f6690f358a26b07939867e3236052668.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 CS 102 – GUI AWT & Swing • • Components & Containers, Layout Managers, Events & Listeners MVC design pattern. David Davenport
CS 102 – GUI AWT & Swing • • Components & Containers, Layout Managers, Events & Listeners MVC design pattern. David Davenport
 IMPORTANT… n Students… This presentation is designed to be used in class as part of a guided discovery sequence. It is not selfexplanatory! Please use it only for revision purposes after having taken the class. Simply flicking through the slides will teach you nothing. You must be actively thinking, doing and questioning to learn! n Instructors… You are free to use this presentation in your classes and to make any modifications to it that you wish. All I ask is an email saying where and when it is/was used. I would also appreciate any suggestions you may have for improving it. thank you, David.
IMPORTANT… n Students… This presentation is designed to be used in class as part of a guided discovery sequence. It is not selfexplanatory! Please use it only for revision purposes after having taken the class. Simply flicking through the slides will teach you nothing. You must be actively thinking, doing and questioning to learn! n Instructors… You are free to use this presentation in your classes and to make any modifications to it that you wish. All I ask is an email saying where and when it is/was used. I would also appreciate any suggestions you may have for improving it. thank you, David.
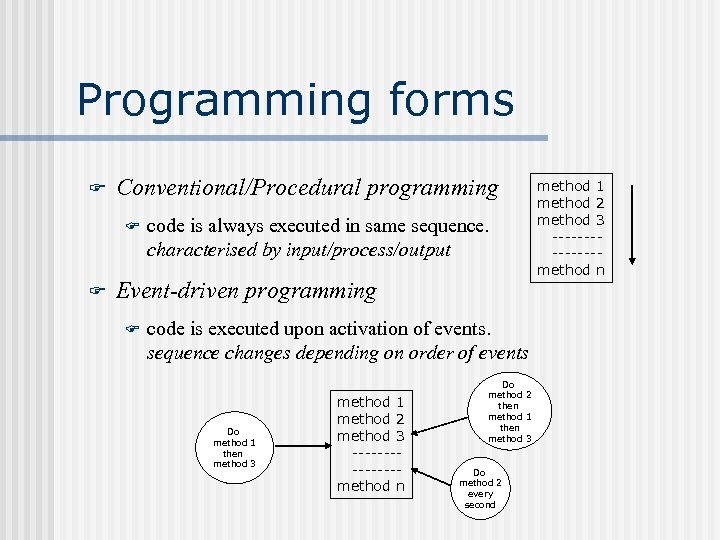 Programming forms F Conventional/Procedural programming F F code is always executed in same sequence. characterised by input/process/output Event-driven programming F code is executed upon activation of events. sequence changes depending on order of events Do method 1 then method 3 method 1 method 2 method 3 -------method n Do method 2 then method 1 then method 3 Do method 2 every second method 1 method 2 method 3 -------method n
Programming forms F Conventional/Procedural programming F F code is always executed in same sequence. characterised by input/process/output Event-driven programming F code is executed upon activation of events. sequence changes depending on order of events Do method 1 then method 3 method 1 method 2 method 3 -------method n Do method 2 then method 1 then method 3 Do method 2 every second method 1 method 2 method 3 -------method n
