21e2fa2902ddb91b9eef4b9ee804c785.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37
 CS 1 A Typical Computer system
CS 1 A Typical Computer system
 A Typical Computer System • Types of Computers • Components of a Computer System
A Typical Computer System • Types of Computers • Components of a Computer System
 Types of Computers • Microcomputer • Handheld/Palmtop/PDA • Notebook/Laptop • Desktop • Network servers/Minicomputer • Mainframe • Supercomputer
Types of Computers • Microcomputer • Handheld/Palmtop/PDA • Notebook/Laptop • Desktop • Network servers/Minicomputer • Mainframe • Supercomputer
 Microcomputer-Handheld • • • Personal digital Assisant (PDA) Pocket size Application: – – – • • e-appointment book address book Calculator Notepad Telephone/ fax Internet and networking feature (e. g. bluetooth, Infra-red, wi-fi, etc. ) Use touch screen, pen-based handwriting recognition, keypad or voice recognition tech. 200 MIPS (Million instruction per second) Single user $2000
Microcomputer-Handheld • • • Personal digital Assisant (PDA) Pocket size Application: – – – • • e-appointment book address book Calculator Notepad Telephone/ fax Internet and networking feature (e. g. bluetooth, Infra-red, wi-fi, etc. ) Use touch screen, pen-based handwriting recognition, keypad or voice recognition tech. 200 MIPS (Million instruction per second) Single user $2000
 Microcomputer-Notebook • Also called Laptop compute • Features: – Portable – Encasing inside a plastic / metal case • • 5000 MIPS Single user $12, 000 At office or home
Microcomputer-Notebook • Also called Laptop compute • Features: – Portable – Encasing inside a plastic / metal case • • 5000 MIPS Single user $12, 000 At office or home
 Microcomputer-Desktop • • • Non-portable 6000 MIPS Single user $10, 000 At home or office
Microcomputer-Desktop • • • Non-portable 6000 MIPS Single user $10, 000 At home or office
 Microcomputer-Desktop power supply ventilation system ports interface card The system unit of a desktop computer (back view)
Microcomputer-Desktop power supply ventilation system ports interface card The system unit of a desktop computer (back view)
 Network servers/Minicomputer • • • A high-end network server - The Sun Fire® E 25 K data center server that uses multiple Ultra. SPARC IV processors Serves other computers Using time-sharing tech. ~10 users $50, 000 as a server in a small company, school, etc.
Network servers/Minicomputer • • • A high-end network server - The Sun Fire® E 25 K data center server that uses multiple Ultra. SPARC IV processors Serves other computers Using time-sharing tech. ~10 users $50, 000 as a server in a small company, school, etc.
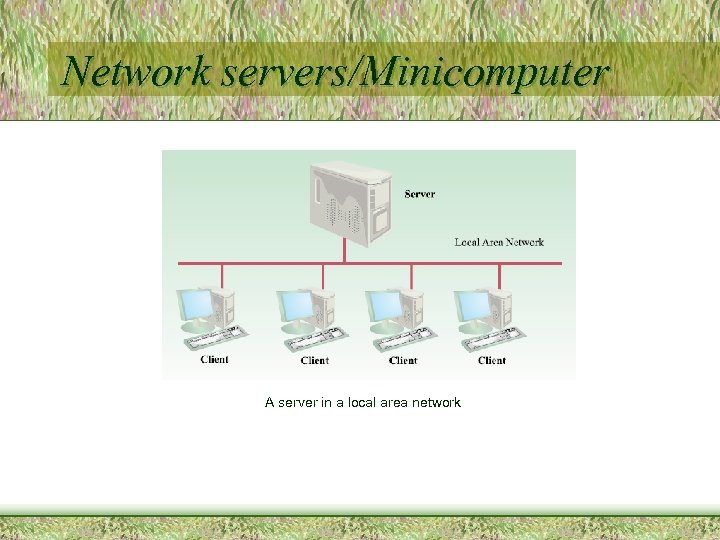 Network servers/Minicomputer A server in a local area network
Network servers/Minicomputer A server in a local area network
 Network servers/Minicomputer A high-end server (or midrange computer) • can store and distribute huge amount of data • has fault-tolerant features that guarantee uptime Fault-tolerant: • even a part fails, the whole system can still operate • redundant components, such as hard disks, power supplies, are required
