a31e03055e5007ef12075b16b5dcc73f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 180
 Critical Access Hospitals (CAH) What every CAH needs to know about the Conditions of Participation 2011
Critical Access Hospitals (CAH) What every CAH needs to know about the Conditions of Participation 2011
 Part 3 of 3 2
Part 3 of 3 2
 Speaker ØSue Dill Calloway RN, Esq. CPHRM ØAD, BA, BSN, MSN, JD ØPresident Ø 5447 Fawnbrook Lane ØDublin, Ohio 43017 Ø 614 791 -1468 Øsdill 1@columbus. rr. com 3 3
Speaker ØSue Dill Calloway RN, Esq. CPHRM ØAD, BA, BSN, MSN, JD ØPresident Ø 5447 Fawnbrook Lane ØDublin, Ohio 43017 Ø 614 791 -1468 Øsdill 1@columbus. rr. com 3 3
 Medical Records 300 Must maintain clinical medical records system in accordance with P&Ps, ØMust have a system of patient records, ways to identify the author and protect security of MR, ØMust be sure MR are not lost, stolen, or altered or reproduced in authorized manner, ØLimit access to only those authorized persons, 4
Medical Records 300 Must maintain clinical medical records system in accordance with P&Ps, ØMust have a system of patient records, ways to identify the author and protect security of MR, ØMust be sure MR are not lost, stolen, or altered or reproduced in authorized manner, ØLimit access to only those authorized persons, 4
 Medical Records 300 Ø Must have current list of authenticates signatures (like signature cards), Ø And computer codes and signature stamps, Ø Must be adequately protected and authorized by governing body, Ø Must cross reference inpatients and outpatients, Ø If transfer to swing bed can use one MR but need divider, 5
Medical Records 300 Ø Must have current list of authenticates signatures (like signature cards), Ø And computer codes and signature stamps, Ø Must be adequately protected and authorized by governing body, Ø Must cross reference inpatients and outpatients, Ø If transfer to swing bed can use one MR but need divider, 5
 Medical Record Both inpatient and swing bed must have MR; Øadmission, discharge orders, progress notes, nursing notes, graphics, laboratory support documents, any other pertinent documents, and discharge summaries, ØMust retain MR and file them, 6
Medical Record Both inpatient and swing bed must have MR; Øadmission, discharge orders, progress notes, nursing notes, graphics, laboratory support documents, any other pertinent documents, and discharge summaries, ØMust retain MR and file them, 6
 Medical Records 300 ØMust have system to be able to pull any old MR within past 6 years, Ø 24 hours a day and 7 days a week, ØInpatient or outpatient, ØSurveyor will verify there is a MR for every patient, ØWill look to be stored in place protected from damage, flood, fire, theft, etc. , ØMust protect confidentiality of MR, ØMR must be adequately staffed, 7
Medical Records 300 ØMust have system to be able to pull any old MR within past 6 years, Ø 24 hours a day and 7 days a week, ØInpatient or outpatient, ØSurveyor will verify there is a MR for every patient, ØWill look to be stored in place protected from damage, flood, fire, theft, etc. , ØMust protect confidentiality of MR, ØMR must be adequately staffed, 7
 Medical Records 302 ØMust be legible, complete, accurate, readily accessible and systematically organized, ØTo ensure accurate and complete documentation of all orders, test results, evaluations, treatments, interventions, care provided and the patient’s response to those treatments, interventions and care. ØMust have director of MR that has been appointed by governing board (303), 8
Medical Records 302 ØMust be legible, complete, accurate, readily accessible and systematically organized, ØTo ensure accurate and complete documentation of all orders, test results, evaluations, treatments, interventions, care provided and the patient’s response to those treatments, interventions and care. ØMust have director of MR that has been appointed by governing board (303), 8
 Medical Records 303 MR must contain: Ø Identification and social data, Ø Evidence of properly executed informed consent forms, Ø Pertinent medical history, Ø Assessment of the health status and health care needs of the patient, Ø Brief summary of the episode, disposition, and instructions to the patient; 9
Medical Records 303 MR must contain: Ø Identification and social data, Ø Evidence of properly executed informed consent forms, Ø Pertinent medical history, Ø Assessment of the health status and health care needs of the patient, Ø Brief summary of the episode, disposition, and instructions to the patient; 9
 Informed Consent 304 Ø Include evidence of properly executed informed consent forms for any procedures or surgical procedures, Ø Specified by the medical staff, Ø Or by Federal or State law, if applicable, that require written patient consent, Ø Informed consent means the patient or patient representative is given the information, explanations, consequences, and options needed in order to consent to a procedure or treatment. Ø See also tag 321, 10
Informed Consent 304 Ø Include evidence of properly executed informed consent forms for any procedures or surgical procedures, Ø Specified by the medical staff, Ø Or by Federal or State law, if applicable, that require written patient consent, Ø Informed consent means the patient or patient representative is given the information, explanations, consequences, and options needed in order to consent to a procedure or treatment. Ø See also tag 321, 10
 Consider List of Procedures Procedure Name Consent Requires Informed ØAblations Yes ØAmniocentesis Yes ØAngiogram Yes ØAngiography Yes ØAngioplasties Yes ØArthrogram Yes ØArterial Line insertion (performed alone) Yes ØAspiration Cyst (simple/minor) No 11
Consider List of Procedures Procedure Name Consent Requires Informed ØAblations Yes ØAmniocentesis Yes ØAngiogram Yes ØAngiography Yes ØAngioplasties Yes ØArthrogram Yes ØArterial Line insertion (performed alone) Yes ØAspiration Cyst (simple/minor) No 11
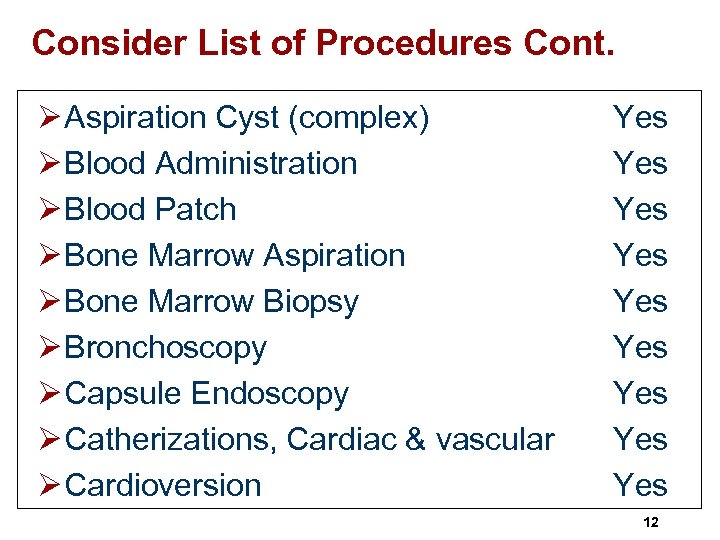 Consider List of Procedures Cont. Ø Aspiration Cyst (complex) Ø Blood Administration Ø Blood Patch Ø Bone Marrow Aspiration Ø Bone Marrow Biopsy Ø Bronchoscopy Ø Capsule Endoscopy Ø Catherizations, Cardiac & vascular Ø Cardioversion Yes Yes Yes 12
Consider List of Procedures Cont. Ø Aspiration Cyst (complex) Ø Blood Administration Ø Blood Patch Ø Bone Marrow Aspiration Ø Bone Marrow Biopsy Ø Bronchoscopy Ø Capsule Endoscopy Ø Catherizations, Cardiac & vascular Ø Cardioversion Yes Yes Yes 12
 Informed Consent 304 Ø A properly executed consent form contains at least the following: § Name of patient, and when appropriate, patient’s legal guardian; § Name of CAH; § Name of procedure(s); § Name of practitioner(s) performing the procedures(s); § Signature of patient or legal guardian; 13
Informed Consent 304 Ø A properly executed consent form contains at least the following: § Name of patient, and when appropriate, patient’s legal guardian; § Name of CAH; § Name of procedure(s); § Name of practitioner(s) performing the procedures(s); § Signature of patient or legal guardian; 13
 Consent Form Must Include § Date and time consent is obtained; § Statement that procedure was explained to patient or guardian; § Signature of professional person witnessing the consent; § Name/signature of person who explained the procedure to the patient or guardian. 14
Consent Form Must Include § Date and time consent is obtained; § Statement that procedure was explained to patient or guardian; § Signature of professional person witnessing the consent; § Name/signature of person who explained the procedure to the patient or guardian. 14
 Medical Records 304 ØMR must contain information such as progress and nursing notes, medical hx. , documentation, records, reports, recordings, test results, assessments etc. to: • Justify admission; • Describe the patient’s progress; and support the diagnosis; • Describe the patient’s response to medications; and • Describe the patient’s response to services such as interventions, care, treatments, 15
Medical Records 304 ØMR must contain information such as progress and nursing notes, medical hx. , documentation, records, reports, recordings, test results, assessments etc. to: • Justify admission; • Describe the patient’s progress; and support the diagnosis; • Describe the patient’s response to medications; and • Describe the patient’s response to services such as interventions, care, treatments, 15
 Medical Records ØMust maintain confidentiality of records, ØWhat precautions are taken to ensure confidentiality and prevent unauthorized persons from gaining access, ØMR retention period is 6 years and longer if required by state (311), ØWhen can records be removed ? ØAHIMA has practice briefs that can be helpful to hospitals at www. ahima. org, 16
Medical Records ØMust maintain confidentiality of records, ØWhat precautions are taken to ensure confidentiality and prevent unauthorized persons from gaining access, ØMR retention period is 6 years and longer if required by state (311), ØWhen can records be removed ? ØAHIMA has practice briefs that can be helpful to hospitals at www. ahima. org, 16
 Discharge Summary 304 A discharge summary discusses: § The outcome of the CAH stay, § The disposition of the patient, § And provisions for follow-up care (any post appointments such as home health, hospice, assisted living, LTC, swing bed services, § Is required for all hospitals stays and prior to and after swing bed admission, 17
Discharge Summary 304 A discharge summary discusses: § The outcome of the CAH stay, § The disposition of the patient, § And provisions for follow-up care (any post appointments such as home health, hospice, assisted living, LTC, swing bed services, § Is required for all hospitals stays and prior to and after swing bed admission, 17
