48fc46fa5d5de7a2450250147c1853ce.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 CS 5038 The Electronic Society Lecture 3: Serving the Customer Lecture Outline • • • Consumer Behaviour Demographics of Internet Surfers Major Roles in Purchasing decision-making model Consumer Satisfaction One-to-One Marketing Personalisation Customer Service Market Research Data Mining Intelligent Agents 1
CS 5038 The Electronic Society Lecture 3: Serving the Customer Lecture Outline • • • Consumer Behaviour Demographics of Internet Surfers Major Roles in Purchasing decision-making model Consumer Satisfaction One-to-One Marketing Personalisation Customer Service Market Research Data Mining Intelligent Agents 1
 Consumer Behaviour 2 Prentice Hall, 2002
Consumer Behaviour 2 Prentice Hall, 2002
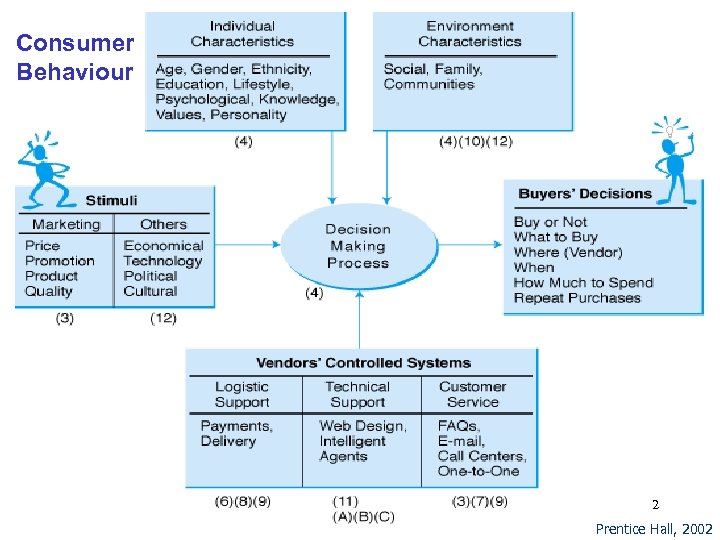
 Consumer Behavior Online Consumer types Ø Individual consumers § Commands most of the media’s attention Ø Organizational buyers § Governments and public organizations § Private corporations § Resellers Purchasing types and experiences Ø 2 dimensions of shopping experiences § Utilitarian—to achieve a goal § Hedonic—because it’s fun Ø 3 categories of consumers § Impulsive buyers—purchase quickly § Patient buyers—make some comparisons first § Analytical buyers—do substantial research before buying 3
Consumer Behavior Online Consumer types Ø Individual consumers § Commands most of the media’s attention Ø Organizational buyers § Governments and public organizations § Private corporations § Resellers Purchasing types and experiences Ø 2 dimensions of shopping experiences § Utilitarian—to achieve a goal § Hedonic—because it’s fun Ø 3 categories of consumers § Impulsive buyers—purchase quickly § Patient buyers—make some comparisons first § Analytical buyers—do substantial research before buying 3
 Demographics of Internet Surfers Environmental variables Ø Social variables – influenced by peers Ø Cultural variables Ø Psychological variables Ø Other environmental variables - e. g. government restrictions Personal characteristics / demographics Ø Consumer resources and lifestyle Ø Age; gender; marital status Ø Knowledge and educational level Ø Attitudes and values Ø Motivation Ø Personality Ø Ethnicity More experience on Web more to buy online Two major reasons people do not buy online Ø Security Ø Difficulty judging the quality of the product 4
Demographics of Internet Surfers Environmental variables Ø Social variables – influenced by peers Ø Cultural variables Ø Psychological variables Ø Other environmental variables - e. g. government restrictions Personal characteristics / demographics Ø Consumer resources and lifestyle Ø Age; gender; marital status Ø Knowledge and educational level Ø Attitudes and values Ø Motivation Ø Personality Ø Ethnicity More experience on Web more to buy online Two major reasons people do not buy online Ø Security Ø Difficulty judging the quality of the product 4
 Major Roles in Purchasing 5 major roles ØInitiator § Suggests/thinks of buying a particular product or service ØInfluencer § Advice/views carry weight in making a final buying decision ØDecider § Makes a buying decision or any part of it ØBuyer § Makes the actual purchase ØUser § Consumes or uses a product or service 5
