01ad5cf48b83006a24e6bb833a87ffcc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Cross-sectional assessment of patient outcomes using a systematic file review process Ambereen Jaffer, Gesine Meyer-Rath, Malebo Maponyane, Aimee Malingan, Ebrahim Variava, Francois Venter
Cross-sectional assessment of patient outcomes using a systematic file review process Ambereen Jaffer, Gesine Meyer-Rath, Malebo Maponyane, Aimee Malingan, Ebrahim Variava, Francois Venter
 Background q RHRU provides technical assistance with HIV related clinical services and capacity building via training and mentorship to Department of Health antiretroviral (ARV) clinic in Gauteng, KZN and North-West provinces. q Wellness clinic at Klerksdorp Hospital is one of the largest partnering treatment sites, providing services to close to 6000 patients requiring HIV related care. q One of the first sites in South Africa to establish a down/up referral model. Referral model is enabling the clinic to continue to initiate large number of patients on ARVs. 2005
Background q RHRU provides technical assistance with HIV related clinical services and capacity building via training and mentorship to Department of Health antiretroviral (ARV) clinic in Gauteng, KZN and North-West provinces. q Wellness clinic at Klerksdorp Hospital is one of the largest partnering treatment sites, providing services to close to 6000 patients requiring HIV related care. q One of the first sites in South Africa to establish a down/up referral model. Referral model is enabling the clinic to continue to initiate large number of patients on ARVs. 2005
 Background q With the increasing number of clients, management of data and defaulters has become an area of concern for the clinic. q In June 2006, the clinic leadership asked RHRU for assistance. A retrospective review of all patient files since the ARV roll out initiated in April 2004 was deemed necessary. 2005
Background q With the increasing number of clients, management of data and defaulters has become an area of concern for the clinic. q In June 2006, the clinic leadership asked RHRU for assistance. A retrospective review of all patient files since the ARV roll out initiated in April 2004 was deemed necessary. 2005