Network servers/Minicomputer A high-end server (or midrange computer) • can store and distribute huge amount of data • has fault-tolerant features that guarantee uptime Fault-tolerant: • even a part fails, the whole system can still operate • redundant components, such as hard disks, power supplies, are required
 Mainframe • Large, fast, powerful and expensive computer • Features: – – – Time-sharing mode Huge main memory Centralised control Highly reliable Strong data security • ~1000 users • >$1, 000 • used by airline companies, banks, universities, government, HK Jockey Club, etc. IBM® z. Series® 990 - enterprise server
Mainframe • Large, fast, powerful and expensive computer • Features: – – – Time-sharing mode Huge main memory Centralised control Highly reliable Strong data security • ~1000 users • >$1, 000 • used by airline companies, banks, universities, government, HK Jockey Club, etc. IBM® z. Series® 990 - enterprise server
 Mainframe Multi-user modes • allow multiple users to access the system at the same time • differences between multi-user modes: – In mainframe-based networks • major processes are done by the mainframe’s CPU • dumb terminals have limited processing power – In client/server networks • end user processes are handled by workstations • the major tasks of a server are to provide resources, enforce securities and coordinate among various CPUs
Mainframe Multi-user modes • allow multiple users to access the system at the same time • differences between multi-user modes: – In mainframe-based networks • major processes are done by the mainframe’s CPU • dumb terminals have limited processing power – In client/server networks • end user processes are handled by workstations • the major tasks of a server are to provide resources, enforce securities and coordinate among various CPUs
 Supercomputer • One of the fastest computers in the world • Handles CPU intensive job • Billion in cost • weather forecast, space research • e. g. blue, deep blue, cray, etc. Top 500 of supercomputers The Web site of Cray® - a supercomputer company (http: //www. cray. com)
Supercomputer • One of the fastest computers in the world • Handles CPU intensive job • Billion in cost • weather forecast, space research • e. g. blue, deep blue, cray, etc. Top 500 of supercomputers The Web site of Cray® - a supercomputer company (http: //www. cray. com)
 Components of a computer system • • • Central Processing Unit (CPU) Memory Input Unit (Device)** Output Unit (Device)** Backing Store ** **Peripheral Device (週邊設備)
Components of a computer system • • • Central Processing Unit (CPU) Memory Input Unit (Device)** Output Unit (Device)** Backing Store ** **Peripheral Device (週邊設備)
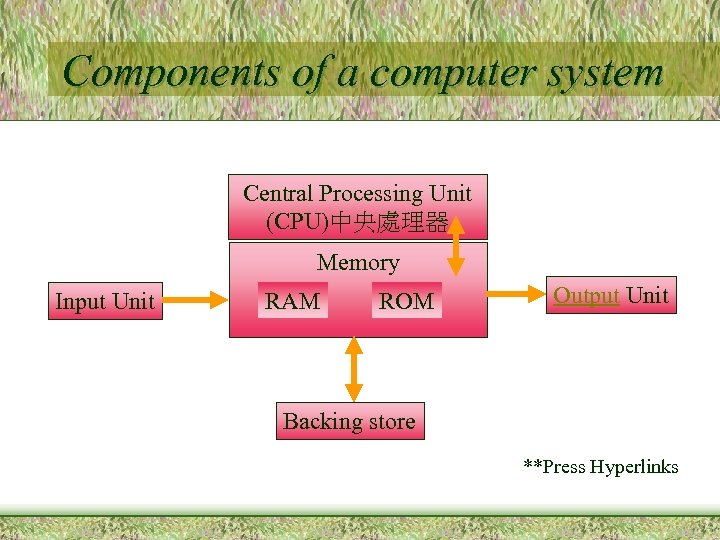 Components of a computer system Central Processing Unit (CPU)中央處理器 Memory Input Unit RAM ROM Output Unit Backing store **Press Hyperlinks
Components of a computer system Central Processing Unit (CPU)中央處理器 Memory Input Unit RAM ROM Output Unit Backing store **Press Hyperlinks
