e962beb27964f9eab137f98276db0587.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Cryptanalysis of Some Proxy Signature Schemes without Certificates Wun-She Yap, Swee-Huay Heng Bok-Min Goi Multimedia University
Cryptanalysis of Some Proxy Signature Schemes without Certificates Wun-She Yap, Swee-Huay Heng Bok-Min Goi Multimedia University
 Proxy Signature n n n Introduced by Mambo et al. in 1996. Allow a designated signer (proxy signer) to sign the message on behalf of an original signer Involve three entities: § § § n n Original Signer Proxy Signer Verifier Convince the verifier that the signature is signed by the proxy signer who obtains the delegation right from the original signer Applications: e-cash system, global distribution network, grid computing, mobile agent applications, etc. 2
Proxy Signature n n n Introduced by Mambo et al. in 1996. Allow a designated signer (proxy signer) to sign the message on behalf of an original signer Involve three entities: § § § n n Original Signer Proxy Signer Verifier Convince the verifier that the signature is signed by the proxy signer who obtains the delegation right from the original signer Applications: e-cash system, global distribution network, grid computing, mobile agent applications, etc. 2
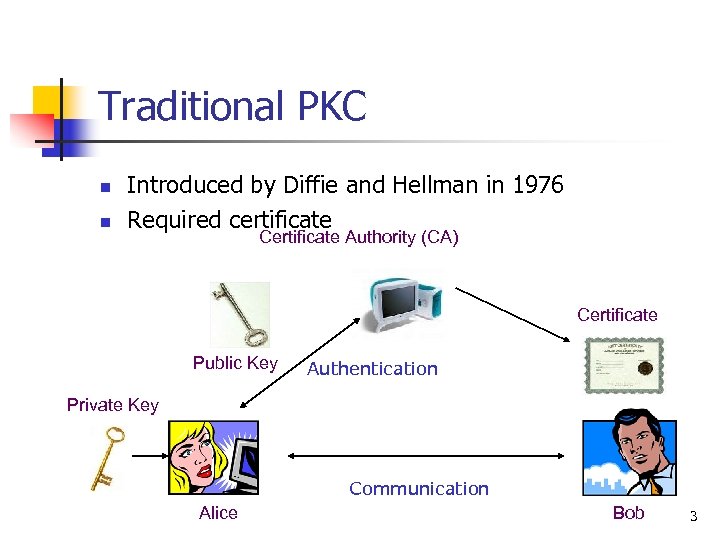 Traditional PKC n n Introduced by Diffie and Hellman in 1976 Required certificate Certificate Authority (CA) Certificate Public Key Authentication Private Key Communication Alice Bob 3
Traditional PKC n n Introduced by Diffie and Hellman in 1976 Required certificate Certificate Authority (CA) Certificate Public Key Authentication Private Key Communication Alice Bob 3
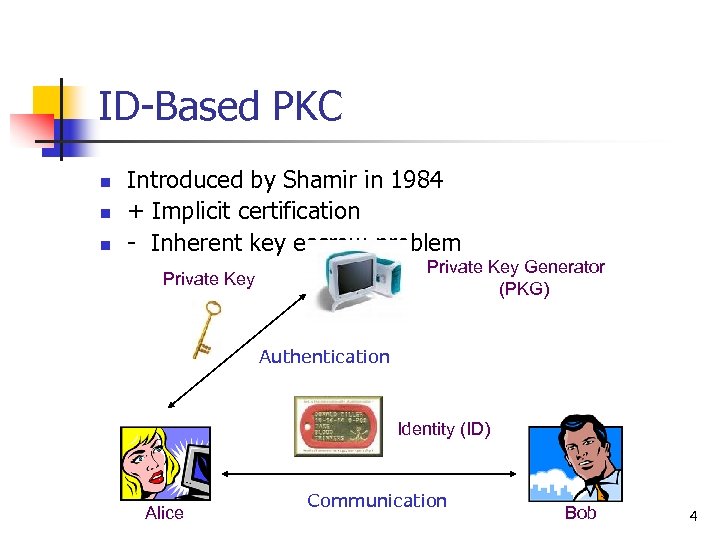 ID-Based PKC n n n Introduced by Shamir in 1984 + Implicit certification - Inherent key escrow problem Private Key Generator (PKG) Private Key Authentication Identity (ID) Alice Communication Bob 4