Major Roles in Purchasing 5 major roles ØInitiator § Suggests/thinks of buying a particular product or service ØInfluencer § Advice/views carry weight in making a final buying decision ØDecider § Makes a buying decision or any part of it ØBuyer § Makes the actual purchase ØUser § Consumes or uses a product or service 5
 Purchasing decision-making model 5 major phases Ø Need identification § marketer must get customer to recognise need § Banner and URL advertising, community discussions Ø Information search § Web directories, search engines Ø Alternatives evaluation § Newsgroup discussions, cross-site comparisons Ø Purchase and delivery § Electronic cash, virtual banking Ø After-purchase evaluation—customer service § Discussions in newsgroups 6
Purchasing decision-making model 5 major phases Ø Need identification § marketer must get customer to recognise need § Banner and URL advertising, community discussions Ø Information search § Web directories, search engines Ø Alternatives evaluation § Newsgroup discussions, cross-site comparisons Ø Purchase and delivery § Electronic cash, virtual banking Ø After-purchase evaluation—customer service § Discussions in newsgroups 6
 Consumer Satisfaction 7 Prentice Hall, 2002
Consumer Satisfaction 7 Prentice Hall, 2002
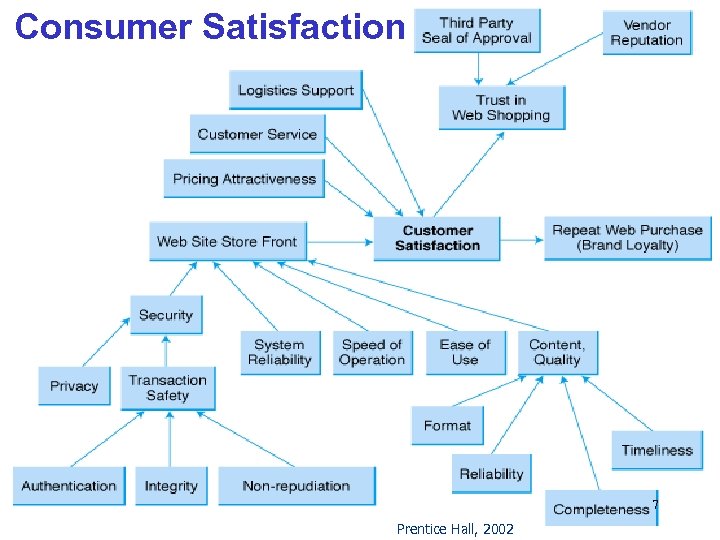
 One-to-One Marketing Build a long term association Meeting customers cognitive needs Ø Customer may have novice, intermediate or expert skill E-loyalty—customer’s loyalty to an e-tailer Ø costs Amazon $15 to acquire a new customer Ø costs Amazon $2 to $4 to keep an existing customer Trust in EC Ø Deterrence-based —threat of punishment Ø Knowledge-based —reputation Ø Identification-based —empathy and common values Ø Referrals – Viral Marketing Personalisation… 8
One-to-One Marketing Build a long term association Meeting customers cognitive needs Ø Customer may have novice, intermediate or expert skill E-loyalty—customer’s loyalty to an e-tailer Ø costs Amazon $15 to acquire a new customer Ø costs Amazon $2 to $4 to keep an existing customer Trust in EC Ø Deterrence-based —threat of punishment Ø Knowledge-based —reputation Ø Identification-based —empathy and common values Ø Referrals – Viral Marketing Personalisation… 8
 Personalisation - Marketing Model “Treat different customers differently” 9 Prentice Hall, 2002
Personalisation - Marketing Model “Treat different customers differently” 9 Prentice Hall, 2002
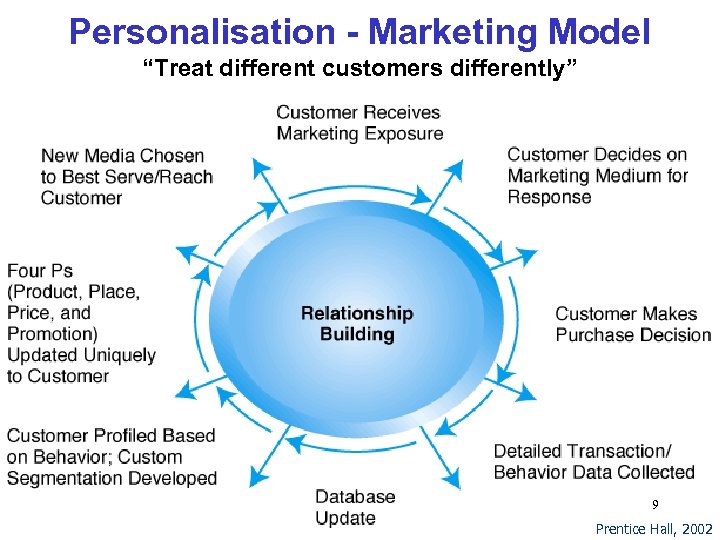
 Personalisation “Process of matching content, services, or products to individuals’ preferences” Build profiles – N. B. Privacy Issues Ø Solicit information from users Ø Use cookies to observe online behavior Ø Use data or Web mining Personalisation applied through Ø Ø Rule-based filtering (35
Personalisation “Process of matching content, services, or products to individuals’ preferences” Build profiles – N. B. Privacy Issues Ø Solicit information from users Ø Use cookies to observe online behavior Ø Use data or Web mining Personalisation applied through Ø Ø Rule-based filtering (35
