88f1d04958ea733877620af7d0d046f7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32
 CRT 2011 Therapeutic Hypothermia After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: PCI Centers should offer Therapeutic Hypothermia Michael R. Mooney MD Director of Interventional Cardiology Director, Therapeutic Hypothermia Program Minneapolis Heart Institute at Abbott Northwestern Hospital
CRT 2011 Therapeutic Hypothermia After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: PCI Centers should offer Therapeutic Hypothermia Michael R. Mooney MD Director of Interventional Cardiology Director, Therapeutic Hypothermia Program Minneapolis Heart Institute at Abbott Northwestern Hospital
 Michael R. Mooney, MD I have no real or apparent conflicts of interest to report. I intend to reference off label or unapproved uses of drugs or devices in my presentation. I intend to discuss therapeutic hypmia which is not FDA approved, it is ILCOR and ACC indicated, however.
Michael R. Mooney, MD I have no real or apparent conflicts of interest to report. I intend to reference off label or unapproved uses of drugs or devices in my presentation. I intend to discuss therapeutic hypmia which is not FDA approved, it is ILCOR and ACC indicated, however.
 Cardiac Arrest • Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OOHCA) • 295, 000 people annually in the U. S. • 7. 9% median survival rate • Anoxic encephalopathy and neurologic deficits • Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) clinical trials • ILCOR, ACC/AHA and EMS recommendation for TH after resuscitation Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2009 update. irculation 2009; 119: e 21 -e 181. C
Cardiac Arrest • Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OOHCA) • 295, 000 people annually in the U. S. • 7. 9% median survival rate • Anoxic encephalopathy and neurologic deficits • Therapeutic hypothermia (TH) clinical trials • ILCOR, ACC/AHA and EMS recommendation for TH after resuscitation Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2009 update. irculation 2009; 119: e 21 -e 181. C
 Hypothermia Pivotal Studies HACA, 2002 Bernard, 2002
Hypothermia Pivotal Studies HACA, 2002 Bernard, 2002