ID-Based PKC n n n Introduced by Shamir in 1984 + Implicit certification - Inherent key escrow problem Private Key Generator (PKG) Private Key Authentication Identity (ID) Alice Communication Bob 4
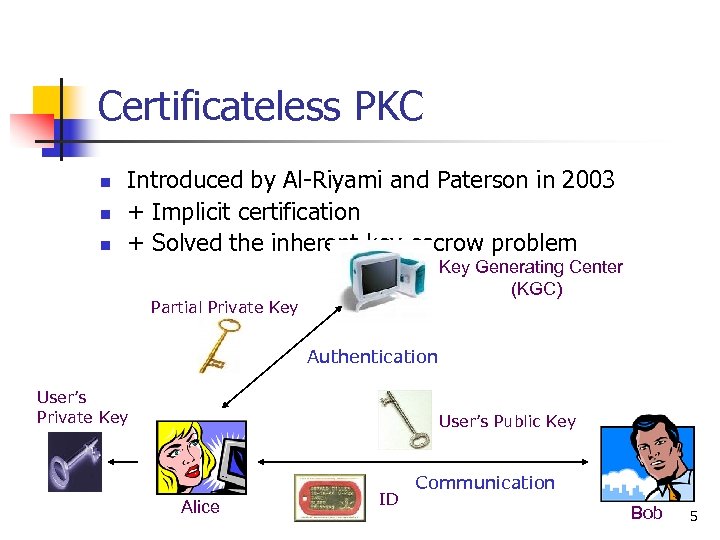 Certificateless PKC n n n Introduced by Al-Riyami and Paterson in 2003 + Implicit certification + Solved the inherent key escrow problem Key Generating Center (KGC) Partial Private Key Authentication User’s Private Key User’s Public Key Alice ID Communication Bob 5
Certificateless PKC n n n Introduced by Al-Riyami and Paterson in 2003 + Implicit certification + Solved the inherent key escrow problem Key Generating Center (KGC) Partial Private Key Authentication User’s Private Key User’s Public Key Alice ID Communication Bob 5
 This Research n Show that the following schemes are insecure against universal forgery n n The Qian and Cao IBPS scheme (ISPA 2005) – RSA-based The Guo et al. IBPS scheme (IMSCCS 2006) – bilinear pairing The Li et al. CLPS scheme (Lithuanian Mathematical Journal 2005) – bilinear pairing Any user can act as a cheating proxy signer, to forge the proxy signature on behalf of the original signer, without obtaining the official delegation from the original signer. 6
This Research n Show that the following schemes are insecure against universal forgery n n The Qian and Cao IBPS scheme (ISPA 2005) – RSA-based The Guo et al. IBPS scheme (IMSCCS 2006) – bilinear pairing The Li et al. CLPS scheme (Lithuanian Mathematical Journal 2005) – bilinear pairing Any user can act as a cheating proxy signer, to forge the proxy signature on behalf of the original signer, without obtaining the official delegation from the original signer. 6