 Discharge Summary 304 ØAdmitting practitioner must do, ØMD/DO may delegate writing the discharge summary to other qualified health care personnel such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants if state allows, ØSurveyor will verify MS have specified which procedures or treatments need informed consent, ØSurveyor will verify consent forms contain all the elements, ØWill do review of closed and open MR-at least 10% of average daily census, 18
Discharge Summary 304 ØAdmitting practitioner must do, ØMD/DO may delegate writing the discharge summary to other qualified health care personnel such as nurse practitioners and physician assistants if state allows, ØSurveyor will verify MS have specified which procedures or treatments need informed consent, ØSurveyor will verify consent forms contain all the elements, ØWill do review of closed and open MR-at least 10% of average daily census, 18
 History and Physicals 305 ØAll or part of H&P must be delegated to other practitioners if allowed by state law and CAH (see also tag 320), ØHowever MD/DO assume full responsibility, ØMD/DO must sign also, ØSurveyor will look at bylaws to determine when H&P must be done, ØMake sure H&P on chart before patient goes to surgery unless an emergency ØImportant issue with CMS and TJC 19
History and Physicals 305 ØAll or part of H&P must be delegated to other practitioners if allowed by state law and CAH (see also tag 320), ØHowever MD/DO assume full responsibility, ØMD/DO must sign also, ØSurveyor will look at bylaws to determine when H&P must be done, ØMake sure H&P on chart before patient goes to surgery unless an emergency ØImportant issue with CMS and TJC 19
 Response to Treatment 306 Ø The following must describe the patient’s response to treatment; § All orders, § Reports of treatment and medications, § Nursing notes, § Documentation of complications, § Other information used to monitor the patients such as progress notes, lab tests, graphics, 20
Response to Treatment 306 Ø The following must describe the patient’s response to treatment; § All orders, § Reports of treatment and medications, § Nursing notes, § Documentation of complications, § Other information used to monitor the patients such as progress notes, lab tests, graphics, 20
 Medical Records 306 ØMust make sure MR get filed promptly, ØAll MR must contain all lab reports, ØRadiology reports, ØAll vital signs, ØAll reports of treatment include complications and hospital acquired infections, ØAll unfavorable reaction to drugs, 21
Medical Records 306 ØMust make sure MR get filed promptly, ØAll MR must contain all lab reports, ØRadiology reports, ØAll vital signs, ØAll reports of treatment include complications and hospital acquired infections, ØAll unfavorable reaction to drugs, 21
 Entries in the MR 307 Ø Only those specified in the MS P&P can write in the MR, Ø All entries must be DATED, TIMED, and authenticated (must sign off each order), Ø If rubber stamps used-person must sign they will be the only one who uses it, Ø Must have sanctions for improper use of stamp, computer key or code signature, Ø Must date and time when a verbal order is signed off, 22
Entries in the MR 307 Ø Only those specified in the MS P&P can write in the MR, Ø All entries must be DATED, TIMED, and authenticated (must sign off each order), Ø If rubber stamps used-person must sign they will be the only one who uses it, Ø Must have sanctions for improper use of stamp, computer key or code signature, Ø Must date and time when a verbal order is signed off, 22
 Confidentiality of MR 308 Ø Must maintain confidentiality of information, Ø Access to information limited to those who need to know, Ø Safeguard MR, videos, audio, Ø Will verify only authorized people can access MR contained in MR department (which many call Health Information Management), Ø Need to release only with written authorization of patient or authorized representative, 23
Confidentiality of MR 308 Ø Must maintain confidentiality of information, Ø Access to information limited to those who need to know, Ø Safeguard MR, videos, audio, Ø Will verify only authorized people can access MR contained in MR department (which many call Health Information Management), Ø Need to release only with written authorization of patient or authorized representative, 23
 MR Policies 309 Ø Need written P&P that govern the use and removal of MR, Ø To include the conditions of release of information, Ø Remember the federal HIPAA law on MR confidentiality and privacy and ARRA, HITECH, and breach notification law, Ø Written consent of patient required to release (310), 24
MR Policies 309 Ø Need written P&P that govern the use and removal of MR, Ø To include the conditions of release of information, Ø Remember the federal HIPAA law on MR confidentiality and privacy and ARRA, HITECH, and breach notification law, Ø Written consent of patient required to release (310), 24
 Retention of MR 311 Ø Records are retained for at least 6 years from date of last entry, Ø And longer if required by State or federal law (OSHA, FDA, EPA), Ø or if the records may be needed in any pending proceeding, Ø Can be in hard copy, microfilm or computer memory banks, Ø AHIMA has practice brief on retention periods, 25
Retention of MR 311 Ø Records are retained for at least 6 years from date of last entry, Ø And longer if required by State or federal law (OSHA, FDA, EPA), Ø or if the records may be needed in any pending proceeding, Ø Can be in hard copy, microfilm or computer memory banks, Ø AHIMA has practice brief on retention periods, 25
 Surgical Procedures 320 ØBe performed in a safe manner, ØBy qualified practitioner with clinical privileges, ØWhat does safe manner mean? ØThe equipment and supplies are sufficient so the type of surgery can be performed safely, ØSurgery dept must be organized and staffed if you have one, 26
Surgical Procedures 320 ØBe performed in a safe manner, ØBy qualified practitioner with clinical privileges, ØWhat does safe manner mean? ØThe equipment and supplies are sufficient so the type of surgery can be performed safely, ØSurgery dept must be organized and staffed if you have one, 26
 Surgical Services 320 Ø Must follow state and federal laws, Ø Must follow standards of practice and recommendations by national recognized organizations (AMA, ACOS, APIC, AORN), Ø Quality of outpatient surgical services must be consistent with inpatient, Ø Scope of surgical services must be writing and approved by MS, Ø OR must be supervised by experienced staff member, address qualifications of supervisor of OR rooms in P&P, 27
Surgical Services 320 Ø Must follow state and federal laws, Ø Must follow standards of practice and recommendations by national recognized organizations (AMA, ACOS, APIC, AORN), Ø Quality of outpatient surgical services must be consistent with inpatient, Ø Scope of surgical services must be writing and approved by MS, Ø OR must be supervised by experienced staff member, address qualifications of supervisor of OR rooms in P&P, 27
 Surgical Procedures 320 Ø If LPN or OR tech used as scrub nurses then must be under RN who is immediately available to physically intervene, Ø There also a number of policies and procedures that need to be in place. Ø AORN Perioperative Standards and Recommended Practices have many resources to help meet CMS and TJC requirements 28
Surgical Procedures 320 Ø If LPN or OR tech used as scrub nurses then must be under RN who is immediately available to physically intervene, Ø There also a number of policies and procedures that need to be in place. Ø AORN Perioperative Standards and Recommended Practices have many resources to help meet CMS and TJC requirements 28
 Surgery Policies 320 Ø Aseptic surveillance and practice, including scrub techniques Ø Identification of infected and non-infected cases Ø Housekeeping requirements/procedures Ø Patient care requirements § Preoperative work-up § Patient consents and releases § Clinical procedures § Safety practices § Patient identification procedures 29
Surgery Policies 320 Ø Aseptic surveillance and practice, including scrub techniques Ø Identification of infected and non-infected cases Ø Housekeeping requirements/procedures Ø Patient care requirements § Preoperative work-up § Patient consents and releases § Clinical procedures § Safety practices § Patient identification procedures 29
 Surgery Policies 320 Ø Duties of scrub and circulating nurse, Ø Safety practices, Ø The requirement to conduct surgical counts in accordance with accepted standards of practice, Ø Scheduling of patients for surgery, Ø Personnel policies unique to the OR, Ø Resuscitative techniques, Ø DNR status, Ø Care of surgical specimens, Ø Malignant hyperthermia, 30
Surgery Policies 320 Ø Duties of scrub and circulating nurse, Ø Safety practices, Ø The requirement to conduct surgical counts in accordance with accepted standards of practice, Ø Scheduling of patients for surgery, Ø Personnel policies unique to the OR, Ø Resuscitative techniques, Ø DNR status, Ø Care of surgical specimens, Ø Malignant hyperthermia, 30
 Surgery Policies 320 Ø Appropriate protocols for all surgical procedures performed. These may be procedure-specific or general in nature and will include a list of equipment, materials, and supplies necessary to properly carry out job assignments. Ø Sterilization and disinfection procedures Ø Acceptable operating room attire Ø Handling infections and biomedical/medical waste 31
Surgery Policies 320 Ø Appropriate protocols for all surgical procedures performed. These may be procedure-specific or general in nature and will include a list of equipment, materials, and supplies necessary to properly carry out job assignments. Ø Sterilization and disinfection procedures Ø Acceptable operating room attire Ø Handling infections and biomedical/medical waste 31
