a56d3ba4006438516d645aa5c75769e8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Cryptree A Folder Tree Structure for Cryptographic File Systems Dominik Grolimund, Luzius Meisser, Stefan Schmid, Roger Wattenhofer Computer Engineering and Networks Laboratory (TIK), ETH Zurich SRDS 06 October 3, Leeds, UK Distributed Computing Group
Cryptree A Folder Tree Structure for Cryptographic File Systems Dominik Grolimund, Luzius Meisser, Stefan Schmid, Roger Wattenhofer Computer Engineering and Networks Laboratory (TIK), ETH Zurich SRDS 06 October 3, Leeds, UK Distributed Computing Group
 Cryptree - A key management scheme developed for Kangoo, our distributed file system - Manages encryption keys of files and folders - Leverages the file systems folder hierarchy to achieve intuitive semantics and efficiency 2
Cryptree - A key management scheme developed for Kangoo, our distributed file system - Manages encryption keys of files and folders - Leverages the file systems folder hierarchy to achieve intuitive semantics and efficiency 2
 Outline § § § Motivation Basics Cryptree Performance Discussion 3
Outline § § § Motivation Basics Cryptree Performance Discussion 3
 Motivation Kangoo: a large-scale distributed file system (comparable to Ocean. Store, Celeste, CFS…) Problem: Enforcement & management of access rights on untrusted (but reliable) storage We cannot trust the storage device to keep our data secret Everything needs to be encrypted We need a clever key management scheme 4
Motivation Kangoo: a large-scale distributed file system (comparable to Ocean. Store, Celeste, CFS…) Problem: Enforcement & management of access rights on untrusted (but reliable) storage We cannot trust the storage device to keep our data secret Everything needs to be encrypted We need a clever key management scheme 4
 Motivation Existing ideas: - Server enforces access rights not feasible here - Classic Access Control List (CACL) Approach, found in systems like Plutus, Si. Ri. Us, Ocean. Store (? ) - Many papers about hierarchical key management in general, focus on crypographic aspects 5