 GUI USING AWT
GUI USING AWT
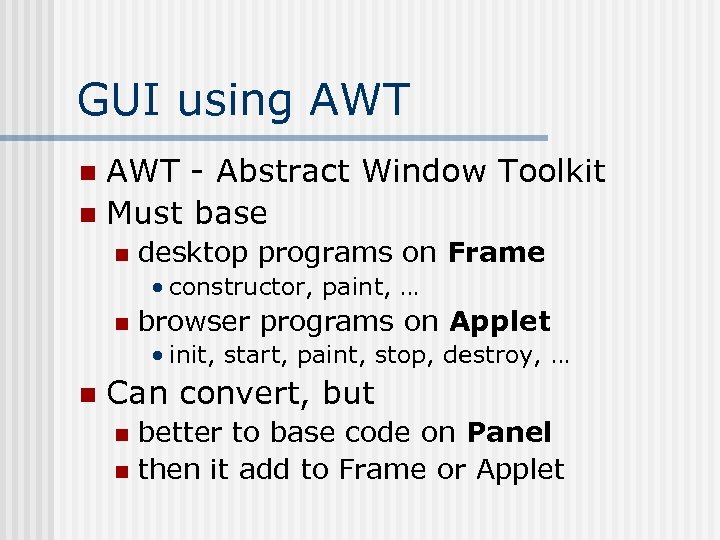 GUI using AWT - Abstract Window Toolkit n Must base n n desktop programs on Frame • constructor, paint, … n browser programs on Applet • init, start, paint, stop, destroy, … n Can convert, but better to base code on Panel n then it add to Frame or Applet n
GUI using AWT - Abstract Window Toolkit n Must base n n desktop programs on Frame • constructor, paint, … n browser programs on Applet • init, start, paint, stop, destroy, … n Can convert, but better to base code on Panel n then it add to Frame or Applet n
 Implementing GUIs n Two steps (1) Create the interface • By add components & containers • & using layout managers (2) Add interaction • Create event listeners • & “Wire-up” events
Implementing GUIs n Two steps (1) Create the interface • By add components & containers • & using layout managers (2) Add interaction • Create event listeners • & “Wire-up” events
 (1) CREATE THE INTERFACE…
(1) CREATE THE INTERFACE…
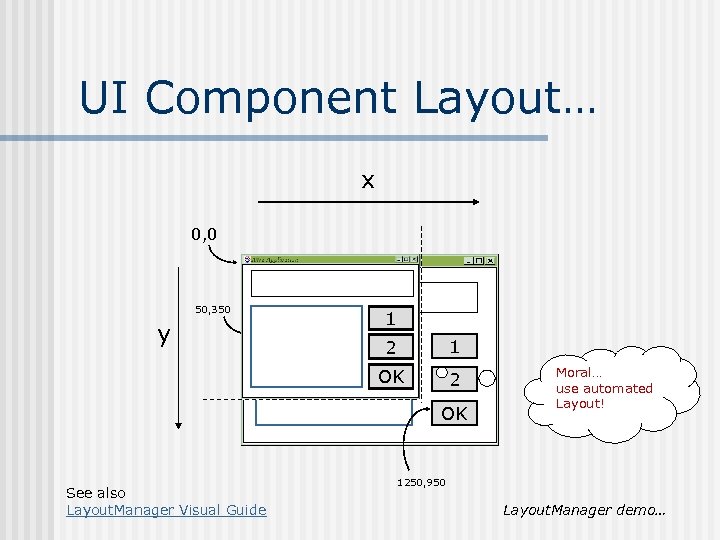 UI Component Layout… x 0, 0 50, 350 y 1 2 1 OK 2 OK See also Layout. Manager Visual Guide Moral… use automated Layout! 1250, 950 Layout. Manager demo…
UI Component Layout… x 0, 0 50, 350 y 1 2 1 OK 2 OK See also Layout. Manager Visual Guide Moral… use automated Layout! 1250, 950 Layout. Manager demo…
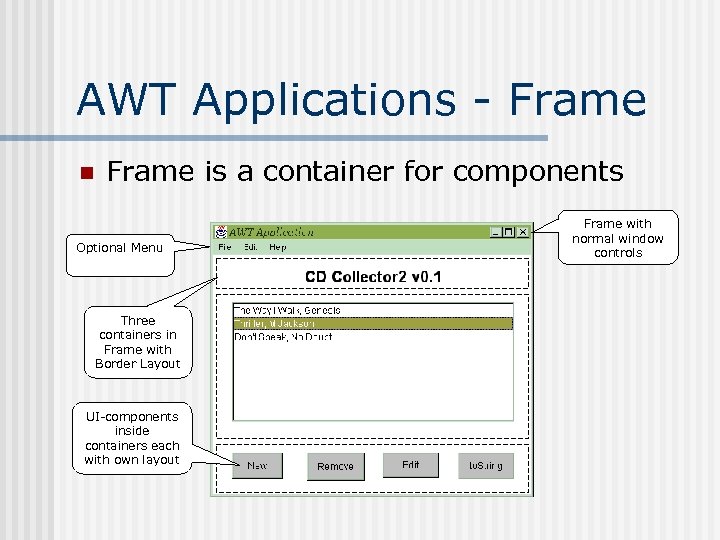 AWT Applications - Frame n Frame is a container for components Optional Menu Three containers in Frame with Border Layout UI-components inside containers each with own layout Frame with normal window controls
AWT Applications - Frame n Frame is a container for components Optional Menu Three containers in Frame with Border Layout UI-components inside containers each with own layout Frame with normal window controls
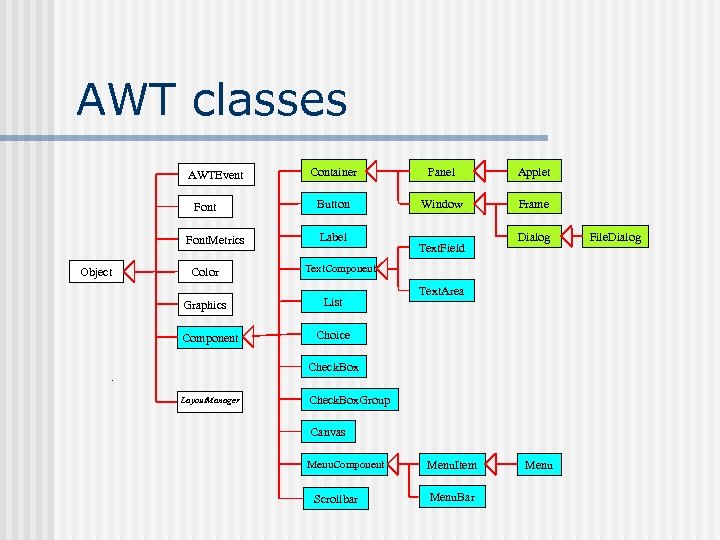 AWT classes AWTEvent Font. Metrics Object Color Graphics Component Container Panel Applet Button Window Frame Label Text. Field Dialog Text. Component List Text. Area Choice Check. Box Layout. Manager Check. Box. Group Canvas Menu. Component Scrollbar Menu. Item Menu. Bar Menu File. Dialog
AWT classes AWTEvent Font. Metrics Object Color Graphics Component Container Panel Applet Button Window Frame Label Text. Field Dialog Text. Component List Text. Area Choice Check. Box Layout. Manager Check. Box. Group Canvas Menu. Component Scrollbar Menu. Item Menu. Bar Menu File. Dialog