 H&P 320 ØComplete H&P must be done in accordance with acceptable standards of practice, ØAll or part may be delegated to other practitioners (like PA or NP) if allowed by your state law and CAH, ØSurgeon must sign and assumes full responsibility, 32
H&P 320 ØComplete H&P must be done in accordance with acceptable standards of practice, ØAll or part may be delegated to other practitioners (like PA or NP) if allowed by your state law and CAH, ØSurgeon must sign and assumes full responsibility, 32
 H&P 320 ØNeed to have H&P on the chart PRIOR to surgery, ØAn exception is an emergency and then need brief admission note on chart, ØNote should include at a minimum critical information about the patient’s condition including pulmonary status, cardiovascular status, BP, vital signs, etc. 33
H&P 320 ØNeed to have H&P on the chart PRIOR to surgery, ØAn exception is an emergency and then need brief admission note on chart, ØNote should include at a minimum critical information about the patient’s condition including pulmonary status, cardiovascular status, BP, vital signs, etc. 33
 Informed Consent 320 ØThis includes all inpatient and outpatient, ØIs informed of who will actually perform the surgery (no ghost surgery), ØMust inform patient if practitioner other than the primary surgeon will perform important parts of the surgical procedure, ØEVEN if it is under the primary surgeon’s supervision, 34
Informed Consent 320 ØThis includes all inpatient and outpatient, ØIs informed of who will actually perform the surgery (no ghost surgery), ØMust inform patient if practitioner other than the primary surgeon will perform important parts of the surgical procedure, ØEVEN if it is under the primary surgeon’s supervision, 34
 Informed Consent 320 Consent must include: ØName of patient or their legal guardian, ØName of hospital (CAH), ØName of specific procedure, ØName of person doing the procedure or important parts of the procedure other than primary surgeon, ØSignificant surgical tasks include: opening and closing, harvesting grafts, dissecting tissue, removing tissue, implanting devices and altering tissue, ØContinued on next page, See tag 302 also, 35
Informed Consent 320 Consent must include: ØName of patient or their legal guardian, ØName of hospital (CAH), ØName of specific procedure, ØName of person doing the procedure or important parts of the procedure other than primary surgeon, ØSignificant surgical tasks include: opening and closing, harvesting grafts, dissecting tissue, removing tissue, implanting devices and altering tissue, ØContinued on next page, See tag 302 also, 35
 Informed Consent 320 ØNature and purpose of proposed treatment, Risks, consequences if no treatment is rendered, alternative procedures or treatments, probability that proposed procedure would be successful ØSignature of patient or guardian, ØDate and time consent obtained, ØStatement that procedure explained to the patient or guardian, ØSignature of professional person witnessing the consent (proposal to change to only witness and they are witness to signature only), ØName of person who explained procedure, 36
Informed Consent 320 ØNature and purpose of proposed treatment, Risks, consequences if no treatment is rendered, alternative procedures or treatments, probability that proposed procedure would be successful ØSignature of patient or guardian, ØDate and time consent obtained, ØStatement that procedure explained to the patient or guardian, ØSignature of professional person witnessing the consent (proposal to change to only witness and they are witness to signature only), ØName of person who explained procedure, 36
 Informed Consent 320 ØMust disclose information to patient necessary to make a decision, ØIt is a process and not a form, ØAuthorization form signed by a patient who does not understand what he is signing is not informed consent, ØGiven in language patient can understand (interpreter and issue of health care literacy), 37
Informed Consent 320 ØMust disclose information to patient necessary to make a decision, ØIt is a process and not a form, ØAuthorization form signed by a patient who does not understand what he is signing is not informed consent, ØGiven in language patient can understand (interpreter and issue of health care literacy), 37
 PACU 320 ØMust be adequate provisions for immediate post-op care, ØMust be in accordance with acceptable standards of care (ASPAN), ØSeparate room with limited access, ØP&P specify transfer requirements to and from PACU, ØPACU assessment includes level of activity, respiration, BP, LOC, patient color (aldrete), ØIf no PACU close observation by RN in patient’s room, 38
PACU 320 ØMust be adequate provisions for immediate post-op care, ØMust be in accordance with acceptable standards of care (ASPAN), ØSeparate room with limited access, ØP&P specify transfer requirements to and from PACU, ØPACU assessment includes level of activity, respiration, BP, LOC, patient color (aldrete), ØIf no PACU close observation by RN in patient’s room, 38
 OR Register 320 ØRegister will include; § § Patient’s name, id number, Date of surgery, Total time of surgery, Name of surgeons, nursing personnel, anesthesiologist, § Type of anesthesia, § Operative findings, preop and post-op diagnosis, age of patient, 39
OR Register 320 ØRegister will include; § § Patient’s name, id number, Date of surgery, Total time of surgery, Name of surgeons, nursing personnel, anesthesiologist, § Type of anesthesia, § Operative findings, preop and post-op diagnosis, age of patient, 39
 Operative Report Must Include 320 ØName and id of patient, ØDate and time of surgery, ØName of surgeons, assistants, ØPre-op and post-op dx, ØName of procedure, ØType of anesthesia, ØComplications and description of techniques and tissue removed, ØGrafts, tissue, devises implanted, ØName and description of significant surgical tasks done by others (see list-opening, closing, harvesting grafts, 40
Operative Report Must Include 320 ØName and id of patient, ØDate and time of surgery, ØName of surgeons, assistants, ØPre-op and post-op dx, ØName of procedure, ØType of anesthesia, ØComplications and description of techniques and tissue removed, ØGrafts, tissue, devises implanted, ØName and description of significant surgical tasks done by others (see list-opening, closing, harvesting grafts, 40
 Surveyor in OR 320 Ø Will verify access to OR and PACU is limited, Ø That there is appropriate cleaning between surgical cases and appropriate terminal cleaning applied; Ø That operating room attire is suitable for the kind of surgical case performed, Ø that persons working in the operating suite must wear only clean surgical costumes, 41
Surveyor in OR 320 Ø Will verify access to OR and PACU is limited, Ø That there is appropriate cleaning between surgical cases and appropriate terminal cleaning applied; Ø That operating room attire is suitable for the kind of surgical case performed, Ø that persons working in the operating suite must wear only clean surgical costumes, 41
 Surveyor in OR 320 Ø That equipment is available for rapid and routine sterilization of OR materials, Ø that equipment is monitored, inspected, tested, and maintained by the CAH’S biomedical equipment program, Ø sterilized materials are packaged, handled, labeled, and stored in a manner that ensures sterility e. g. , in a moisture and dust controlled environment, Ø P&P on expiration dates is followed, 42
Surveyor in OR 320 Ø That equipment is available for rapid and routine sterilization of OR materials, Ø that equipment is monitored, inspected, tested, and maintained by the CAH’S biomedical equipment program, Ø sterilized materials are packaged, handled, labeled, and stored in a manner that ensures sterility e. g. , in a moisture and dust controlled environment, Ø P&P on expiration dates is followed, 42
 Surveyor in OR 320 Ø OR organizational chart show lines of authority and delegation within the dept, Ø Make sure have the following: Ø On-call system, Ø Cardiac monitor, Ø Resuscitator, Defibrillator, Aspirator (suction equipment), Ø Tracheotomy set (a cricothyroidotomy set is not a substitute), 43
Surveyor in OR 320 Ø OR organizational chart show lines of authority and delegation within the dept, Ø Make sure have the following: Ø On-call system, Ø Cardiac monitor, Ø Resuscitator, Defibrillator, Aspirator (suction equipment), Ø Tracheotomy set (a cricothyroidotomy set is not a substitute), 43
 Surgical Privileges 321 ØMust designate who are allowed to perform surgery, ØMust conform to P&Ps, Ømust be within scope of practice laws, ØReview the list of physician privileges to determine if current, ØSurgical privileges updated every 2 years, ØAre procedures performed by appropriate physicians, 44
Surgical Privileges 321 ØMust designate who are allowed to perform surgery, ØMust conform to P&Ps, Ømust be within scope of practice laws, ØReview the list of physician privileges to determine if current, ØSurgical privileges updated every 2 years, ØAre procedures performed by appropriate physicians, 44
 Surgical Privileges 321 Ø Surgery service must maintain roster specifying the surgical privilege, Ø Current list of surgeons suspended must also be retained, Ø MS bylaws must have criteria for determining privileges, Ø Surveyor will review written assessment of the practitioner's training, experience, health status, and performance. 45
Surgical Privileges 321 Ø Surgery service must maintain roster specifying the surgical privilege, Ø Current list of surgeons suspended must also be retained, Ø MS bylaws must have criteria for determining privileges, Ø Surveyor will review written assessment of the practitioner's training, experience, health status, and performance. 45
 Surgical Privileges 321 ØSurgical privileges are granted in accordance with the competence of each, ØMS appraisal procedure must evaluate each practitioner’s training, education, experience, and competence, ØAs established by the QI program, credentialing, adherence to hospital P&P, and laws, 46
