755075763bfd564039976cc6feda3f5d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12

CS 5038 The Electronic Society Lecture 5: B 2 B Models and Services Lecture Outline • • Concepts and Characteristics of B 2 B Models Sell-Side Marketplaces: One-to-Many Buy Side Marketplaces: One-from-Many Exchanges Managing exchanges Services Hypermediation 1
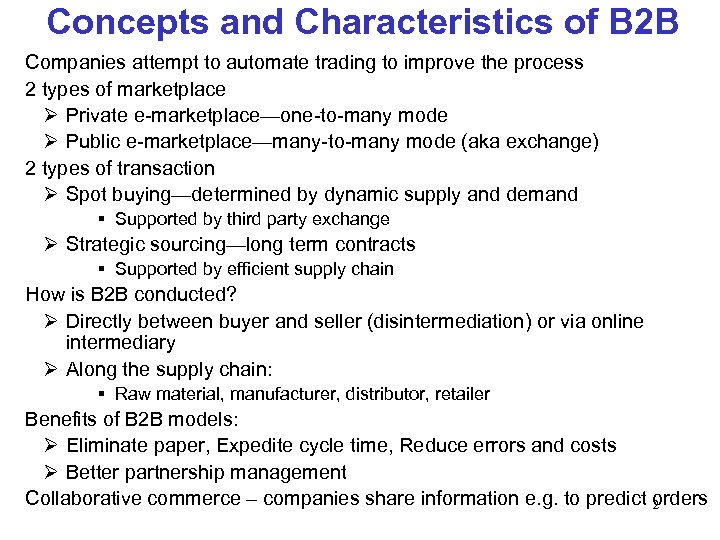
Concepts and Characteristics of B 2 B Companies attempt to automate trading to improve the process 2 types of marketplace Private e-marketplace—one-to-many mode Public e-marketplace—many-to-many mode (aka exchange) 2 types of transaction Spot buying—determined by dynamic supply and demand § Supported by third party exchange Strategic sourcing—long term contracts § Supported by efficient supply chain How is B 2 B conducted? Directly between buyer and seller (disintermediation) or via online intermediary Along the supply chain: § Raw material, manufacturer, distributor, retailer Benefits of B 2 B models: Eliminate paper, Expedite cycle time, Reduce errors and costs Better partnership management Collaborative commerce – companies share information e. g. to predict orders 2

B 2 B Business Models 1. Company-centric models Sell-side marketplace (one-to-many) Buy-side marketplace (many-to-one) 2. Many-to-many marketplaces—the exchange (lecture 6) Buyers and sellers meet to trade 3. Other B 2 B models and services Helping to optimise the value chain Vertical vs. horizontal marketplaces Vertical—one industry or industry section – steel, chemicals Horizontal—service or product used in several industries Virtual service industries in B 2 B Travel and tourism services Online stock trading Real estate Online financing Other online services Electronic payments 3

Sell-Side Marketplaces: One-to-Many Three main methods: 1. Direct sales from catalogs Like B 2 C - Configuration and customisation Successful cases: Dell, Intel, IBM, Cisco 2. Selling via intermediaries 3. Forward Auctions (highest bidder wins) Increases: revenue, page views and membership Can be done on seller’s site or through intermediary § Intermediary services: Search and report all auction activities Calculate billing and handle payment 4

Buy Side: One-from-Many, E-Procurement No equivalent in B 2 C Purchasing agents (buyers) Direct materials - Use material in manufacture § Critical to keep production line running § Usually involves long term relationship with vendor Indirect materials – Maintenance, repairs, operations (MRO) § 20% of cost but 80% of purchased items receive less attention § Inefficiencies in procurement management for MROs § Procurement reengineering – automation; save money; reduce maverick buying - From non contract vendor Buy-Side marketplaces – let the sellers do the work Reverse auctions (lowest bidder wins) § Web based auctions are faster and cheaper – lecture 6 Aggregate suppliers’ catalogs on organisation’s server Group purchasing § Internal aggregation – quantity discounts + less overhead e. g. GE 5 § External aggregation – third party aggregates demand

Exchanges Classification: Direct Material Indirect MROs Systematic Sourcing Vertical Distributors Aggregation, fixed prices Horizontal Distributors Aggregation, fixed prices Spot Sourcing Vertical Exchanges Horizontal Exchanges Matching, Dynamic Pricing (Dynamic pricing = different prices to different customers) Also: Purchasing oriented or selling oriented Ownership Industry Giant – IBM’s patent exchange delphian. com Neutral Entrepreneur – third party intermediary – unbiased § Liquidity = ability to recruit large numbers of buyers/sellers Consortia – several industry players – no one dominates § Purchasing oriented consortia – group of buyers pressure sellers to lower prices § Can also have selling oriented consortia § Legal challenges – anti-trust scrutiny e. g. industry pricing policies § Warning signs: price increases, reduced quality, denial of qualified parties § Response: less information transparency to inhibit access to competitors’ information, participation broadly available, neutral 6 autonomous management