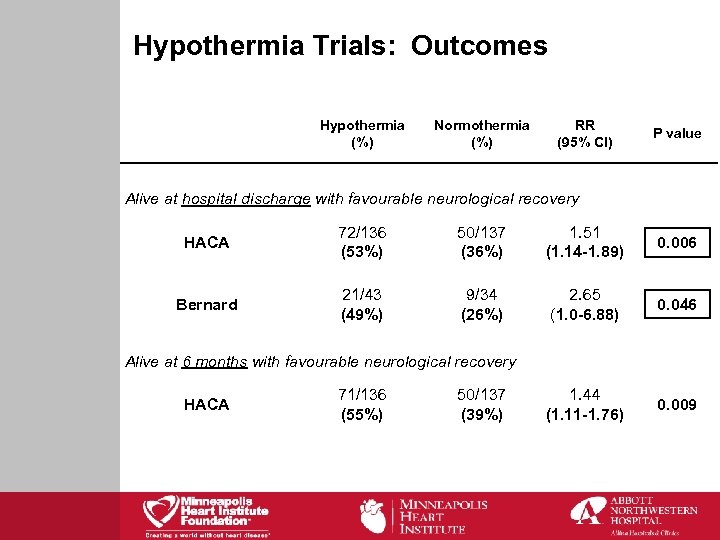 Hypothermia Trials: Outcomes Hypothermia (%) Normothermia (%) RR (95% CI) P value Alive at hospital discharge with favourable neurological recovery HACA 72/136 (53%) 50/137 (36%) 1. 51 (1. 14 -1. 89) 0. 006 Bernard 21/43 (49%) 9/34 (26%) 2. 65 (1. 0 -6. 88) 0. 046 1. 44 (1. 11 -1. 76) 0. 009 Alive at 6 months with favourable neurological recovery HACA 71/136 (55%) 50/137 (39%)
Hypothermia Trials: Outcomes Hypothermia (%) Normothermia (%) RR (95% CI) P value Alive at hospital discharge with favourable neurological recovery HACA 72/136 (53%) 50/137 (36%) 1. 51 (1. 14 -1. 89) 0. 006 Bernard 21/43 (49%) 9/34 (26%) 2. 65 (1. 0 -6. 88) 0. 046 1. 44 (1. 11 -1. 76) 0. 009 Alive at 6 months with favourable neurological recovery HACA 71/136 (55%) 50/137 (39%)
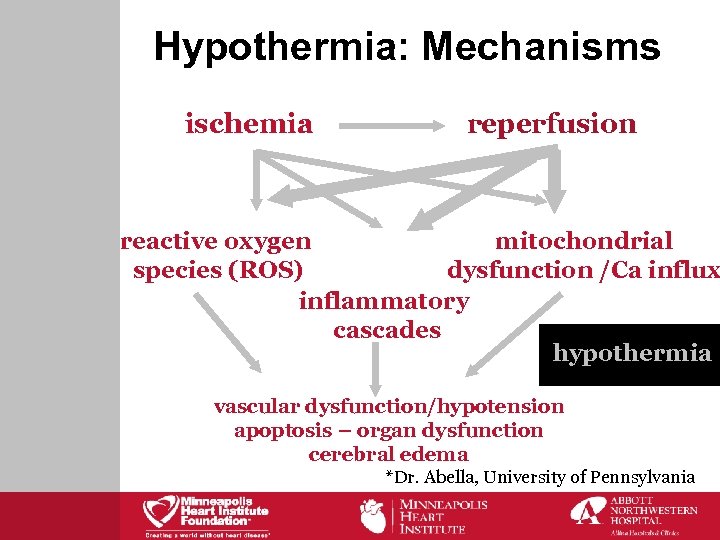 Hypothermia: Mechanisms ischemia reperfusion reactive oxygen mitochondrial species (ROS) dysfunction /Ca influx inflammatory cascades hypothermia vascular dysfunction/hypotension apoptosis – organ dysfunction cerebral edema *Dr. Abella, University of Pennsylvania
Hypothermia: Mechanisms ischemia reperfusion reactive oxygen mitochondrial species (ROS) dysfunction /Ca influx inflammatory cascades hypothermia vascular dysfunction/hypotension apoptosis – organ dysfunction cerebral edema *Dr. Abella, University of Pennsylvania
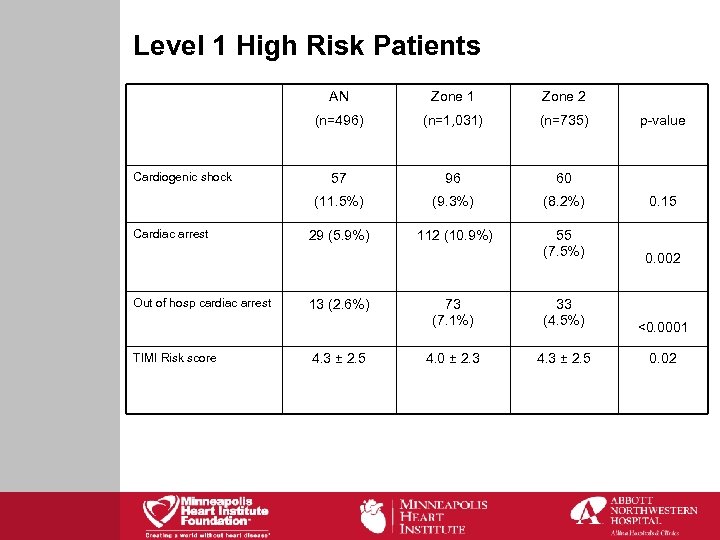 Level 1 High Risk Patients AN Out of hosp cardiac arrest TIMI Risk score (n=1, 031) (n=735) 57 96 60 (11. 5%) Cardiac arrest Zone 2 (n=496) Cardiogenic shock Zone 1 (9. 3%) (8. 2%) 0. 15 29 (5. 9%) 112 (10. 9%) 55 (7. 5%) 0. 002 73 (7. 1%) 33 (4. 5%) <0. 0001 4. 0 ± 2. 3 4. 3 ± 2. 5 0. 02 13 (2. 6%) 4. 3 ± 2. 5 p-value
Level 1 High Risk Patients AN Out of hosp cardiac arrest TIMI Risk score (n=1, 031) (n=735) 57 96 60 (11. 5%) Cardiac arrest Zone 2 (n=496) Cardiogenic shock Zone 1 (9. 3%) (8. 2%) 0. 15 29 (5. 9%) 112 (10. 9%) 55 (7. 5%) 0. 002 73 (7. 1%) 33 (4. 5%) <0. 0001 4. 0 ± 2. 3 4. 3 ± 2. 5 0. 02 13 (2. 6%) 4. 3 ± 2. 5 p-value
 MHI Level 1 MI Program -2003 “Cool it” Therapeutic Hypothermia -2006 • High volume cardiac center • 400 -500 STEMI –PCI /yr • 3 critical care units • Rapid Response Team • Inhouse intensivists 24/7 • Inhouse cardiologist 24/7 • Inhouse anesthesiologist • Clinical Pharm. D 24/7 • 12% of STEMI had cardiac arrest
