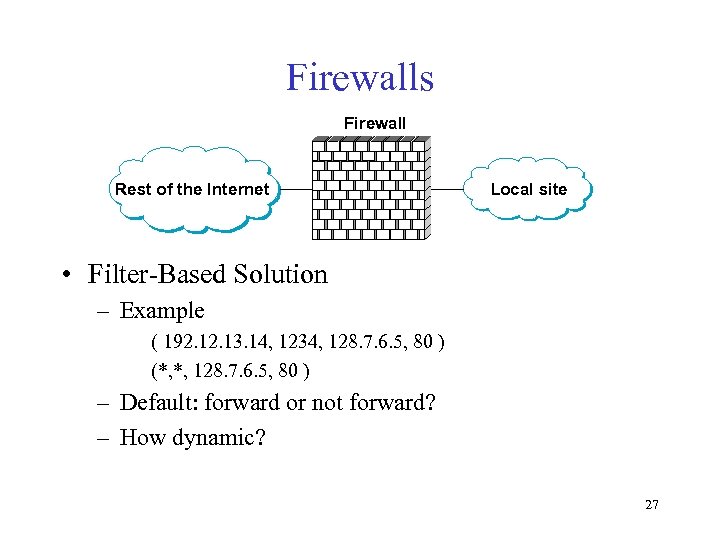
Firewalls Firewall Rest of the Internet Local site • Filter-Based Solution – Example ( 192. 13. 14, 1234, 128. 7. 6. 5, 80 ) (*, *, 128. 7. 6. 5, 80 ) – Default: forward or not forward? – How dynamic? 27
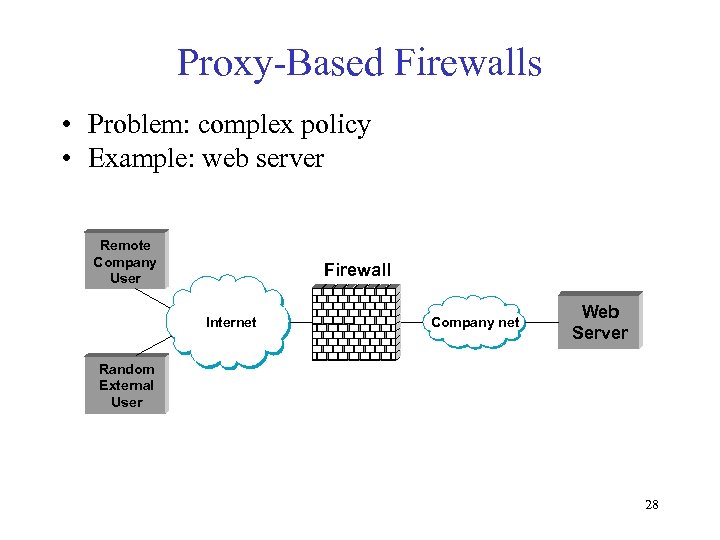
Proxy-Based Firewalls • Problem: complex policy • Example: web server Remote Company User Firewall Internet Company net Web Server Random External User 28
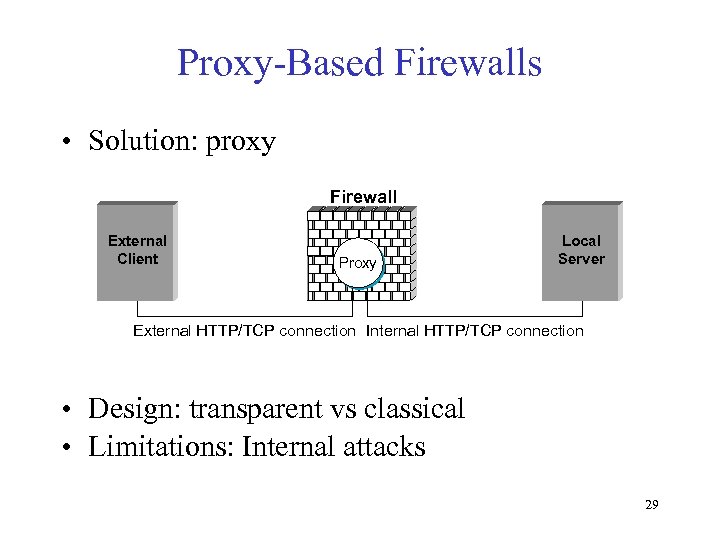
Proxy-Based Firewalls • Solution: proxy Firewall External Client Proxy Local Server External HTTP/TCP connection Internal HTTP/TCP connection • Design: transparent vs classical • Limitations: Internal attacks 29
Simple Proxy Scenario S P R 30

Denial of Service • Attacks on end hosts – SYN attack • Attacks on routers – Christmas tree packets – Pollute route cache • Authentication attacks • Distributed Do. S attacks 31
b9c4b210bfccd7c830b98e249dc24eaa.ppt