 Cryptanalysis of Short Exponent RSA with Primes Sharing Least Significant Bits Hung-Min Sun, Mu-En Wu Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Ron Steinfeld Centre for Advanced Computing - Algorithms and Cryptography, Department of Computing, Macquarie University, Australia Jian Guo, Huaxiong Wang School of Physical and Mathematical Science, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Date: 2008/12/02
Cryptanalysis of Short Exponent RSA with Primes Sharing Least Significant Bits Hung-Min Sun, Mu-En Wu Department of Computer Science, National Tsing Hua University, Taiwan Ron Steinfeld Centre for Advanced Computing - Algorithms and Cryptography, Department of Computing, Macquarie University, Australia Jian Guo, Huaxiong Wang School of Physical and Mathematical Science, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore Date: 2008/12/02
 Outline l LSBS RSA l Lattice Reduction Technique l Zhao-Qi Attack l Our Improvement l Comparison and Experiment l Conclusion and Future Work
Outline l LSBS RSA l Lattice Reduction Technique l Zhao-Qi Attack l Our Improvement l Comparison and Experiment l Conclusion and Future Work
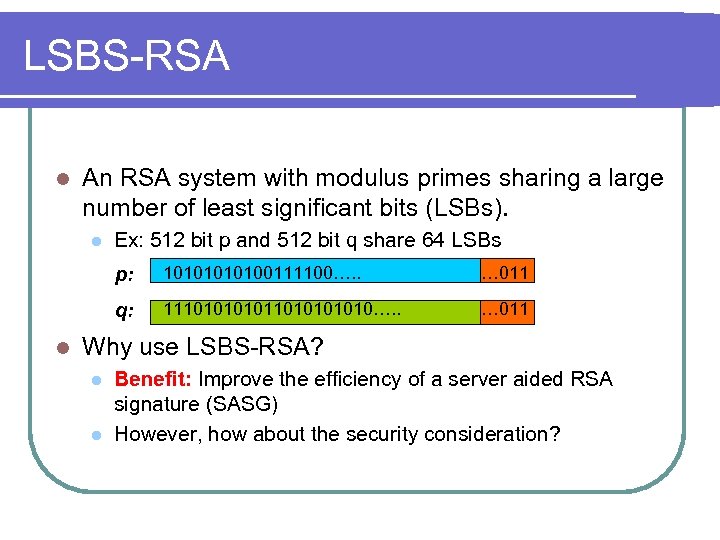 LSBS-RSA l An RSA system with modulus primes sharing a large number of least significant bits (LSBs). l Ex: 512 bit p and 512 bit q share 64 LSBs p: … 011 q: l 1010100111100…. . 111010101010…. . … 011 Why use LSBS-RSA? l l Benefit: Improve the efficiency of a server aided RSA signature (SASG) However, how about the security consideration?
LSBS-RSA l An RSA system with modulus primes sharing a large number of least significant bits (LSBs). l Ex: 512 bit p and 512 bit q share 64 LSBs p: … 011 q: l 1010100111100…. . 111010101010…. . … 011 Why use LSBS-RSA? l l Benefit: Improve the efficiency of a server aided RSA signature (SASG) However, how about the security consideration?
