512875a67ed03b5f2e7472dbad841ea9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 42

CS 634 Information Systems Dr Deepak B Phatak Subrao Nilekani Chair Professor Kanwal Rekhi Building, Department of CSE IIT Bombay Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS IIT BOMBAY
SESSION OVERVIEW IIT BOMBAY • • • Principles of Software Engineering Activities Process Maturity Measures Review of ER Model Functional Model • Data Flow Model • User Interface Issues • Software Requirement Specifications (SRS) Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 2

ROLE OF SOFTWARE IIT BOMBAY • Business Functionality Depends Mainly On Software • Good Systems S/W Is The Basis • OS, Programming Languages (3 GL) • Tools To Build S/W Keep Evolving • 4 GL (SQL), RAD Tools • Typical Life Cycle: 10 -15 Years Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 3

Software Characteristics IIT BOMBAY • Software is Developed or Engineered • Not Manufactured • Software Does Not “Wear Out” • May Become Un-Maintainable • Hardware Does wear out • Most Software is Custom-Built • Limited Role for Packaged Products Which Need Customization and Integration With Other Apps. Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 4
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING IIT BOMBAY • Application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation and maintenance of software; i. e. , The application of engineering to software • IEEE Definition 1993 Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 5
SOFTWARE ENGINEERING IIT BOMBAY • Engineering is the analysis, design, construction, verification and management of technical (or) social entities • To engineer S/W, we must define A development process Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 6
Building Information Systems IIT BOMBAY • Functional Specifications • System Engineering • Feasibility Study • Allocation To H/W, S/W, People • • System Analysis System Design Coding, Testing, Integration Acceptance and Deployment Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 7
Software Process Models IIT BOMBAY • Linear Sequential Model • The Waterfall Model • User Knows Inadequacies Too Late • Prototyping Model • Model Business, Data, and Processes • Generate Application • Test and Turnover Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 8
Software Process Models IIT BOMBAY • Rapid Application Development • Evolutionary Models • The Incremental Model • Sequential + Prototyping • The Spiral Model • Concurrent Development Model • Formal Methods Model Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 9

UMBRELLA ACTIVITIES IIT BOMBAY • • Project Tracking And Control Formal Technical Reviews S/w Quality Assurance Configuration Management Document Production Reusability Management Measurement, Risk management Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 10

Software Project Management IIT BOMBAY • Basic Project Management • Software Teams • Coordination & Communication • Process and Project Metrics • Based on Lines of Code (Lo. C) • Function Point Oriented • Project Scheduling and Tracking Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 11
Software Engineering IIT BOMBAY • • A Quality Focus Process Methods Tools Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 12
SEI MODEL IIT BOMBAY • Software Engineering Institute • At Carnegie Mellon University • Capability Maturity Model • Five Levels of Maturity to Measure Effectiveness of an Organization in its Software Development Practices (CMM levels) Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 13

CMM LEVEL 1 (Initial) IIT BOMBAY • Process is Ad Hoc (Even Chaotic) • Very Few Processes Are Defined • Success Depends Entirely On Individual Efforts Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 14

CMM LEVEL 2 (Repeatable) IIT BOMBAY • Basic Management Processes Are Established • Cost Schedule And Functionality Is Tracked • Discipline To Successfully Repeat Projects With Similar Applications Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 15

CMM LEVEL 3 (Defined) IIT BOMBAY • Software process for both management and engineering activities is standardized, documented, and integrated across the organization • All projects use the documented approved version Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 16

CMM LEVEL 4 (Managed) IIT BOMBAY • Detailed measures of process and product quality are collected • Process and products quantitatively understood and controlled using detailed measures Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 17