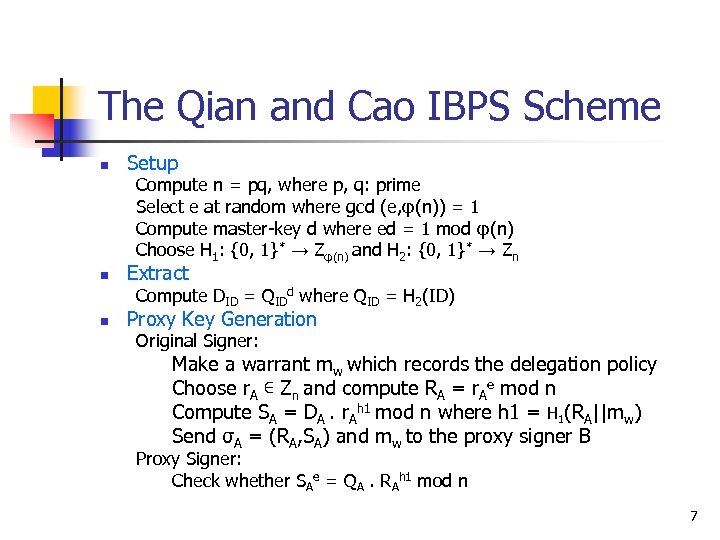 The Qian and Cao IBPS Scheme n Setup Compute n = pq, where p, q: prime Select e at random where gcd (e, φ(n)) = 1 Compute master-key d where ed = 1 mod φ(n) Choose H 1: {0, 1}* → Zφ(n) and H 2: {0, 1}* → Zn n Extract Compute DID = QIDd where QID = H 2(ID) n Proxy Key Generation Original Signer: Make a warrant mw which records the delegation policy Choose r. A ∊ Zn and compute RA = r. Ae mod n Compute SA = DA. r. Ah 1 mod n where h 1 = H 1(RA||mw) Send σA = (RA, SA) and mw to the proxy signer B Proxy Signer: Check whether SAe = QA. RAh 1 mod n 7
The Qian and Cao IBPS Scheme n Setup Compute n = pq, where p, q: prime Select e at random where gcd (e, φ(n)) = 1 Compute master-key d where ed = 1 mod φ(n) Choose H 1: {0, 1}* → Zφ(n) and H 2: {0, 1}* → Zn n Extract Compute DID = QIDd where QID = H 2(ID) n Proxy Key Generation Original Signer: Make a warrant mw which records the delegation policy Choose r. A ∊ Zn and compute RA = r. Ae mod n Compute SA = DA. r. Ah 1 mod n where h 1 = H 1(RA||mw) Send σA = (RA, SA) and mw to the proxy signer B Proxy Signer: Check whether SAe = QA. RAh 1 mod n 7
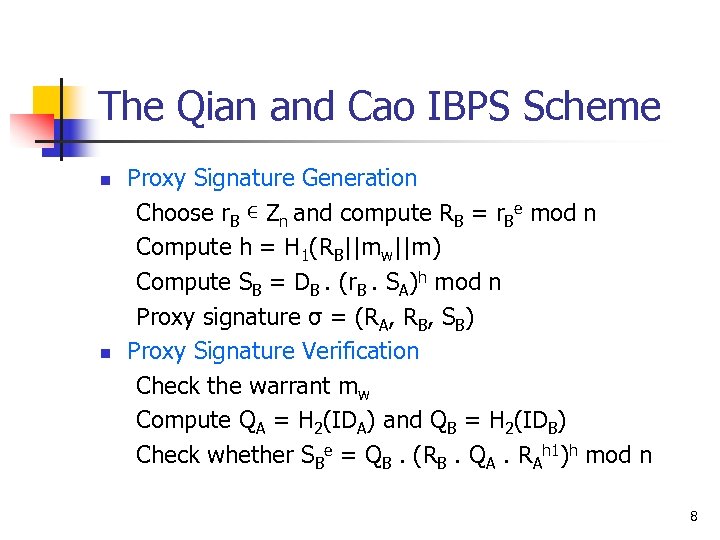 The Qian and Cao IBPS Scheme n n Proxy Signature Generation Choose r. B ∊ Zn and compute RB = r. Be mod n Compute h = H 1(RB||mw||m) Compute SB = DB. (r. B. SA)h mod n Proxy signature σ = (RA, RB, SB) Proxy Signature Verification Check the warrant mw Compute QA = H 2(IDA) and QB = H 2(IDB) Check whether SBe = QB. (RB. QA. RAh 1)h mod n 8
The Qian and Cao IBPS Scheme n n Proxy Signature Generation Choose r. B ∊ Zn and compute RB = r. Be mod n Compute h = H 1(RB||mw||m) Compute SB = DB. (r. B. SA)h mod n Proxy signature σ = (RA, RB, SB) Proxy Signature Verification Check the warrant mw Compute QA = H 2(IDA) and QB = H 2(IDB) Check whether SBe = QB. (RB. QA. RAh 1)h mod n 8
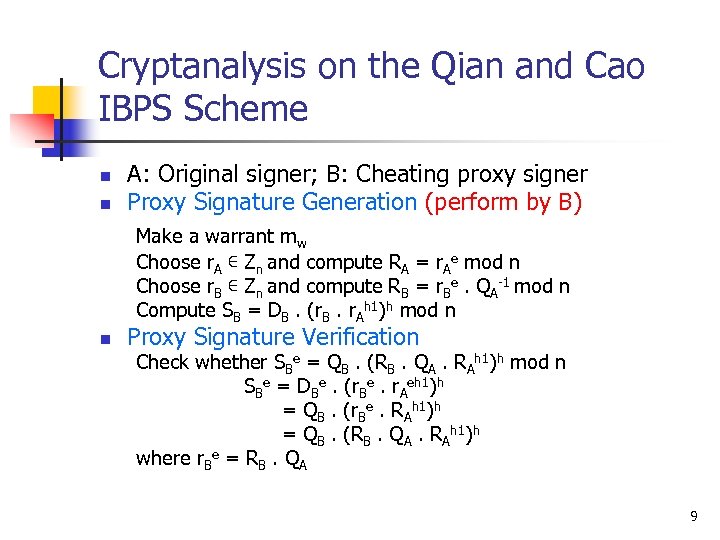 Cryptanalysis on the Qian and Cao IBPS Scheme n n A: Original signer; B: Cheating proxy signer Proxy Signature Generation (perform by B) Make a warrant mw Choose r. A ∊ Zn and compute RA = r. Ae mod n Choose r. B ∊ Zn and compute RB = r. Be. QA-1 mod n Compute SB = DB. (r. B. r. Ah 1)h mod n n Proxy Signature Verification Check whether SBe = QB. (RB. QA. RAh 1)h mod n SBe = DBe. (r. Be. r. Aeh 1)h = QB. (r. Be. RAh 1)h = QB. (RB. QA. RAh 1)h where r. Be = RB. QA 9