MHI Level 1 MI Program -2003 “Cool it” Therapeutic Hypothermia -2006 • High volume cardiac center • 400 -500 STEMI –PCI /yr • 3 critical care units • Rapid Response Team • Inhouse intensivists 24/7 • Inhouse cardiologist 24/7 • Inhouse anesthesiologist • Clinical Pharm. D 24/7 • 12% of STEMI had cardiac arrest
 Goals of the Therapeutic Hypothermia Program: • Provide therapeutic hypothermia to the appropriate patient, at the appropriate setting. • Provide a multidiscipline approach to the care of these patients • Measure data immediately and continuously to improve both the care and the outcomes • Perform therapeutic hypothermia in a collaborative approach from EMS to emergency departments to cardiology • To address the neurocognitive recovery and support • To find cause of arrest and treat the condition including follow up clinically
Goals of the Therapeutic Hypothermia Program: • Provide therapeutic hypothermia to the appropriate patient, at the appropriate setting. • Provide a multidiscipline approach to the care of these patients • Measure data immediately and continuously to improve both the care and the outcomes • Perform therapeutic hypothermia in a collaborative approach from EMS to emergency departments to cardiology • To address the neurocognitive recovery and support • To find cause of arrest and treat the condition including follow up clinically
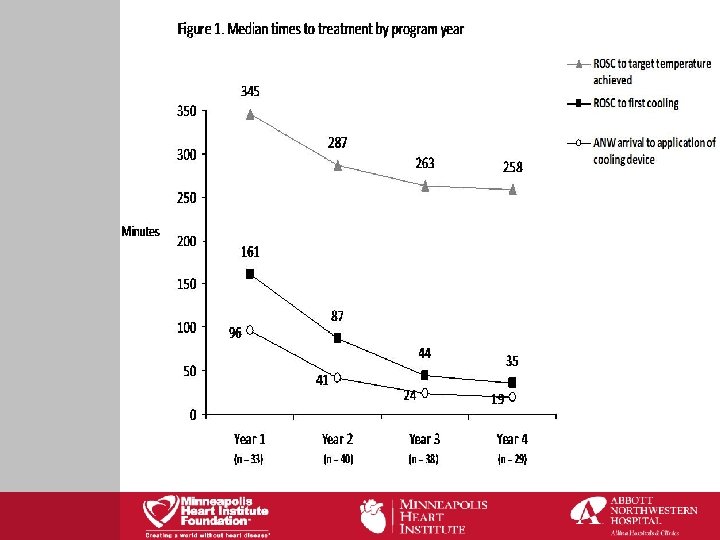
 Average time: 6 minutes
Average time: 6 minutes
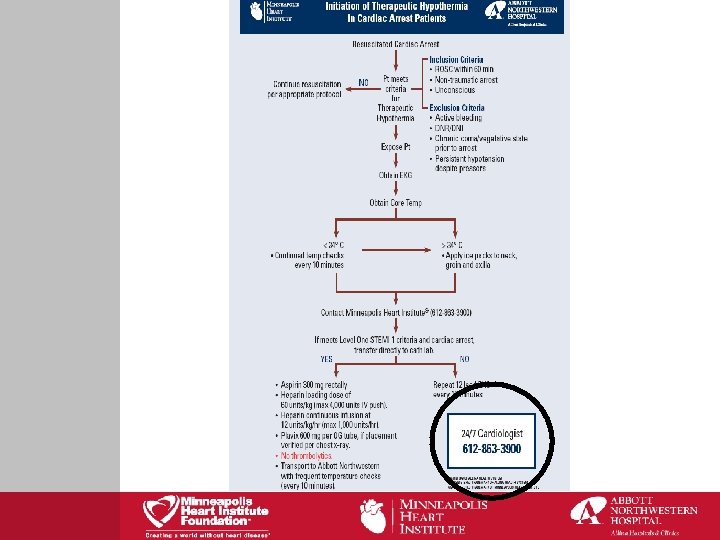
 Education: 33 Community Hospitals in MN & WI Inclusion/exclusion Is patient also a STEMI? Treatment What is needed to treat Times
Education: 33 Community Hospitals in MN & WI Inclusion/exclusion Is patient also a STEMI? Treatment What is needed to treat Times
 Standing Orders
Standing Orders

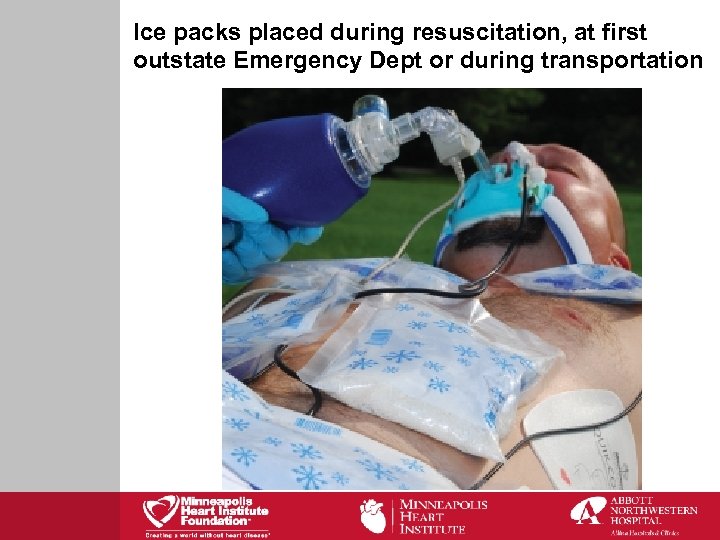 Ice packs placed during resuscitation, at first outstate Emergency Dept or during transportation
Ice packs placed during resuscitation, at first outstate Emergency Dept or during transportation
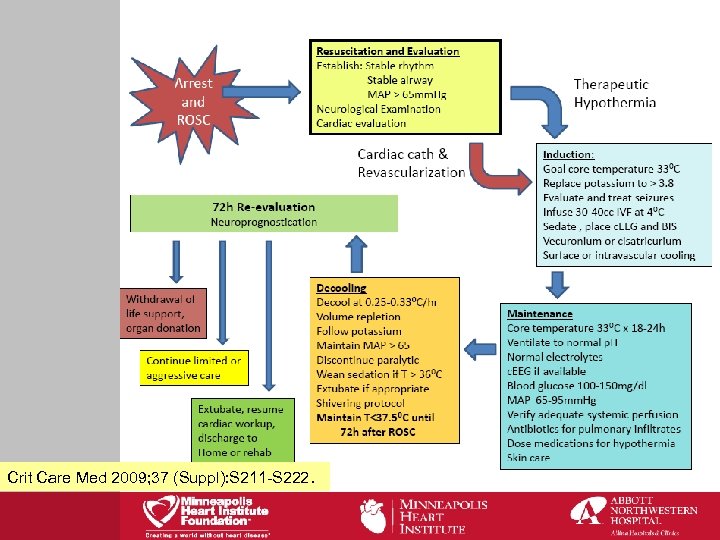 Crit Care Med 2009; 37 (Suppl): S 211 -S 222.