CMM LEVEL 5 (Optimizing) IIT BOMBAY • Quantitative feedback exists from process for continuous process improvement • Testing innovative ideas and technologies Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 18
Classical Analysis Modeling IIT BOMBAY • Data Object Description • Entity Relationship Diagram • Relational Model • Process Specification • Data Flow Diagram • Control Specifications • State Transition Diagram Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 19
SYSTEM ANALYSIS IIT BOMBAY • Represent Information Domain Of The Problem • Which Data, How Manipulated • Five Ws and One H • Understand S/W Requirements • Specify S/W Functions, Interfaces, Constraints Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 20
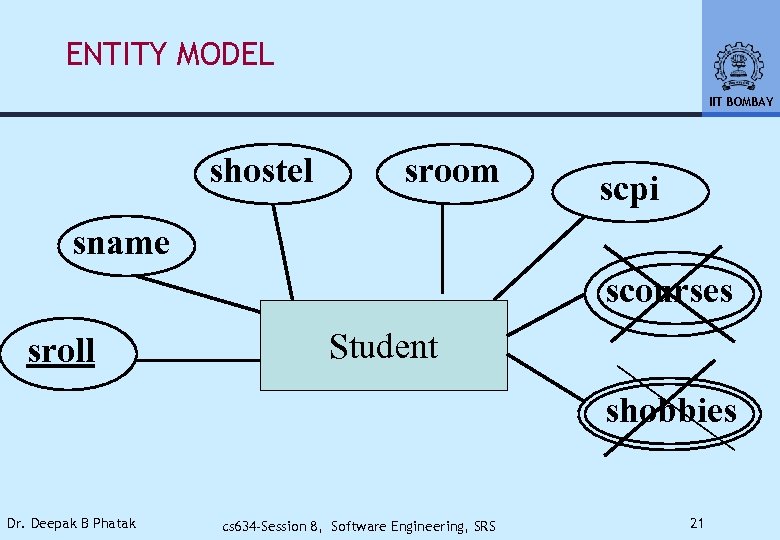
ENTITY MODEL IIT BOMBAY shostel sroom scpi sname scourses sroll Student shobbies Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 21
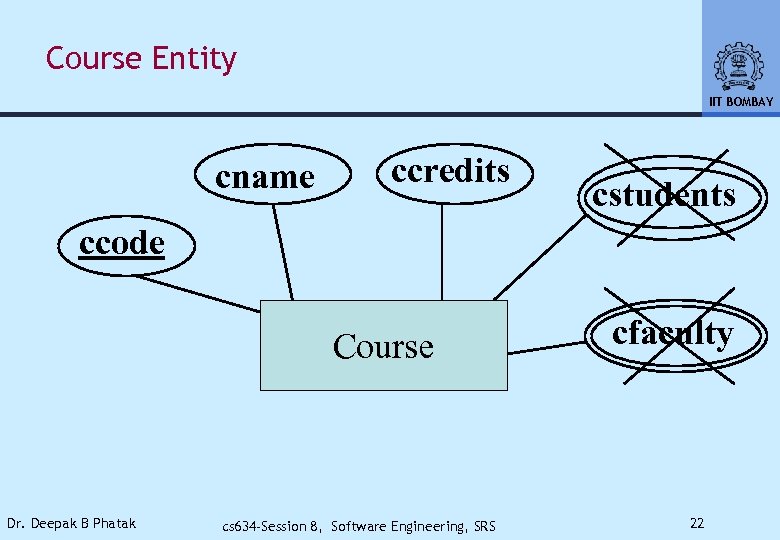
Course Entity IIT BOMBAY cname ccredits cstudents ccode Course Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS cfaculty 22
