a6dbf032a7f799aad88d92d30b6bd1a8.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 37

Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Clinic Sessions – Understanding the Rationale for the Elements of 21 st Century Curriculum Cheryl Lemke Metiri Group

Critical Thinking & Problem Solving TODAY • What is it? • Why is it important? TOMORROW • How can you develop it in students, teachers, administrators, community?

1 The WHY…

Shifts in Medical Services Then Now

Critical Thinking: The Why…

Bertrand Russell

Think USA • ESP vs Evolution • Astrology vs Astronomy • Chiropractors vs Orthopaedic

Recent Election Issues • • • Increase in property taxes Construction of a canal to divert water Mandatory AIDS testing for criminals Rent control ordinance Plus vote for elected officials

Economic Success Innovation Knowledge Worker Business Climate
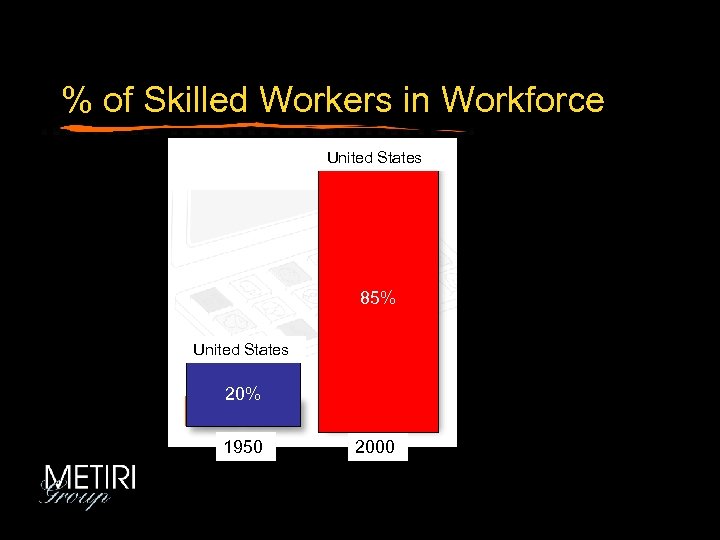
% of Skilled Workers in Workforce United States 85% United States 20% 1950 2000

Global Competition

Source: Microsoft

THEN NOW Managers Leaders Follow rules Think, solve problems, deal with ambiguity Punch time clock Get the job done ~ 24/7 Compete Team/Collaborate Communicate F 2 F mostly with text Communicate F 2 F and virtually, using multimedia Degree = career Degree = interview
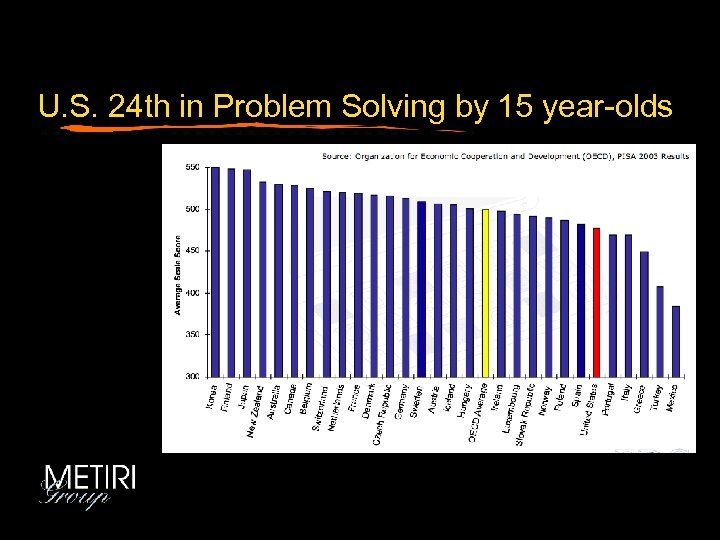
U. S. 24 th in Problem Solving by 15 year-olds

Question #1: Americans routinely score higher than comparable test takers from other countries in international comparisons of academic and thinking skills. False

