2cde87eb0310ecb368e71ada957fdae2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 CS 5038 The Electronic Society Lecture 8: e-Government Lecture Outline • • • Terminology - G 2 C, G 2 B, G 2 E Major areas of G 2 C activities Six stages to implementation Implementation Problems Current state in UK E-Government - Increasing Inequality? Addressing the Democratic Deficit e. Participation e. Government in the Developing World – Sri Lanka e. Government in Singapore 1
CS 5038 The Electronic Society Lecture 8: e-Government Lecture Outline • • • Terminology - G 2 C, G 2 B, G 2 E Major areas of G 2 C activities Six stages to implementation Implementation Problems Current state in UK E-Government - Increasing Inequality? Addressing the Democratic Deficit e. Participation e. Government in the Developing World – Sri Lanka e. Government in Singapore 1
 E-Government The use of electronic technology by a government to: Ø Deliver its services better Ø Improve its efficiency and effectiveness (just like e. Commerce) § Less staff needed to serve people quicker/cheaper Ø Make governments more transparent to citizens and businesses Ø Access to more of the information generated by government Government to citizens (G 2 C) Ø Delivery of public services etc. (next slide) Government-to-employees (G 2 E) Ø Activities and services between government units and their employees Government to Government (G 2 G) Ø Intragovernmental activities § Within a Government department and between Government bodies 2
E-Government The use of electronic technology by a government to: Ø Deliver its services better Ø Improve its efficiency and effectiveness (just like e. Commerce) § Less staff needed to serve people quicker/cheaper Ø Make governments more transparent to citizens and businesses Ø Access to more of the information generated by government Government to citizens (G 2 C) Ø Delivery of public services etc. (next slide) Government-to-employees (G 2 E) Ø Activities and services between government units and their employees Government to Government (G 2 G) Ø Intragovernmental activities § Within a Government department and between Government bodies 2
 E-Government to business (G 2 B) ØE-Procurement – reverse auctions for MROs § Group purchasing • e. FAST service (gsa. gov) conducts reverse auctions for aggregated orders ØE-Auctions § § § government surpluses real estate seized goods ØTax collection and management § electronic filing of taxes is now available in over 100 countries 3
E-Government to business (G 2 B) ØE-Procurement – reverse auctions for MROs § Group purchasing • e. FAST service (gsa. gov) conducts reverse auctions for aggregated orders ØE-Auctions § § § government surpluses real estate seized goods ØTax collection and management § electronic filing of taxes is now available in over 100 countries 3
 E-Government Major areas of G 2 C activities: http: //www. direct. gov. uk/Homepage/fs/en Ø tourism and recreation Ø research and education Ø downloadable forms Ø discovery of government services Ø information about public policy Ø advice about health and safety issues Ø Pay tax & bills, receive documents and payments § Nationwide Electronic benefit transfer (EBT) system in U. S. to deliver government benefits electronically • deliver benefits to recipients’ bank accounts • smart card system for those without bank accounts Ø Makes government more transparent to citizens - access to information Ø Greater opportunities to participate in democratic institutions Ø Future: voting Useful in solving constituents’ problems Ø Track problems using CRM-type software 4
E-Government Major areas of G 2 C activities: http: //www. direct. gov. uk/Homepage/fs/en Ø tourism and recreation Ø research and education Ø downloadable forms Ø discovery of government services Ø information about public policy Ø advice about health and safety issues Ø Pay tax & bills, receive documents and payments § Nationwide Electronic benefit transfer (EBT) system in U. S. to deliver government benefits electronically • deliver benefits to recipients’ bank accounts • smart card system for those without bank accounts Ø Makes government more transparent to citizens - access to information Ø Greater opportunities to participate in democratic institutions Ø Future: voting Useful in solving constituents’ problems Ø Track problems using CRM-type software 4