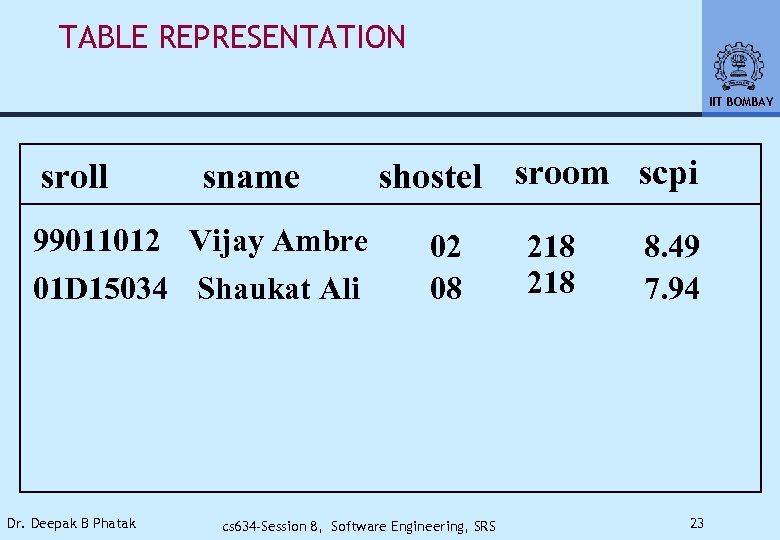
TABLE REPRESENTATION IIT BOMBAY sroll sname 99011012 Vijay Ambre 01 D 15034 Shaukat Ali Dr. Deepak B Phatak shostel sroom scpi 02 08 cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 218 8. 49 7. 94 23
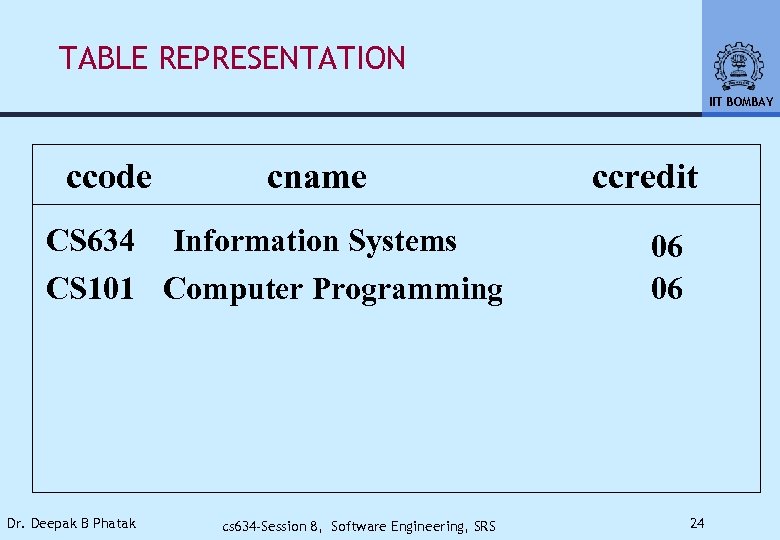
TABLE REPRESENTATION IIT BOMBAY ccode cname CS 634 Information Systems CS 101 Computer Programming Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS ccredit 06 06 24
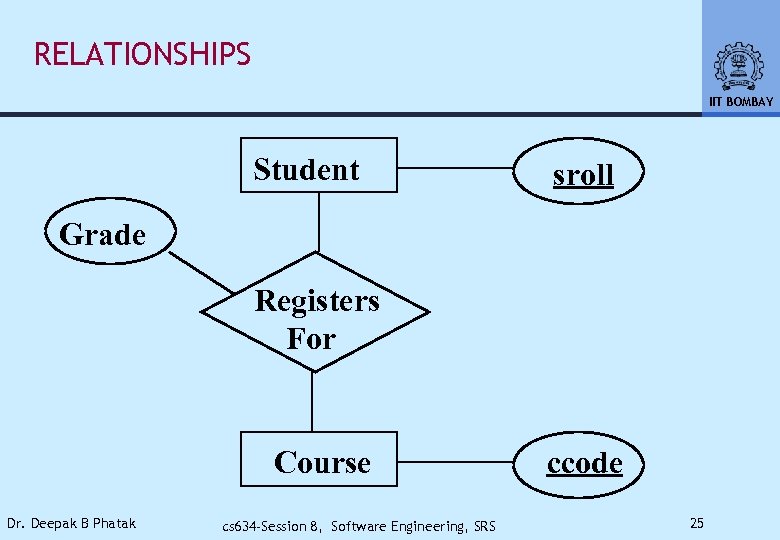
RELATIONSHIPS IIT BOMBAY Student sroll Grade Registers For Course Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS ccode 25
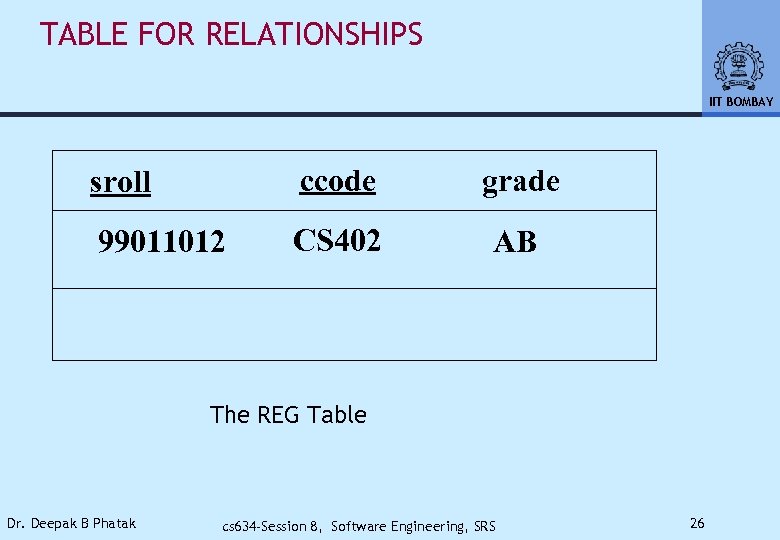
TABLE FOR RELATIONSHIPS IIT BOMBAY sroll ccode grade 99011012 CS 402 AB The REG Table Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 26
ER MODEL IIT BOMBAY • Captures Static Characteristics • Associations May Be • One To One (Shown By A Dot) • One To Many, Many To One • Easy To Map The Structure To Files Or Data Base Schema This Model Does Not Cover Dynamic Features, Workflow, Interfaces, etc. Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 27
