Presentation_CCM_-_Project_1_final.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Cross-Cultural Management Group Project 1 : Measuring cross-cultural differences: Russian vs French Culture
Cross-Cultural Management Group Project 1 : Measuring cross-cultural differences: Russian vs French Culture
 Agenda Hofstede Approach Ø Ø Ø Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner Approach Ø Ø Ø Method Presentation Our Sample Our Results Conclusion
Agenda Hofstede Approach Ø Ø Ø Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner Approach Ø Ø Ø Method Presentation Our Sample Our Results Conclusion
 Agenda Hofstede Approach Ø Ø Ø Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner Approach Ø Ø Ø Method Presentation Our Sample Our Results Conclusion
Agenda Hofstede Approach Ø Ø Ø Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner Approach Ø Ø Ø Method Presentation Our Sample Our Results Conclusion
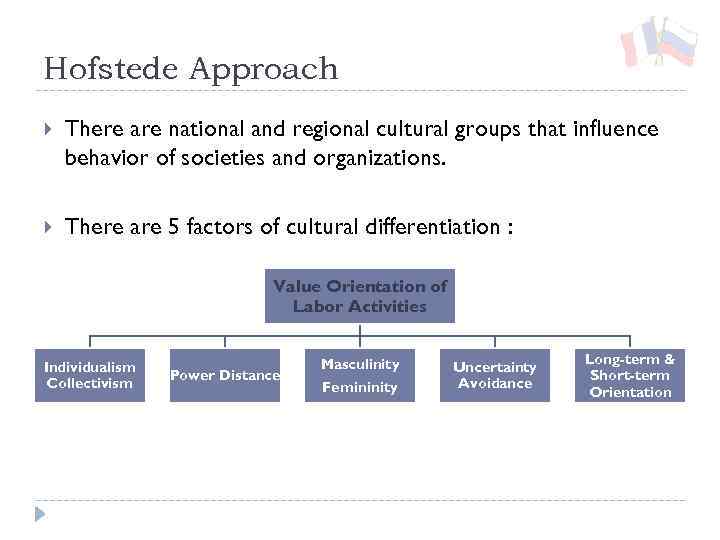 Hofstede Approach There are national and regional cultural groups that influence behavior of societies and organizations. There are 5 factors of cultural differentiation : Value Orientation of Labor Activities Individualism Collectivism Power Distance Masculinity Femininity Uncertainty Avoidance Long-term & Short-term Orientation
Hofstede Approach There are national and regional cultural groups that influence behavior of societies and organizations. There are 5 factors of cultural differentiation : Value Orientation of Labor Activities Individualism Collectivism Power Distance Masculinity Femininity Uncertainty Avoidance Long-term & Short-term Orientation
 Indexes calculated (1) Power Distance Index (PDI) • Extent to which the less powerful members of institutions and organisations within a country expect and accept that power is distributed unequally Individualism Index (IDV) • Degree of interdependence a society maintains among its members (if they speak in terms of “I” or in terms of “we”) • Business : how people take their responsibilities Masculinity Index (MAS) • What motivates people : • Wanting to be the best (masculine) • Liking what they do (feminine)
Indexes calculated (1) Power Distance Index (PDI) • Extent to which the less powerful members of institutions and organisations within a country expect and accept that power is distributed unequally Individualism Index (IDV) • Degree of interdependence a society maintains among its members (if they speak in terms of “I” or in terms of “we”) • Business : how people take their responsibilities Masculinity Index (MAS) • What motivates people : • Wanting to be the best (masculine) • Liking what they do (feminine)
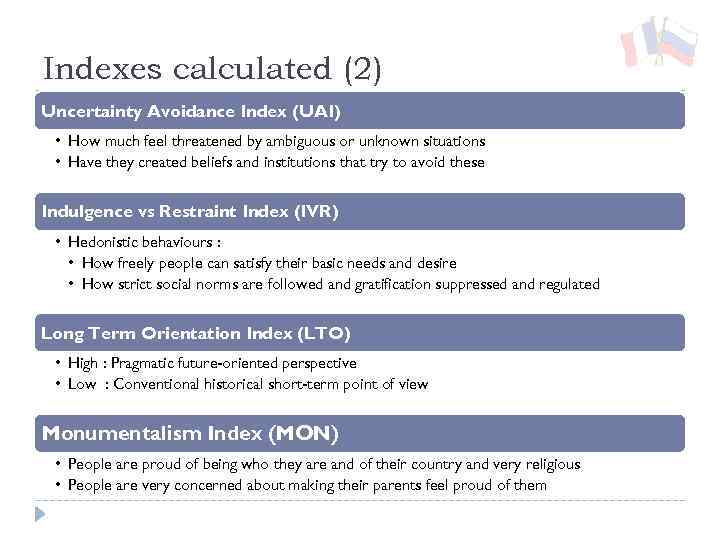 Indexes calculated (2) Uncertainty Avoidance Index (UAI) • How much feel threatened by ambiguous or unknown situations • Have they created beliefs and institutions that try to avoid these Indulgence vs Restraint Index (IVR) • Hedonistic behaviours : • How freely people can satisfy their basic needs and desire • How strict social norms are followed and gratification suppressed and regulated Long Term Orientation Index (LTO) • High : Pragmatic future-oriented perspective • Low : Conventional historical short-term point of view Monumentalism Index (MON) • People are proud of being who they are and of their country and very religious • People are very concerned about making their parents feel proud of them