Surgical Privileges 321 ØSurgical privileges are granted in accordance with the competence of each, ØMS appraisal procedure must evaluate each practitioner’s training, education, experience, and competence, ØAs established by the QI program, credentialing, adherence to hospital P&P, and laws, 46
 Surgical Privileges 321 ØMust specify for each practitioner that performs surgical tasks including MD, DO, dentists, oral surgeon, podiatrists, ØRNFA, NP, surgical PA, surgical tech et. al. , ØMust be based on compliance with what they are allowed to do under state law, ØIf task requires it to be under supervision of MD/DO this means supervising doctor is present in the same room working with the patient, 47
Surgical Privileges 321 ØMust specify for each practitioner that performs surgical tasks including MD, DO, dentists, oral surgeon, podiatrists, ØRNFA, NP, surgical PA, surgical tech et. al. , ØMust be based on compliance with what they are allowed to do under state law, ØIf task requires it to be under supervision of MD/DO this means supervising doctor is present in the same room working with the patient, 47
 48
48
 Pre-Anesthesia Assessment 322 ØPre-anesthesia evaluation must be performed immediately prior to the surgery, ØBy qualified person to administer anesthetic to evaluate risk of anesthesia, ØMust include; notation of risk of anesthesia, drug, and allergy history, ØPotential anesthesia problems id, ØPatient’s condition prior to induction, 49
Pre-Anesthesia Assessment 322 ØPre-anesthesia evaluation must be performed immediately prior to the surgery, ØBy qualified person to administer anesthetic to evaluate risk of anesthesia, ØMust include; notation of risk of anesthesia, drug, and allergy history, ØPotential anesthesia problems id, ØPatient’s condition prior to induction, 49
 Pre-anesthesia ASA Guideline ØPreanesthesia Evaluation 1 § Patient interview to assess Medical history, Anesthetic history, Medication history ØAppropriate physical examination ØReview of objective diagnostic data (e. g. , laboratory, ECG, X-ray) ØAssignment of ASA physical status ØFormulation of the anesthetic plan and discussion of the risks and benefits of the plan with the patient or the patient’s legal representative Ø 1 www. asahq. org/publications. And. Services/standards/03. pdf 50
Pre-anesthesia ASA Guideline ØPreanesthesia Evaluation 1 § Patient interview to assess Medical history, Anesthetic history, Medication history ØAppropriate physical examination ØReview of objective diagnostic data (e. g. , laboratory, ECG, X-ray) ØAssignment of ASA physical status ØFormulation of the anesthetic plan and discussion of the risks and benefits of the plan with the patient or the patient’s legal representative Ø 1 www. asahq. org/publications. And. Services/standards/03. pdf 50
 51
51
 52
52
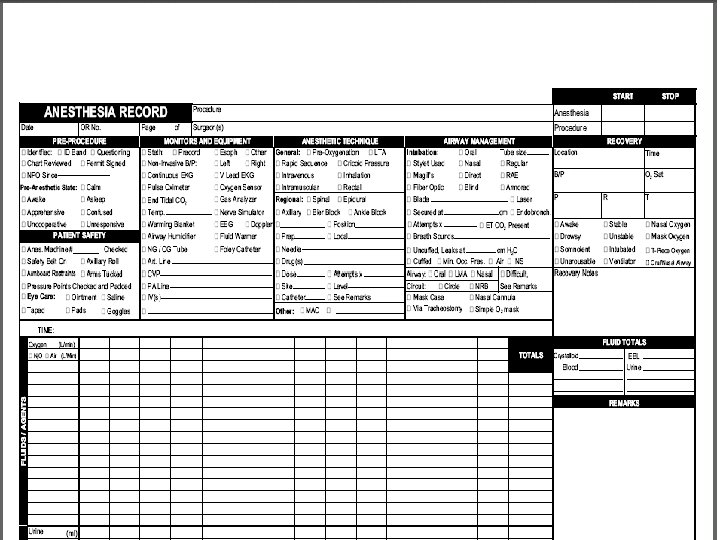
 Post Anesthesia Evaluation 321 Ø Post-anesthesia follow-up report must be written on all inpatients and outpatients prior to discharge, Ø Written by the individual who is qualified to administer the anesthesia. Ø Must include at a minimum: Cardiopulmonary status, LOC, follow-up care and/or observations; and, Ø Any complications occurring during PACU. 53
Post Anesthesia Evaluation 321 Ø Post-anesthesia follow-up report must be written on all inpatients and outpatients prior to discharge, Ø Written by the individual who is qualified to administer the anesthesia. Ø Must include at a minimum: Cardiopulmonary status, LOC, follow-up care and/or observations; and, Ø Any complications occurring during PACU. 53
 Post Anesthesia ASA Guidelines ØPatient evaluation on admission and discharge from the postanesthesia care unit ØA time-based record of vital signs and level of consciousness ØA time-based record of drugs administered, their dosage and route of administration ØType and amounts of intravenous fluids administered, including blood and blood products ØAny unusual events including post-anesthesia or post procedural complications ØPost-anesthesia visits 54
Post Anesthesia ASA Guidelines ØPatient evaluation on admission and discharge from the postanesthesia care unit ØA time-based record of vital signs and level of consciousness ØA time-based record of drugs administered, their dosage and route of administration ØType and amounts of intravenous fluids administered, including blood and blood products ØAny unusual events including post-anesthesia or post procedural complications ØPost-anesthesia visits 54
 55
55
 American Association of Nurse Anesthetists Ø AANA has excellent website 1 § Information on how to become a CRNA § Has position statement on documenting the standard of care for the anesthesia record § Sample forms 1 www. aana. com/resources. aspx? uc. Nav. Menu_TSMenu. Target. ID=51&uc. Nav. Menu_ TSMenu. Target. Type=4&uc. Nav. Menu_TSMenu. ID=6&id=713 56
American Association of Nurse Anesthetists Ø AANA has excellent website 1 § Information on how to become a CRNA § Has position statement on documenting the standard of care for the anesthesia record § Sample forms 1 www. aana. com/resources. aspx? uc. Nav. Menu_TSMenu. Target. ID=51&uc. Nav. Menu_ TSMenu. Target. Type=4&uc. Nav. Menu_TSMenu. ID=6&id=713 56
 57
57
 58
58
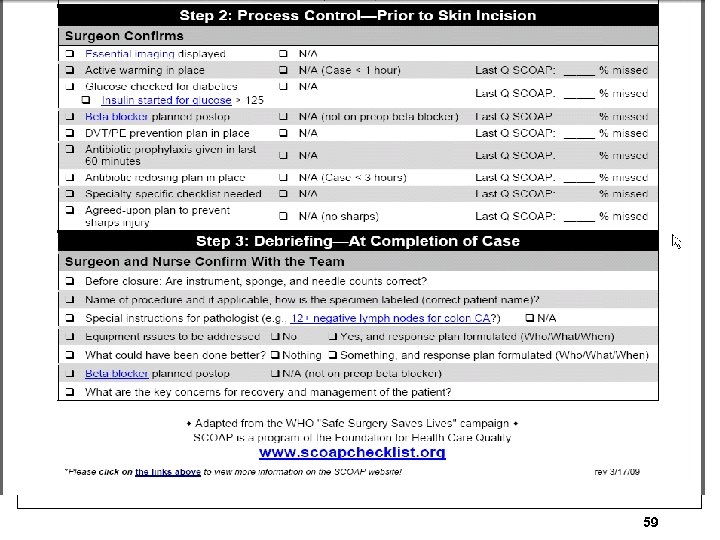 59
59
 Anesthesia 323 ØCAH must designate who can administer anesthesia, ØMS include criteria for determining privileges, In accordance with P&P and scope of practice and state law, ØOnly by anesthesiologist, MD/DO, CRNA, anesthesiology assistant, supervised trainee in education program, dentist, podiatrist, ØState exemption process of MD supervision for CRNA, 60
Anesthesia 323 ØCAH must designate who can administer anesthesia, ØMS include criteria for determining privileges, In accordance with P&P and scope of practice and state law, ØOnly by anesthesiologist, MD/DO, CRNA, anesthesiology assistant, supervised trainee in education program, dentist, podiatrist, ØState exemption process of MD supervision for CRNA, 60
 Anesthesia 323 Ø A CRNA may administer anesthesia when under the supervision of the operating practitioner or of an anesthesiologist who is immediately available if needed, Ø An anesthesiologist’s assistant (AA) may administer anesthesia when under the supervision of an anesthesiologist who is immediately available if needed. 61
Anesthesia 323 Ø A CRNA may administer anesthesia when under the supervision of the operating practitioner or of an anesthesiologist who is immediately available if needed, Ø An anesthesiologist’s assistant (AA) may administer anesthesia when under the supervision of an anesthesiologist who is immediately available if needed. 61
 Immediately Available Means ØPhysically located within the OR or in the L&D unit; Øand Is prepared to immediately conduct hands-on intervention if needed; Øand Is not engaged in activities that could prevent the supervising practitioner from being able to immediately intervene and conduct hands-on interventions if needed 62
Immediately Available Means ØPhysically located within the OR or in the L&D unit; Øand Is prepared to immediately conduct hands-on intervention if needed; Øand Is not engaged in activities that could prevent the supervising practitioner from being able to immediately intervene and conduct hands-on interventions if needed 62
 Discharge 325 ØAll patients are discharged in the company of a responsible adult, ØAny exceptions to this requirement must be made by the attending practitioner and documented in the medical record, ØSurveyor will verify that the CAH has P&Ps in place to govern discharge procedures and instructions, 63
Discharge 325 ØAll patients are discharged in the company of a responsible adult, ØAny exceptions to this requirement must be made by the attending practitioner and documented in the medical record, ØSurveyor will verify that the CAH has P&Ps in place to govern discharge procedures and instructions, 63
 Quality Assurance 331 ØMust periodically review total program (will look at who is to do this), ØAt least once per year, ØInclude services provided and number of patients served, Ø look at volume of service (332), ØInclude at least 10% of charts- active and closed charts (333), 64
Quality Assurance 331 ØMust periodically review total program (will look at who is to do this), ØAt least once per year, ØInclude services provided and number of patients served, Ø look at volume of service (332), ØInclude at least 10% of charts- active and closed charts (333), 64
 Quality Assurance 335 Ø Review all P&Ps also (show evidence of how these are evaluated and reviewed), Ø Purpose of the evaluation is to determine whether the utilization of services was appropriate, Ø And whether the P&P we revised if needed, 65
Quality Assurance 335 Ø Review all P&Ps also (show evidence of how these are evaluated and reviewed), Ø Purpose of the evaluation is to determine whether the utilization of services was appropriate, Ø And whether the P&P we revised if needed, 65
 Quality Assurance 336 An effective program includes; ØOngoing monitoring and data collection, ØProblem prevention, id analysis, ØId of corrective actions, ØImplementation of corrective actions, ØEvaluation of corrective actions, ØMeasures to improve quality on a continuous basis, 66
Quality Assurance 336 An effective program includes; ØOngoing monitoring and data collection, ØProblem prevention, id analysis, ØId of corrective actions, ØImplementation of corrective actions, ØEvaluation of corrective actions, ØMeasures to improve quality on a continuous basis, 66
 Quality Assurance 336 ØQA program to evaluate appropriateness of diagnosis and treatment and in treatment outcomes, ØFacility wide QA program (QI), ØCan have QA by arrangement, ØSurveyor will look at your QI PLAN, QI minutes, 67