 Background q Developed & piloted a one page data collection tool. q Over 70 (clinical & non-clinical) individuals from Do. H, RHRU & Aurum participated in the file review activity in July 2006. q Two additional file reviews have been conducted at: n ARV Clinic at Johannesburg Hospital: Completed Jan 2007 n Wellness Clinic at Taung Hospital, NW: Completed Mar 2007 2005
Background q Developed & piloted a one page data collection tool. q Over 70 (clinical & non-clinical) individuals from Do. H, RHRU & Aurum participated in the file review activity in July 2006. q Two additional file reviews have been conducted at: n ARV Clinic at Johannesburg Hospital: Completed Jan 2007 n Wellness Clinic at Taung Hospital, NW: Completed Mar 2007 2005
 Background q. Interested in finding out : n How many patients are currently on treatment? n How many patients have been down-referred? n How many patients are lost to follow-up? n What regimens are the patients on? n Side effects, treatment changes, other illnesses information n CD 4 & viral load information on the patients 2005
Background q. Interested in finding out : n How many patients are currently on treatment? n How many patients have been down-referred? n How many patients are lost to follow-up? n What regimens are the patients on? n Side effects, treatment changes, other illnesses information n CD 4 & viral load information on the patients 2005
 Results - Klerksdorp q Total of 5750 files were reviewed. q Approx 63% of patients accessing service at this clinic are females & 36% are males. q Mean age of patients is 38 yrs q Patients files were classified as follows: n Active Patients n Pre-ART Defaulters (never started on ARVs & did not return after initial visit which was >6 weeks ago) n Down Referred n Post Treatment Defaulters (Started on ARVs but have not returned to clinic in > 6 weeks since the last clinic or pharmacy visit). n Deceased 2005