Motivation Existing ideas: - Server enforces access rights not feasible here - Classic Access Control List (CACL) Approach, found in systems like Plutus, Si. Ri. Us, Ocean. Store (? ) - Many papers about hierarchical key management in general, focus on crypographic aspects 5
 Talk Outline § § § Motivation Basics Cryptree Performance Discussion 6
Talk Outline § § § Motivation Basics Cryptree Performance Discussion 6
 Basics: Access Control with Keys - Read Access Control: Items are encrypted such that only legitimate accessors can decrypt them - Write Access Control: A sign/verify key pair is used to prove the legitimacy of write operations 7
Basics: Access Control with Keys - Read Access Control: Items are encrypted such that only legitimate accessors can decrypt them - Write Access Control: A sign/verify key pair is used to prove the legitimacy of write operations 7
 Basics: Lazy Revocation When someone loses access to an item, that item needs to be encrypted with a new key in order to prevent the former accessor to access the item in future. Lazy revocation allows to postpone this (expensive) reencryption until the next update of the item. Better performance at the price of slightly lower security. An adversary and former accessor of an item could continue to access it if he has kept a copy of the encryption key. Without lazy revocation, he would have had to keep a copy of the item itself to do so. 8
Basics: Lazy Revocation When someone loses access to an item, that item needs to be encrypted with a new key in order to prevent the former accessor to access the item in future. Lazy revocation allows to postpone this (expensive) reencryption until the next update of the item. Better performance at the price of slightly lower security. An adversary and former accessor of an item could continue to access it if he has kept a copy of the encryption key. Without lazy revocation, he would have had to keep a copy of the item itself to do so. 8