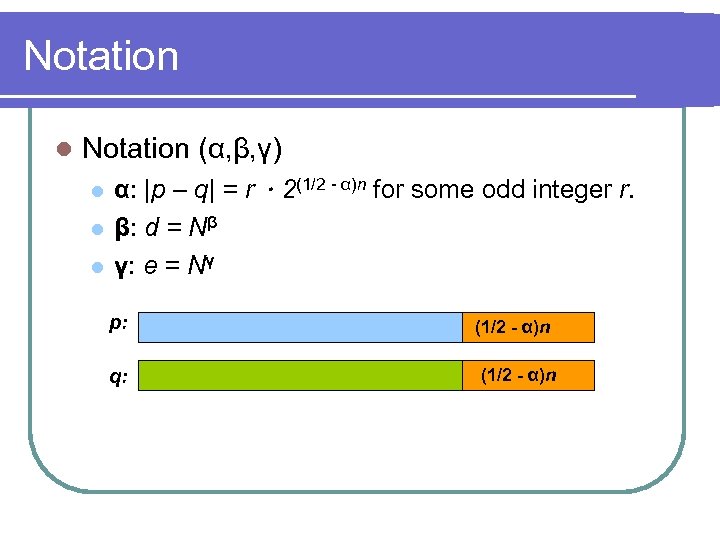 Notation l Notation (α, β, γ) l α: |p – q| = r.2(1/2 - α)n for some odd integer r. l l β: d = Nβ γ: e = Nγ p: q: (1/2 - α)n
Notation l Notation (α, β, γ) l α: |p – q| = r.2(1/2 - α)n for some odd integer r. l l β: d = Nβ γ: e = Nγ p: q: (1/2 - α)n
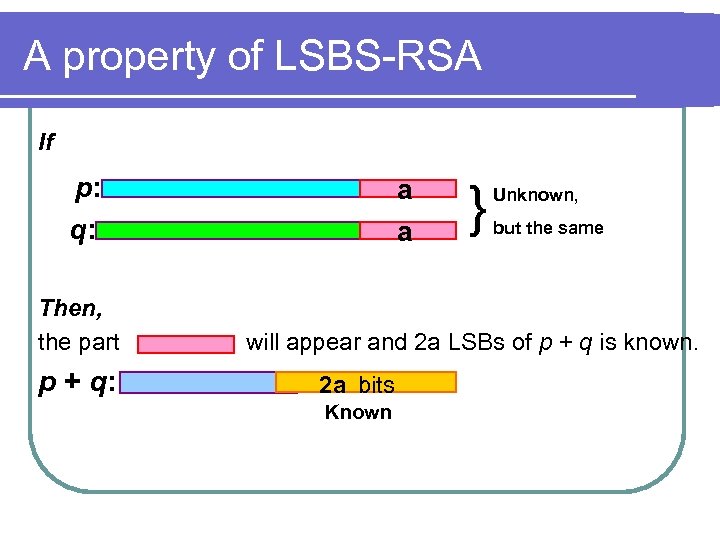 A property of LSBS-RSA If p: q: Then, the part p + q: a a } Unknown, but the same will appear and 2 a LSBs of p + q is known. 2 a bits Known
A property of LSBS-RSA If p: q: Then, the part p + q: a a } Unknown, but the same will appear and 2 a LSBs of p + q is known. 2 a bits Known
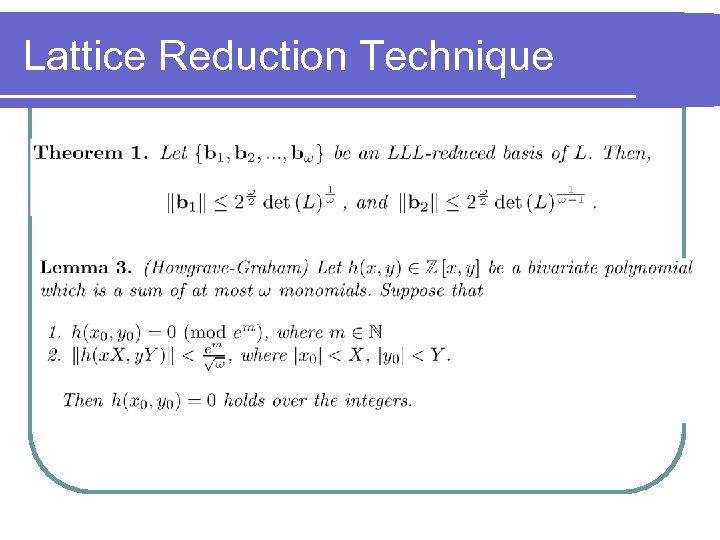 Lattice Reduction Technique
Lattice Reduction Technique
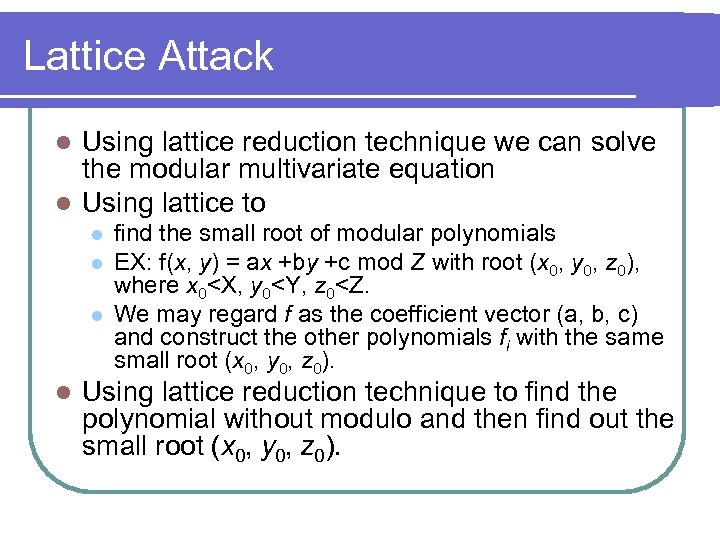 Lattice Attack Using lattice reduction technique we can solve the modular multivariate equation l Using lattice to l l l find the small root of modular polynomials EX: f(x, y) = ax +by +c mod Z with root (x 0, y 0, z 0), where x 0