Results - Klerksdorp q Total of 5750 files were reviewed. q Approx 63% of patients accessing service at this clinic are females & 36% are males. q Mean age of patients is 38 yrs q Patients files were classified as follows: n Active Patients n Pre-ART Defaulters (never started on ARVs & did not return after initial visit which was >6 weeks ago) n Down Referred n Post Treatment Defaulters (Started on ARVs but have not returned to clinic in > 6 weeks since the last clinic or pharmacy visit). n Deceased 2005
 Results: Klerksdorp 2005
Results: Klerksdorp 2005
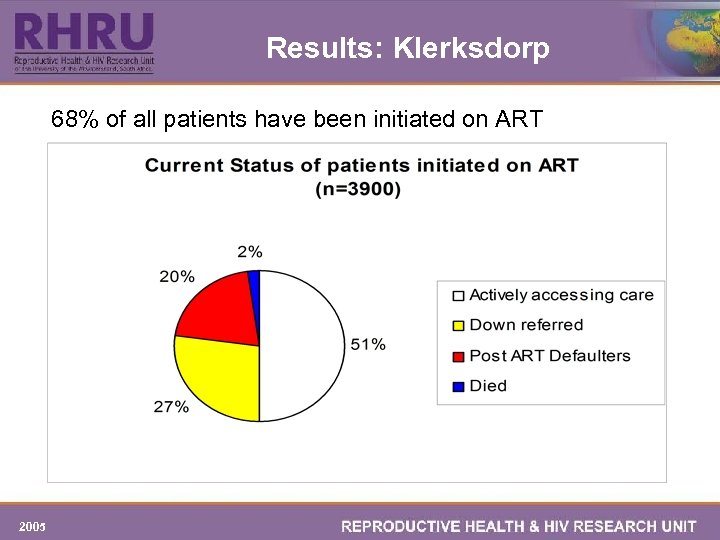 Results: Klerksdorp 68% of all patients have been initiated on ART 2005
Results: Klerksdorp 68% of all patients have been initiated on ART 2005
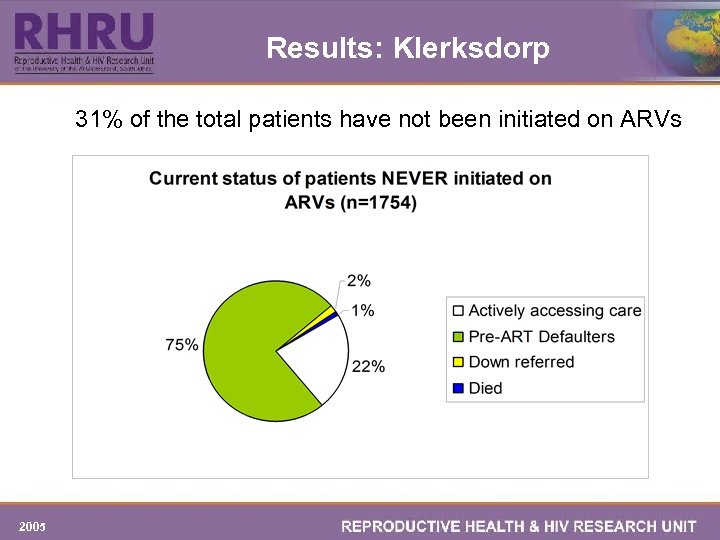 Results: Klerksdorp 31% of the total patients have not been initiated on ARVs 2005
Results: Klerksdorp 31% of the total patients have not been initiated on ARVs 2005
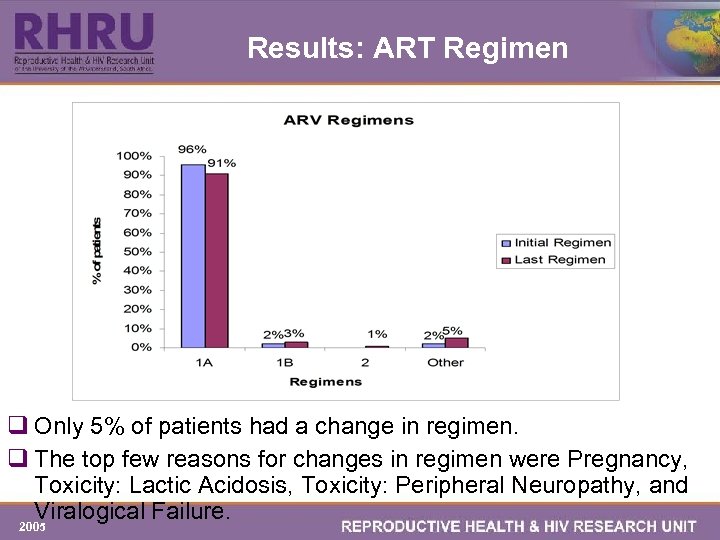 Results: ART Regimen q Only 5% of patients had a change in regimen. q The top few reasons for changes in regimen were Pregnancy, Toxicity: Lactic Acidosis, Toxicity: Peripheral Neuropathy, and Viralogical Failure. 2005
Results: ART Regimen q Only 5% of patients had a change in regimen. q The top few reasons for changes in regimen were Pregnancy, Toxicity: Lactic Acidosis, Toxicity: Peripheral Neuropathy, and Viralogical Failure. 2005
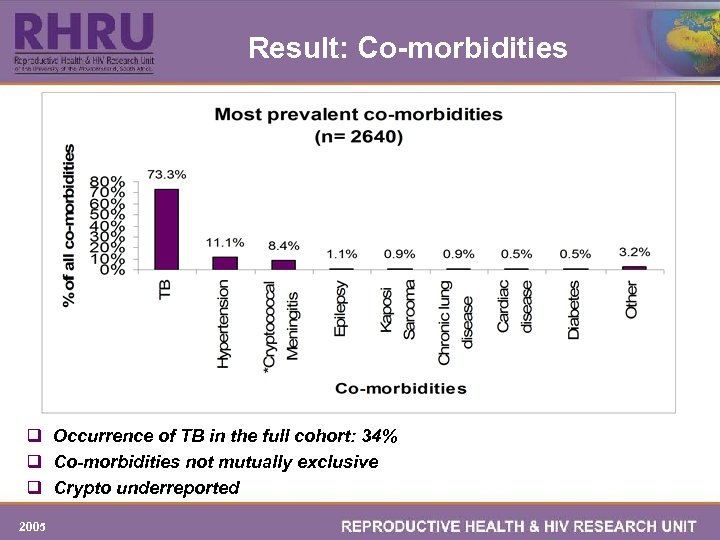 Result: Co-morbidities q Occurrence of TB in the full cohort: 34% q Co-morbidities not mutually exclusive q Crypto underreported 2005
Result: Co-morbidities q Occurrence of TB in the full cohort: 34% q Co-morbidities not mutually exclusive q Crypto underreported 2005
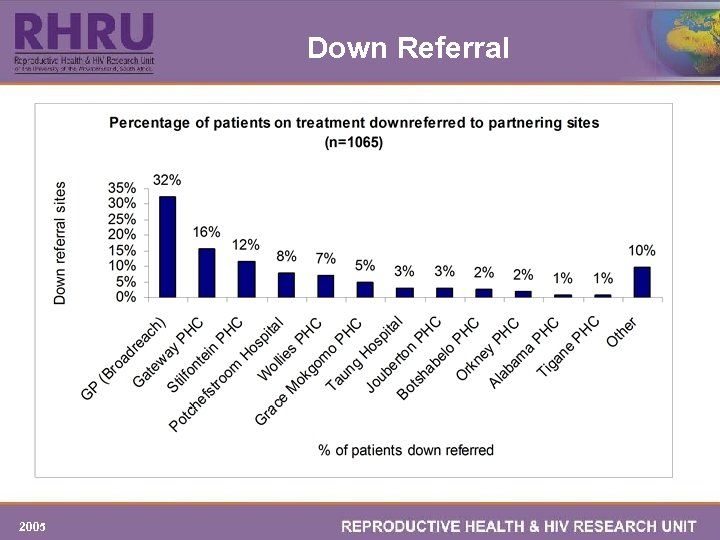 Down Referral 2005
Down Referral 2005
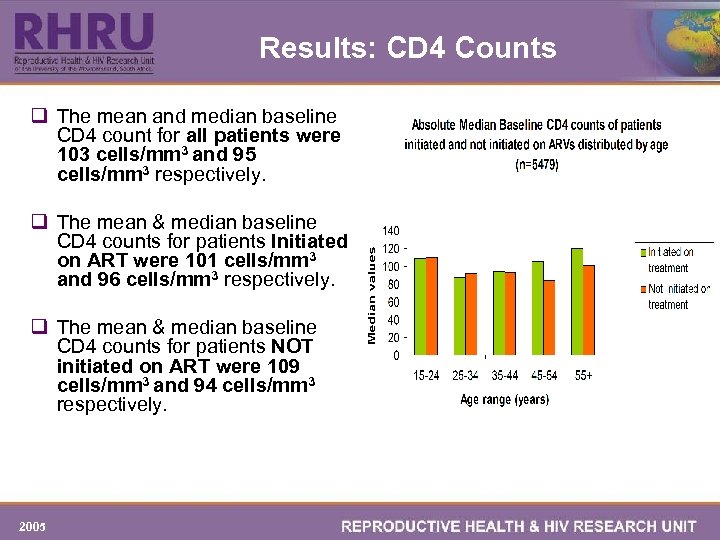 Results: CD 4 Counts q The mean and median baseline CD 4 count for all patients were 103 cells/mm 3 and 95 cells/mm 3 respectively. q The mean & median baseline CD 4 counts for patients Initiated on ART were 101 cells/mm 3 and 96 cells/mm 3 respectively. q The mean & median baseline CD 4 counts for patients NOT initiated on ART were 109 cells/mm 3 and 94 cells/mm 3 respectively. 2005