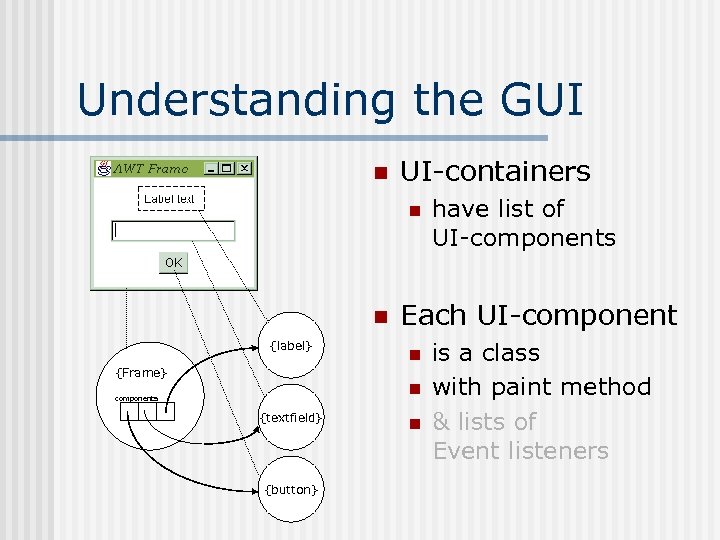 Understanding the GUI n UI-containers n n {label} Each UI-component n {Frame} n components {textfield} {button} have list of UI-components n is a class with paint method & lists of Event listeners
Understanding the GUI n UI-containers n n {label} Each UI-component n {Frame} n components {textfield} {button} have list of UI-components n is a class with paint method & lists of Event listeners
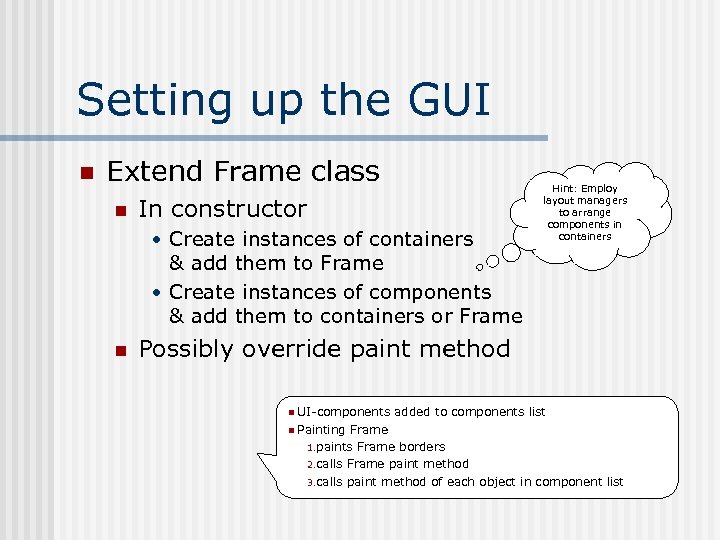 Setting up the GUI n Extend Frame class n In constructor • Create instances of containers & add them to Frame • Create instances of components & add them to containers or Frame n Hint: Employ layout managers to arrange components in containers Possibly override paint method n UI-components n Painting added to components list Frame 1. paints Frame borders 2. calls Frame paint method 3. calls paint method of each object in component list
Setting up the GUI n Extend Frame class n In constructor • Create instances of containers & add them to Frame • Create instances of components & add them to containers or Frame n Hint: Employ layout managers to arrange components in containers Possibly override paint method n UI-components n Painting added to components list Frame 1. paints Frame borders 2. calls Frame paint method 3. calls paint method of each object in component list
 (2) ADD INTERACTION…
(2) ADD INTERACTION…
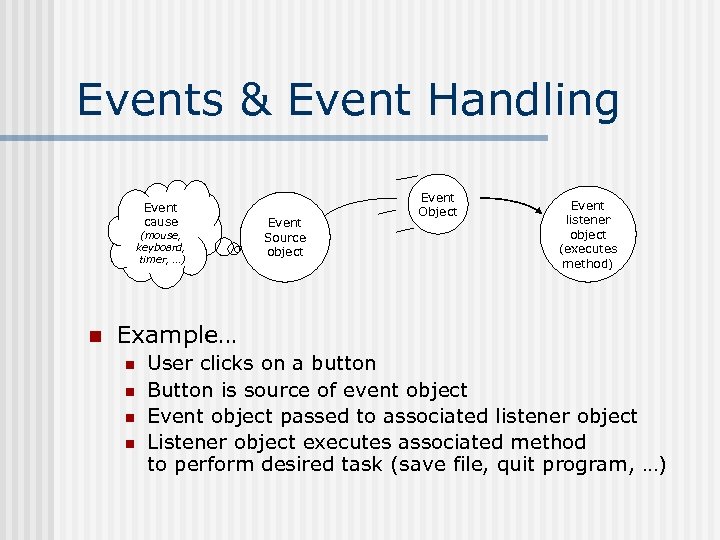 Events & Event Handling Event cause (mouse, keyboard, timer, …) n Event Source object Event Object Event listener object (executes method) Example… n n User clicks on a button Button is source of event object Event object passed to associated listener object Listener object executes associated method to perform desired task (save file, quit program, …)
Events & Event Handling Event cause (mouse, keyboard, timer, …) n Event Source object Event Object Event listener object (executes method) Example… n n User clicks on a button Button is source of event object Event object passed to associated listener object Listener object executes associated method to perform desired task (save file, quit program, …)
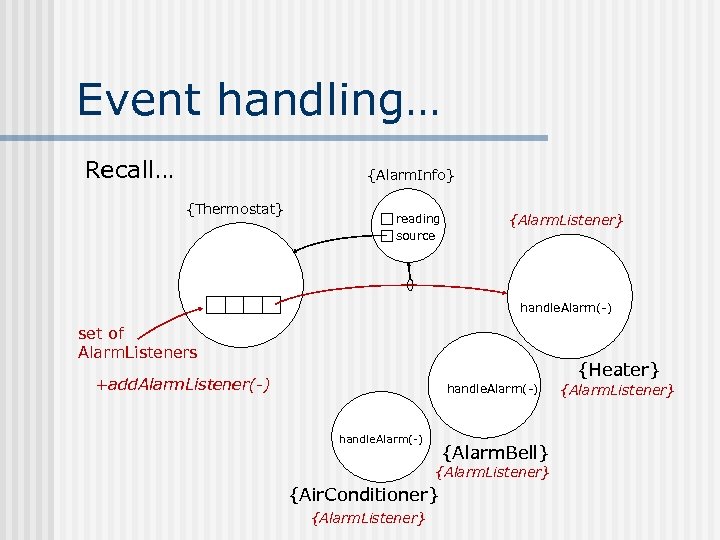 Event handling… Recall… {Alarm. Info} {Thermostat} reading source {Alarm. Listener} handle. Alarm(-) set of Alarm. Listeners {Heater} +add. Alarm. Listener(-) handle. Alarm(-) {Alarm. Bell} {Alarm. Listener} {Air. Conditioner} {Alarm. Listener}