Cryptanalysis on the Qian and Cao IBPS Scheme n n A: Original signer; B: Cheating proxy signer Proxy Signature Generation (perform by B) Make a warrant mw Choose r. A ∊ Zn and compute RA = r. Ae mod n Choose r. B ∊ Zn and compute RB = r. Be. QA-1 mod n Compute SB = DB. (r. B. r. Ah 1)h mod n n Proxy Signature Verification Check whether SBe = QB. (RB. QA. RAh 1)h mod n SBe = DBe. (r. Be. r. Aeh 1)h = QB. (r. Be. RAh 1)h = QB. (RB. QA. RAh 1)h where r. Be = RB. QA 9
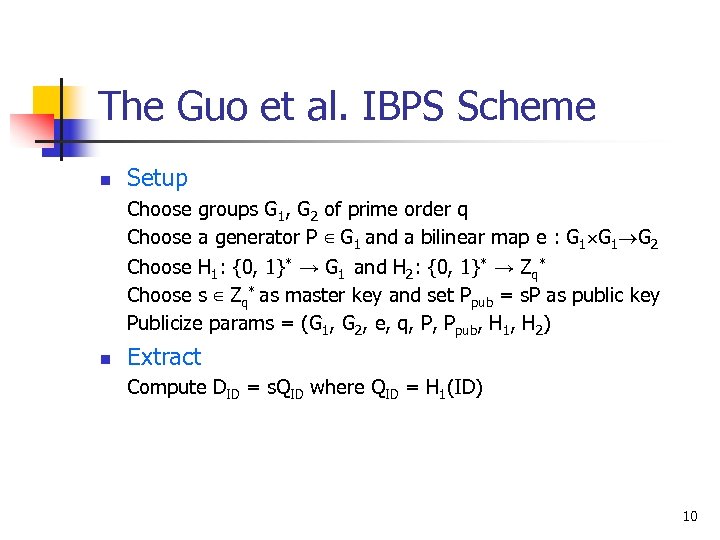 The Guo et al. IBPS Scheme n Setup Choose groups G 1, G 2 of prime order q Choose a generator P ∈ G 1 and a bilinear map e : G 1 G 2 Choose H 1: {0, 1}* → G 1 and H 2: {0, 1}* → Zq* Choose s ∈ Zq* as master key and set Ppub = s. P as public key Publicize params = (G 1, G 2, e, q, P, Ppub, H 1, H 2) n Extract Compute DID = s. QID where QID = H 1(ID) 10
The Guo et al. IBPS Scheme n Setup Choose groups G 1, G 2 of prime order q Choose a generator P ∈ G 1 and a bilinear map e : G 1 G 2 Choose H 1: {0, 1}* → G 1 and H 2: {0, 1}* → Zq* Choose s ∈ Zq* as master key and set Ppub = s. P as public key Publicize params = (G 1, G 2, e, q, P, Ppub, H 1, H 2) n Extract Compute DID = s. QID where QID = H 1(ID) 10
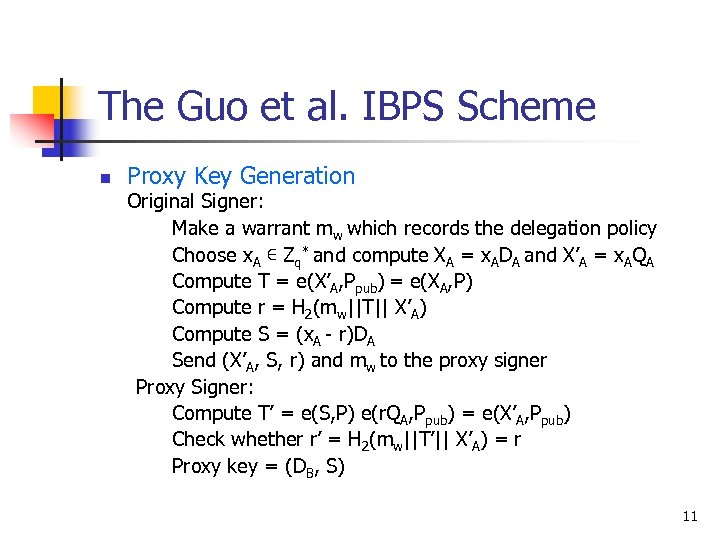 The Guo et al. IBPS Scheme n Proxy Key Generation Original Signer: Make a warrant mw which records the delegation policy Choose x. A ∊ Zq* and compute XA = x. ADA and X’A = x. AQA Compute T = e(X’A, Ppub) = e(XA, P) Compute r = H 2(mw||T|| X’A) Compute S = (x. A - r)DA Send (X’A, S, r) and mw to the proxy signer Proxy Signer: Compute T’ = e(S, P) e(r. QA, Ppub) = e(X’A, Ppub) Check whether r’ = H 2(mw||T’|| X’A) = r Proxy key = (DB, S) 11