Crit Care Med 2009; 37 (Suppl): S 211 -S 222.
 Other Key Elements of Program • EMS initiate field ice packs and “Cool-It” protocol w/o Level 1 STEMI • Cath lab immediately for all STEMI and many others 70% of total. Excellent stabilization room for shock • Combined cooling methods effective • No lytics, heparin ½ life • Cardiology supervising inpt care • Mutidisciplinary “by in”
Other Key Elements of Program • EMS initiate field ice packs and “Cool-It” protocol w/o Level 1 STEMI • Cath lab immediately for all STEMI and many others 70% of total. Excellent stabilization room for shock • Combined cooling methods effective • No lytics, heparin ½ life • Cardiology supervising inpt care • Mutidisciplinary “by in”
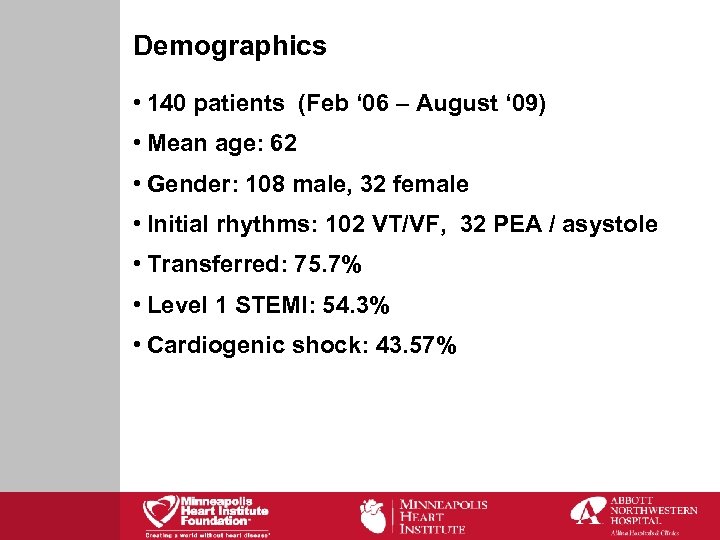 Demographics • 140 patients (Feb ‘ 06 – August ‘ 09) • Mean age: 62 • Gender: 108 male, 32 female • Initial rhythms: 102 VT/VF, 32 PEA / asystole • Transferred: 75. 7% • Level 1 STEMI: 54. 3% • Cardiogenic shock: 43. 57%
Demographics • 140 patients (Feb ‘ 06 – August ‘ 09) • Mean age: 62 • Gender: 108 male, 32 female • Initial rhythms: 102 VT/VF, 32 PEA / asystole • Transferred: 75. 7% • Level 1 STEMI: 54. 3% • Cardiogenic shock: 43. 57%
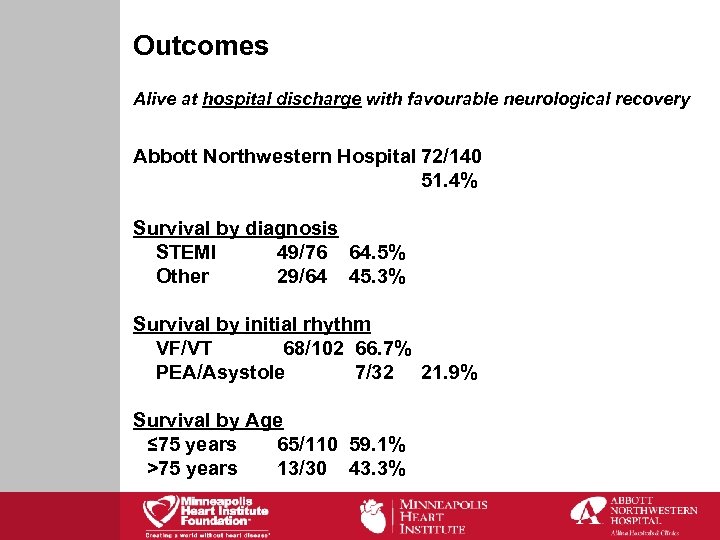 Outcomes Alive at hospital discharge with favourable neurological recovery Abbott Northwestern Hospital 72/140 51. 4% Survival by diagnosis STEMI 49/76 64. 5% Other 29/64 45. 3% Survival by initial rhythm VF/VT 68/102 66. 7% PEA/Asystole 7/32 21. 9% Survival by Age ≤ 75 years 65/110 59. 1% >75 years 13/30 43. 3%
Outcomes Alive at hospital discharge with favourable neurological recovery Abbott Northwestern Hospital 72/140 51. 4% Survival by diagnosis STEMI 49/76 64. 5% Other 29/64 45. 3% Survival by initial rhythm VF/VT 68/102 66. 7% PEA/Asystole 7/32 21. 9% Survival by Age ≤ 75 years 65/110 59. 1% >75 years 13/30 43. 3%
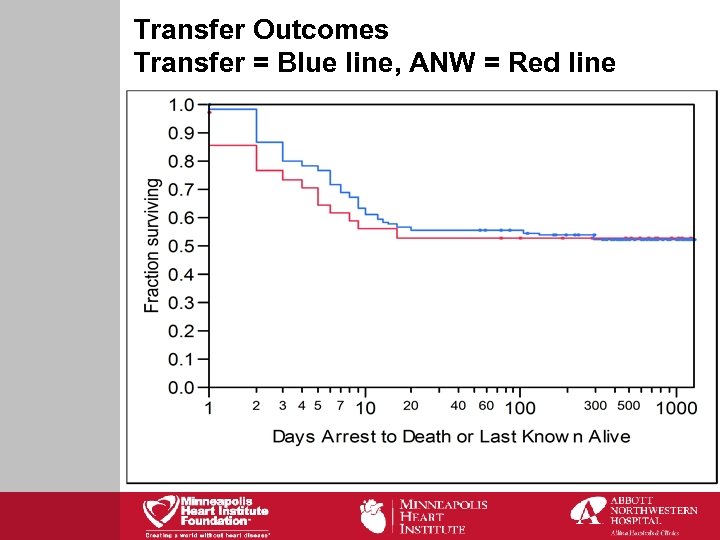 Transfer Outcomes Transfer = Blue line, ANW = Red line
Transfer Outcomes Transfer = Blue line, ANW = Red line
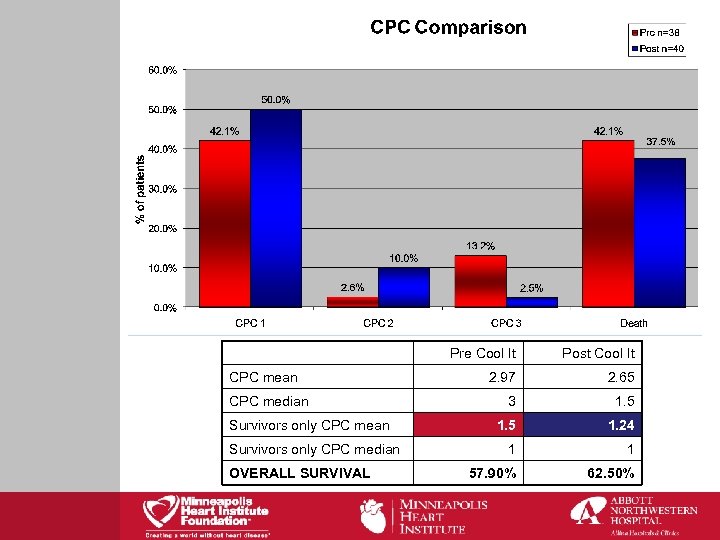 CPC mean CPC median Survivors only CPC median OVERALL SURVIVAL Pre Cool It Post Cool It 2. 97 2. 65 3 1. 5 1. 24 1 1 57. 90% 62. 50%