Quality Assurance 336 ØQA program to evaluate appropriateness of diagnosis and treatment and in treatment outcomes, ØFacility wide QA program (QI), ØCan have QA by arrangement, ØSurveyor will look at your QI PLAN, QI minutes, 67
 Healthcare Associated Infections 337 ØMust evaluate nosocomial infections, ØMust look at medication therapies, ØMust evaluate the quality of care of LIPs (NP, PA, CNS) by doctor on MS or under contract, ØWill look at how their performance is evaluated (339), ØQuality of care and appropriateness of dx and tx by doctors must be reviewed by QIO (PRO), hospital that is member of network, or as identified in state rural health plan (340), 68
Healthcare Associated Infections 337 ØMust evaluate nosocomial infections, ØMust look at medication therapies, ØMust evaluate the quality of care of LIPs (NP, PA, CNS) by doctor on MS or under contract, ØWill look at how their performance is evaluated (339), ØQuality of care and appropriateness of dx and tx by doctors must be reviewed by QIO (PRO), hospital that is member of network, or as identified in state rural health plan (340), 68
 Quality Improvement 341 ØStaff consider the findings and evaluations and recommendations of the evaluations and take corrective actions, ØTake steps to remedial action to address deficiencies found thru QI process, ØWill look to see who is responsible for implementing actions, ØDocument the outcomes of all remedial actions (343) 69
Quality Improvement 341 ØStaff consider the findings and evaluations and recommendations of the evaluations and take corrective actions, ØTake steps to remedial action to address deficiencies found thru QI process, ØWill look to see who is responsible for implementing actions, ØDocument the outcomes of all remedial actions (343) 69
 Organ, Tissue, and Eye 344 ØHospital must have written P&P to address its organ procurement, Ømust have agreement with OPO, ØMust timely notify OPO if death is imminent or has patient has died, ØOPO to determine medical suitability for organ donation, ØDefines what must be in your written agreement (definitions, criteria for referral, access to your death record information 70
Organ, Tissue, and Eye 344 ØHospital must have written P&P to address its organ procurement, Ømust have agreement with OPO, ØMust timely notify OPO if death is imminent or has patient has died, ØOPO to determine medical suitability for organ donation, ØDefines what must be in your written agreement (definitions, criteria for referral, access to your death record information 70
 Organ, Tissue, and Eye 345 ØBoard must approve your organ procurement policy, ØMust integrate into hospital’s QAPI program, ØSurveyor will review written agreement with the OPO to make sure it has all the required information (42 CFR Part 486), ØCheck off the long list to ensure all elements are present (such as definition of imminent death, what is timely notification, allows them access to your death records etc. , 71
Organ, Tissue, and Eye 345 ØBoard must approve your organ procurement policy, ØMust integrate into hospital’s QAPI program, ØSurveyor will review written agreement with the OPO to make sure it has all the required information (42 CFR Part 486), ØCheck off the long list to ensure all elements are present (such as definition of imminent death, what is timely notification, allows them access to your death records etc. , 71
 Imminent Death 345 Definition of imminent death might include a patient with severe, acute brain injury who: ØRequires mechanical ventilation (due to brain injury); ØIs in an ICU or ED; AND ØHas clinical findings consistent with a Glascow Coma Score that is less than or equal to a mutually-agreed-upon threshold; or ØMD/DOs are evaluating a diagnosis of brain death (within 1 hour) ; or ØAn MD/DO has ordered that life sustaining therapies be withdrawn, pursuant to the family’s decision (notify them before withdrawing life sustaining therapies), ØMake sure your staff is aware of the P&P, 72
Imminent Death 345 Definition of imminent death might include a patient with severe, acute brain injury who: ØRequires mechanical ventilation (due to brain injury); ØIs in an ICU or ED; AND ØHas clinical findings consistent with a Glascow Coma Score that is less than or equal to a mutually-agreed-upon threshold; or ØMD/DOs are evaluating a diagnosis of brain death (within 1 hour) ; or ØAn MD/DO has ordered that life sustaining therapies be withdrawn, pursuant to the family’s decision (notify them before withdrawing life sustaining therapies), ØMake sure your staff is aware of the P&P, 72
 Tissue and Eye Bank 346 ØNeed an agreement with at least one tissue and eye bank, ØOPO is gatekeeper and notifies the tissue or eye bank chosen by the hospital, ØOPO determines medical suitability, ØDon’t need separate agreement with tissue bank if agreement with OPO to provide tissue and eye procurement, 73
Tissue and Eye Bank 346 ØNeed an agreement with at least one tissue and eye bank, ØOPO is gatekeeper and notifies the tissue or eye bank chosen by the hospital, ØOPO determines medical suitability, ØDon’t need separate agreement with tissue bank if agreement with OPO to provide tissue and eye procurement, 73
 Family Notification 347 ØOnce OPO has selected a potential donor, person’s family must be informed of the donor’s family’s option, ØOPO and hospital will decide how and by whom the family will be approached, 74
Family Notification 347 ØOnce OPO has selected a potential donor, person’s family must be informed of the donor’s family’s option, ØOPO and hospital will decide how and by whom the family will be approached, 74
 Organ Donation 347 ØPerson to initiate request must be a designated requestor or organized representative of tissue or eye bank, ØDesignated requestor must have completed course approved by OPO, ØEncourage discretion and sensitivity to the circumstances, views and beliefs of the families (348), ØSurveyor will review complaint file for relevant complaints, 75
Organ Donation 347 ØPerson to initiate request must be a designated requestor or organized representative of tissue or eye bank, ØDesignated requestor must have completed course approved by OPO, ØEncourage discretion and sensitivity to the circumstances, views and beliefs of the families (348), ØSurveyor will review complaint file for relevant complaints, 75
 Organ Donation Training 349 ØPatient care staff must be trained on organ donation issues, ØTraining program at a minimum should include: consent process, importance of discretion, role of designated requestor, transplantation and donation, QI, and role of OPO, ØTrain all new employees, when change in P&P, and when problems identified in QAPI process, 76
Organ Donation Training 349 ØPatient care staff must be trained on organ donation issues, ØTraining program at a minimum should include: consent process, importance of discretion, role of designated requestor, transplantation and donation, QI, and role of OPO, ØTrain all new employees, when change in P&P, and when problems identified in QAPI process, 76
 Organ Donation 349 ØHospital must cooperate with OPO to review death records to improve id of potential donors, ØSurveyor will verify P&P that hospital works with OPO, ØMaintain potential donors while necessary testing and placement of donated organs take place, ØMust have P&P to maintain viability of organs, 77
Organ Donation 349 ØHospital must cooperate with OPO to review death records to improve id of potential donors, ØSurveyor will verify P&P that hospital works with OPO, ØMaintain potential donors while necessary testing and placement of donated organs take place, ØMust have P&P to maintain viability of organs, 77
 Organ Transplantation ØHospital in which organ transplants are performed must be member of OPTN-Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, ØMust abide by its rules-42 USC 274, section 372 of the Public Health Service Act, ØMust provide data to OPTN, Scientific Registry and OPO, 78
Organ Transplantation ØHospital in which organ transplants are performed must be member of OPTN-Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network, ØMust abide by its rules-42 USC 274, section 372 of the Public Health Service Act, ØMust provide data to OPTN, Scientific Registry and OPO, 78
 Swing Beds LTC Services 350 -408 ØMust meet following to provide posthospital SNF care (350), ØMust be certified by CMS, ØSNF services must be in compliance with Subpart B of part 483, ØAllows CAH to use beds interchangeable for either acute care or SNF level, ØSwings from acute care reimbursement to SNF services and reimbursement, 79
Swing Beds LTC Services 350 -408 ØMust meet following to provide posthospital SNF care (350), ØMust be certified by CMS, ØSNF services must be in compliance with Subpart B of part 483, ØAllows CAH to use beds interchangeable for either acute care or SNF level, ØSwings from acute care reimbursement to SNF services and reimbursement, 79
 Swing Beds Ø Must be discharge orders from acute care, progress notes and discharge summary and subsequent admission orders, Ø If patient does not change facilities can use same MR with chart separator, Ø Medicare requires 3 day qualifying stay in CAH prior to admission to swing bed, Ø 3 day rule only applies to Medicare patients, 80
Swing Beds Ø Must be discharge orders from acute care, progress notes and discharge summary and subsequent admission orders, Ø If patient does not change facilities can use same MR with chart separator, Ø Medicare requires 3 day qualifying stay in CAH prior to admission to swing bed, Ø 3 day rule only applies to Medicare patients, 80
 Swing Beds ØNo LOS restriction for swing bed, ØNo transfer agreement needed between CAH and nursing home, ØCAH does not have to use the MDS form for recording patient assessment, ØSwing bed patients receive SNF level of care and CAH is reimbursed for SNF level. 81