The Guo et al. IBPS Scheme n Proxy Key Generation Original Signer: Make a warrant mw which records the delegation policy Choose x. A ∊ Zq* and compute XA = x. ADA and X’A = x. AQA Compute T = e(X’A, Ppub) = e(XA, P) Compute r = H 2(mw||T|| X’A) Compute S = (x. A - r)DA Send (X’A, S, r) and mw to the proxy signer Proxy Signer: Compute T’ = e(S, P) e(r. QA, Ppub) = e(X’A, Ppub) Check whether r’ = H 2(mw||T’|| X’A) = r Proxy key = (DB, S) 11
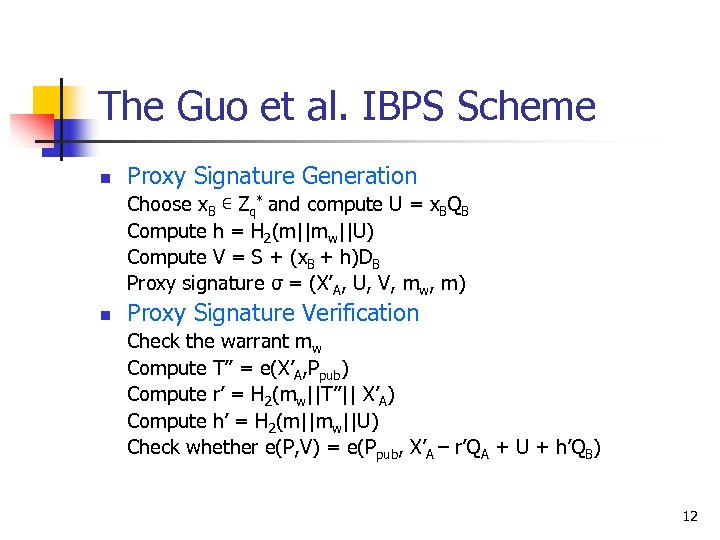 The Guo et al. IBPS Scheme n Proxy Signature Generation Choose x. B ∊ Zq* and compute U = x. BQB Compute h = H 2(m||mw||U) Compute V = S + (x. B + h)DB Proxy signature σ = (X’A, U, V, mw, m) n Proxy Signature Verification Check the warrant mw Compute T’’ = e(X’A, Ppub) Compute r’ = H 2(mw||T’’|| X’A) Compute h’ = H 2(m||mw||U) Check whether e(P, V) = e(Ppub, X’A – r’QA + U + h’QB) 12
The Guo et al. IBPS Scheme n Proxy Signature Generation Choose x. B ∊ Zq* and compute U = x. BQB Compute h = H 2(m||mw||U) Compute V = S + (x. B + h)DB Proxy signature σ = (X’A, U, V, mw, m) n Proxy Signature Verification Check the warrant mw Compute T’’ = e(X’A, Ppub) Compute r’ = H 2(mw||T’’|| X’A) Compute h’ = H 2(m||mw||U) Check whether e(P, V) = e(Ppub, X’A – r’QA + U + h’QB) 12
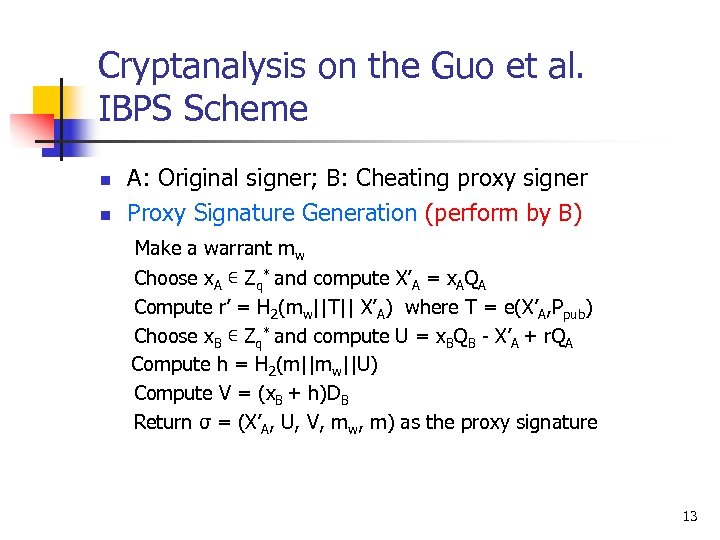 Cryptanalysis on the Guo et al. IBPS Scheme n n A: Original signer; B: Cheating proxy signer Proxy Signature Generation (perform by B) Make a warrant mw Choose x. A ∊ Zq* and compute X’A = x. AQA Compute r’ = H 2(mw||T|| X’A) where T = e(X’A, Ppub) Choose x. B ∊ Zq* and compute U = x. BQB - X’A + r. QA Compute h = H 2(m||mw||U) Compute V = (x. B + h)DB Return σ = (X’A, U, V, mw, m) as the proxy signature 13