Managing Exchanges Revenue models Transaction fees – commission on each sale Service fees - i. e. level of service: consultancy on policy, phone calls etc. Membership fees – annual or monthly Advertisement fees – ads on the portal Critical Success factors Early liquidity – leads to low transaction fees, increases liquidity § Liquidity refers to volume of business conducted § Business’s chance of survival is best when liquidity is achieved early Openness – organisational and technological (open standards) Targeting right industries – high product search/comparison costs Brand building is critical – because switching costs are low Value added services – industry news, hosting, financial services § Exchanges team up with banks, logistic services and IT companies to help Multiple revenue streams from services lower fees 7

Why Outsource B 2 B Services? Desire to concentrate on core business Need to have services up and running quickly Lack of expertise for support services Economy of scale not possible from inside In-house options do not meet changing demands Too many services for one company to handle 8

B 2 B Services I Consulting Services – for strategy + technology (IBM) Application building services Licensed and incorporated in client system or real-time via ASP Industry standards—XML, XSL (extensible style language) Web Hosting and Other Services Business hosting - popular for SMEs; Large businesses need a dedicated server – dellhost. com Free Web hosting – advertising revenue MSPs – like ASPs but manage IT infrastructure (not applications) Directory services – listings, search engines, matching services 9

B 2 B Services II Order Fulfillment, Logistics, and Supply Chain Services supply chain management and transportation services – e. g. UPS Marketing and advertising Ad server network provider – brokers banner ad sales Electronic wholesalers – intermediary who sells to businesses Infomediaries and Online Data Mining Services Collect consumer data analyse it repackage sell for marketing Clickstream data – monitor user’s clicks Providing content Syndication: knowledge creators use syndicators to distribute content § For dynamic content E. g. news, sports, weather, stock quotes § Cheaper than producing your own content Catalog content § full service exchanges offer catalog services Content maximization and streaming services § companies provide media rich content to reach target audience 10 § E. g. Video clips, Music, Flash media

B 2 B Services III Financial B 2 B services Payment Systems § Purchasing cards – used by governments or universities – geographical limits § Electronic letters of credit (LC) – can work internationally (payment upon presentation of documents that comply with terms) § Trade. Card. com – cheaper than LCs; uses Master. Card’s trusted brand Venture capital to fund EC initiatives – VC firms and “angel investors” § Internet incubators – develop EC initiatives then move on Credit reporting firms Credit intermediaries – guarantee against loss Reintermediation: redefining value added role of traditional intermediaries new electronic intermediaries Cybermediation Hypermediation: intermediaries flourishing Content providers Affiliate sites Search engines Portals ISPs Software makers Other entities in future 11
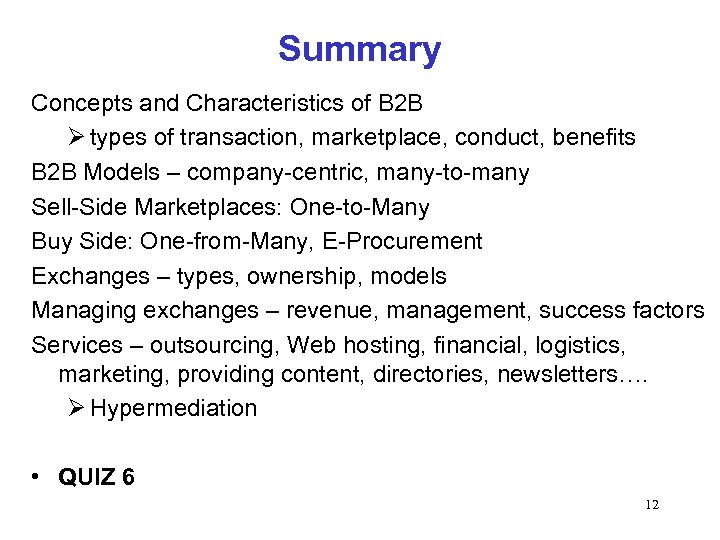
Summary Concepts and Characteristics of B 2 B types of transaction, marketplace, conduct, benefits B 2 B Models – company-centric, many-to-many Sell-Side Marketplaces: One-to-Many Buy Side: One-from-Many, E-Procurement Exchanges – types, ownership, models Managing exchanges – revenue, management, success factors Services – outsourcing, Web hosting, financial, logistics, marketing, providing content, directories, newsletters…. Hypermediation • QUIZ 6 12
755075763bfd564039976cc6feda3f5d.ppt