 5
5
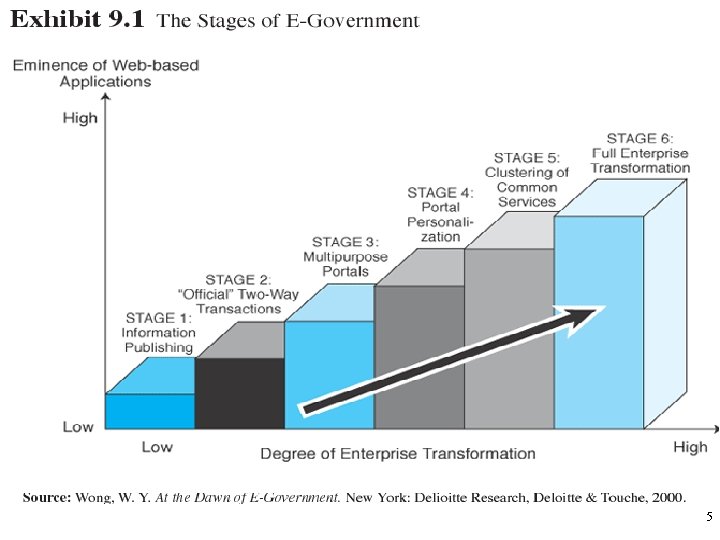
 E-Government Stages Six stages to implementation (most governments are at stage 1) 1. Information publishing/dissemination – services available, contact details 2. Two-way transactions - Submit personal information, monetary transactions 3. Multipurpose portals – in Australia: www. sa. gov. au 4. Portal personalisation – must allow interfaces to be manipulated by user 5. Clustering of common services – people see clusters of services rather than agencies – reorganisation of government structure 6. Full integration and enterprise transformation – full service centre personalised to customer 6
E-Government Stages Six stages to implementation (most governments are at stage 1) 1. Information publishing/dissemination – services available, contact details 2. Two-way transactions - Submit personal information, monetary transactions 3. Multipurpose portals – in Australia: www. sa. gov. au 4. Portal personalisation – must allow interfaces to be manipulated by user 5. Clustering of common services – people see clusters of services rather than agencies – reorganisation of government structure 6. Full integration and enterprise transformation – full service centre personalised to customer 6
 E-Government Implementation issues Ø Transformation speed - usually slow: § Resistance by employees § Limited budget § Legal environment Ø G 2 B implementation § Easier than G 2 C § Can be outsourced (Hong Kong) Ø Security and privacy issues § Citizens’ data § Especially healthcare Ø Wireless applications § E. g. wireless tourist service (Bergen) 7
E-Government Implementation issues Ø Transformation speed - usually slow: § Resistance by employees § Limited budget § Legal environment Ø G 2 B implementation § Easier than G 2 C § Can be outsourced (Hong Kong) Ø Security and privacy issues § Citizens’ data § Especially healthcare Ø Wireless applications § E. g. wireless tourist service (Bergen) 7
 E-Government in UK Implementation issues Ø Has reached the stage of two-way transactions with many sites Ø Fast uptake of broadband in UK, but sparse use of online e. Government services by citizens Ø Few government employees have completed their first ECDL module Ø 800 Government bodies spawned 3000 sites (2003) § Need for sites offering related services in one place § Each distinct site needs to be clear and focused § E. g. housing, transport, education, immigration § Public will learn to associate that site with its particular services Ø Fragmented view of a citizen § Many different departments hold records § Often Different formats § Implementation of cross agency infrastructure lacking 8
E-Government in UK Implementation issues Ø Has reached the stage of two-way transactions with many sites Ø Fast uptake of broadband in UK, but sparse use of online e. Government services by citizens Ø Few government employees have completed their first ECDL module Ø 800 Government bodies spawned 3000 sites (2003) § Need for sites offering related services in one place § Each distinct site needs to be clear and focused § E. g. housing, transport, education, immigration § Public will learn to associate that site with its particular services Ø Fragmented view of a citizen § Many different departments hold records § Often Different formats § Implementation of cross agency infrastructure lacking 8
 E-Government - Increasing Inequality? Digital divide within UK: Ø The haves – Broadband access from the home Ø The have-nots – no Internet access § Except in Public libraries perhaps § May lack skills/education to use it effectively Ø The elderly – may lack skills, and may not trust faceless interaction Those on the wrong side of the digital divide may be even more excluded from participation in democracy Ø Important information on candidates at election time Ø Submission to e. Petitions – for lobbying parliament Solutions? Ø Brazil offering half a million computers to citizens at low prices Ø Credit schemes to assist citizens to buy 9