Results: CD 4 Counts q The mean and median baseline CD 4 count for all patients were 103 cells/mm 3 and 95 cells/mm 3 respectively. q The mean & median baseline CD 4 counts for patients Initiated on ART were 101 cells/mm 3 and 96 cells/mm 3 respectively. q The mean & median baseline CD 4 counts for patients NOT initiated on ART were 109 cells/mm 3 and 94 cells/mm 3 respectively. 2005
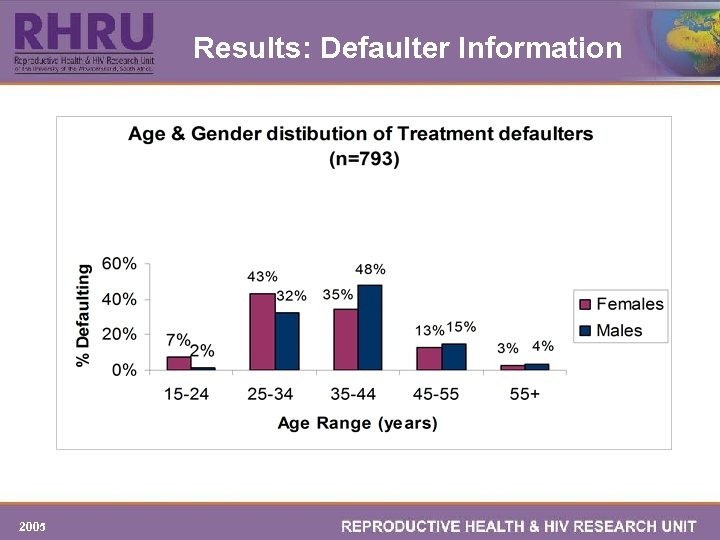 Results: Defaulter Information 2005
Results: Defaulter Information 2005
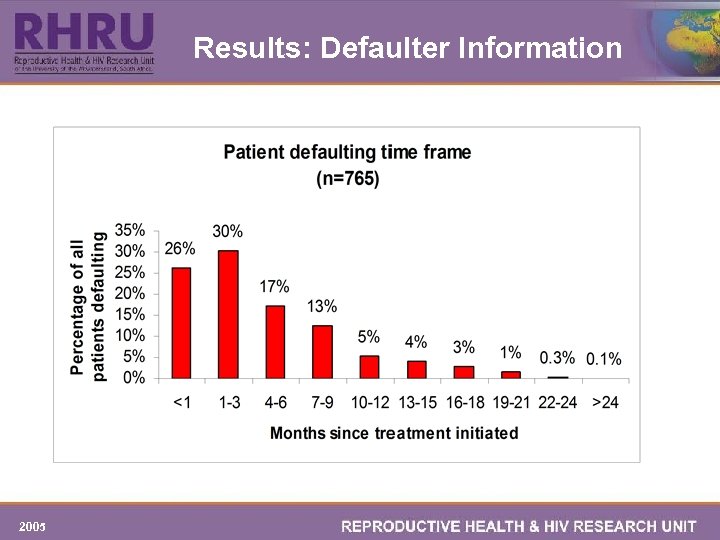 Results: Defaulter Information 2005
Results: Defaulter Information 2005
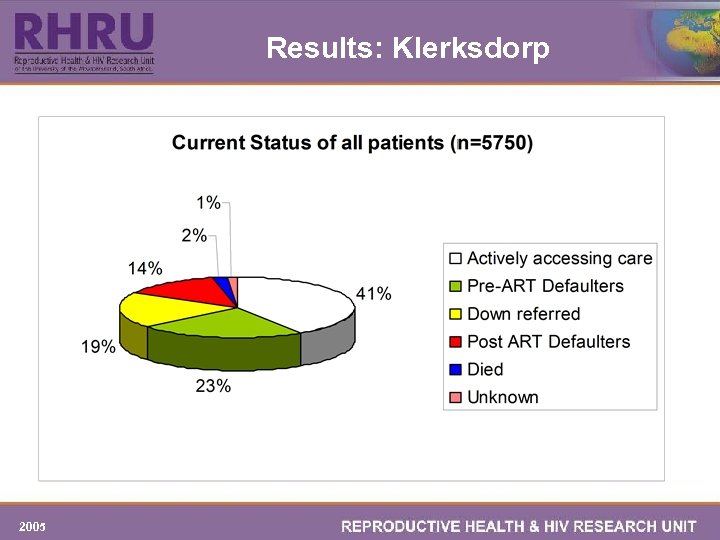
 DISCUSSION q A large number of patients accessing care at the wellness clinic are women. This is congruent with the patterns seen at other HIV clinics around the country. q Less than half of the patients who have visited the clinic since it opened in 2004, are currently actively seeking services at this facility. q Post Treatment defaulters (21%) are a major concern for clinic. These patients are at high risk of developing drug resistance and earlier onset of AIDS. It is imperative to identify defaulters early and get them back on treatment as soon as possible. 2005
DISCUSSION q A large number of patients accessing care at the wellness clinic are women. This is congruent with the patterns seen at other HIV clinics around the country. q Less than half of the patients who have visited the clinic since it opened in 2004, are currently actively seeking services at this facility. q Post Treatment defaulters (21%) are a major concern for clinic. These patients are at high risk of developing drug resistance and earlier onset of AIDS. It is imperative to identify defaulters early and get them back on treatment as soon as possible. 2005
 DISCUSSION The file review identified Pre-Treatment Defaulters as another group equally at risk as the Post-Treatment defaulters. n They were probably tested for HIV and in most cases a CD 4 count was also done, and they were clinically staged. n There are multiple areas where these patients could have been lost to follow up. The clinic may have lost them after the first appointment, during or after other treatments such as for