Lattice Attack Using lattice reduction technique we can solve the modular multivariate equation l Using lattice to l l l find the small root of modular polynomials EX: f(x, y) = ax +by +c mod Z with root (x 0, y 0, z 0), where x 0
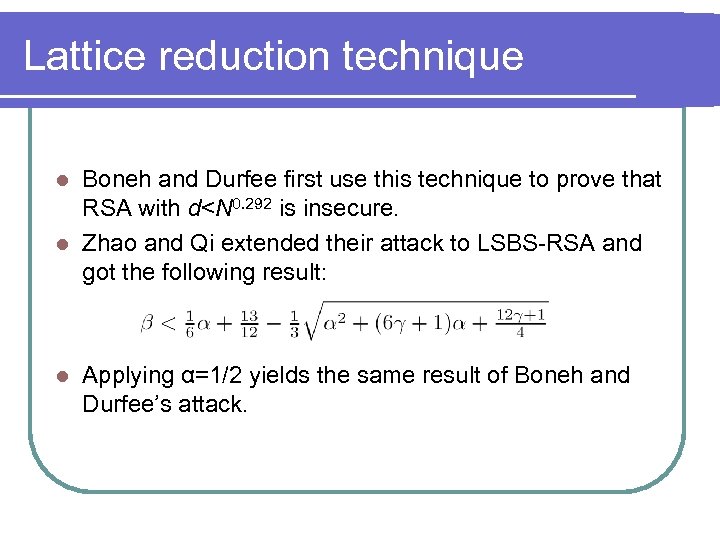 Lattice reduction technique Boneh and Durfee first use this technique to prove that RSA with d
Lattice reduction technique Boneh and Durfee first use this technique to prove that RSA with d
![The Zhao-Qi Attack ed = k[(N+1)-(p+q)]+1 l ed = k[(N+1)-2 q- r.2(1/2 - α) The Zhao-Qi Attack ed = k[(N+1)-(p+q)]+1 l ed = k[(N+1)-2 q- r.2(1/2 - α)](https://present5.com/presentation/abe1171202fe464de4aa09b364006f5f/image-9.jpg) The Zhao-Qi Attack ed = k[(N+1)-(p+q)]+1 l ed = k[(N+1)-2 q- r.2(1/2 - α) )]+1 l l Let A=N+1, a= 2(1/2 - α) Let x 0=k, y 0=q, and z 0=r Then, (x 0, y 0, z 0) is a root of l l f(x, y, z)=x(A-2 y-az)+1 (mod e) with the bounds |x 0|