Swing Beds ØNo LOS restriction for swing bed, ØNo transfer agreement needed between CAH and nursing home, ØCAH does not have to use the MDS form for recording patient assessment, ØSwing bed patients receive SNF level of care and CAH is reimbursed for SNF level. 81
 Swing Beds-Requirements ØResident rights, ØAdmission, transfer, and discharge rights, ØResident behavior and family practices (restraints), ØPatient activities, ØSocial services, comprehensive assessment, dental services, and nutrition, 82
Swing Beds-Requirements ØResident rights, ØAdmission, transfer, and discharge rights, ØResident behavior and family practices (restraints), ØPatient activities, ØSocial services, comprehensive assessment, dental services, and nutrition, 82
 Eligibility 351 ØMust be certified as CAH, ØHave no more than 25 beds, ØSection on facilities participating as rural health care hospital (see 352), Ø Have to be in compliance with SNF requirements in subpart B of part 483, (residents rights, nutrition, dental, admission and discharge rights, patient activities, social services, comprehensive assessment etc. , 83
Eligibility 351 ØMust be certified as CAH, ØHave no more than 25 beds, ØSection on facilities participating as rural health care hospital (see 352), Ø Have to be in compliance with SNF requirements in subpart B of part 483, (residents rights, nutrition, dental, admission and discharge rights, patient activities, social services, comprehensive assessment etc. , 83
 Resident Rights 361 ØRight to dignified existence, ØSelf determination, ØCommunicate and access to persons and services outside the facility, ØRight to a copy of a notice of their rights, ØIn language they can understand, ØRight to refuse treatment, 84
Resident Rights 361 ØRight to dignified existence, ØSelf determination, ØCommunicate and access to persons and services outside the facility, ØRight to a copy of a notice of their rights, ØIn language they can understand, ØRight to refuse treatment, 84
 Resident Rights 361 Ø Right to get access to their records within 24 hours (excluding weekends/holidays), Ø A right to buy a copy of their medical records with 2 working days notice, Ø Rights in writing about their conduct and responsibilities during their stay, Ø Facility must assure patient’s rights are followed, Ø Right to know what their rights are, 85
Resident Rights 361 Ø Right to get access to their records within 24 hours (excluding weekends/holidays), Ø A right to buy a copy of their medical records with 2 working days notice, Ø Rights in writing about their conduct and responsibilities during their stay, Ø Facility must assure patient’s rights are followed, Ø Right to know what their rights are, 85
 Resident Rights 361 ØRight to choose attending MD, ØRight to share room with their spouse, ØParticipate in their plan of care, ØRight to privacy and confidentiality, ØRight to get mail and send mail unopened, ØRight to personal property and visitors, ØWork or not work, ØProvide interpreters, sign language when needed, 86
Resident Rights 361 ØRight to choose attending MD, ØRight to share room with their spouse, ØParticipate in their plan of care, ØRight to privacy and confidentiality, ØRight to get mail and send mail unopened, ØRight to personal property and visitors, ØWork or not work, ØProvide interpreters, sign language when needed, 86
 Resident Rights 362 Ø Right to refuse treatment, Ø Right to refuse to participate in experimental research, Ø A resident being considered for participation in experimental research must be fully informed of the nature of the experiment and understand the possible consequences of participating, Ø Will look to see if IRB has approved experimental treatment, Ø Right to make an advance directive, 87
Resident Rights 362 Ø Right to refuse treatment, Ø Right to refuse to participate in experimental research, Ø A resident being considered for participation in experimental research must be fully informed of the nature of the experiment and understand the possible consequences of participating, Ø Will look to see if IRB has approved experimental treatment, Ø Right to make an advance directive, 87
 Resident Rights 363 Ø Inform each Medicaid patient that items and services that will be included and for which the resident will be charged and amount, Ø If M/M does not make payment for service, must notify the resident of what is not covered, Ø May charge for phone, TV, radio, personal clothing, confections, flowers, plants, private room unless isolation, social events, books etc. , Ø Must have P&P for advance directives, educate your staff on advance directives, Ø Must document in the MR if they have one, Ø Provide for community education on advance directives (can use videotapes and audiotapes), 88
Resident Rights 363 Ø Inform each Medicaid patient that items and services that will be included and for which the resident will be charged and amount, Ø If M/M does not make payment for service, must notify the resident of what is not covered, Ø May charge for phone, TV, radio, personal clothing, confections, flowers, plants, private room unless isolation, social events, books etc. , Ø Must have P&P for advance directives, educate your staff on advance directives, Ø Must document in the MR if they have one, Ø Provide for community education on advance directives (can use videotapes and audiotapes), 88
 Free Choice 364 ØRight to choose an attending MD/DO, ØBut doctor must fulfill given requirements such as the frequency of visits, ØFacility has right to inform resident to seek another doctor, ØFacility must help patient to find another physician, 89
Free Choice 364 ØRight to choose an attending MD/DO, ØBut doctor must fulfill given requirements such as the frequency of visits, ØFacility has right to inform resident to seek another doctor, ØFacility must help patient to find another physician, 89
 Consent 365 Ø Right to be fully informed in advance about care and treatment, Ø Including any changes, Ø They have right to receive information in order to make healthcare decisions, Ø information should include medical condition, changes in condition, the benefits, reasonable risks of the recommended treatment, and reasonable alternatives, Ø Financial costs to treatment options must be disclosed in advance and in writing, 90
Consent 365 Ø Right to be fully informed in advance about care and treatment, Ø Including any changes, Ø They have right to receive information in order to make healthcare decisions, Ø information should include medical condition, changes in condition, the benefits, reasonable risks of the recommended treatment, and reasonable alternatives, Ø Financial costs to treatment options must be disclosed in advance and in writing, 90
 Privacy/Confidentiality 367 Ø Right to personal privacy, Ø Right to confidentiality, Ø Privacy to written and telephone calls, Ø Right to privacy for visits in office, dining room, vacant chapel, Ø Privacy when using bathroom, Ø Staff should pull curtains, close doors, 91
Privacy/Confidentiality 367 Ø Right to personal privacy, Ø Right to confidentiality, Ø Privacy to written and telephone calls, Ø Right to privacy for visits in office, dining room, vacant chapel, Ø Privacy when using bathroom, Ø Staff should pull curtains, close doors, 91
 Work 368 Ø Resident has right to refuse to perform services for the facility, Ø Perform services if she wants (housekeeping, laundry, meal preparation), Ø Document need or desire to work in the plan of care, Ø Specify if services performed are paid or voluntary, Ø Rate must be at prevailing rate, laundry 92
Work 368 Ø Resident has right to refuse to perform services for the facility, Ø Perform services if she wants (housekeeping, laundry, meal preparation), Ø Document need or desire to work in the plan of care, Ø Specify if services performed are paid or voluntary, Ø Rate must be at prevailing rate, laundry 92
 Mail 369 ØRight to send and promptly receive mail that is unopened; and ØHave access to stationery, postage, and writing implements at the resident’s own expense. ØDeliver mail within 24 hours of delivery by us post office, 93
Mail 369 ØRight to send and promptly receive mail that is unopened; and ØHave access to stationery, postage, and writing implements at the resident’s own expense. ØDeliver mail within 24 hours of delivery by us post office, 93
 Access and Visitation 370 Ø The resident has the right and the facility must provide immediate access to any resident by the following, Ø immediate family or other relatives of the resident, Ø others who are visiting with the consent of the resident. Ø Resident can withdrawal consent at any time, 94
Access and Visitation 370 Ø The resident has the right and the facility must provide immediate access to any resident by the following, Ø immediate family or other relatives of the resident, Ø others who are visiting with the consent of the resident. Ø Resident can withdrawal consent at any time, 94
 Personal Property 371 Ø Right to retain and use personal possessions, Ø Including some furnishings, and appropriate clothing, as space permits, Ø Unless to do so would infringe upon the rights or health and safety of other residents, Ø Surveyor will look to see if residents are encouraged to have and use personal items, 95
Personal Property 371 Ø Right to retain and use personal possessions, Ø Including some furnishings, and appropriate clothing, as space permits, Ø Unless to do so would infringe upon the rights or health and safety of other residents, Ø Surveyor will look to see if residents are encouraged to have and use personal items, 95
 Married Couples 372 Ø Resident has the right to share a room with his or her spouse, Ø When married residents live in the same facility, Ø And both spouses consent to the arrangement. Ø If there is a room available, 96
Married Couples 372 Ø Resident has the right to share a room with his or her spouse, Ø When married residents live in the same facility, Ø And both spouses consent to the arrangement. Ø If there is a room available, 96