CPC mean CPC median Survivors only CPC median OVERALL SURVIVAL Pre Cool It Post Cool It 2. 97 2. 65 3 1. 5 1. 24 1 1 57. 90% 62. 50%
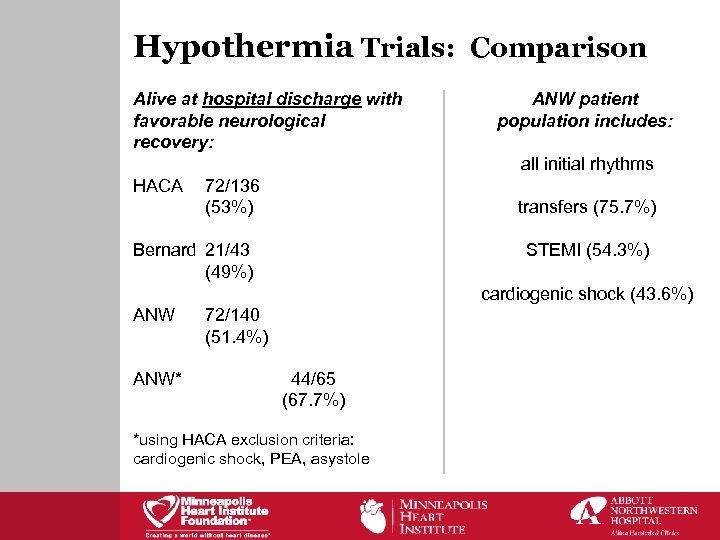 Hypothermia Trials: Comparison Alive at hospital discharge with favorable neurological recovery: ANW patient population includes: all initial rhythms HACA 72/136 (53%) transfers (75. 7%) Bernard 21/43 (49%) STEMI (54. 3%) cardiogenic shock (43. 6%) ANW* 72/140 (51. 4%) 44/65 (67. 7%) *using HACA exclusion criteria: cardiogenic shock, PEA, asystole
Hypothermia Trials: Comparison Alive at hospital discharge with favorable neurological recovery: ANW patient population includes: all initial rhythms HACA 72/136 (53%) transfers (75. 7%) Bernard 21/43 (49%) STEMI (54. 3%) cardiogenic shock (43. 6%) ANW* 72/140 (51. 4%) 44/65 (67. 7%) *using HACA exclusion criteria: cardiogenic shock, PEA, asystole
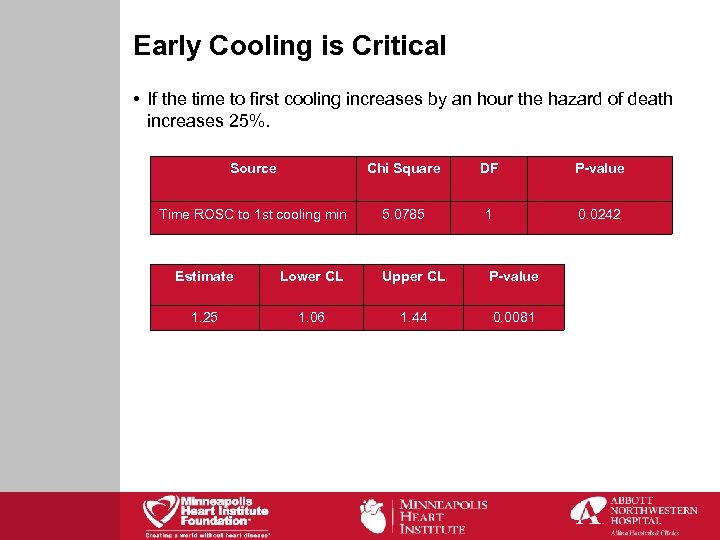 Early Cooling is Critical • If the time to first cooling increases by an hour the hazard of death increases 25%. Source Chi Square DF P-value Time ROSC to 1 st cooling min 5. 0785 1 0. 0242 Estimate Lower CL Upper CL P-value 1. 25 1. 06 1. 44 0. 0081
Early Cooling is Critical • If the time to first cooling increases by an hour the hazard of death increases 25%. Source Chi Square DF P-value Time ROSC to 1 st cooling min 5. 0785 1 0. 0242 Estimate Lower CL Upper CL P-value 1. 25 1. 06 1. 44 0. 0081
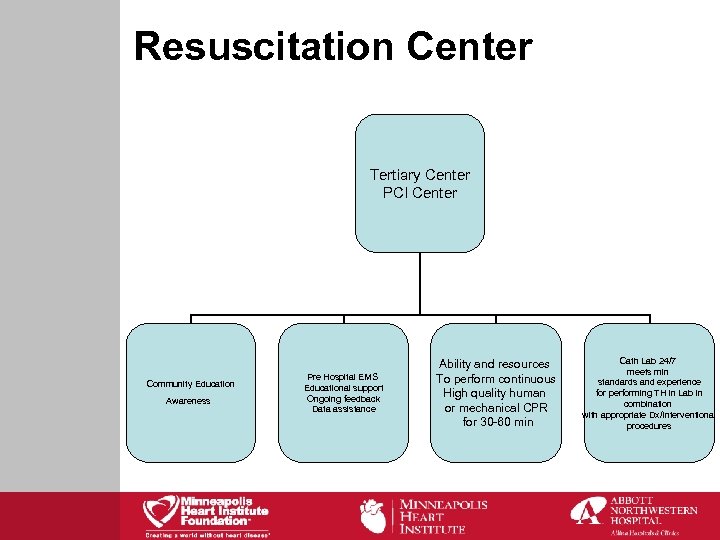 Resuscitation Center Tertiary Center PCI Center Community Education Awareness Pre Hospital EMS Educational support Ongoing feedback Data assistance Ability and resources To perform continuous High quality human or mechanical CPR for 30 -60 min Cath Lab 24/7 meets min standards and experience for performing TH in Lab in combination with appropriate Dx/Interventional procedures
Resuscitation Center Tertiary Center PCI Center Community Education Awareness Pre Hospital EMS Educational support Ongoing feedback Data assistance Ability and resources To perform continuous High quality human or mechanical CPR for 30 -60 min Cath Lab 24/7 meets min standards and experience for performing TH in Lab in combination with appropriate Dx/Interventional procedures
