eaa81623101fb9574f212d9af7628b5b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27

CS 161 INTRO TO PROGRAMMING I Dr. Blaise W. Liffick Fall 2014 1
Programming Techniques Languages Problem Analysis Program Design • Algorithms & Design Patterns • Data Structures Paradigms Java C++ Hardware Network Linux Eclipse Programming Environments 2

Early Computers • Late 1930’s, John Atanasoff, Clifford Berry • ENIAC – 1946 – University of Pennsylvania – J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchley – John von Neumann, stored-program concept and use of binary 3
Categories of Computers • • • Supercomputers Mainframe Minicomputers Microcomputers Mobile devices Power Size Cost 4
Computer Hardware • CPU - central processing unit – Where decisions are made, computations are performed, and input/output requests are delegated • Main Memory – Stores information being processed by the CPU • Secondary Memory (Mass Storage) – Stores data and programs 5

Computer Hardware • Input devices – Allow people to supply information to computers • Output devices – Allow people to receive information from computers • Peripheral Devices – Generally I/O, mass storage • Network connection – Modems – Ethernet interface 6
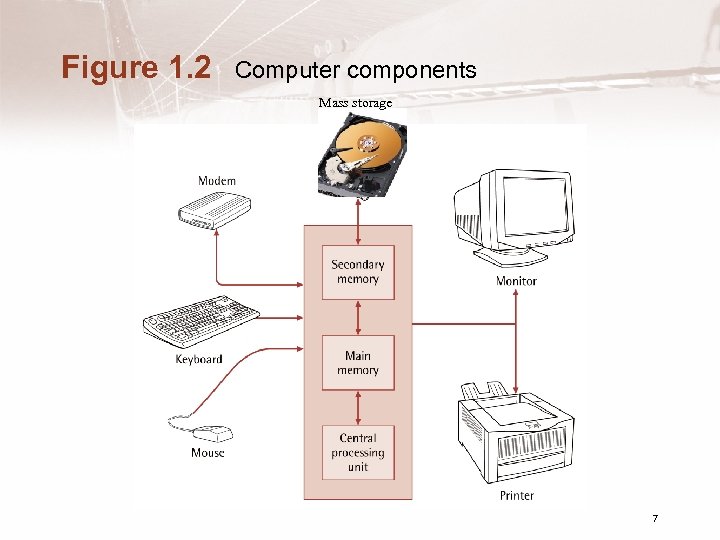
Figure 1. 2 Computer components Mass storage 7
CPU • “Brains” of the computer – Arithmetic calculations are performed using the Arithmetic/Logical Unit or ALU – Control unit decodes and executes instructions – Registers hold information and instructions for CPU to process • Arithmetic operations are performed using binary number system 8
Memory • Stores – programs • operating system • applications – data • Types – RAM - volatile – ROM • Composed of bits, which are combined into bytes 9
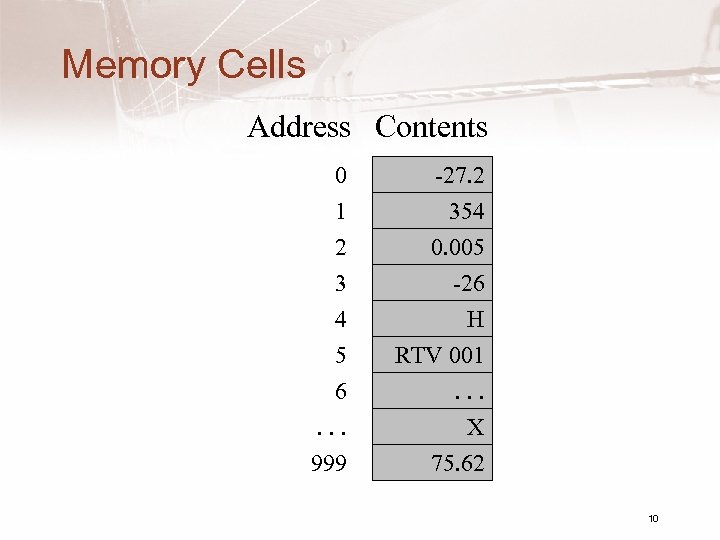
Memory Cells Address Contents 0 1 2 3 4 5 6. . . 999 -27. 2 354 0. 005 -26 H RTV 001. . . X 75. 62 10
Input / Output Devices • Accessories that allow computer to perform specific tasks – Receiving information for processing – Return the results of processing • Common input and output devices – Keyboard – Printer Joystick Monitor Scanner Speaker 11

Computer Networks • Allows multiple computers to connect together to share resources and/or data • LAN - Local area network – Organizational • WAN - Wide area network – Internet • Requires additional hardware – modem – network interface – servers 12

The “Cloud” • Wireless access – Wi. Fi – Cell • Servers – Storage – Applications 13

World Wide Web • Introduced 1989 • Developed by CERN – European Laboratory for Particle Physics • Web browser - GUI – Netscape – IE – Firefox 14

1. 3 Computer Software • Operating system • Other system software – utilities – programming language systems • Applications 15