 Admission, Transfers, Discharge ØTransfer means outside of the facility, ØPurpose to restrict transfer by facility-to prevent dumping of high care or difficult residents (373), ØOnly when initiated by the facility not the patient, ØMay not transfer or discharge a resident unless necessary to meet their welfare, ØAppropriate because no longer needs the services provided (374), ØSafety or health of individuals in facility is endangered, 97
Admission, Transfers, Discharge ØTransfer means outside of the facility, ØPurpose to restrict transfer by facility-to prevent dumping of high care or difficult residents (373), ØOnly when initiated by the facility not the patient, ØMay not transfer or discharge a resident unless necessary to meet their welfare, ØAppropriate because no longer needs the services provided (374), ØSafety or health of individuals in facility is endangered, 97
 Admission, Transfers, Discharge ØMust document these in the medical record, ØMust notify resident and family members and document reasons, Ø 30 days notice with exceptions, endangerment to others, condition improved, urgent medical needs to be transferred, ØNot a resident for 30 days, 98
Admission, Transfers, Discharge ØMust document these in the medical record, ØMust notify resident and family members and document reasons, Ø 30 days notice with exceptions, endangerment to others, condition improved, urgent medical needs to be transferred, ØNot a resident for 30 days, 98
 Payment of Care 375 ØResident has failed to pay for care after reasonable notice, ØIf eligible for Medicare after admission, may only charge allowable rate, ØMust provide notice to the patient and document reason in MR (377), ØMust be made within 30 days before resident is transferred, unless safety or health of individuals would be in danger, ØNeed to document accurate assessments to address resident’s needs, 99
Payment of Care 375 ØResident has failed to pay for care after reasonable notice, ØIf eligible for Medicare after admission, may only charge allowable rate, ØMust provide notice to the patient and document reason in MR (377), ØMust be made within 30 days before resident is transferred, unless safety or health of individuals would be in danger, ØNeed to document accurate assessments to address resident’s needs, 99
 Content of Notice 370 Ø The reason for transfer or discharge; Ø (The effective date of transfer or discharge; Ø location to which the resident is transferred or discharged; Ø A statement that the resident has the right to appeal the action to the State; Ø The name, address and telephone number of the State LTC ombudsman; Ø For nursing facility residents with DD the mailing address and telephone number of the agency responsible for the protection and advocacy of MR/DR individuals established under Developmental Disabilities Assistance and Bill of Rights Act; and 100
Content of Notice 370 Ø The reason for transfer or discharge; Ø (The effective date of transfer or discharge; Ø location to which the resident is transferred or discharged; Ø A statement that the resident has the right to appeal the action to the State; Ø The name, address and telephone number of the State LTC ombudsman; Ø For nursing facility residents with DD the mailing address and telephone number of the agency responsible for the protection and advocacy of MR/DR individuals established under Developmental Disabilities Assistance and Bill of Rights Act; and 100
 Content of Notice 370 Ø For nursing facility residents who are mentally ill, the mailing address and telephone number of the agency responsible for the protection and advocacy of mentally ill individuals established under the Protection and Advocacy for Mentally Ill Individuals Act. Ø Must provide sufficient preparation and orientation to residents so they know where they are going and have safe transportation (380), 101
Content of Notice 370 Ø For nursing facility residents who are mentally ill, the mailing address and telephone number of the agency responsible for the protection and advocacy of mentally ill individuals established under the Protection and Advocacy for Mentally Ill Individuals Act. Ø Must provide sufficient preparation and orientation to residents so they know where they are going and have safe transportation (380), 101
 Resident Behavior-Restraints ØRight to be free from restraints (381), ØBoth physical and chemical, ØMust do assessment and care planning, ØNever used for discipline or convenience, ØNeed to have process of assessment and evaluation before restraints used, ØInclude in the plan of care, 102
Resident Behavior-Restraints ØRight to be free from restraints (381), ØBoth physical and chemical, ØMust do assessment and care planning, ØNever used for discipline or convenience, ØNeed to have process of assessment and evaluation before restraints used, ØInclude in the plan of care, 102
 Abuse 382 ØRight to be free from verbal, sexual, physical, and mental abuse, ØFree from involuntary seclusion, ØDefines each of these, ØMust have written policies that prohibit neglect, and abuse and mistreatment, Øinclude the definitions of each in your policy, ØWill review any records of abuse, ØNeed P&P that prohibit mistreatment, neglect, and abuse and misappropriation of resident property, 103
Abuse 382 ØRight to be free from verbal, sexual, physical, and mental abuse, ØFree from involuntary seclusion, ØDefines each of these, ØMust have written policies that prohibit neglect, and abuse and mistreatment, Øinclude the definitions of each in your policy, ØWill review any records of abuse, ØNeed P&P that prohibit mistreatment, neglect, and abuse and misappropriation of resident property, 103
 Hiring of Employees 384 ØNot hire if found guilty of abusing, neglecting, or mistreating residents by a court of law, ØOr entered into state NA registry for this, ØReport any alleged violation involving neglect or abuse, or misappropriation of property to administrator and to other officials as required by state law, ØMust investigate, ØShould check all references, 104
Hiring of Employees 384 ØNot hire if found guilty of abusing, neglecting, or mistreating residents by a court of law, ØOr entered into state NA registry for this, ØReport any alleged violation involving neglect or abuse, or misappropriation of property to administrator and to other officials as required by state law, ØMust investigate, ØShould check all references, 104
 Surveyor will look at…. 384 Was relevant documentation reviewed and preserved (e. g. , dated dressing which was not changed when treatment recorded change)? Was the alleged victim examined promptly (if injury was suspected) and the finding documented in the report? What steps were taken to protect the alleged victim from further abuse (particularly where no suspect has been identified)? 105
Surveyor will look at…. 384 Was relevant documentation reviewed and preserved (e. g. , dated dressing which was not changed when treatment recorded change)? Was the alleged victim examined promptly (if injury was suspected) and the finding documented in the report? What steps were taken to protect the alleged victim from further abuse (particularly where no suspect has been identified)? 105
 Surveyor Will Look At (continued) What actions were taken as a result of the investigation? What corrective action was taken, including informing the nurse aide registry, State licensure authorities, and other agencies (e. g. , LTC ombudsman; adult protective services; Medicaid fraud and abuse unit)? 106
Surveyor Will Look At (continued) What actions were taken as a result of the investigation? What corrective action was taken, including informing the nurse aide registry, State licensure authorities, and other agencies (e. g. , LTC ombudsman; adult protective services; Medicaid fraud and abuse unit)? 106
 Quality of Life ØMust care for residents in way that promotes quality of life, ØHave activities directed by qualified person, ØQualified occupational therapist, ØMust provide social services to attain physical, mental and psychosocial well being, 107
Quality of Life ØMust care for residents in way that promotes quality of life, ØHave activities directed by qualified person, ØQualified occupational therapist, ØMust provide social services to attain physical, mental and psychosocial well being, 107
 Activities 385 Ø Facility must provide for an ongoing program of activities designed the interests and the physical, mental, and psychosocial well-being of each resident. Ø Activities program by a qualified therapeutic recreation specialist or activity professional who is licensed or registered by state, Ø Or 2 yr experience on social or recreational program within the last 5 years, or Ø Is qualified OT or OT assistant, Ø Or had completed training by the state, 108
Activities 385 Ø Facility must provide for an ongoing program of activities designed the interests and the physical, mental, and psychosocial well-being of each resident. Ø Activities program by a qualified therapeutic recreation specialist or activity professional who is licensed or registered by state, Ø Or 2 yr experience on social or recreational program within the last 5 years, or Ø Is qualified OT or OT assistant, Ø Or had completed training by the state, 108
 Activities 385 Ø Surveyor will observe individual and group activity, Ø Long list of things under the survey procedures on this one, Ø What activities are planned, Ø Outcomes and responses, Ø Included in care plans based on resident’s assessment, Ø Adequate supplies, 109
Activities 385 Ø Surveyor will observe individual and group activity, Ø Long list of things under the survey procedures on this one, Ø What activities are planned, Ø Outcomes and responses, Ø Included in care plans based on resident’s assessment, Ø Adequate supplies, 109