Event handling… Recall… {Alarm. Info} {Thermostat} reading source {Alarm. Listener} handle. Alarm(-) set of Alarm. Listeners {Heater} +add. Alarm. Listener(-) handle. Alarm(-) {Alarm. Bell} {Alarm. Listener} {Air. Conditioner} {Alarm. Listener}
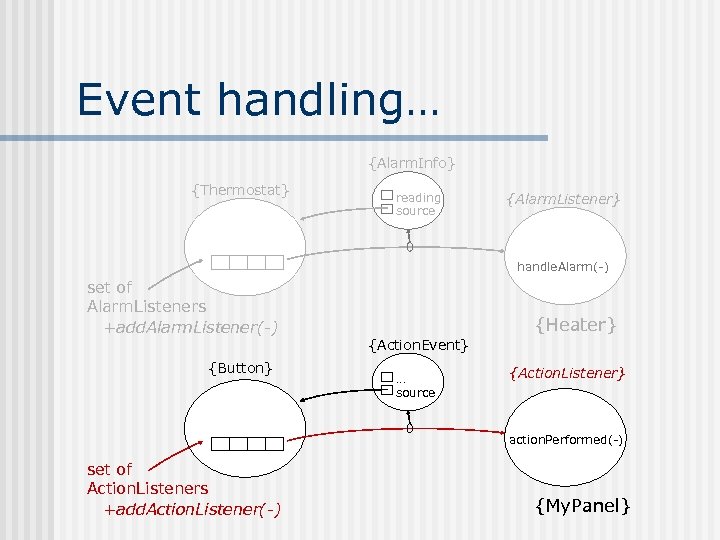 Event handling… {Alarm. Info} {Thermostat} reading source {Alarm. Listener} handle. Alarm(-) set of Alarm. Listeners +add. Alarm. Listener(-) {Button} {Heater} {Action. Event} … source {Action. Listener} action. Performed(-) set of Action. Listeners +add. Action. Listener(-) {My. Panel}
Event handling… {Alarm. Info} {Thermostat} reading source {Alarm. Listener} handle. Alarm(-) set of Alarm. Listeners +add. Alarm. Listener(-) {Button} {Heater} {Action. Event} … source {Action. Listener} action. Performed(-) set of Action. Listeners +add. Action. Listener(-) {My. Panel}
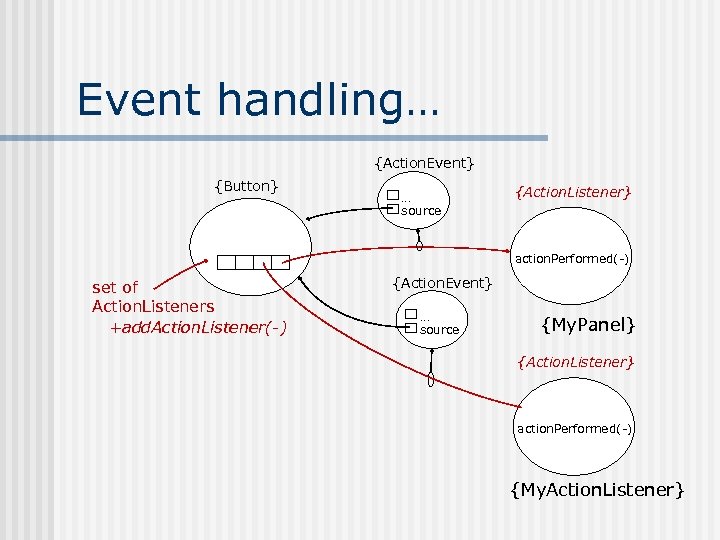 Event handling… {Action. Event} {Button} … source {Action. Listener} action. Performed(-) set of Action. Listeners +add. Action. Listener(-) {Action. Event} … source {My. Panel} {Action. Listener} action. Performed(-) {My. Action. Listener}
Event handling… {Action. Event} {Button} … source {Action. Listener} action. Performed(-) set of Action. Listeners +add. Action. Listener(-) {Action. Event} … source {My. Panel} {Action. Listener} action. Performed(-) {My. Action. Listener}
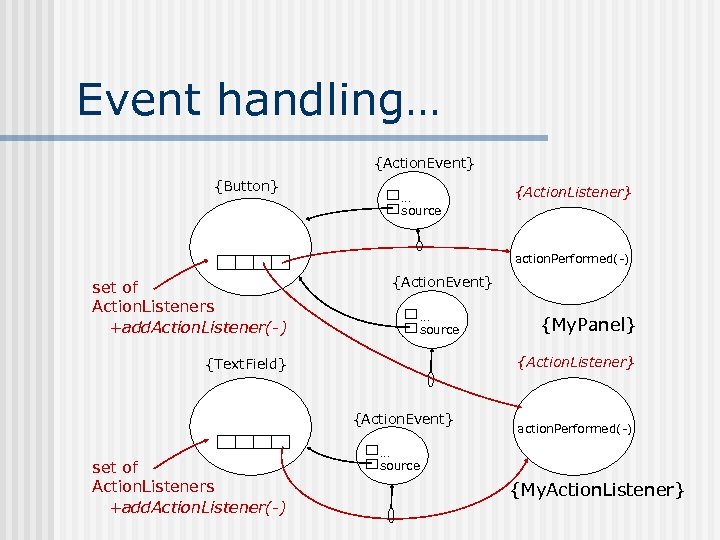 Event handling… {Action. Event} {Button} … source {Action. Listener} action. Performed(-) set of Action. Listeners +add. Action. Listener(-) {Action. Event} … source {Action. Listener} {Text. Field} {Action. Event} set of Action. Listeners +add. Action. Listener(-) {My. Panel} action. Performed(-) … source {My. Action. Listener}
Event handling… {Action. Event} {Button} … source {Action. Listener} action. Performed(-) set of Action. Listeners +add. Action. Listener(-) {Action. Event} … source {Action. Listener} {Text. Field} {Action. Event} set of Action. Listeners +add. Action. Listener(-) {My. Panel} action. Performed(-) … source {My. Action. Listener}
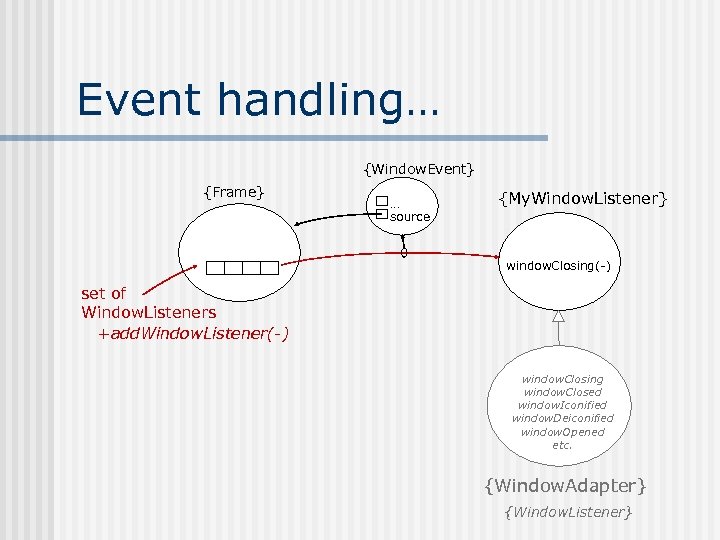 Event handling… {Window. Event} {Frame} … source {My. Window. Listener} window. Closing(-) set of Window. Listeners +add. Window. Listener(-) window. Closing window. Closed window. Iconified window. Deiconified window. Opened etc. {Window. Adapter} {Window. Listener}