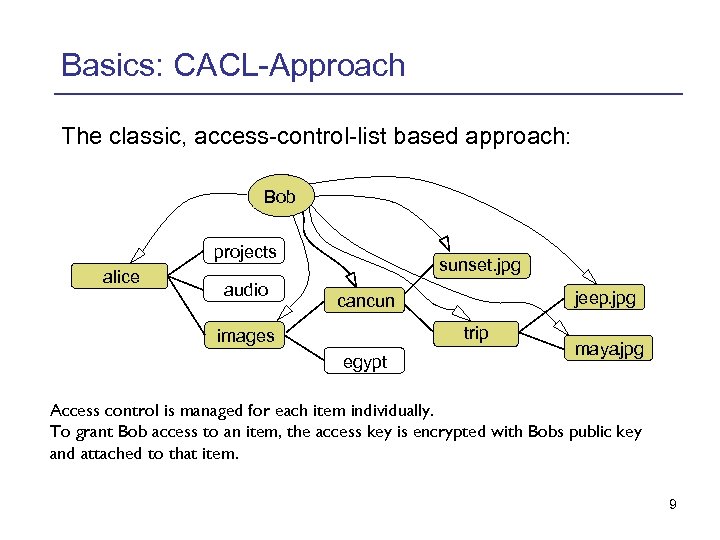 Basics: CACL-Approach The classic, access-control-list based approach: Bob projects alice audio sunset. jpg jeep. jpg cancun trip images egypt maya. jpg Access control is managed for each item individually. To grant Bob access to an item, the access key is encrypted with Bobs public key and attached to that item. 9
Basics: CACL-Approach The classic, access-control-list based approach: Bob projects alice audio sunset. jpg jeep. jpg cancun trip images egypt maya. jpg Access control is managed for each item individually. To grant Bob access to an item, the access key is encrypted with Bobs public key and attached to that item. 9
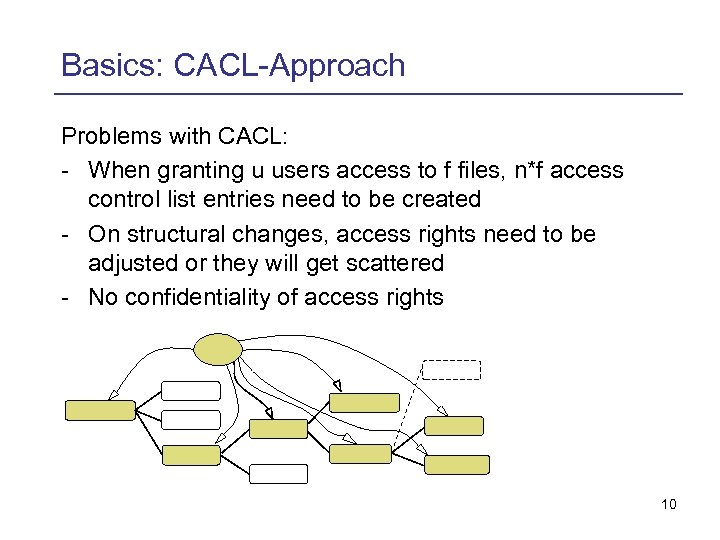 Basics: CACL-Approach Problems with CACL: - When granting u users access to f files, n*f access control list entries need to be created - On structural changes, access rights need to be adjusted or they will get scattered - No confidentiality of access rights 10
Basics: CACL-Approach Problems with CACL: - When granting u users access to f files, n*f access control list entries need to be created - On structural changes, access rights need to be adjusted or they will get scattered - No confidentiality of access rights 10
 Outline § § § Motivation Basics Cryptree Performance Discussion 11
Outline § § § Motivation Basics Cryptree Performance Discussion 11
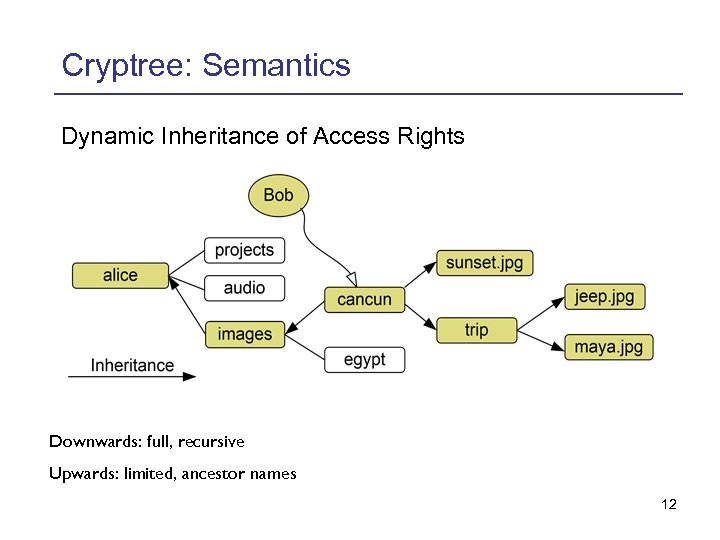 Cryptree: Semantics Dynamic Inheritance of Access Rights Downwards: full, recursive Upwards: limited, ancestor names 12
Cryptree: Semantics Dynamic Inheritance of Access Rights Downwards: full, recursive Upwards: limited, ancestor names 12
 Cryptree: Cryptographic Links Knowing K 1 and the link allows to derive K 2 Symmetric Link: symmetric cryptography, requires knowledge of K 1 to update Asymmetric Link: asymmetric cryptography, K 2 can be replaced without knowing K 1 More flexible than symmetric link, but expensive 13