DATA DICTIONARY (Entity Sets) IIT BOMBAY • A Repository Of All Information About Entities And Associations • For An Entity • • Name, Brief Description Approximate Number in The Set Frequency of Changes Any Other Information Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 28
DATA DICTIONARY (Attributes) IIT BOMBAY • For Each Attribute • • Name, Brief Description Data Type and Field Width Valid Values (Domain) Typical Values Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 29
FLOW MODELING (DFD) IIT BOMBAY • As information flows through A system, it is transformed • A transformation represents part of a system function • Such flow and the attendant transformation can be captured using a model for data flow • Represented using data flow diagrams Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 30
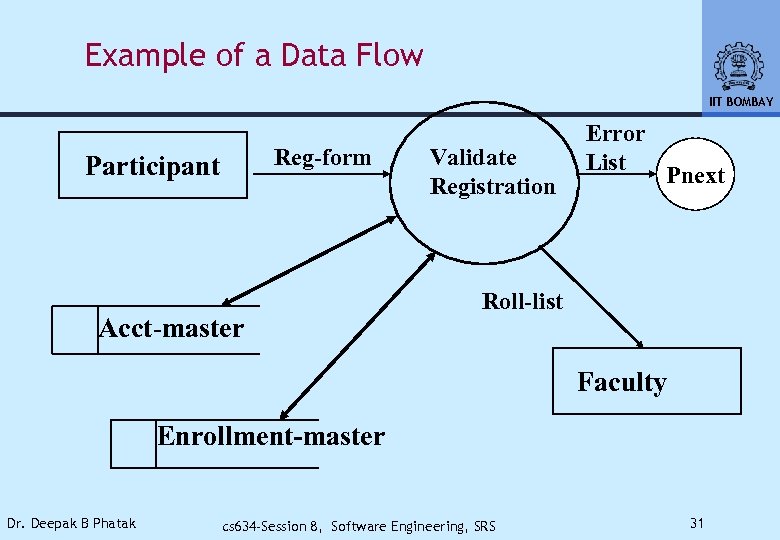