Indexes calculated (2) Uncertainty Avoidance Index (UAI) • How much feel threatened by ambiguous or unknown situations • Have they created beliefs and institutions that try to avoid these Indulgence vs Restraint Index (IVR) • Hedonistic behaviours : • How freely people can satisfy their basic needs and desire • How strict social norms are followed and gratification suppressed and regulated Long Term Orientation Index (LTO) • High : Pragmatic future-oriented perspective • Low : Conventional historical short-term point of view Monumentalism Index (MON) • People are proud of being who they are and of their country and very religious • People are very concerned about making their parents feel proud of them
 Our Sample Through Hofstede questionnaire, our study analyses Russian and French people People over 18 Experimenting their first job or internship in a company Our effective sample comprises 22 French people (10 women and 12 men) 28 Russian people (18 women and 10 men) 62% of the respondents are “academically trained professional or equivalent (but not a manager of people)”
Our Sample Through Hofstede questionnaire, our study analyses Russian and French people People over 18 Experimenting their first job or internship in a company Our effective sample comprises 22 French people (10 women and 12 men) 28 Russian people (18 women and 10 men) 62% of the respondents are “academically trained professional or equivalent (but not a manager of people)”
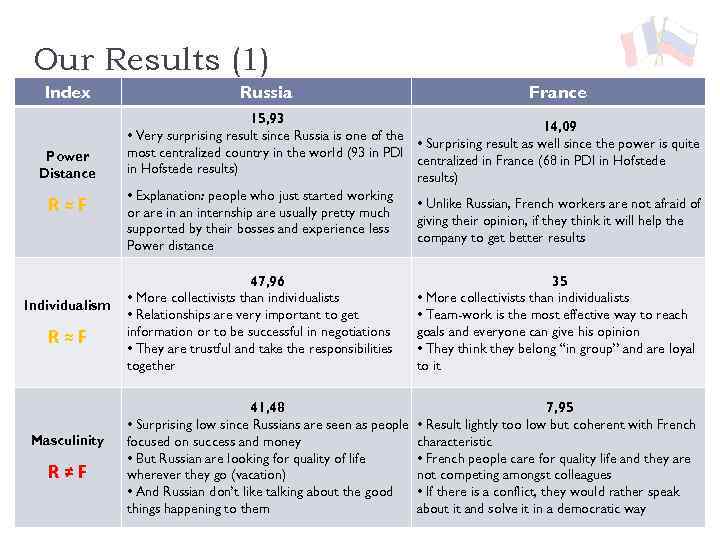 Our Results (1) Index Power Distance R≈F Individualism R≈F Masculinity R≠F Russia France 15, 93 14, 09 • Very surprising result since Russia is one of the • Surprising result as well since the power is quite most centralized country in the world (93 in PDI centralized in France (68 in PDI in Hofstede results) • Explanation: people who just started working • Unlike Russian, French workers are not afraid of or are in an internship are usually pretty much giving their opinion, if they think it will help the supported by their bosses and experience less company to get better results Power distance 47, 96 • More collectivists than individualists • Relationships are very important to get information or to be successful in negotiations • They are trustful and take the responsibilities together 35 • More collectivists than individualists • Team-work is the most effective way to reach goals and everyone can give his opinion • They think they belong “in group” and are loyal to it 41, 48 • Surprising low since Russians are seen as people focused on success and money • But Russian are looking for quality of life wherever they go (vacation) • And Russian don’t like talking about the good things happening to them 7, 95 • Result lightly too low but coherent with French characteristic • French people care for quality life and they are not competing amongst colleagues • If there is a conflict, they would rather speak about it and solve it in a democratic way
Our Results (1) Index Power Distance R≈F Individualism R≈F Masculinity R≠F Russia France 15, 93 14, 09 • Very surprising result since Russia is one of the • Surprising result as well since the power is quite most centralized country in the world (93 in PDI centralized in France (68 in PDI in Hofstede results) • Explanation: people who just started working • Unlike Russian, French workers are not afraid of or are in an internship are usually pretty much giving their opinion, if they think it will help the supported by their bosses and experience less company to get better results Power distance 47, 96 • More collectivists than individualists • Relationships are very important to get information or to be successful in negotiations • They are trustful and take the responsibilities together 35 • More collectivists than individualists • Team-work is the most effective way to