Cryptree: Cryptographic Links Knowing K 1 and the link allows to derive K 2 Symmetric Link: symmetric cryptography, requires knowledge of K 1 to update Asymmetric Link: asymmetric cryptography, K 2 can be replaced without knowing K 1 More flexible than symmetric link, but expensive 13
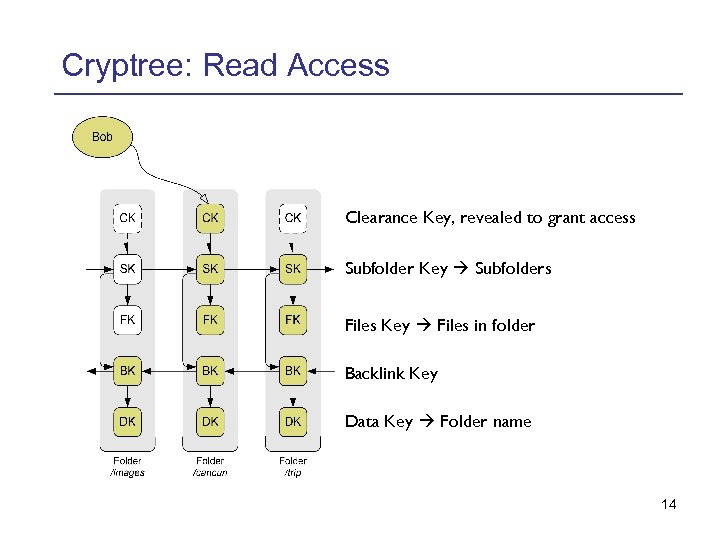 Cryptree: Read Access Clearance Key, revealed to grant access Subfolder Key Subfolders Files Key Files in folder Backlink Key Data Key Folder name 14
Cryptree: Read Access Clearance Key, revealed to grant access Subfolder Key Subfolders Files Key Files in folder Backlink Key Data Key Folder name 14
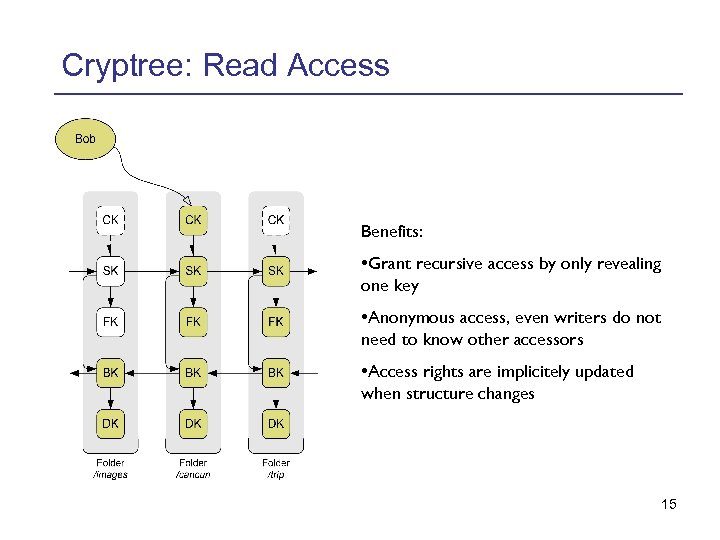 Cryptree: Read Access Benefits: • Grant recursive access by only revealing one key • Anonymous access, even writers do not need to know other accessors • Access rights are implicitely updated when structure changes 15
Cryptree: Read Access Benefits: • Grant recursive access by only revealing one key • Anonymous access, even writers do not need to know other accessors • Access rights are implicitely updated when structure changes 15
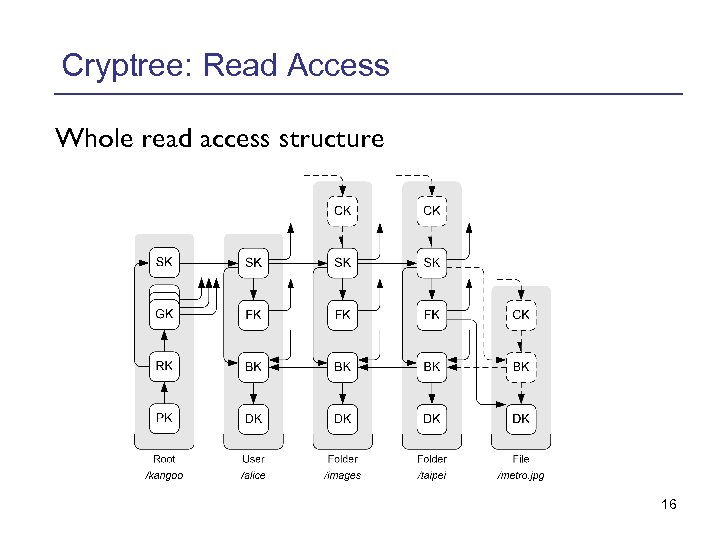 Cryptree: Read Access Whole read access structure 16
Cryptree: Read Access Whole read access structure 16
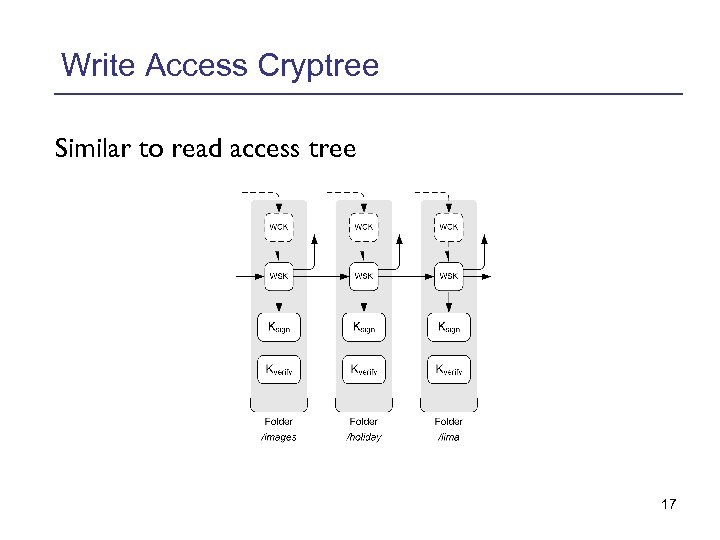 Write Access Cryptree Similar to read access tree 17
Write Access Cryptree Similar to read access tree 17
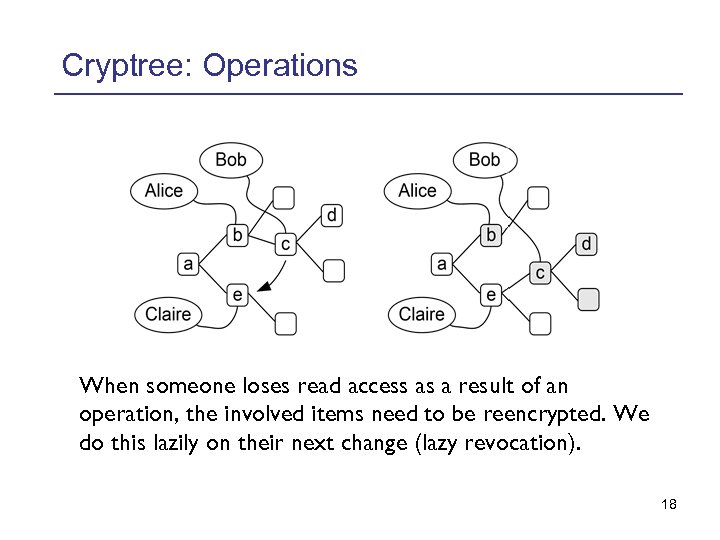 Cryptree: Operations When someone loses read access as a result of an operation, the involved items need to be reencrypted. We do this lazily on their next change (lazy revocation). 18
Cryptree: Operations When someone loses read access as a result of an operation, the involved items need to be reencrypted. We do this lazily on their next change (lazy revocation). 18