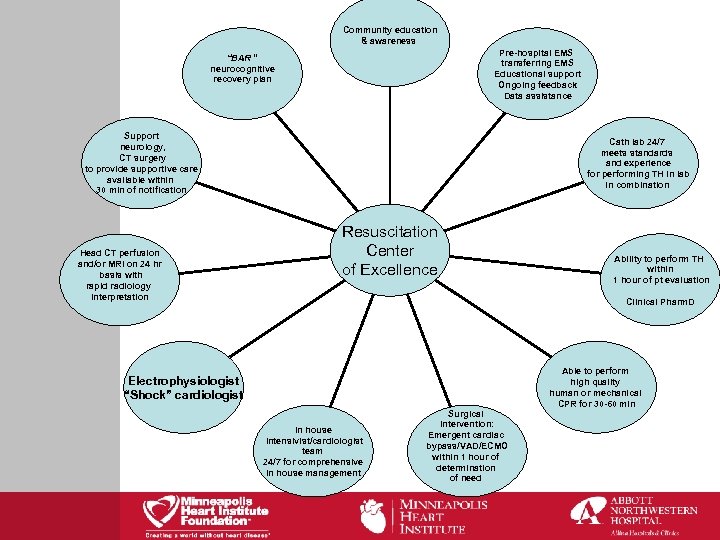 Community education & awareness Pre-hospital EMS transferring EMS Educational support Ongoing feedback Data assistance “BAR “ neurocognitive recovery plan Support neurology, CT surgery to provide supportive care available within 30 min of notification Head CT perfusion and/or MRI on 24 hr basis with rapid radiology interpretation Cath lab 24/7 meets standards and experience for performing TH in lab in combination Resuscitation Center of Excellence Ability to perform TH within 1 hour of pt evaluation Clinical Pharm. D Electrophysiologist “Shock” cardiologist In house intensivist/cardiologist team 24/7 for comprehensive In house management Surgical intervention: Emergent cardiac bypass/VAD/ECMO within 1 hour of determination of need Able to perform high quality human or mechanical CPR for 30 -60 min
Community education & awareness Pre-hospital EMS transferring EMS Educational support Ongoing feedback Data assistance “BAR “ neurocognitive recovery plan Support neurology, CT surgery to provide supportive care available within 30 min of notification Head CT perfusion and/or MRI on 24 hr basis with rapid radiology interpretation Cath lab 24/7 meets standards and experience for performing TH in lab in combination Resuscitation Center of Excellence Ability to perform TH within 1 hour of pt evaluation Clinical Pharm. D Electrophysiologist “Shock” cardiologist In house intensivist/cardiologist team 24/7 for comprehensive In house management Surgical intervention: Emergent cardiac bypass/VAD/ECMO within 1 hour of determination of need Able to perform high quality human or mechanical CPR for 30 -60 min
 Key Components 1) Integrate into existing STEMI networks 2) Extensive training 3) Early cooling 4) Individualized transfer arrangements 5) Single phone call 6) Standardized protocol 7) Feedback/quality assurance 8) Data should expand to national standards and continue to work with Centers of Resuscitation to promote best practices