reach goals and everyone can give his opinion • They think they belong “in group” and are loyal to it 41, 48 • Surprising low since Russians are seen as people focused on success and money • But Russian are looking for quality of life wherever they go (vacation) • And Russian don’t like talking about the good things happening to them 7, 95 • Result lightly too low but coherent with French characteristic • French people care for quality life and they are not competing amongst colleagues • If there is a conflict, they would rather speak about it and solve it in a democratic way
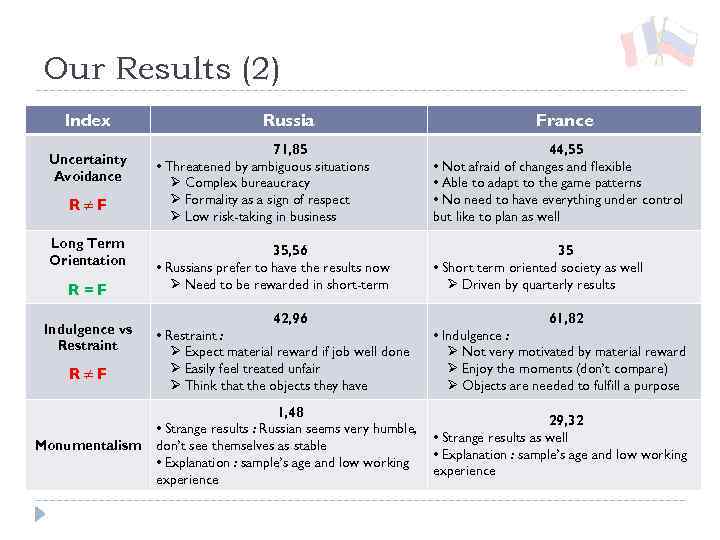 Our Results (2) Index Uncertainty Avoidance R≠F Long Term Orientation R=F Indulgence vs Restraint R≠F Monumentalism Russia France 71, 85 • Threatened by ambiguous situations Ø Complex bureaucracy Ø Formality as a sign of respect Ø Low risk-taking in business 44, 55 • Not afraid of changes and flexible • Able to adapt to the game patterns • No need to have everything under control but like to plan as well 35, 56 • Russians prefer to have the results now Ø Need to be rewarded in short-term 35 • Short term oriented society as well Ø Driven by quarterly results 42, 96 61, 82 • Restraint : Ø Expect material reward if job well done Ø Easily feel treated unfair Ø Think that the objects they have • Indulgence : Ø Not very motivated by material reward Ø Enjoy the moments (don’t compare) Ø Objects are needed to fulfill a purpose 1, 48 • Strange results : Russian seems very humble, don’t see themselves as stable • Explanation : sample’s age and low working experience 29, 32 • Strange results as well • Explanation : sample’s age and low working experience
Our Results (2) Index Uncertainty Avoidance R≠F Long Term Orientation R=F Indulgence vs Restraint R≠F Monumentalism Russia France 71, 85 • Threatened by ambiguous situations Ø Complex bureaucracy Ø Formality as a sign of respect Ø Low risk-taking in business 44, 55 • Not afraid of changes and flexible • Able to adapt to the game patterns • No need to have everything under control but like to plan as well 35, 56 • Russians prefer to have the results now Ø Need to be rewarded in short-term 35 • Short term oriented society as well Ø Driven by quarterly results 42, 96 61, 82 • Restraint : Ø Expect material reward if job well done Ø Easily feel treated unfair Ø Think that the objects they have • Indulgence : Ø Not very motivated by material reward Ø Enjoy the moments (don’t compare) Ø Objects are needed to fulfill a purpose 1, 48 • Strange results : Russian seems very humble, don’t see themselves as stable • Explanation : sample’s age and low working experience 29, 32 • Strange results as well • Explanation : sample’s age and low working experience
 What conclusions from our results ? Similarities between the countries: Both Russian and French feel that relations are very important in the business background While French people do it, because they are used to work in teams and share responsabilities, Russians do this, because they like to support each other even if they work more on their own, once they have a strong relationship Both cultures like quality life, but while Russians don’t like to speak about success, because of possible envies, French people just don’t do it, because they don’t like to compete with each other The results of our sample show that both Russians and Frenchs don’t follow a strong buroucracy and feel supported by their bosses, but that’s actually quite strange in the first culture in general, so that it may be due to our young sample, as they are just starting and need the support of their bosses.