 Customer Service • • • Provide search and comparison capabilities Provide free products and services Provide specialized information and services – ge. com Allow customers to order customized products and services – dell. com Enable customers to track accounts or order status – e. g. Fed. Ex, Amazon Personalized Web pages - record purchases and preferences – aa. com FAQs - Customers find answers quickly Troubleshooting tools—assist customers in solving their own problems Chat rooms — discuss with experts and other customers E-mail (most popular: inexpensive and fast) and automated response Help desks and call centers Ø Well trained personnel with access to customer history, purchases • Metrics—standards to determine appropriate level of support Ø Response to problem (hours for human, real-time for agents) Ø Site availability and download times (<30 seconds) Ø Up-to-date site and availability of relevant content Ø Order fulfillment – fast 11 Ø Return policy
Customer Service • • • Provide search and comparison capabilities Provide free products and services Provide specialized information and services – ge. com Allow customers to order customized products and services – dell. com Enable customers to track accounts or order status – e. g. Fed. Ex, Amazon Personalized Web pages - record purchases and preferences – aa. com FAQs - Customers find answers quickly Troubleshooting tools—assist customers in solving their own problems Chat rooms — discuss with experts and other customers E-mail (most popular: inexpensive and fast) and automated response Help desks and call centers Ø Well trained personnel with access to customer history, purchases • Metrics—standards to determine appropriate level of support Ø Response to problem (hours for human, real-time for agents) Ø Site availability and download times (<30 seconds) Ø Up-to-date site and availability of relevant content Ø Order fulfillment – fast 11 Ø Return policy
 Market Research for EC Market segmentation - divide consumer market into groups to conduct marketing research, advertising, sales Ø E. g. by geography, demographics or psychographics § (psychological characterization: the study of the psychological profiles of potential buyers of a product, to improve its marketing) Ø Tailor mailing campaigns to each segment Ø Easier and cheaper than one-one personalisation Online market research methods Ø Conducting Web-based surveys Ø Track customer activities – possibly illegal Limitations of online research Ø Skewed toward educated males with high income Ø >40% answers to questionnaires inaccurate How to analyse the gathered data? Data Mining… 12
Market Research for EC Market segmentation - divide consumer market into groups to conduct marketing research, advertising, sales Ø E. g. by geography, demographics or psychographics § (psychological characterization: the study of the psychological profiles of potential buyers of a product, to improve its marketing) Ø Tailor mailing campaigns to each segment Ø Easier and cheaper than one-one personalisation Online market research methods Ø Conducting Web-based surveys Ø Track customer activities – possibly illegal Limitations of online research Ø Skewed toward educated males with high income Ø >40% answers to questionnaires inaccurate How to analyse the gathered data? Data Mining… 12
 Data Mining searching for valuable information in extremely large databases Automated prediction of trends and behaviors Ø Example: from data on past promotional mailings, find out targets most likely to respond in future Automated discovery of previously unknown patterns Ø Example: find seemingly unrelated products often purchased together Ø Example: Find anomalous data representing data entry errors Mining tools: Ø Neural computing Ø Intelligent agents Ø Association analysis - statistical rules Web Mining - Mining meaningful patterns from Web resources Ø Web content mining – searching Web documents 13 Ø Web usage mining – searching Web access logs