Key Components 1) Integrate into existing STEMI networks 2) Extensive training 3) Early cooling 4) Individualized transfer arrangements 5) Single phone call 6) Standardized protocol 7) Feedback/quality assurance 8) Data should expand to national standards and continue to work with Centers of Resuscitation to promote best practices
 Impella/Tandem Heart
Impella/Tandem Heart
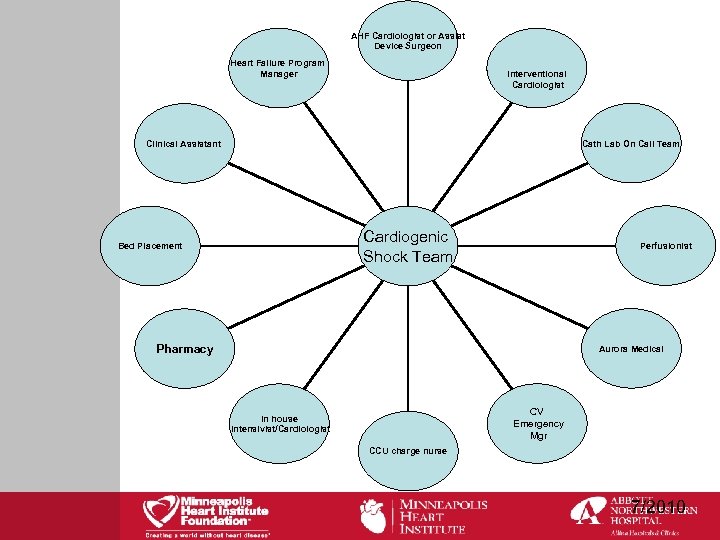 AHF Cardiologist or Assist Device Surgeon Heart Failure Program Manager Interventional Cardiologist Cath Lab On Call Team Clinical Assistant Cardiogenic Shock Team Bed Placement Perfusionist Pharmacy Aurora Medical CV Emergency Mgr In house Intensivist/Cardiologist CCU charge nurse 7/2010
AHF Cardiologist or Assist Device Surgeon Heart Failure Program Manager Interventional Cardiologist Cath Lab On Call Team Clinical Assistant Cardiogenic Shock Team Bed Placement Perfusionist Pharmacy Aurora Medical CV Emergency Mgr In house Intensivist/Cardiologist CCU charge nurse 7/2010
 PCI Centers Should Offer Therapeutic Hypothermia 1. Half of the patients have STEMI 2. Extensive training with protocolized care 3. Collaboration on presenting patient 4. Interhospital transfer systems 5. Exisiting transfer protocols and EMS relations 6. Data collection/evaluation/improvements 7. Care across continuum 8. Communication methods (FEEDBACK) 9. Research 10. Cardiac arrest is a Cardiovascular Emergency
PCI Centers Should Offer Therapeutic Hypothermia 1. Half of the patients have STEMI 2. Extensive training with protocolized care 3. Collaboration on presenting patient 4. Interhospital transfer systems 5. Exisiting transfer protocols and EMS relations 6. Data collection/evaluation/improvements 7. Care across continuum 8. Communication methods (FEEDBACK) 9. Research 10. Cardiac arrest is a Cardiovascular Emergency
 Cardiovascular Emergency Centers To maximize benefits, cooling should be initiated as soon as possible. Survival benefits are dramatic. But, we under-deliver this lifesaving treatment. TH capable Acute MI PCI centers should offer this lifesaving treatment, it is a public health care imperative. We can achieve equivalent access and outcomes in rural and metro patients by providing one Standard of Care for an entire Region for the most complex cardiac emergencies.