What conclusions from our results ? Similarities between the countries: Both Russian and French feel that relations are very important in the business background While French people do it, because they are used to work in teams and share responsabilities, Russians do this, because they like to support each other even if they work more on their own, once they have a strong relationship Both cultures like quality life, but while Russians don’t like to speak about success, because of possible envies, French people just don’t do it, because they don’t like to compete with each other The results of our sample show that both Russians and Frenchs don’t follow a strong buroucracy and feel supported by their bosses, but that’s actually quite strange in the first culture in general, so that it may be due to our young sample, as they are just starting and need the support of their bosses.
 What conclusions from our results ? Differences between French and Russian people: While Russians don’t like ambiguity and are not very flexible, French people are not afraid of changes and don’t need to have everything under control. Another very important difference is that Russians feel very connected to material things, as they are a sign of their social status, while French use them just as an instrument, looking to fulfill their function. One of the things that much surprised us was the low monumentarism rate in both cultures, specially in the Russian culture, as they are seen as people, who in fact like success and feel very proud of who they are, their country and religion. But again, maybe the background our young sample is changing. → So we can see that even if these both cultures seem to be very different, generally, they have many common points, at least in our sample
What conclusions from our results ? Differences between French and Russian people: While Russians don’t like ambiguity and are not very flexible, French people are not afraid of changes and don’t need to have everything under control. Another very important difference is that Russians feel very connected to material things, as they are a sign of their social status, while French use them just as an instrument, looking to fulfill their function. One of the things that much surprised us was the low monumentarism rate in both cultures, specially in the Russian culture, as they are seen as people, who in fact like success and feel very proud of who they are, their country and religion. But again, maybe the background our young sample is changing. → So we can see that even if these both cultures seem to be very different, generally, they have many common points, at least in our sample
 Agenda Hofstede Approach Ø Ø Ø Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner Approach Ø Ø Ø Method Presentation Our Sample Our Results Conclusion
Agenda Hofstede Approach Ø Ø Ø Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner Approach Ø Ø Ø Method Presentation Our Sample Our Results Conclusion
 Trompenaars & Hampden-Turner Approach The approach is also called “Seven modern dilemmas” Universalism VS particularism Communitarianism VS individualism Neutral VS emotional Defuse VS specific cultures Achievement VS ascription Human-Time relationship Human-Nature relationship
Trompenaars & Hampden-Turner Approach The approach is also called “Seven modern dilemmas” Universalism VS particularism Communitarianism VS individualism Neutral VS emotional Defuse VS specific cultures Achievement VS ascription Human-Time relationship Human-Nature relationship
 Our Sample Through Trompenaars & Hampden-Turner questionnaire, our study analyses Russian and French people People over 18 Experimenting their first job or internship in a company Our effective sample comprises 22 French people (10 women and 12 men) 28 Russian people (18 women and 10 men) 62% of the respondents are “academically trained professional or equivalent (but not a manager of people)”
Our Sample Through Trompenaars & Hampden-Turner questionnaire, our study analyses Russian and French people People over 18 Experimenting their first job or internship in a company Our effective sample comprises 22 French people (10 women and 12 men) 28 Russian people (18 women and 10 men) 62% of the respondents are “academically trained professional or equivalent (but not a manager of people)”