Operating System • E. g. Windows®, Linux, Mac OS X, Unix® • Controls – the interaction of system with the user – hardware interactions • Part is usually stored on ROM, rest on hard drive – This arrangement requires booting the system 16

Some OS Responsibilities • Communicating with the user; receiving user commands • Managing allocation of memory, processor time, file system, and other resources • Collecting input from keyboard, mouse, etc. • Conveying output to screen, printer, etc. • Writing data to secondary storage devices 17

Application Software • Does the “real” work • Common application software – Word processors – Desktop publishing programs – Spreadsheets – Presentation managers – Drawing programs 18

Programming Languages • Machine Language – Most fundamental language of the computer – Unique for each processor type – Binary 0 s and 1 s that specify what to do • 0010 0000 0100 • 1000 0000 0101 • 0011 0000 0110 19
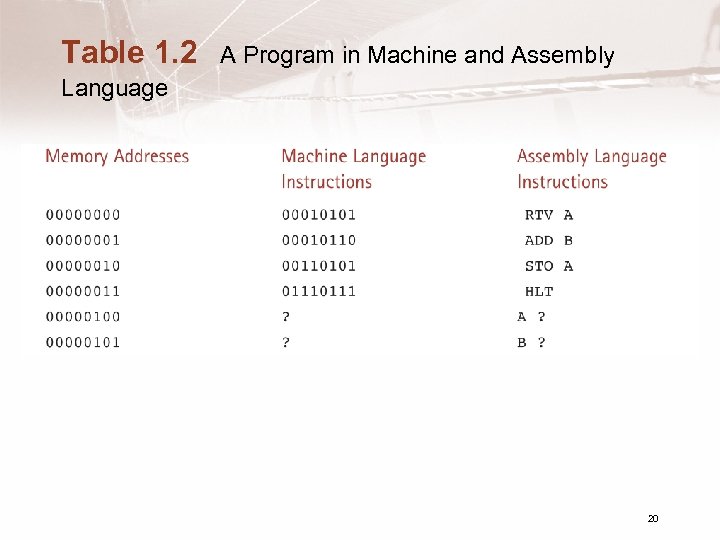
Table 1. 2 A Program in Machine and Assembly Language 20

High - Level Languages • Resemble human language – Java, C++, C, Pascal, FORTRAN, Ada a = a + b; • More compact and human understandable than machine language • Must be translated into machine language 21

1. 4 Processing a High-Level Language Program • Set of programs used to develop software • A key component is a translator – Compiler • Examples – Java, g++, Microsoft Visual C++® • Other programs needed – Editor – Linker – Loader IDE (e. g. Eclipse) 22

Processing a Program • Editor used to enter the program – Like minimal word processor – Creates source program file • Compiler translates the source program – Displays syntax errors – Creates (usually) temporary object code file • Linker/Loader to combine object file with other object files and execute program – Creates final executable program 23

Executing a Program • CPU – examines each program instruction in memory – sends out command signals required to carry out the instruction • Special instructions used to – input data into memory for the program to use – output data to display or printer (or other device) 24
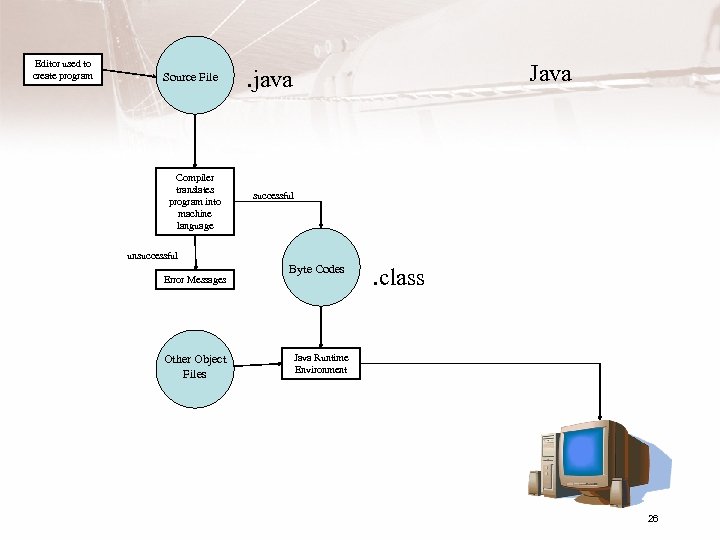
Editor used to create program Source File Compiler translates program into machine language Java . java successful unsuccessful Error Messages Other Object Files Byte Codes . class Java Runtime Environment 26

1. 5 Software Development Method 1. Problem Analysis – Identify data objects – Determine Input / Output data – Constraints on the problem 2. Design – Decompose into smaller problems – Top-down design (divide and conquer) – Develop Algorithm (Desk check) • Algorithm refinement 27

Software Development Method 3. Implementation Converting the algorithm into programming language 4. Testing – Verify the program meets requirements – System and Unit test 5. Maintenance – All programs undergo change over time 28
eaa81623101fb9574f212d9af7628b5b.ppt