opportunistic infections, TB, STIs, etc, or while attending the adherence training session. n From the information collected during this review, it is not possible to identify where and when the clinic has lost these patients. However, a detailed review of the files of these patients may reveal reasons/patterns for defaulting. 2005
DISCUSSION The file review identified Pre-Treatment Defaulters as another group equally at risk as the Post-Treatment defaulters. n They were probably tested for HIV and in most cases a CD 4 count was also done, and they were clinically staged. n There are multiple areas where these patients could have been lost to follow up. The clinic may have lost them after the first appointment, during or after other treatments such as for opportunistic infections, TB, STIs, etc, or while attending the adherence training session. n From the information collected during this review, it is not possible to identify where and when the clinic has lost these patients. However, a detailed review of the files of these patients may reveal reasons/patterns for defaulting. 2005
 DISCUSSION q It is important to find out how well the down referral system is working. One way to ascertain this is by reviewing files of the patients at the respective down referral sites. q If the down referral system is found to be effective, it will considerably ease the pressure on the tertiary health care facilities and improve quality of services through out the referral network. 2005
DISCUSSION q It is important to find out how well the down referral system is working. One way to ascertain this is by reviewing files of the patients at the respective down referral sites. q If the down referral system is found to be effective, it will considerably ease the pressure on the tertiary health care facilities and improve quality of services through out the referral network. 2005