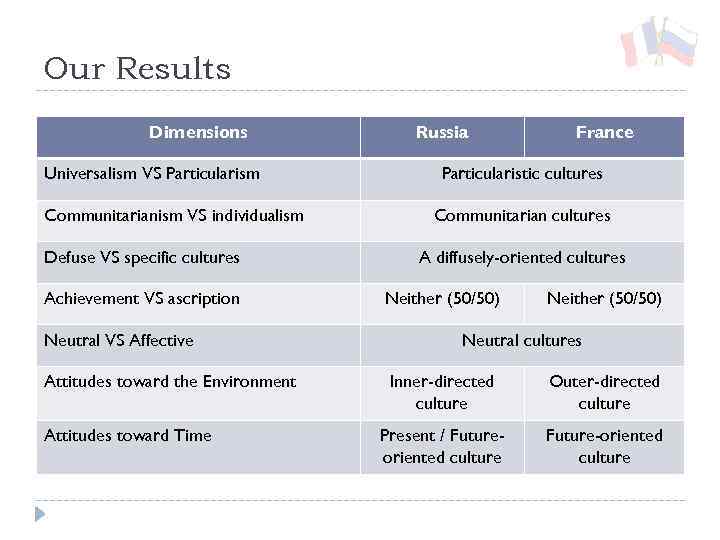 Our Results Dimensions Universalism VS Particularism Communitarianism VS individualism Defuse VS specific cultures Achievement VS ascription Neutral VS Affective Attitudes toward the Environment Attitudes toward Time Russia France Particularistic cultures Communitarian cultures A diffusely-oriented cultures Neither (50/50) Neutral cultures Inner-directed culture Outer-directed culture Present / Futureoriented culture Future-oriented culture
Our Results Dimensions Universalism VS Particularism Communitarianism VS individualism Defuse VS specific cultures Achievement VS ascription Neutral VS Affective Attitudes toward the Environment Attitudes toward Time Russia France Particularistic cultures Communitarian cultures A diffusely-oriented cultures Neither (50/50) Neutral cultures Inner-directed culture Outer-directed culture Present / Futureoriented culture Future-oriented culture
 What conclusion from our results ? According to the Trompenaars & Hampden-Turner approach our two cultures have much in common, they are both Particularistic Communitarian people place the community before the individual Diffusely-oriented people see culture in terms of human friendship and intimate relationships individual elements are seen from the perspective of the total; relationships between elements are more important than individual elements Neutral Individuals do not display their emotions overtly
What conclusion from our results ? According to the Trompenaars & Hampden-Turner approach our two cultures have much in common, they are both Particularistic Communitarian people place the community before the individual Diffusely-oriented people see culture in terms of human friendship and intimate relationships individual elements are seen from the perspective of the total; relationships between elements are more important than individual elements Neutral Individuals do not display their emotions overtly
 What conclusion from our results ? These two cultures have different attitudes towards environment : Russian culture is more Inner-directed (they believe that nature is complex but can be controlled with the right expertise) French - outer-directed (people should adapt themselves to external circumstances) These two cultures have different attitudes towards time : Russian are Present / Future-oriented French are Future-oriented
What conclusion from our results ? These two cultures have different attitudes towards environment : Russian culture is more Inner-directed (they believe that nature is complex but can be controlled with the right expertise) French - outer-directed (people should adapt themselves to external circumstances) These two cultures have different attitudes towards time : Russian are Present / Future-oriented French are Future-oriented
 Agenda Hofstede Approach Ø Ø Ø Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner Approach Ø Ø Ø Method Presentation Our Sample Our Results Conclusion
Agenda Hofstede Approach Ø Ø Ø Trompenaars and Hampden-Turner Approach Ø Ø Ø Method Presentation Our Sample Our Results Conclusion
 Conclusion The results of the two methods: Both Russian and French consider relationships as very important Russia and France – collectivistic cultures Difference between the two methods: Attitude towards time: Attitude towards Environment: Hofstede questionnaire – both Russian and French – short-term oriented Trompenaars questionnaire - Russian are more Present-oriented; French are Futureoriented Hofstede questionnaire - Uncertainty Avoidance in Russia is very high Trompenaars questionnaire - Russian are Inner-directed (believe that they can control the environment) French – vice versa (Uncertainty Avoidance is quite low, while outer-directed) Due to the small sample the results may not be representative for the whole countries; they represent young people’s cultures in both countries
Conclusion The results of the two methods: Both Russian and French consider relationships as very important Russia and France – collectivistic cultures Difference between the two methods: Attitude towards time: Attitude towards Environment: Hofstede questionnaire – both Russian and French – short-term oriented Trompenaars questionnaire - Russian are more Present-oriented; French are Futureoriented Hofstede questionnaire - Uncertainty Avoidance in Russia is very high Trompenaars questionnaire - Russian are Inner-directed (believe that they can control the environment) French – vice versa (Uncertainty Avoidance is quite low, while outer-directed) Due to the small sample the results may not be representative for the whole countries; they represent young people’s cultures in both countries
 Questions Thank you for you attention !
Questions Thank you for you attention !