2 Thinking and Reasoning Skills

Problem Solving Class
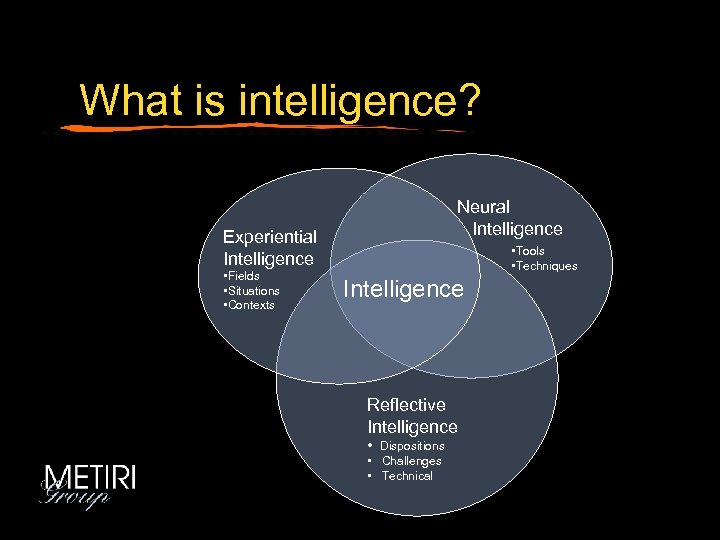
What is intelligence? Neural Intelligence Experiential Intelligence • Fields • Situations • Contexts • Tools • Techniques Intelligence Reflective Intelligence • Dispositions • Challenges • Technical

Intelligence Fixed vs Growth Mindsets

Critical Thinking …the use of those cognitive skills or strategies that increase the probability of a desirable outcome.
Can we teach thinking? Venezuela • Co. RT • Odyssey
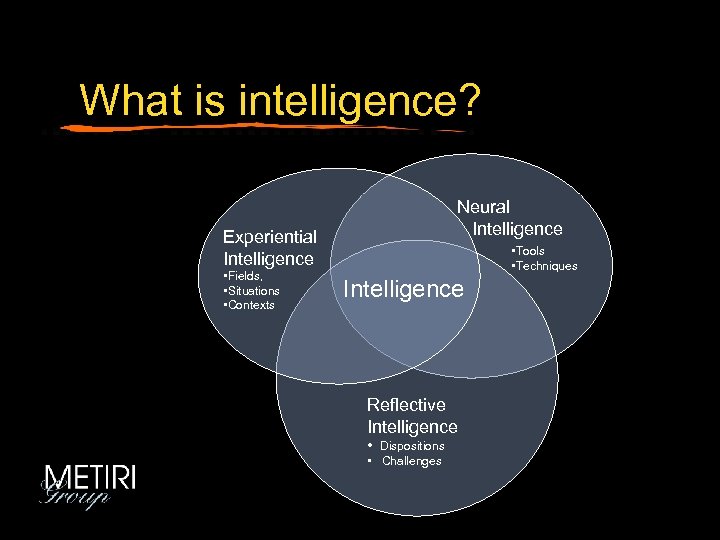
What is intelligence? Neural Intelligence Experiential Intelligence • Fields, • Situations • Contexts • Tools • Techniques Intelligence Reflective Intelligence • Dispositions • Challenges
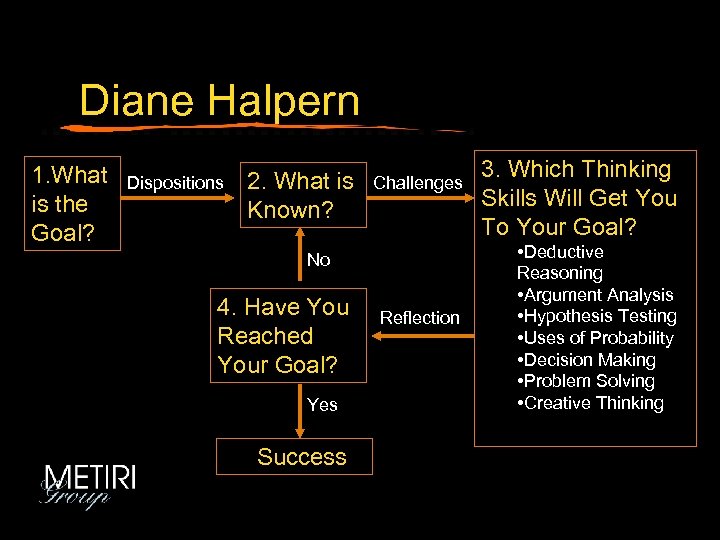
Diane Halpern 1. What is the Goal? Dispositions 2. What is Known? Challenges No 4. Have You Reached Your Goal? Yes Success Reflection 3. Which Thinking Skills Will Get You To Your Goal? • Deductive Reasoning • Argument Analysis • Hypothesis Testing • Uses of Probability • Decision Making • Problem Solving • Creative Thinking
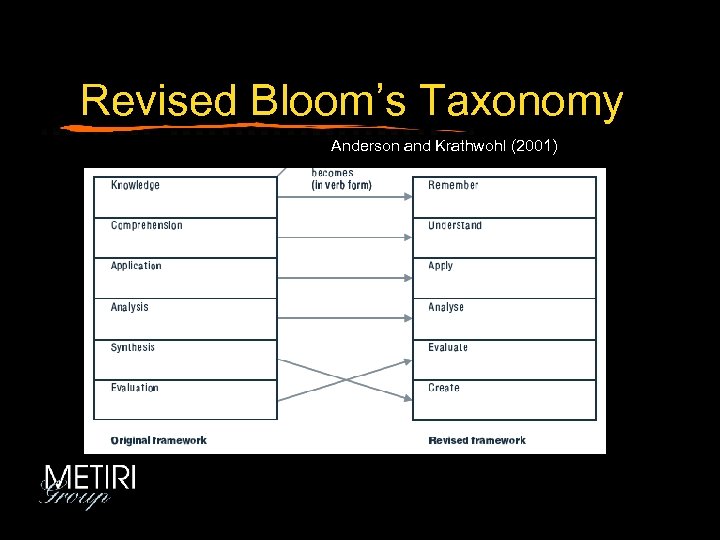
Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy Anderson and Krathwohl (2001)