Data Mining searching for valuable information in extremely large databases Automated prediction of trends and behaviors Ø Example: from data on past promotional mailings, find out targets most likely to respond in future Automated discovery of previously unknown patterns Ø Example: find seemingly unrelated products often purchased together Ø Example: Find anomalous data representing data entry errors Mining tools: Ø Neural computing Ø Intelligent agents Ø Association analysis - statistical rules Web Mining - Mining meaningful patterns from Web resources Ø Web content mining – searching Web documents 13 Ø Web usage mining – searching Web access logs
 Intelligent Agents in Customer Applications Need identification - determine what to buy to satisfy a need Ø looks for product information and evaluates - Querybot. com Product brokering – find best product to match need Merchant brokering - find vendor offering best deal Ø Jango (embedded in excite program) Negotiation - determine price and other terms of transaction Ø Kasbah - users create agents for selling or buying goods Purchase and delivery—arrange payment and delivery of goods After sale service and evaluation - automatic answering Auction support agents Fraud and detection protection agents – e. Falcon Character-based interactive (animated) agents – extempo. com Future agents - Delegation 14
Intelligent Agents in Customer Applications Need identification - determine what to buy to satisfy a need Ø looks for product information and evaluates - Querybot. com Product brokering – find best product to match need Merchant brokering - find vendor offering best deal Ø Jango (embedded in excite program) Negotiation - determine price and other terms of transaction Ø Kasbah - users create agents for selling or buying goods Purchase and delivery—arrange payment and delivery of goods After sale service and evaluation - automatic answering Auction support agents Fraud and detection protection agents – e. Falcon Character-based interactive (animated) agents – extempo. com Future agents - Delegation 14
 Summary Consumer Behaviour – characteristics, stimuli decisions Consumer Behavior Online – consumer types and purchasing experiences Demographics of Internet Surfers – environmental, personal Major Roles in Purchasing – 5 roles Purchasing decision-making model – 5 stages Consumer Satisfaction loyalty One-to-One Marketing Personalisation – build profiles, filter information Customer Service – personalised information, help desks Market Research – surveys, surreptitious tracking Data Mining – extracting useful information about customers Intelligent Agents – gather data, facilitate customer 15
Summary Consumer Behaviour – characteristics, stimuli decisions Consumer Behavior Online – consumer types and purchasing experiences Demographics of Internet Surfers – environmental, personal Major Roles in Purchasing – 5 roles Purchasing decision-making model – 5 stages Consumer Satisfaction loyalty One-to-One Marketing Personalisation – build profiles, filter information Customer Service – personalised information, help desks Market Research – surveys, surreptitious tracking Data Mining – extracting useful information about customers Intelligent Agents – gather data, facilitate customer 15
 QUIZ 4 16
QUIZ 4 16