Event handling… {Window. Event} {Frame} … source {My. Window. Listener} window. Closing(-) set of Window. Listeners +add. Window. Listener(-) window. Closing window. Closed window. Iconified window. Deiconified window. Opened etc. {Window. Adapter} {Window. Listener}
 Setting up Event Handling n Create listener class n n Using new or existing class, simply Implement desired event listener interface Putting code for desired action in its methods In application n n (e. g. Frame) Create instance of listener class Add as listener of source object • can have any number of listeners for each event • Source & listener can be same object!
Setting up Event Handling n Create listener class n n Using new or existing class, simply Implement desired event listener interface Putting code for desired action in its methods In application n n (e. g. Frame) Create instance of listener class Add as listener of source object • can have any number of listeners for each event • Source & listener can be same object!
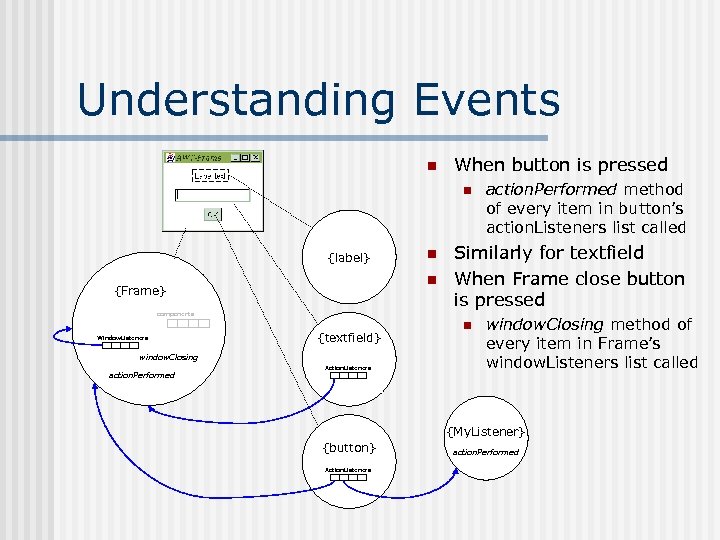 Understanding Events n When button is pressed n {label} n {Frame} components Window. Listeners {textfield} window. Closing action. Performed n Action. Listeners action. Performed method of every item in button’s action. Listeners list called Similarly for textfield When Frame close button is pressed n window. Closing method of every item in Frame’s window. Listeners list called {My. Listener} {button} Action. Listeners action. Performed
Understanding Events n When button is pressed n {label} n {Frame} components Window. Listeners {textfield} window. Closing action. Performed n Action. Listeners action. Performed method of every item in button’s action. Listeners list called Similarly for textfield When Frame close button is pressed n window. Closing method of every item in Frame’s window. Listeners list called {My. Listener} {button} Action. Listeners action. Performed
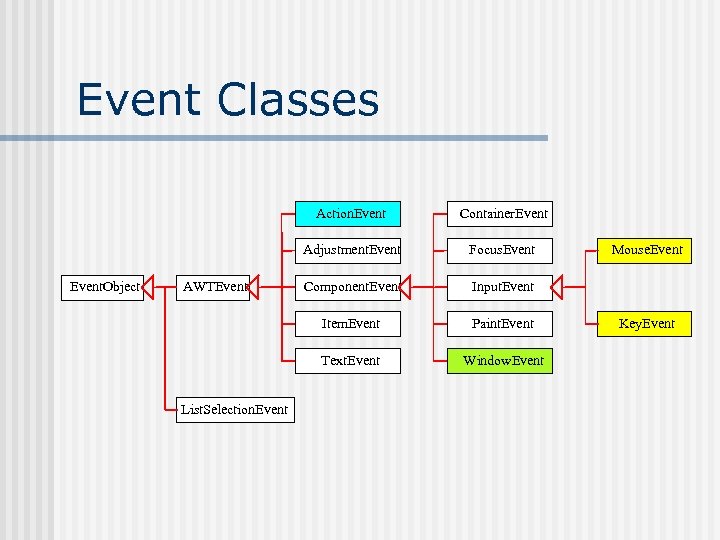 Event Classes Action. Event Adjustment. Event. Object Component. Event Input. Event Paint. Event Text. Event List. Selection. Event Focus. Event Item. Event AWTEvent Container. Event Window. Event Mouse. Event Key. Event
Event Classes Action. Event Adjustment. Event. Object Component. Event Input. Event Paint. Event Text. Event List. Selection. Event Focus. Event Item. Event AWTEvent Container. Event Window. Event Mouse. Event Key. Event
 GUI USING SWING
GUI USING SWING