Example of a Data Flow IIT BOMBAY Reg-form Participant Acct-master Validate Registration Error List Pnext Roll-list Faculty Enrollment-master Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 31
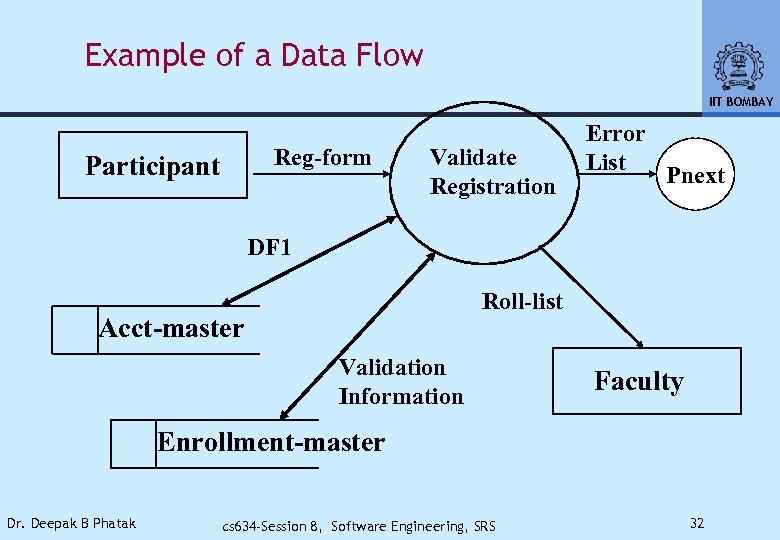
Example of a Data Flow IIT BOMBAY Reg-form Participant Validate Registration Error List Pnext DF 1 Roll-list Acct-master Validation Information Faculty Enrollment-master Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 32
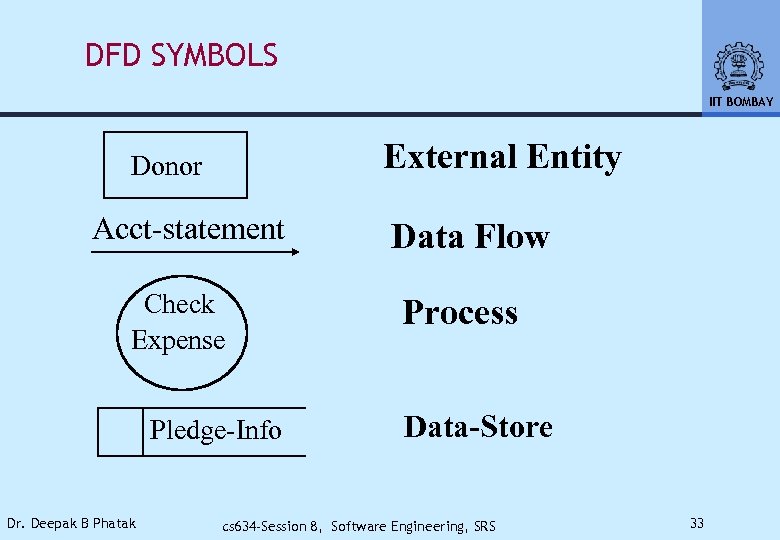
DFD SYMBOLS IIT BOMBAY External Entity Donor Acct-statement Check Expense Pledge-Info Dr. Deepak B Phatak Data Flow Process Data-Store cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 33
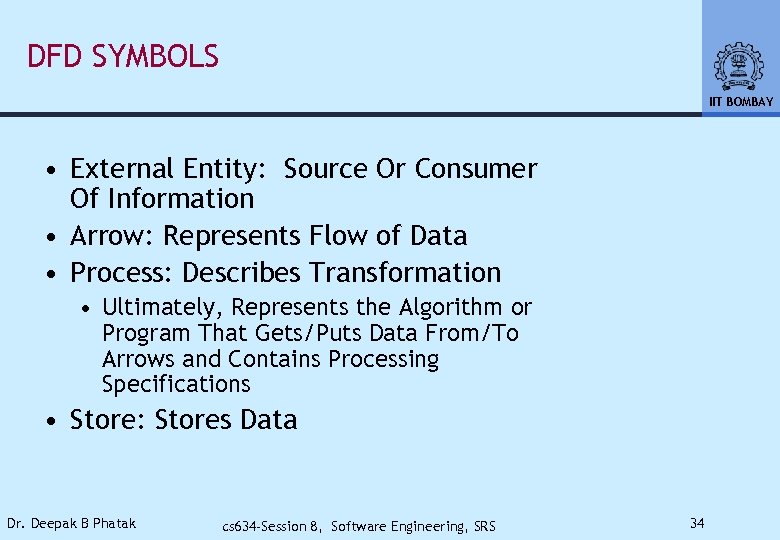
DFD SYMBOLS IIT BOMBAY • External Entity: Source Or Consumer Of Information • Arrow: Represents Flow of Data • Process: Describes Transformation • Ultimately, Represents the Algorithm or Program That Gets/Puts Data From/To Arrows and Contains Processing Specifications • Store: Stores Data Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 34