 Central Processing Unit (CPU) 286 386 486 Pentium MMX Pentium III P 4
Central Processing Unit (CPU) 286 386 486 Pentium MMX Pentium III P 4
 CPU • Built on a processor chip (晶片) • Accept and executed instructions stored in main memory • Brain of a computer • Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) (calculation) • Control Unit (CU) (give order) • Registers (small storage units inside CPU)
CPU • Built on a processor chip (晶片) • Accept and executed instructions stored in main memory • Brain of a computer • Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) (calculation) • Control Unit (CU) (give order) • Registers (small storage units inside CPU)
 CPU • Clock speed – Measured in MHz or GHz – Number of clock cycles or ticks per second – The higher the clock speed, the faster the computer (∵each instruction is processed in a fixed number of clock cycles) • Cache Memory – Faster memory – Located between the CPU and RAM – Increasing the speed of memory access
CPU • Clock speed – Measured in MHz or GHz – Number of clock cycles or ticks per second – The higher the clock speed, the faster the computer (∵each instruction is processed in a fixed number of clock cycles) • Cache Memory – Faster memory – Located between the CPU and RAM – Increasing the speed of memory access
 Memory (1) • Many names… – Central memory, main store, primary memory, internal memory • • • ROM/ RAM Part of the CPU Access quickly Expensive Limited storage capacity
Memory (1) • Many names… – Central memory, main store, primary memory, internal memory • • • ROM/ RAM Part of the CPU Access quickly Expensive Limited storage capacity
 Memory - It stores. . • • • Information from Input Unit Data for processing Calculated results Processed output Data accessing time fast
Memory - It stores. . • • • Information from Input Unit Data for processing Calculated results Processed output Data accessing time fast
 Input Unit • Reading of Information • Encoded in input medium • E. g. keyboard, mouse, scanner, etc.
Input Unit • Reading of Information • Encoded in input medium • E. g. keyboard, mouse, scanner, etc.
 Output Unit • Writing the processed results • to human readable form • Visual Display Unit (VDU) and printer.
Output Unit • Writing the processed results • to human readable form • Visual Display Unit (VDU) and printer.
 Visual Display Unit Compaq TFT 8000 EIZO T 765
Visual Display Unit Compaq TFT 8000 EIZO T 765
 Visual Display Unit - LCD • Flat display surface • Save space • Expensive
Visual Display Unit - LCD • Flat display surface • Save space • Expensive
 Backing Store CD ROM Hard Disk Magnetic Tape • Also called Secondary memory • Permanent(? ? ? ) storage • Larger capacity • Lower cost • But slower speed
Backing Store CD ROM Hard Disk Magnetic Tape • Also called Secondary memory • Permanent(? ? ? ) storage • Larger capacity • Lower cost • But slower speed
 Backing store consists of. . . • Storage Media • Storage Device • Other example. . Media Device