Cryptanalysis on the Guo et al. IBPS Scheme n n A: Original signer; B: Cheating proxy signer Proxy Signature Generation (perform by B) Make a warrant mw Choose x. A ∊ Zq* and compute X’A = x. AQA Compute r’ = H 2(mw||T|| X’A) where T = e(X’A, Ppub) Choose x. B ∊ Zq* and compute U = x. BQB - X’A + r. QA Compute h = H 2(m||mw||U) Compute V = (x. B + h)DB Return σ = (X’A, U, V, mw, m) as the proxy signature 13
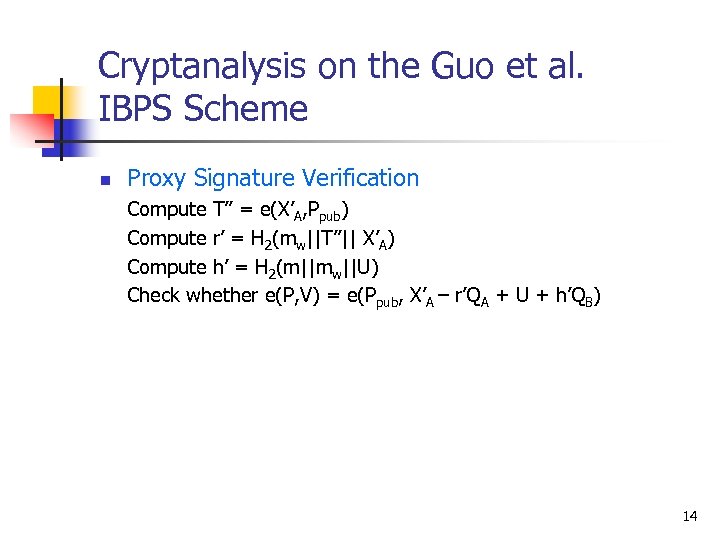 Cryptanalysis on the Guo et al. IBPS Scheme n Proxy Signature Verification Compute T’’ = e(X’A, Ppub) Compute r’ = H 2(mw||T’’|| X’A) Compute h’ = H 2(m||mw||U) Check whether e(P, V) = e(Ppub, X’A – r’QA + U + h’QB) 14
Cryptanalysis on the Guo et al. IBPS Scheme n Proxy Signature Verification Compute T’’ = e(X’A, Ppub) Compute r’ = H 2(mw||T’’|| X’A) Compute h’ = H 2(m||mw||U) Check whether e(P, V) = e(Ppub, X’A – r’QA + U + h’QB) 14
 Li et al. CLPS Scheme n Derived from the Cha and Cheon IBS scheme and the Hess IBS scheme The only CLPS scheme n Setup n Choose groups G 1, G 2 of prime order q Choose a generator P ∈ G 1 and a bilinear map e : G 1 G 2 Choose H 1: {0, 1}* → G 1 and H 2: {0, 1}* x G 1 → Zq* Choose s ∈ Zq* as master key and set Ppub = s. P as public key Publicize params = (G 1, G 2, e, q, P, Ppub, H 1, H 2) n Set-Partial-Private-Key Compute DID = s. QID where QID = H 1(ID) n Set-Secret-Value Select a random x. ID ∈ Zq* 15
Li et al. CLPS Scheme n Derived from the Cha and Cheon IBS scheme and the Hess IBS scheme The only CLPS scheme n Setup n Choose groups G 1, G 2 of prime order q Choose a generator P ∈ G 1 and a bilinear map e : G 1 G 2 Choose H 1: {0, 1}* → G 1 and H 2: {0, 1}* x G 1 → Zq* Choose s ∈ Zq* as master key and set Ppub = s. P as public key Publicize params = (G 1, G 2, e, q, P, Ppub, H 1, H 2) n Set-Partial-Private-Key Compute DID = s. QID where QID = H 1(ID) n Set-Secret-Value Select a random x. ID ∈ Zq* 15