DFD Data Dictionary IIT BOMBAY • Each Symbol Must Have An Associated Label • Data Dictionary Entries Must Define That Label in Terms Of its Meta-Data • Process Narrative (PSPEC) Must be Included Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 35

Example Entries IIT BOMBAY • Reg-Form • Roll Number, Name, Course, Audit/Credit, Time-table slot, … • Validation-Information • Input to Store: Roll-number • Return From Store • Name, CPI, fees-payment status, … Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 36
CONTEXT DIAGRAM IIT BOMBAY • Called level 0 DFD, or the fundamental system model • Single bubble with incoming and outgoing arrows mainly showing the entities involved • Functional partitioning further done to derive several level 1 DFDs Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 37
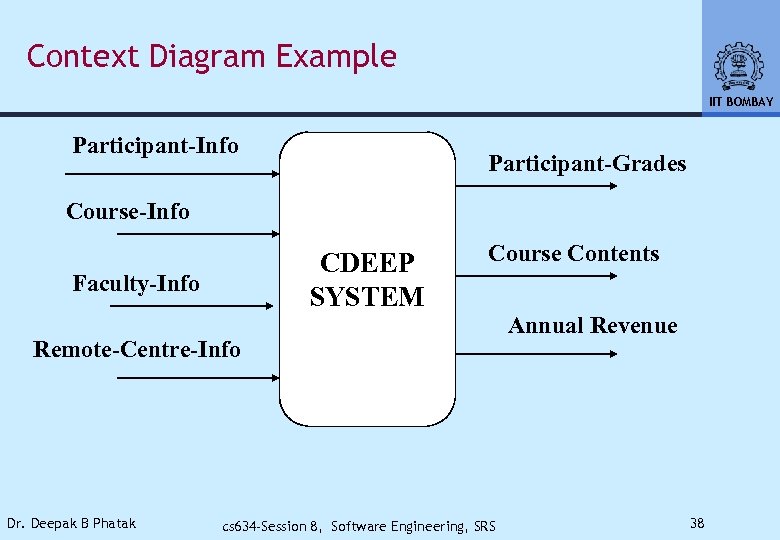
Context Diagram Example IIT BOMBAY Participant-Info Participant-Grades Course-Info CDEEP SYSTEM Faculty-Info Course Contents Remote-Centre-Info Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS Annual Revenue 38

REFINEMENT IIT BOMBAY • Expansion Of a Level 1 DFD To Add Detailed Processes • Flow Continuity Necessary • Expansion Must Have Same I/O Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 39
USER INTERFACE IIT BOMBAY • Modeling Interactive Screens • Capture And Validate Input • Query Retrieval • Modeling Reports • Contents and Format • On Screen, On Printer • Special Interfaces Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 40

USER INTERFACE IIT BOMBAY • Screen And Forms Layouts • Source And Target Stores • Operational Considerations • Ease Of Use (User Friendliness) • Keystroke Minimization Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 41

SRS Document (Draft Contents) IIT BOMBAY • Introduction • Functional Specifications • Data Models and Data Dictionary • ER Model • Data Flow Model • • • User Interface Requirements Interfaces to Other Systems Procedures and Workflow Acceptance Criteria Appendices Dr. Deepak B Phatak cs 634 -Session 8, Software Engineering, SRS 42
512875a67ed03b5f2e7472dbad841ea9.ppt