 Recommendations q Development and implementation of appropriate data recording and storing mechanisms, q Processes to closely monitor and follow up patients initiating on treatment, q Systems to immediately identify pre & post treatment defaulters and have them return to the clinic, q Inquire into reasons why patients default on treatment, q Appropriate follow up processes for patients who are not eligible to start on ARVs – either because their CD 4 is greater than 200 or they have to complete treatment of other opportunistic infections, q Standardizing down referral systems and protocols q Inquiry into the low percentage of regimen changes at this site. 2005
Recommendations q Development and implementation of appropriate data recording and storing mechanisms, q Processes to closely monitor and follow up patients initiating on treatment, q Systems to immediately identify pre & post treatment defaulters and have them return to the clinic, q Inquire into reasons why patients default on treatment, q Appropriate follow up processes for patients who are not eligible to start on ARVs – either because their CD 4 is greater than 200 or they have to complete treatment of other opportunistic infections, q Standardizing down referral systems and protocols q Inquiry into the low percentage of regimen changes at this site. 2005
 Challenges & Benefits of File Reviews Challenges q Resource Intensive n Need HR for audits n Need HR for DQA q Buy in from clinic staff & leadership imperative q Need people with minimum understanding of HIV care & treatment 2005 Benefits q Get an accurate picture of the situation q Identify the weak areas and propose appropriate interventions. q Building the clinic staff capacity to understand the importance of the information collected and to assist them to continue with such activities
Challenges & Benefits of File Reviews Challenges q Resource Intensive n Need HR for audits n Need HR for DQA q Buy in from clinic staff & leadership imperative q Need people with minimum understanding of HIV care & treatment 2005 Benefits q Get an accurate picture of the situation q Identify the weak areas and propose appropriate interventions. q Building the clinic staff capacity to understand the importance of the information collected and to assist them to continue with such activities