Vertical vs Lateral Thinking Acting on an anonymous phone call, the police raid a house to arrest a suspected murderer. They don't know what he looks like but they know his name is John and that he is inside the house. The police bust in on a carpenter, a lorry driver, a mechanic and a fireman all playing poker. Without hesitation or communication of any kind, they immediately arrest the fireman. How do they know they've got their man?

Argument Analysis Tavis Smiley and Guest show on TAAS
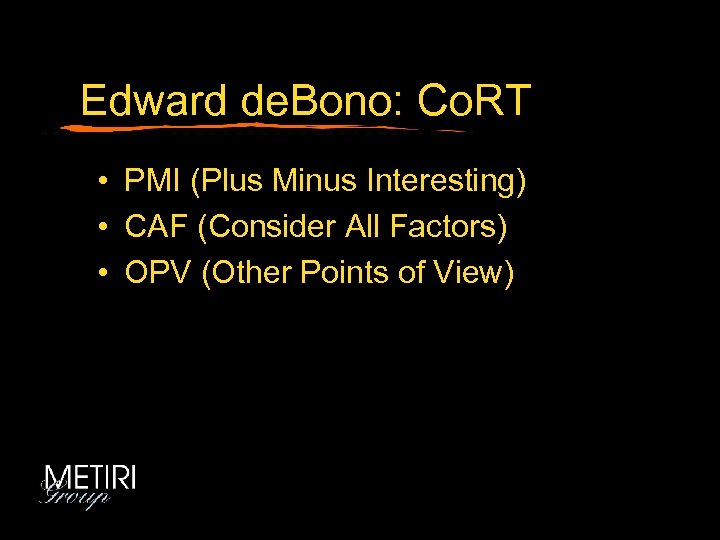
Edward de. Bono: Co. RT • PMI (Plus Minus Interesting) • CAF (Consider All Factors) • OPV (Other Points of View)

Question… Fact: The safest vehicle color is school bus yellow. Question: Should the U. S. mandate that all vehicles be SB Yellow? PMI (Plus Minus Interesting)