 Outline § § § Motivation Basics Cryptree Evaluation Discussion 19
Outline § § § Motivation Basics Cryptree Evaluation Discussion 19
 Performance Besides its semantical advantages, the Cryptree should also perform better than the CACL-Approach. We wrote sandbox implementations of different approaches and let them perform a given set of operations. Test set: 30‘ 000 files (avg. size 2. 5 MB), 2‘ 500 folders, 1‘ 000 operations (ordered by likelihood: read, create, delete, move, modify, grant access, revoke access, grant write access, revoke write access) 20
Performance Besides its semantical advantages, the Cryptree should also perform better than the CACL-Approach. We wrote sandbox implementations of different approaches and let them perform a given set of operations. Test set: 30‘ 000 files (avg. size 2. 5 MB), 2‘ 500 folders, 1‘ 000 operations (ordered by likelihood: read, create, delete, move, modify, grant access, revoke access, grant write access, revoke write access) 20
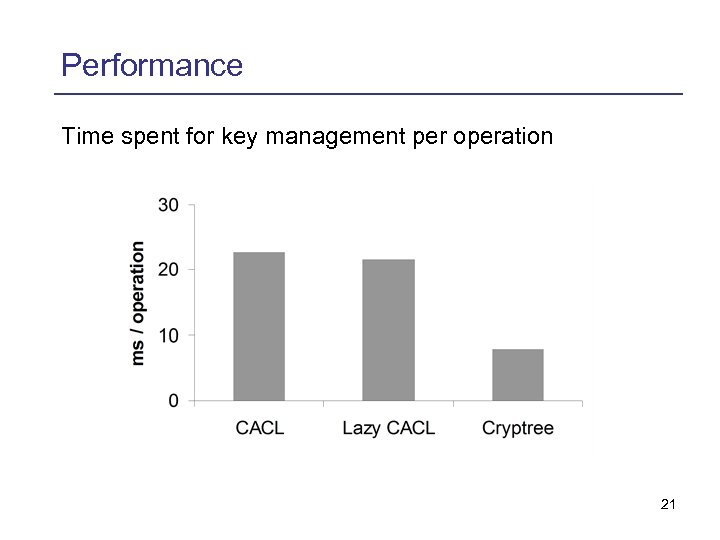 Performance Time spent for key management per operation 21
Performance Time spent for key management per operation 21
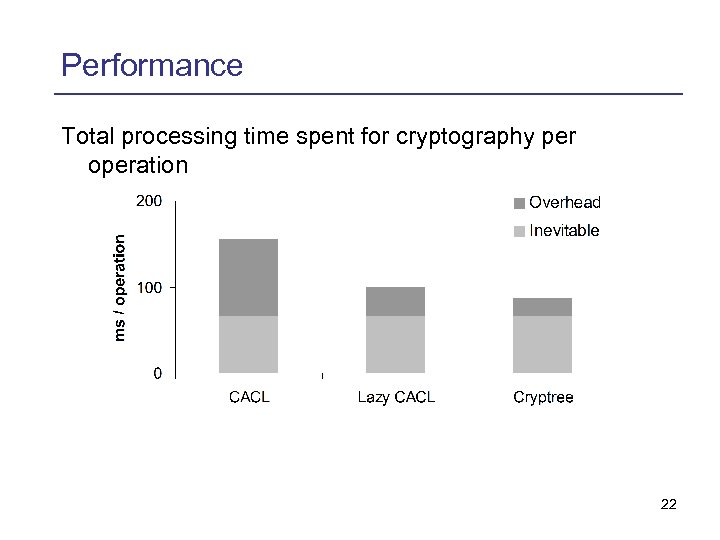 Performance Total processing time spent for cryptography per operation 22
Performance Total processing time spent for cryptography per operation 22
 Outline § § § Motivation Basics Cryptree Performance Discussion 23
Outline § § § Motivation Basics Cryptree Performance Discussion 23
 Discussion: Conclusions We have leveraged the file systems folder hierarchy for key management and achieved - Intuitive Access Control Semantics - Efficiency - Simplicity, no elaborate cryptographic knowledge required 24
Discussion: Conclusions We have leveraged the file systems folder hierarchy for key management and achieved - Intuitive Access Control Semantics - Efficiency - Simplicity, no elaborate cryptographic knowledge required 24
 Discussion: Questions ? 25
Discussion: Questions ? 25