 GUI using Swing n Advantages n n n OS independent Prettier! More sophisticated components & options • • n n Pluggable “Look & feel” Borders, Tooltips, etc. Drag ‘n Drop File & Color. Choosers, Tables, editors, etc. Conceptually same as AWT Still uses AWT events package
GUI using Swing n Advantages n n n OS independent Prettier! More sophisticated components & options • • n n Pluggable “Look & feel” Borders, Tooltips, etc. Drag ‘n Drop File & Color. Choosers, Tables, editors, etc. Conceptually same as AWT Still uses AWT events package
 GUI using Swing n Few differences (from AWT) n Use javax. swing package (equivalent Swing components start with “J”) n Frames can close automatically n Add components to JFrame’s content. Pane n Override paint. Component, not paint (well sort of…!) (v 1. 5+ no longer explicitly needed) (except for Jframe, JApplet & JDialog) (also, must call super. paint. Component)
GUI using Swing n Few differences (from AWT) n Use javax. swing package (equivalent Swing components start with “J”) n Frames can close automatically n Add components to JFrame’s content. Pane n Override paint. Component, not paint (well sort of…!) (v 1. 5+ no longer explicitly needed) (except for Jframe, JApplet & JDialog) (also, must call super. paint. Component)
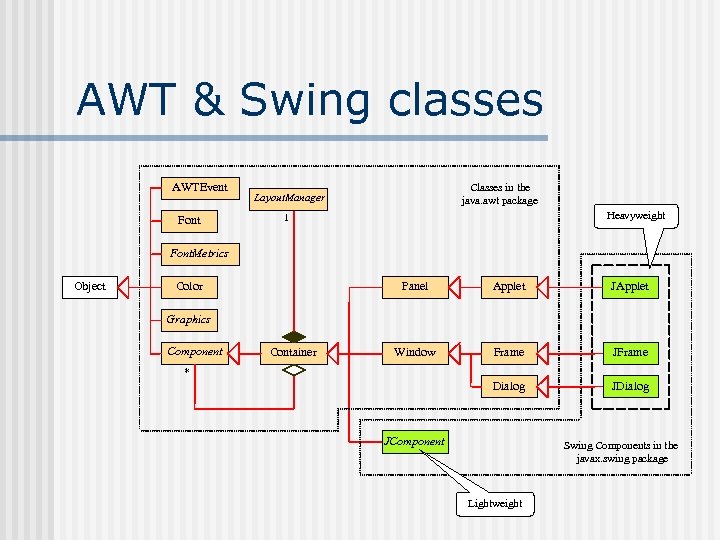 AWT & Swing classes AWTEvent Font Classes in the java. awt package Layout. Manager Heavyweight 1 Font. Metrics Object Color Panel Applet JApplet Window Frame JFrame Dialog JDialog Graphics Component Container * JComponent Swing Components in the javax. swing package Lightweight
AWT & Swing classes AWTEvent Font Classes in the java. awt package Layout. Manager Heavyweight 1 Font. Metrics Object Color Panel Applet JApplet Window Frame JFrame Dialog JDialog Graphics Component Container * JComponent Swing Components in the javax. swing package Lightweight
 Swing - JComponents See this Visual Guide to Swing Components
Swing - JComponents See this Visual Guide to Swing Components
 DESIGNING GUI’S…
DESIGNING GUI’S…
 Design Tips n GUI code can get very messy n Do not put everything in one class (as many Visual IDE’s do) Quick & dirty = impossible to change! n Employ design patterns, e. g. MVC n n Think Design first. . .
Design Tips n GUI code can get very messy n Do not put everything in one class (as many Visual IDE’s do) Quick & dirty = impossible to change! n Employ design patterns, e. g. MVC n n Think Design first. . .