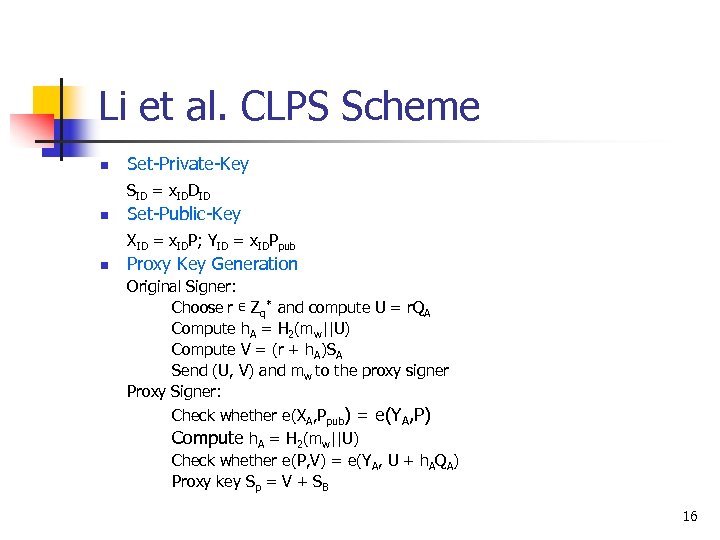 Li et al. CLPS Scheme n Set-Private-Key SID = x. IDDID n Set-Public-Key XID = x. IDP; YID = x. IDPpub n Proxy Key Generation Original Signer: Choose r ∊ Zq* and compute U = r. QA Compute h. A = H 2(mw||U) Compute V = (r + h. A)SA Send (U, V) and mw to the proxy signer Proxy Signer: Check whether e(XA, Ppub) = e(YA, P) Compute h. A = H 2(mw||U) Check whether e(P, V) = e(YA, U + h. AQA) Proxy key Sp = V + SB 16
Li et al. CLPS Scheme n Set-Private-Key SID = x. IDDID n Set-Public-Key XID = x. IDP; YID = x. IDPpub n Proxy Key Generation Original Signer: Choose r ∊ Zq* and compute U = r. QA Compute h. A = H 2(mw||U) Compute V = (r + h. A)SA Send (U, V) and mw to the proxy signer Proxy Signer: Check whether e(XA, Ppub) = e(YA, P) Compute h. A = H 2(mw||U) Check whether e(P, V) = e(YA, U + h. AQA) Proxy key Sp = V + SB 16
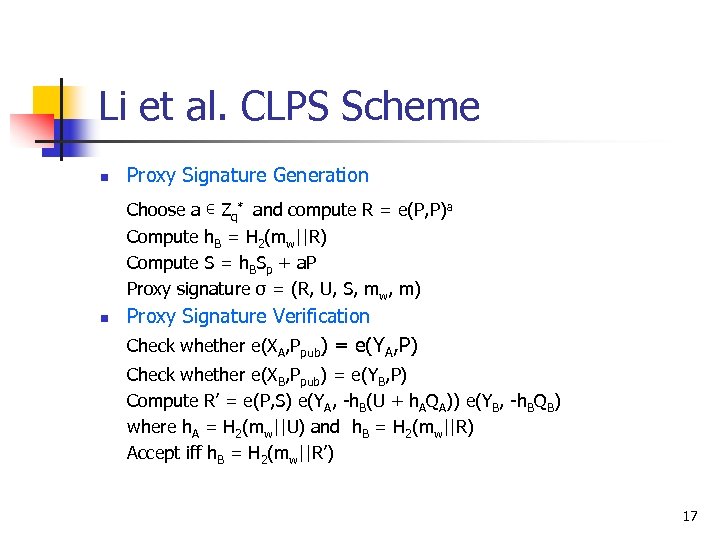 Li et al. CLPS Scheme n Proxy Signature Generation Choose a ∊ Zq* and compute R = e(P, P)a Compute h. B = H 2(mw||R) Compute S = h. BSp + a. P Proxy signature σ = (R, U, S, mw, m) n Proxy Signature Verification Check whether e(XA, Ppub) = e(YA, P) Check whether e(XB, Ppub) = e(YB, P) Compute R’ = e(P, S) e(YA, -h. B(U + h. AQA)) e(YB, -h. BQB) where h. A = H 2(mw||U) and h. B = H 2(mw||R) Accept iff h. B = H 2(mw||R’) 17
Li et al. CLPS Scheme n Proxy Signature Generation Choose a ∊ Zq* and compute R = e(P, P)a Compute h. B = H 2(mw||R) Compute S = h. BSp + a. P Proxy signature σ = (R, U, S, mw, m) n Proxy Signature Verification Check whether e(XA, Ppub) = e(YA, P) Check whether e(XB, Ppub) = e(YB, P) Compute R’ = e(P, S) e(YA, -h. B(U + h. AQA)) e(YB, -h. BQB) where h. A = H 2(mw||U) and h. B = H 2(mw||R) Accept iff h. B = H 2(mw||R’) 17
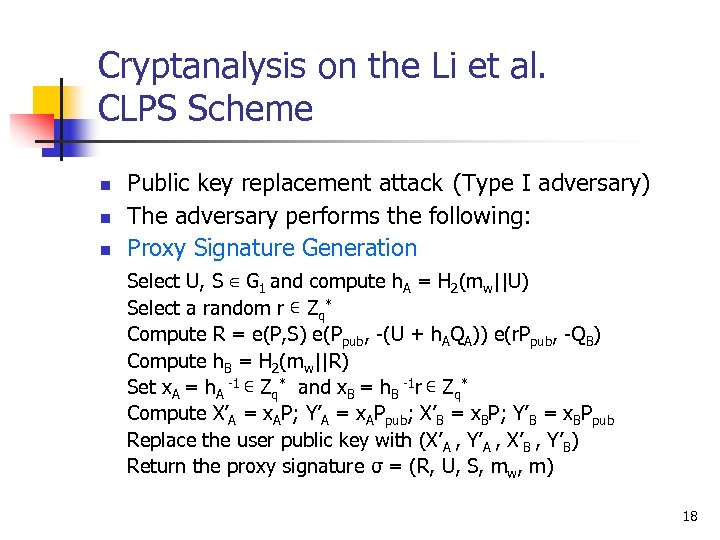 Cryptanalysis on the Li et al. CLPS Scheme n n n Public key replacement attack (Type I adversary) The adversary performs the following: Proxy Signature Generation Select U, S ∈ G 1 and compute h. A = H 2(mw||U) Select a random r ∊ Zq* Compute R = e(P, S) e(Ppub, -(U + h. AQA)) e(r. Ppub, -QB) Compute h. B = H 2(mw||R) Set x. A = h. A -1 ∊ Zq* and x. B = h. B -1 r ∊ Zq* Compute X’A = x. AP; Y’A = x. APpub; X’B = x. BP; Y’B = x. BPpub Replace the user public key with (X’A , Y’A , X’B , Y’B) Return the proxy signature σ = (R, U, S, mw, m) 18