Cardiovascular Emergency Centers To maximize benefits, cooling should be initiated as soon as possible. Survival benefits are dramatic. But, we under-deliver this lifesaving treatment. TH capable Acute MI PCI centers should offer this lifesaving treatment, it is a public health care imperative. We can achieve equivalent access and outcomes in rural and metro patients by providing one Standard of Care for an entire Region for the most complex cardiac emergencies.
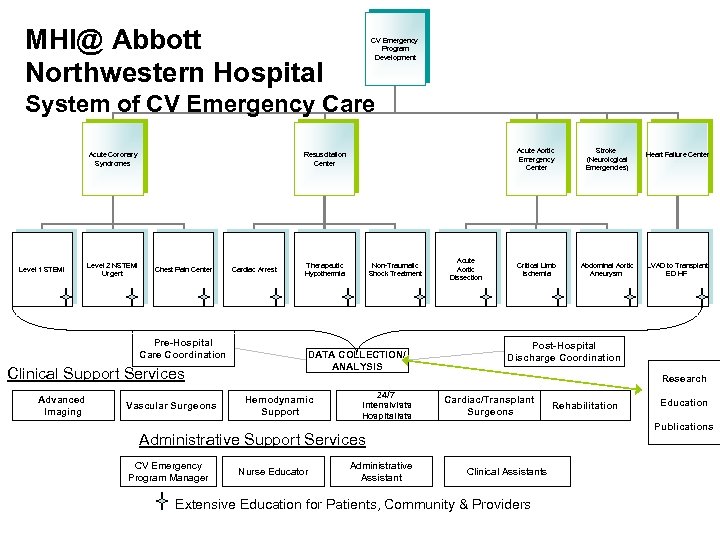 MHI@ Abbott Northwestern Hospital CV Emergency Program Development System of CV Emergency Care Acute Coronary Syndromes Level 1 STEMI Level 2 NSTEMI Urgent Chest Pain Center Pre-Hospital Care Coordination Clinical Support Services Advanced Imaging Acute Aortic Emergency Center Resuscitation Center Vascular Surgeons Cardiac Arrest Therapeutic Hypothermia Non-Traumatic Shock Treatment DATA COLLECTION/ ANALYSIS Acute Aortic Dissection Stroke (Neurological Emergencies) Critical Limb Ischemia Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm LVAD to Transplant ED HF Post-Hospital Discharge Coordination Research Hemodynamic Support 24/7 Intensivists Hospitalists Cardiac/Transplant Surgeons Nurse Educator Administrative Assistant Rehabilitation Education Publications Administrative Support Services CV Emergency Program Manager Heart Failure Center Clinical Assistants Extensive Education for Patients, Community & Providers
MHI@ Abbott Northwestern Hospital CV Emergency Program Development System of CV Emergency Care Acute Coronary Syndromes Level 1 STEMI Level 2 NSTEMI Urgent Chest Pain Center Pre-Hospital Care Coordination Clinical Support Services Advanced Imaging Acute Aortic Emergency Center Resuscitation Center Vascular Surgeons Cardiac Arrest Therapeutic Hypothermia Non-Traumatic Shock Treatment DATA COLLECTION/ ANALYSIS Acute Aortic Dissection Stroke (Neurological Emergencies) Critical Limb Ischemia Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm LVAD to Transplant ED HF Post-Hospital Discharge Coordination Research Hemodynamic Support 24/7 Intensivists Hospitalists Cardiac/Transplant Surgeons Nurse Educator Administrative Assistant Rehabilitation Education Publications Administrative Support Services CV Emergency Program Manager Heart Failure Center Clinical Assistants Extensive Education for Patients, Community & Providers