The Zhao-Qi Attack ed = k[(N+1)-(p+q)]+1 l ed = k[(N+1)-2 q- r.2(1/2 - α) )]+1 l l Let A=N+1, a= 2(1/2 - α) Let x 0=k, y 0=q, and z 0=r Then, (x 0, y 0, z 0) is a root of l l f(x, y, z)=x(A-2 y-az)+1 (mod e) with the bounds |x 0|
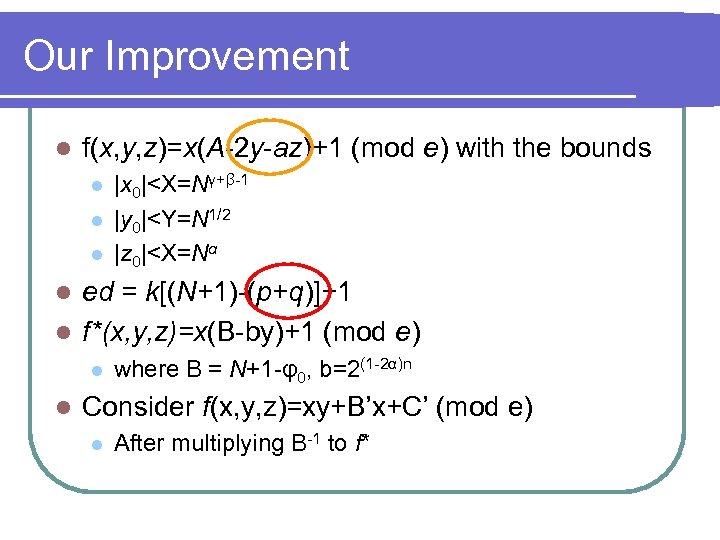 Our Improvement l f(x, y, z)=x(A-2 y-az)+1 (mod e) with the bounds l l l |x 0|
Our Improvement l f(x, y, z)=x(A-2 y-az)+1 (mod e) with the bounds l l l |x 0|
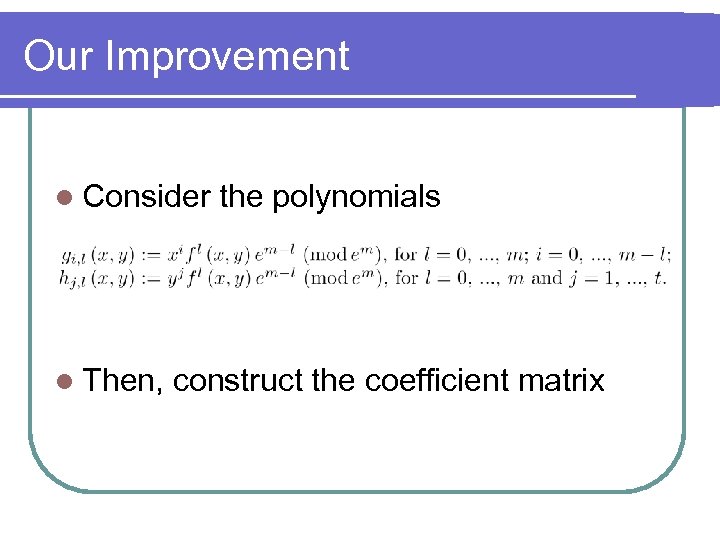 Our Improvement l Consider l Then, the polynomials construct the coefficient matrix
Our Improvement l Consider l Then, the polynomials construct the coefficient matrix
 The case m=3, t=1
The case m=3, t=1
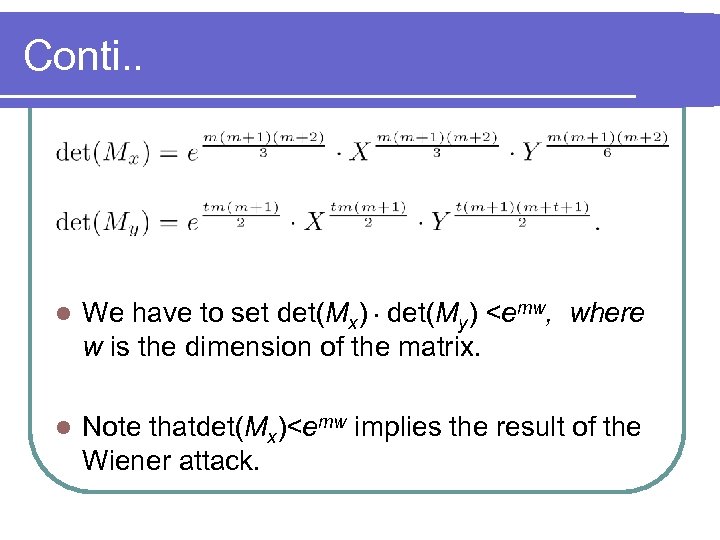 Conti. . l We have to set det(Mx).det(My)
Conti. . l We have to set det(Mx).det(My)
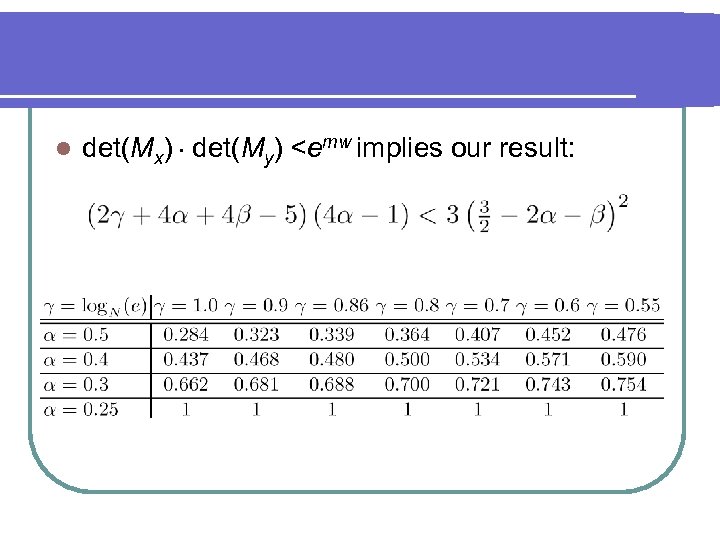 l det(Mx).det(My)
l det(Mx).det(My)