 Future Plans q Continue with file reviews at partnering Do. H sites q Create a file review package of services for other agencies & Do. H sites q Support clinic staff to conduct periodic file reviews. q Klerksdorp & Jhb Hospital: n Have put in place a defaulter tracer program based on the outcomes of the file reviews. n Evaluate this program. 2005
Future Plans q Continue with file reviews at partnering Do. H sites q Create a file review package of services for other agencies & Do. H sites q Support clinic staff to conduct periodic file reviews. q Klerksdorp & Jhb Hospital: n Have put in place a defaulter tracer program based on the outcomes of the file reviews. n Evaluate this program. 2005
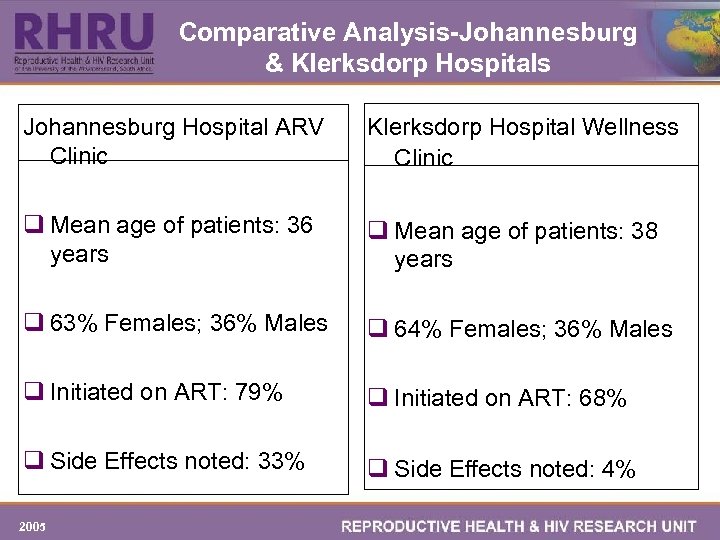 Comparative Analysis-Johannesburg & Klerksdorp Hospitals Johannesburg Hospital ARV Clinic Klerksdorp Hospital Wellness Clinic q Mean age of patients: 36 years q Mean age of patients: 38 years q 63% Females; 36% Males q 64% Females; 36% Males q Initiated on ART: 79% q Initiated on ART: 68% q Side Effects noted: 33% q Side Effects noted: 4% 2005
Comparative Analysis-Johannesburg & Klerksdorp Hospitals Johannesburg Hospital ARV Clinic Klerksdorp Hospital Wellness Clinic q Mean age of patients: 36 years q Mean age of patients: 38 years q 63% Females; 36% Males q 64% Females; 36% Males q Initiated on ART: 79% q Initiated on ART: 68% q Side Effects noted: 33% q Side Effects noted: 4% 2005
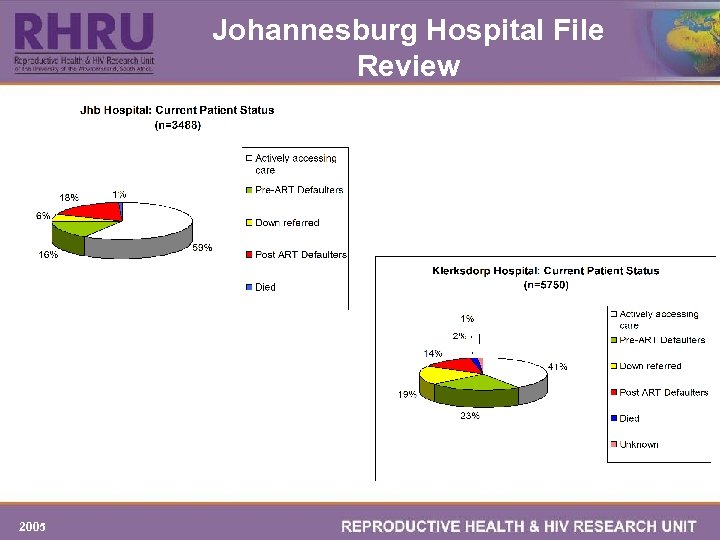 Johannesburg Hospital File Review 2005
Johannesburg Hospital File Review 2005
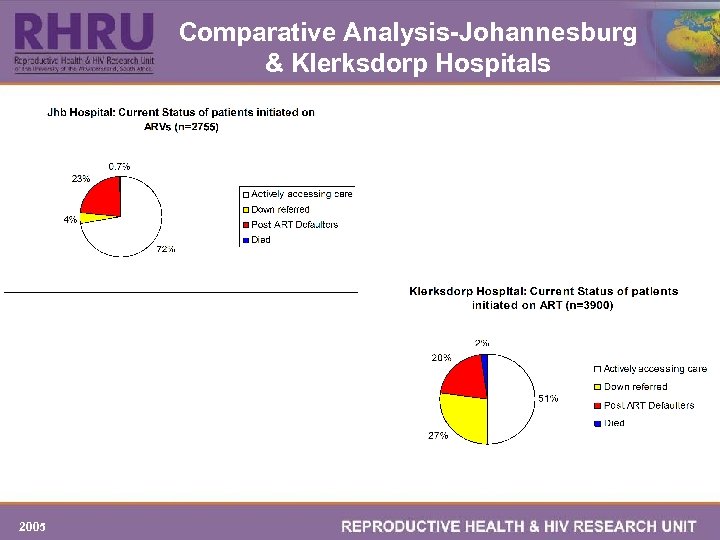 Comparative Analysis-Johannesburg & Klerksdorp Hospitals 2005
Comparative Analysis-Johannesburg & Klerksdorp Hospitals 2005
 Acknowledgements This project is funded by PEPFAR Acknowledgements q Department of Health – NW Province q Gauteng Provincial Government q Klerksdorp Hospital Wellness Clinic Leadership & Staff q Johannesburg Hospital ARV Clinic Leadership & Staff q Aurum q RHRU Team 2005
Acknowledgements This project is funded by PEPFAR Acknowledgements q Department of Health – NW Province q Gauteng Provincial Government q Klerksdorp Hospital Wellness Clinic Leadership & Staff q Johannesburg Hospital ARV Clinic Leadership & Staff q Aurum q RHRU Team 2005