Is the Hot Hand Phenomenon REAL? a. SSSSMM b. SMSMMS


You Decide… Has she convinced you to stop buying items produced in sweatshops? What other options might you consider to impact this situation?
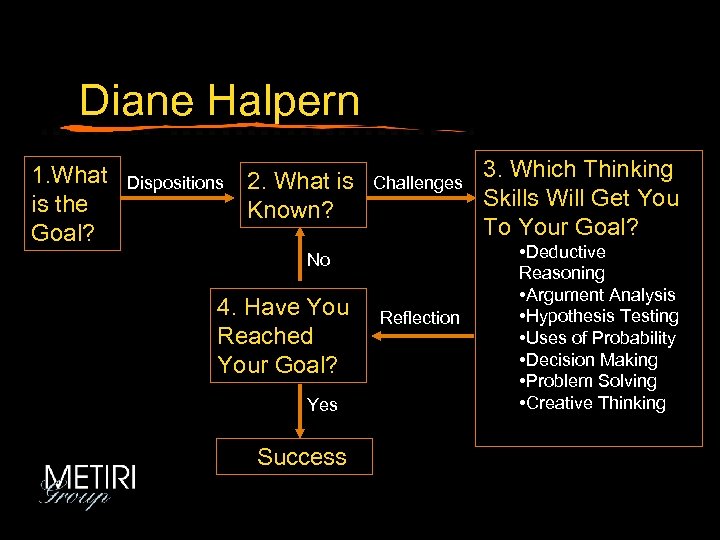
Diane Halpern 1. What is the Goal? Dispositions 2. What is Known? Challenges No 4. Have You Reached Your Goal? Yes Success Reflection 3. Which Thinking Skills Will Get You To Your Goal? • Deductive Reasoning • Argument Analysis • Hypothesis Testing • Uses of Probability • Decision Making • Problem Solving • Creative Thinking

Critical Thinking: The What…
www. metiri. com
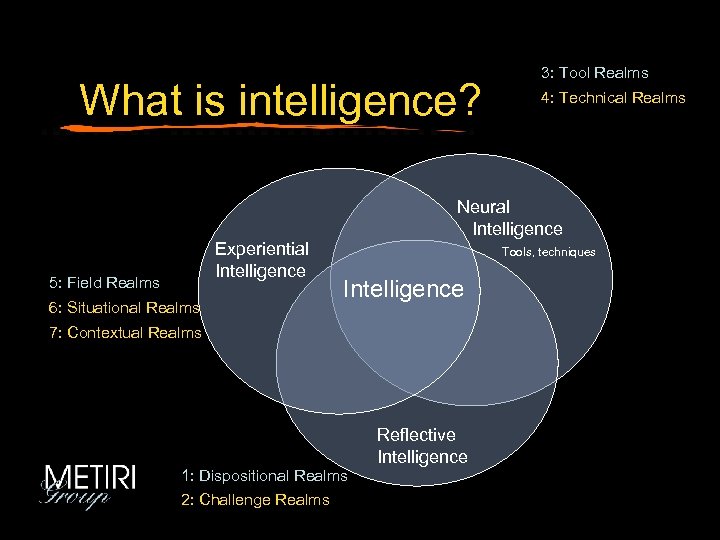
What is intelligence? 3: Tool Realms 4: Technical Realms Neural Intelligence Experiential Intelligence 5: Field Realms 6: Situational Realms Tools, techniques Intelligence 7: Contextual Realms Reflective Intelligence 1: Dispositional Realms 2: Challenge Realms

The Ladder of Generality David Perkins - Outsmarting IQ 1: Dispositional Realms (attention, aware, clear, sound, deep, curious, etc. ) 2: Challenge Realms (explanation, design, decision making, plan, etc. ) 3: Tool Realms (brainstorming, pro-con lists, concept maps, organizers, etc. ) 4: Technical Realms (deduction, systems thinking, game theory, stats, etc. ) 5: Field Realms (law, business, social sciences mathematics, history, arts, etc. ) 6: Situational Realms (purchase decisions, conflict resolution, managing emotions) 7: Contextual Realms (career choices, used car buying, treaty negotiations)
a6dbf032a7f799aad88d92d30b6bd1a8.ppt