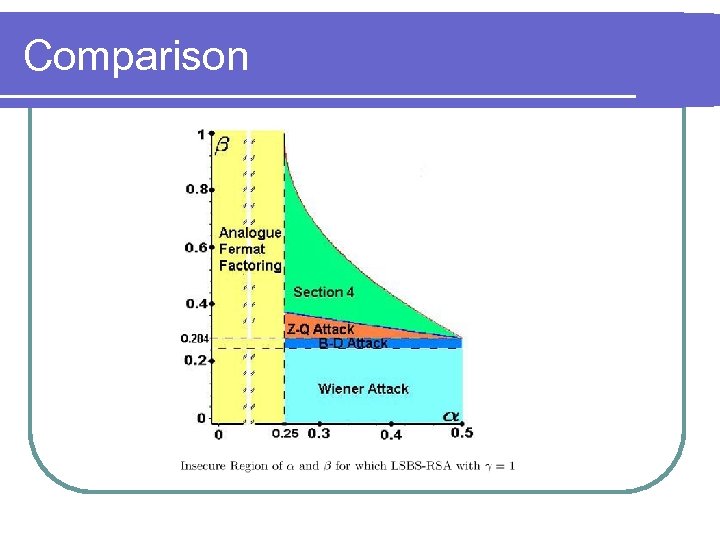 Comparison
Comparison
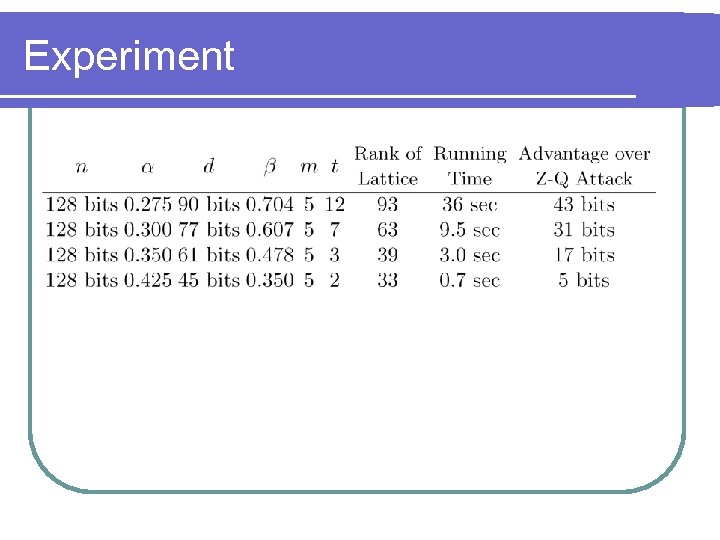 Experiment
Experiment
 Conclusion and Future work We extend the Boneh-Durfee attack to the general case by considering the prime sharing LSBs. l How about the case of prime sharing LSBs and MSBs simultaneously l In order to enhance the efficiency of the operation, how to design LSBS-RSA with short public exponent and private exponent? l
Conclusion and Future work We extend the Boneh-Durfee attack to the general case by considering the prime sharing LSBs. l How about the case of prime sharing LSBs and MSBs simultaneously l In order to enhance the efficiency of the operation, how to design LSBS-RSA with short public exponent and private exponent? l
 l Thanks l for your attention!! Any question please contact to mn@is. cs. nthu. edu. tw
l Thanks l for your attention!! Any question please contact to mn@is. cs. nthu. edu. tw