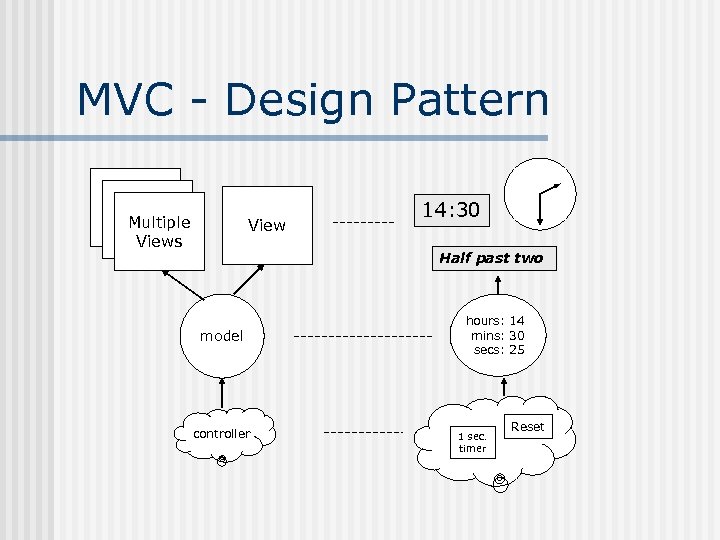 MVC - Design Pattern View Multiple Views View 14: 30 Half past two model controller hours: 14 mins: 30 secs: 25 1 sec. timer Reset
MVC - Design Pattern View Multiple Views View 14: 30 Half past two model controller hours: 14 mins: 30 secs: 25 1 sec. timer Reset
 Design Tips n Think & design first n n Use layout managers Use OOP • begin with Panel rather than Frame/Applet • then add instance(s) to whichever you want • What do you want? • What existing class is closest? • Extend it! • digital clock view - centered text in plain box, extend label • analogue clock view - graphics in plain box, extend panel
Design Tips n Think & design first n n Use layout managers Use OOP • begin with Panel rather than Frame/Applet • then add instance(s) to whichever you want • What do you want? • What existing class is closest? • Extend it! • digital clock view - centered text in plain box, extend label • analogue clock view - graphics in plain box, extend panel
 THE FUTURE… JAVAFX?
THE FUTURE… JAVAFX?
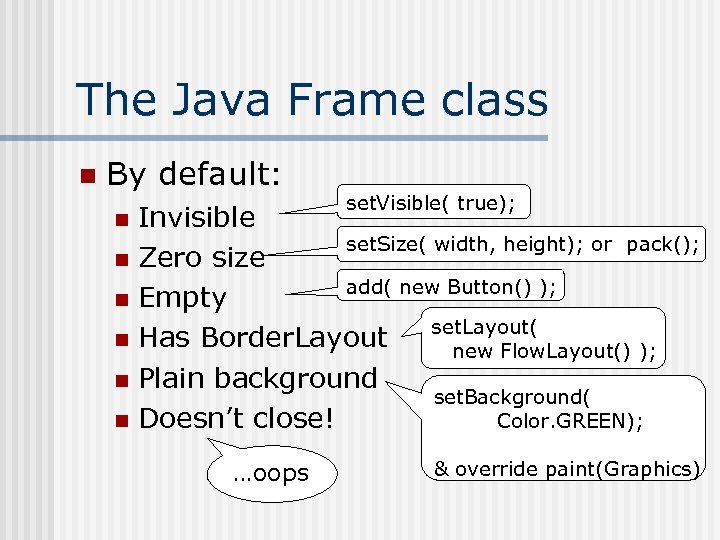 The Java Frame class n By default: set. Visible( true); Invisible set. Size( width, height); or pack(); n Zero size add( new Button() ); n Empty set. Layout( n Has Border. Layout new Flow. Layout() ); n Plain background set. Background( n Doesn’t close! Color. GREEN); n …oops & override paint(Graphics)
The Java Frame class n By default: set. Visible( true); Invisible set. Size( width, height); or pack(); n Zero size add( new Button() ); n Empty set. Layout( n Has Border. Layout new Flow. Layout() ); n Plain background set. Background( n Doesn’t close! Color. GREEN); n …oops & override paint(Graphics)
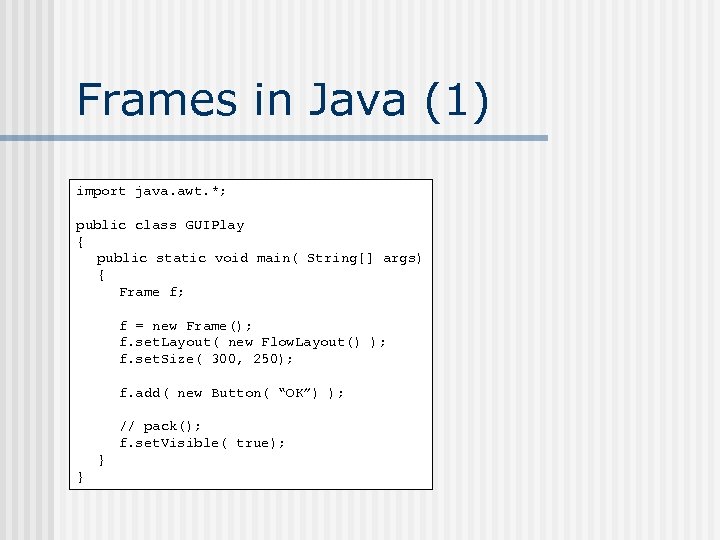 Frames in Java (1) import java. awt. *; public class GUIPlay { public static void main( String[] args) { Frame f; f = new Frame(); f. set. Layout( new Flow. Layout() ); f. set. Size( 300, 250); f. add( new Button( “OK”) ); // pack(); f. set. Visible( true); } }
Frames in Java (1) import java. awt. *; public class GUIPlay { public static void main( String[] args) { Frame f; f = new Frame(); f. set. Layout( new Flow. Layout() ); f. set. Size( 300, 250); f. add( new Button( “OK”) ); // pack(); f. set. Visible( true); } }
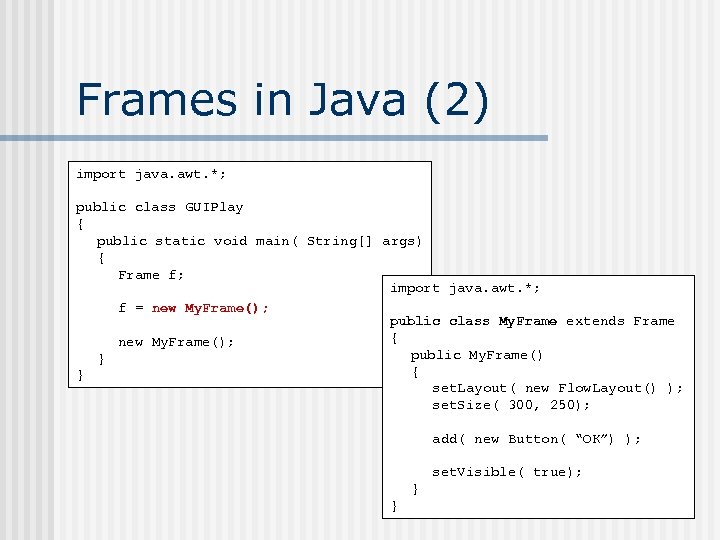 Frames in Java (2) import java. awt. *; public class GUIPlay { public static void main( String[] args) { Frame f; import java. awt. *; f = new My. Frame(); public class My. Frame extends Frame { new My. Frame(); public My. Frame() } { } set. Layout( new Flow. Layout() ); set. Size( 300, 250); add( new Button( “OK”) ); set. Visible( true); } }
Frames in Java (2) import java. awt. *; public class GUIPlay { public static void main( String[] args) { Frame f; import java. awt. *; f = new My. Frame(); public class My. Frame extends Frame { new My. Frame(); public My. Frame() } { } set. Layout( new Flow. Layout() ); set. Size( 300, 250); add( new Button( “OK”) ); set. Visible( true); } }