Backing store consists of. . . • Storage Media • Storage Device • Other example. . Media Device
 Ports and Interface cards • Ports – Built on the motherboard – Interface between peripheral devices and memory – Connect directly to Peripheral buses • Interface cards – Circuit board that connects a peripheral device to the motherboard – Inserted into Interface slots which are built on the motherboard – Connect directly to Peripheral buses
Ports and Interface cards • Ports – Built on the motherboard – Interface between peripheral devices and memory – Connect directly to Peripheral buses • Interface cards – Circuit board that connects a peripheral device to the motherboard – Inserted into Interface slots which are built on the motherboard – Connect directly to Peripheral buses
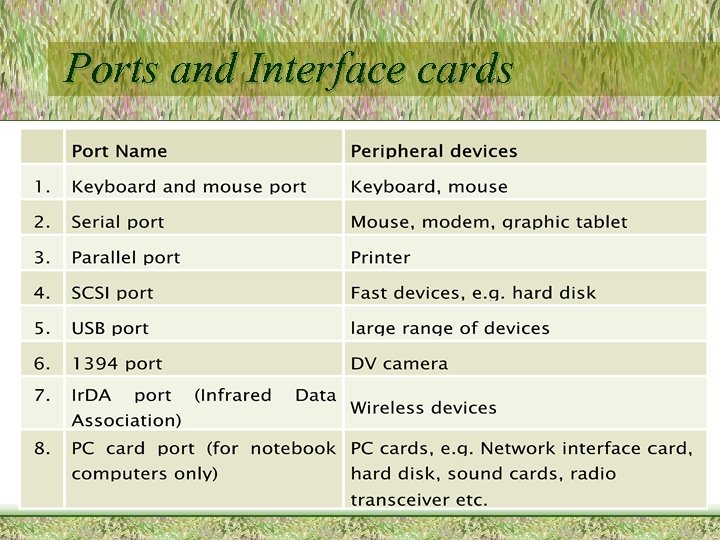 Ports and Interface cards
Ports and Interface cards
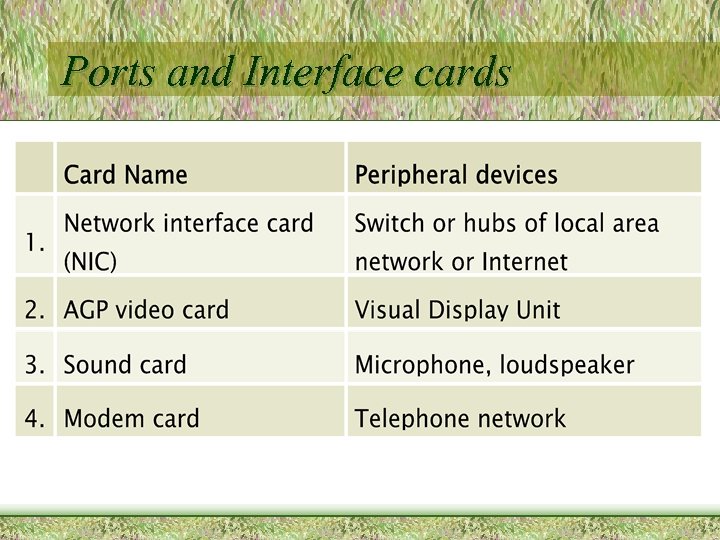 Ports and Interface cards
Ports and Interface cards
 BUS • A group of wire transmits digital (0/1) signals 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 01010101010101010 0101010101010101 101001010010101010 A group of wire
BUS • A group of wire transmits digital (0/1) signals 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 01010101010101010 0101010101010101 101001010010101010 A group of wire
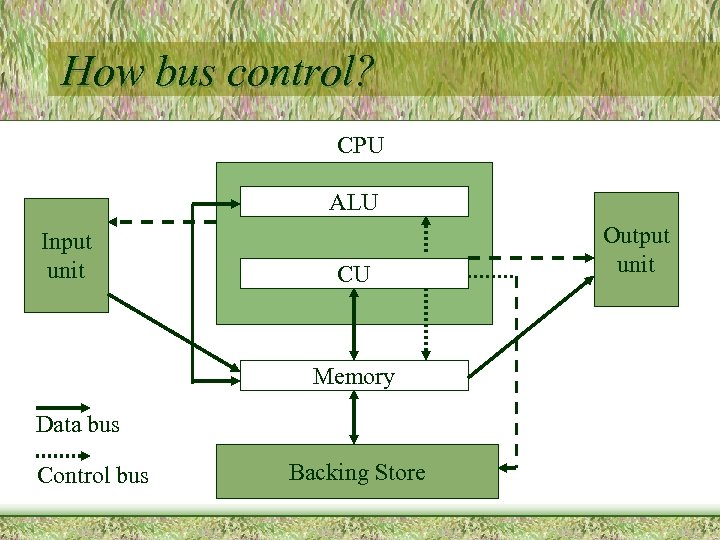 How bus control? CPU ALU Input unit CU Memory Data bus Control bus Backing Store Output unit
How bus control? CPU ALU Input unit CU Memory Data bus Control bus Backing Store Output unit
 Three types of BUS • Control BUS • Data BUS • Address BUS
Three types of BUS • Control BUS • Data BUS • Address BUS
 Control BUS • Carry control signals • Signal like control memory Read/Write, • Control peripheral access • Control all execution
Control BUS • Carry control signals • Signal like control memory Read/Write, • Control peripheral access • Control all execution
 Data BUS • Carry Data signals through different Units • Bi-directional • Data transmit in parallel
Data BUS • Carry Data signals through different Units • Bi-directional • Data transmit in parallel
 Address BUS • Carry Address signals • In need when you want to read/write from memory
Address BUS • Carry Address signals • In need when you want to read/write from memory
 Exercise • (a) Write down the name of the component represented by box X. Name one device which is an example of this component. • Soln: ü X is the secondary memory ü Example is Hard disk
Exercise • (a) Write down the name of the component represented by box X. Name one device which is an example of this component. • Soln: ü X is the secondary memory ü Example is Hard disk
 Exercise • (b) Write down the name of the component represented by box Y. Name one device which is an example of this component. • Soln: ü Y is the output unit ü Example is visual display unit (VDU)
Exercise • (b) Write down the name of the component represented by box Y. Name one device which is an example of this component. • Soln: ü Y is the output unit ü Example is visual display unit (VDU)