E-Government - Increasing Inequality? Digital divide within UK: Ø The haves – Broadband access from the home Ø The have-nots – no Internet access § Except in Public libraries perhaps § May lack skills/education to use it effectively Ø The elderly – may lack skills, and may not trust faceless interaction Those on the wrong side of the digital divide may be even more excluded from participation in democracy Ø Important information on candidates at election time Ø Submission to e. Petitions – for lobbying parliament Solutions? Ø Brazil offering half a million computers to citizens at low prices Ø Credit schemes to assist citizens to buy 9
 Addressing the Democratic Deficit Voter turnout has dropped 10
Addressing the Democratic Deficit Voter turnout has dropped 10
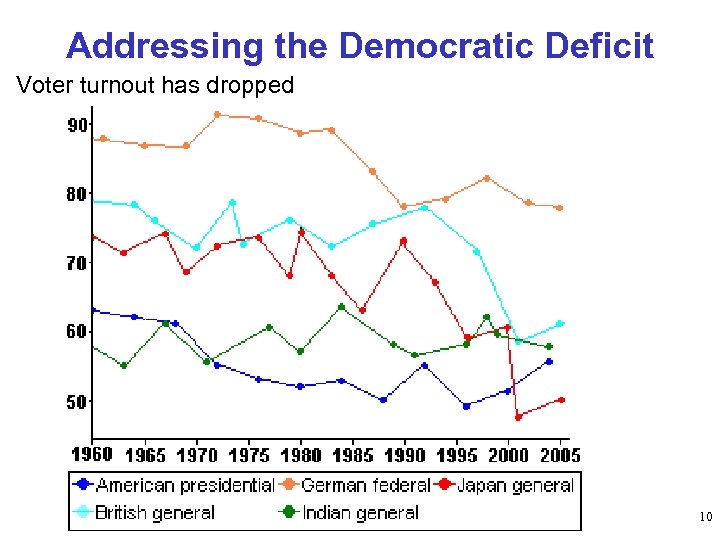
 Addressing the Democratic Deficit (Many facts from essay by Robert Glasgow) Voter turnout has dropped Ø in the United States: § 70% of eligible population register to vote § 50% vote in presidential elections Ø Western Europe: average 77% turnout Ø UK: 60% § Especially low among young, unemployed, ethnic minorities Ø Latin America: 54% Ø Decline almost wholly concentrated among young people Membership in political parties: Ø 1950 s – 3. 5 M Ø 2000 s – 0. 5 M Public Trust in: Ø Politicians 18% Ø Doctors 91% 11
Addressing the Democratic Deficit (Many facts from essay by Robert Glasgow) Voter turnout has dropped Ø in the United States: § 70% of eligible population register to vote § 50% vote in presidential elections Ø Western Europe: average 77% turnout Ø UK: 60% § Especially low among young, unemployed, ethnic minorities Ø Latin America: 54% Ø Decline almost wholly concentrated among young people Membership in political parties: Ø 1950 s – 3. 5 M Ø 2000 s – 0. 5 M Public Trust in: Ø Politicians 18% Ø Doctors 91% 11
 Addressing the Democratic Deficit Participation in new social movements has increased Ø Campaign groups Ø ~1 M demonstrated against Iraq war Ø NGOs (e. g. Amnesty International) Ø Increasingly on the Internet People disillusioned with traditional political system? 12
Addressing the Democratic Deficit Participation in new social movements has increased Ø Campaign groups Ø ~1 M demonstrated against Iraq war Ø NGOs (e. g. Amnesty International) Ø Increasingly on the Internet People disillusioned with traditional political system? 12
 Electronic Participation e. Revolution? Ø Top down benefits: Potential to make citizens § More informed • Streaming footage of debates • Political information § More engaged • Webchats with elected representatives • Online Voting (Estonia and Switzerland) § More trusting Ø Bottom up benefits: Potential for citizens to § Contribute to policy making • Online Questionnaires • Discussion Forums § Propose policies themselves § Hold politicians to account Ø Reach to young people § 30% of 15 -24 yr olds have engaged in online political activity (10% offline) 13
Electronic Participation e. Revolution? Ø Top down benefits: Potential to make citizens § More informed • Streaming footage of debates • Political information § More engaged • Webchats with elected representatives • Online Voting (Estonia and Switzerland) § More trusting Ø Bottom up benefits: Potential for citizens to § Contribute to policy making • Online Questionnaires • Discussion Forums § Propose policies themselves § Hold politicians to account Ø Reach to young people § 30% of 15 -24 yr olds have engaged in online political activity (10% offline) 13
 Electronic Participation Criticisms: Ø Unrealistic Ø Ignores existing political process § De-legitimises existing institutions § Power devolved from elected representatives and placed in hands of administrative side § Politicians may be unable to fulfil campaign promises Ø Ignores problems in web technologies § Easy to set up forum § Hard to analyse and collate results – unrealistic software § Too open to deception/malicious use Ø Some politicians view public participation as a threat 14