Cryptanalysis on the Li et al. CLPS Scheme n n n Public key replacement attack (Type I adversary) The adversary performs the following: Proxy Signature Generation Select U, S ∈ G 1 and compute h. A = H 2(mw||U) Select a random r ∊ Zq* Compute R = e(P, S) e(Ppub, -(U + h. AQA)) e(r. Ppub, -QB) Compute h. B = H 2(mw||R) Set x. A = h. A -1 ∊ Zq* and x. B = h. B -1 r ∊ Zq* Compute X’A = x. AP; Y’A = x. APpub; X’B = x. BP; Y’B = x. BPpub Replace the user public key with (X’A , Y’A , X’B , Y’B) Return the proxy signature σ = (R, U, S, mw, m) 18
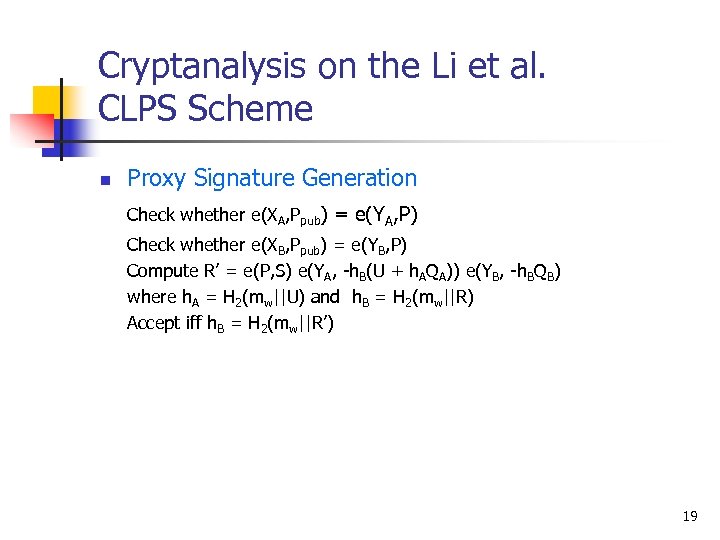 Cryptanalysis on the Li et al. CLPS Scheme n Proxy Signature Generation Check whether e(XA, Ppub) = e(YA, P) Check whether e(XB, Ppub) = e(YB, P) Compute R’ = e(P, S) e(YA, -h. B(U + h. AQA)) e(YB, -h. BQB) where h. A = H 2(mw||U) and h. B = H 2(mw||R) Accept iff h. B = H 2(mw||R’) 19
Cryptanalysis on the Li et al. CLPS Scheme n Proxy Signature Generation Check whether e(XA, Ppub) = e(YA, P) Check whether e(XB, Ppub) = e(YB, P) Compute R’ = e(P, S) e(YA, -h. B(U + h. AQA)) e(YB, -h. BQB) where h. A = H 2(mw||U) and h. B = H 2(mw||R) Accept iff h. B = H 2(mw||R’) 19
 Conclusion n n We have shown that following schemes are insecure n The Qian and Cao IBPS scheme n The Guo et al. IBPS scheme n The Li et al. CLPS scheme The security of the proxy signature schemes deriving from the provable secure IBS scheme is not guaranteed. 20
Conclusion n n We have shown that following schemes are insecure n The Qian and Cao IBPS scheme n The Guo et al. IBPS scheme n The Li et al. CLPS scheme The security of the proxy signature schemes deriving from the provable secure IBS scheme is not guaranteed. 20