 Frames in Java (3) import java. awt. *; public class GUIPlay { public class My. Panel extends Panel public static void main( String[] args) { { public My. Panel() import java. awt. *; Frame f; { Button b; public= class. My. Frame(); My. Frame extends Frame f new { set. Background( Color. GREEN ); public My. Frame() new My. Frame(); set. Preferred. Size( { } new Dimension( 200, 150) ); set. Layout( new Flow. Layout() ); } set. Size( 300, 250); b = new Button( “OK”); add( b); add( new My. Panel() ); add( new Label( “Welcome”) ); add( new Text. Field(20) ); set. Visible( true); } }
Frames in Java (3) import java. awt. *; public class GUIPlay { public class My. Panel extends Panel public static void main( String[] args) { { public My. Panel() import java. awt. *; Frame f; { Button b; public= class. My. Frame(); My. Frame extends Frame f new { set. Background( Color. GREEN ); public My. Frame() new My. Frame(); set. Preferred. Size( { } new Dimension( 200, 150) ); set. Layout( new Flow. Layout() ); } set. Size( 300, 250); b = new Button( “OK”); add( b); add( new My. Panel() ); add( new Label( “Welcome”) ); add( new Text. Field(20) ); set. Visible( true); } }
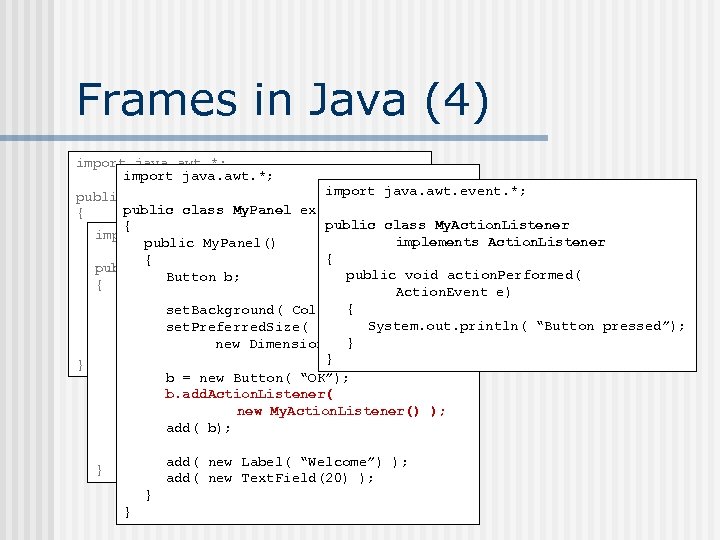 Frames in Java (4) import java. awt. *; import java. awt. event. *; public class GUIPlay public class My. Panel extends Panel { public class My. Action. Listener { public static void import java. awt. *; main( String[] args) implements Action. Listener public My. Panel() { { { Frame f; public class My. Frame public void action. Performed( Button b; { Action. Event e) f = new My. Frame(); public My. Frame() { set. Background( Color. GREEN ); { System. out. println( “Button pressed”); set. Preferred. Size( new My. Frame(); set. Layout( new Flow. Layout() ); } new Dimension( 200, 150) ); } set. Size( 300, 250); } } b = new Button( “OK”); add( new My. Panel() ); b. add. Action. Listener( add( new My. Panel() ); new My. Action. Listener() ); add( b); set. Visible( true); } add( new Label( “Welcome”) ); } add( new Text. Field(20) ); } }
Frames in Java (4) import java. awt. *; import java. awt. event. *; public class GUIPlay public class My. Panel extends Panel { public class My. Action. Listener { public static void import java. awt. *; main( String[] args) implements Action. Listener public My. Panel() { { { Frame f; public class My. Frame public void action. Performed( Button b; { Action. Event e) f = new My. Frame(); public My. Frame() { set. Background( Color. GREEN ); { System. out. println( “Button pressed”); set. Preferred. Size( new My. Frame(); set. Layout( new Flow. Layout() ); } new Dimension( 200, 150) ); } set. Size( 300, 250); } } b = new Button( “OK”); add( new My. Panel() ); b. add. Action. Listener( add( new My. Panel() ); new My. Action. Listener() ); add( b); set. Visible( true); } add( new Label( “Welcome”) ); } add( new Text. Field(20) ); } }