Electronic Participation Criticisms: Ø Unrealistic Ø Ignores existing political process § De-legitimises existing institutions § Power devolved from elected representatives and placed in hands of administrative side § Politicians may be unable to fulfil campaign promises Ø Ignores problems in web technologies § Easy to set up forum § Hard to analyse and collate results – unrealistic software § Too open to deception/malicious use Ø Some politicians view public participation as a threat 14
 Electronic Participation “Big Conversation” - http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/uk_politics/3245620. stm Ø 77 -page document setting out challenges faced by Britain Ø Website gives people a chance to air their views on policies Ø Issues: § § Ban workplace smoking? Should rowdy city centre pubs contribute towards policing? Funding in further education and UK How important is the euro to locking in macroeconomic stability? Ø Criticisms: § Merely a publicity stunt § Danger of pressure groups hijacking exercise 15
Electronic Participation “Big Conversation” - http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/uk_politics/3245620. stm Ø 77 -page document setting out challenges faced by Britain Ø Website gives people a chance to air their views on policies Ø Issues: § § Ban workplace smoking? Should rowdy city centre pubs contribute towards policing? Funding in further education and UK How important is the euro to locking in macroeconomic stability? Ø Criticisms: § Merely a publicity stunt § Danger of pressure groups hijacking exercise 15
 Electronic Participation “Big Conversation” - Guardian Article: http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/uk_politics/3245620. stm Ø “For the duration of its life, the Big Conversation website carried not a single comment from a single voter on: § Iraq § Terrorism § Blair's relationship with Bush Ø “Working on this newspaper's Diary column at the time, I was contacted almost daily by people who had attempted to address one of the above issues in either an email or text message (price: 25 p), but whose comments mysteriously never materialised on the site…” Ø “As for those that made it through… § "I am so proud to have voted Labour with my first ever vote a few years ago, " read one comment. "Everywhere I look I see new cars, wealth, opportunities, investment and most favourable mortgage rates. " 16
Electronic Participation “Big Conversation” - Guardian Article: http: //news. bbc. co. uk/1/hi/uk_politics/3245620. stm Ø “For the duration of its life, the Big Conversation website carried not a single comment from a single voter on: § Iraq § Terrorism § Blair's relationship with Bush Ø “Working on this newspaper's Diary column at the time, I was contacted almost daily by people who had attempted to address one of the above issues in either an email or text message (price: 25 p), but whose comments mysteriously never materialised on the site…” Ø “As for those that made it through… § "I am so proud to have voted Labour with my first ever vote a few years ago, " read one comment. "Everywhere I look I see new cars, wealth, opportunities, investment and most favourable mortgage rates. " 16
 e. Government in the Developing World "About 99% of the benefits of having a PC come when you've provided reasonable health and literacy to the person who's going to sit down and use it". Bill Gates, Chairman of Microsoft 17
e. Government in the Developing World "About 99% of the benefits of having a PC come when you've provided reasonable health and literacy to the person who's going to sit down and use it". Bill Gates, Chairman of Microsoft 17
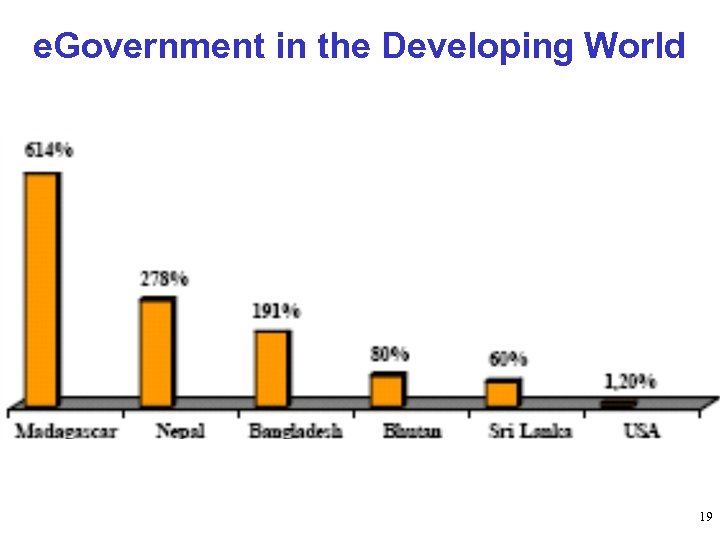
 e. Government in the Developing World 18
e. Government in the Developing World 18
 e. Government in the Developing World 19
e. Government in the Developing World 19
 e. Government in the Developing World Case study in Sri Lanka (by Geeth de Mel): ICT Programme established in 2002 Aims: Ø Improved delivery off social services § Let people access information efficiently Ø Improve inter organisation communication Ø Reducing the vulnerabilities to natural disasters § Example of existing problems: § Tsunami of 2004 – still no accurate figures on affected people § No mechanisms to support aid organisations in immediate aftermath Ø Greater transparency Ø Reduce corruption Ø Increased social participation Ø Empowerment off poor Ø Further socio-economic development 20
e. Government in the Developing World Case study in Sri Lanka (by Geeth de Mel): ICT Programme established in 2002 Aims: Ø Improved delivery off social services § Let people access information efficiently Ø Improve inter organisation communication Ø Reducing the vulnerabilities to natural disasters § Example of existing problems: § Tsunami of 2004 – still no accurate figures on affected people § No mechanisms to support aid organisations in immediate aftermath Ø Greater transparency Ø Reduce corruption Ø Increased social participation Ø Empowerment off poor Ø Further socio-economic development 20
 e. Government in the Developing World Case study in Sri Lanka (by Geeth de Mel): Example Failure/Success Ø Ministry of Education went online with exam results § System poorly planned and crashed § Took department longer than old manual system Ø Success story from same department in 2004 § Introduced new ICT curriculum § Success due to Internet+television+radio (more accessible) 21
e. Government in the Developing World Case study in Sri Lanka (by Geeth de Mel): Example Failure/Success Ø Ministry of Education went online with exam results § System poorly planned and crashed § Took department longer than old manual system Ø Success story from same department in 2004 § Introduced new ICT curriculum § Success due to Internet+television+radio (more accessible) 21
 e. Government in the Developing World Case study in Sri Lanka (by Geeth de Mel): Difficulties Ø Lack cash flow – encourage assistance of 3 rd parties § Vested Interest by 3 rd parties can change project goals Ø Corruption by high ranking officials Ø Schools starting to get computer labs § But not all villages have electricity Ø IT literacy § City: 35% § Rural: <10% Ø Computer ownership § Urban: 10% § Rural: 3% § Estate: 0. 3% 22
e. Government in the Developing World Case study in Sri Lanka (by Geeth de Mel): Difficulties Ø Lack cash flow – encourage assistance of 3 rd parties § Vested Interest by 3 rd parties can change project goals Ø Corruption by high ranking officials Ø Schools starting to get computer labs § But not all villages have electricity Ø IT literacy § City: 35% § Rural: <10% Ø Computer ownership § Urban: 10% § Rural: 3% § Estate: 0. 3% 22
 e. Government in Singapore http: //www. ecitizen. gov. sg/ e. Citizen can Ø do passport application Ø register as resident Ø find jobs in government Ø pay road tax Ø donate to Charities Government’s role changes from manager to service provider Citizens become like customers Dangers: Ø Dependence on technology also brings vulnerability Ø Hackers/terrorists § easier than physical attacks on government Ø privacy 23
e. Government in Singapore http: //www. ecitizen. gov. sg/ e. Citizen can Ø do passport application Ø register as resident Ø find jobs in government Ø pay road tax Ø donate to Charities Government’s role changes from manager to service provider Citizens become like customers Dangers: Ø Dependence on technology also brings vulnerability Ø Hackers/terrorists § easier than physical attacks on government Ø privacy 23
 e. Government Summary • • • Terminology - G 2 C, G 2 B, G 2 E Major areas of G 2 C activities Six stages to implementation Implementation Problems Current state in UK E-Government - Increasing Inequality? Addressing the Democratic Deficit e. Participation e. Government in the Developing World – Sri Lanka e. Government in Singapore 24
e. Government Summary • • • Terminology - G 2 C, G 2 B, G 2 E Major areas of G 2 C activities Six stages to implementation Implementation Problems Current state in UK E-Government - Increasing Inequality? Addressing the Democratic Deficit e. Participation e. Government in the Developing World – Sri Lanka e. Government in Singapore 24