 Social Services 386 Ø Facility must provide medically-related social services to attain or maintain the highest practicable physical, mental, and psychosocial well-being of each resident, Ø with more than 120 beds must employ a qualified social worker on a full-time basis. Ø Need bachelor’s degree in social work or human services field (psychology, rehab counseling, etc. ) and 1 year supervised social work experience in health care setting, 110
Social Services 386 Ø Facility must provide medically-related social services to attain or maintain the highest practicable physical, mental, and psychosocial well-being of each resident, Ø with more than 120 beds must employ a qualified social worker on a full-time basis. Ø Need bachelor’s degree in social work or human services field (psychology, rehab counseling, etc. ) and 1 year supervised social work experience in health care setting, 110
 Social Services 386 Making arrangements for obtaining needed adaptive equipment, clothing, and personal items; Maintaining contact with family (with resident’s permission) to report on changes in health, current goals, discharge planning, and encouragement to participate in care planning; Assisting staff to inform residents and those they designate about the resident’s health status and health care choices; Making referrals and obtaining services from outside entities (e. g. , talking books, absentee ballots, community wheelchair transportation); 111
Social Services 386 Making arrangements for obtaining needed adaptive equipment, clothing, and personal items; Maintaining contact with family (with resident’s permission) to report on changes in health, current goals, discharge planning, and encouragement to participate in care planning; Assisting staff to inform residents and those they designate about the resident’s health status and health care choices; Making referrals and obtaining services from outside entities (e. g. , talking books, absentee ballots, community wheelchair transportation); 111
 Social Services (continued) 386 Assisting residents with financial and legal matters (e. g. , applying for pensions, referrals to lawyers, referrals to funeral homes for preplanning arrangements); Discharge planning services (e. g. , helping to place a resident on a waiting list for community congregate living, arranging intake for home care services for residents returning home, assisting with transfer arrangements to other facilities); Providing or arranging provision of needed counseling services; 112
Social Services (continued) 386 Assisting residents with financial and legal matters (e. g. , applying for pensions, referrals to lawyers, referrals to funeral homes for preplanning arrangements); Discharge planning services (e. g. , helping to place a resident on a waiting list for community congregate living, arranging intake for home care services for residents returning home, assisting with transfer arrangements to other facilities); Providing or arranging provision of needed counseling services; 112
 Resident Assessments 388 Conduct initial and periodic and reproducible assessments of each resident’s functional capacity, and includes; ØIdentification and demographic information. Ø Customary routine. Ø Cognitive patterns. Ø Communication. Ø Vision. Ø Mood and behavior patterns. Ø Psychosocial well-being. 113
Resident Assessments 388 Conduct initial and periodic and reproducible assessments of each resident’s functional capacity, and includes; ØIdentification and demographic information. Ø Customary routine. Ø Cognitive patterns. Ø Communication. Ø Vision. Ø Mood and behavior patterns. Ø Psychosocial well-being. 113
 Resident Assessments 388 Ø Physical functioning and structural problems. Ø Continence. Ø Disease diagnoses and health conditions. Ø Dental and nutritional status. Ø Skin condition. Ø Activity pursuit. Ø Medications 114
Resident Assessments 388 Ø Physical functioning and structural problems. Ø Continence. Ø Disease diagnoses and health conditions. Ø Dental and nutritional status. Ø Skin condition. Ø Activity pursuit. Ø Medications 114
 Resident Assessments 388 Ø Special treatments and procedures. Ø Discharge potential. Ø Documentation of summary information regarding the additional assessment performed through the resident assessment protocols. Ø Documentation of participation in assessment. Ø Must do direct observation and communicate with resident and licensed members on all shifts, Ø Intent to do this to develop care plan, 115
Resident Assessments 388 Ø Special treatments and procedures. Ø Discharge potential. Ø Documentation of summary information regarding the additional assessment performed through the resident assessment protocols. Ø Documentation of participation in assessment. Ø Must do direct observation and communicate with resident and licensed members on all shifts, Ø Intent to do this to develop care plan, 115
 Assessments ØAssessment within 14 days after admission, ØAssessment if significant change (390), ØExcludes readmissions if no significant change in condition (389), ØVery detailed information on what constitutes a significant change (394), ØMust have a comprehensive care plan (395), ØCare plan must include measurable objectives to met patient’s needs, 116
Assessments ØAssessment within 14 days after admission, ØAssessment if significant change (390), ØExcludes readmissions if no significant change in condition (389), ØVery detailed information on what constitutes a significant change (394), ØMust have a comprehensive care plan (395), ØCare plan must include measurable objectives to met patient’s needs, 116
 Care Plans 395 Ø Interdisciplinary team should develop objectives to attain highest level of functioning, Ø Document if patient refuses something staff feel would help, Ø Care plan must be developed within 7 days after comprehensive assessment done, Ø Prepared by interdisciplinary team that includes doctor, RN with responsibility for resident, resident and family, Ø Review and revise as necessary, 117
Care Plans 395 Ø Interdisciplinary team should develop objectives to attain highest level of functioning, Ø Document if patient refuses something staff feel would help, Ø Care plan must be developed within 7 days after comprehensive assessment done, Ø Prepared by interdisciplinary team that includes doctor, RN with responsibility for resident, resident and family, Ø Review and revise as necessary, 117
 Care Plan 395 Ø Did an occupational therapist design needed adaptive equipment or a speech therapist provide techniques to improve swallowing ability? Ø Do the dietitian and the speech therapist determine, for example, the optimum textures and consistency for the resident’s food that provide both a nutritionally adequate diet and effectively use oropharyngeal capabilities of the resident, Ø Does staff make an effort to schedule care plan meetings at the best time of the day for residents and their families? 118
Care Plan 395 Ø Did an occupational therapist design needed adaptive equipment or a speech therapist provide techniques to improve swallowing ability? Ø Do the dietitian and the speech therapist determine, for example, the optimum textures and consistency for the resident’s food that provide both a nutritionally adequate diet and effectively use oropharyngeal capabilities of the resident, Ø Does staff make an effort to schedule care plan meetings at the best time of the day for residents and their families? 118
 Service Provided 397 Ø Services provided must meet the standard of care, Ø Make sure person providing care qualified, Ø Are residents with acute conditions promptly hospitalized, as appropriate? Ø Are there errors in medication administration? Ø Make sure they follow the care plan (399), 119
Service Provided 397 Ø Services provided must meet the standard of care, Ø Make sure person providing care qualified, Ø Are residents with acute conditions promptly hospitalized, as appropriate? Ø Are there errors in medication administration? Ø Make sure they follow the care plan (399), 119
 Discharge Summary 399 Resident must have a discharge summary that includes; ØRecapitulation of the resident’s stay, ØFinal summary of the resident’s status, ØA post-discharge plan of care that is developed with the participation of the resident and his or her family, which will assist the resident to adjust to his or her new living environment. 120
Discharge Summary 399 Resident must have a discharge summary that includes; ØRecapitulation of the resident’s stay, ØFinal summary of the resident’s status, ØA post-discharge plan of care that is developed with the participation of the resident and his or her family, which will assist the resident to adjust to his or her new living environment. 120
 Nutrition 400 The facility must ensure that a resident; Ø Maintains acceptable parameters of nutritional status, such as body weight and protein levels, Ø unless the resident’s clinical condition demonstrates that this is not possible, Ø Unacceptable parameters include unplanned weight loss, peripheral edema, cachexia and laboratory tests indicating malnourishment (e. g. , serum albumin levels). 121
Nutrition 400 The facility must ensure that a resident; Ø Maintains acceptable parameters of nutritional status, such as body weight and protein levels, Ø unless the resident’s clinical condition demonstrates that this is not possible, Ø Unacceptable parameters include unplanned weight loss, peripheral edema, cachexia and laboratory tests indicating malnourishment (e. g. , serum albumin levels). 121
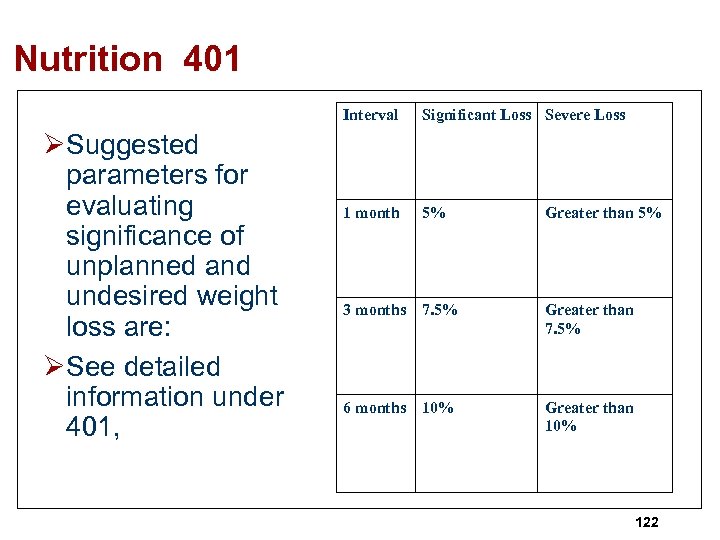 Nutrition 401 Interval ØSuggested parameters for evaluating significance of unplanned and undesired weight loss are: ØSee detailed information under 401, Significant Loss Severe Loss 1 month 5% Greater than 5% 3 months 7. 5% Greater than 7. 5% 6 months 10% Greater than 10% 122
Nutrition 401 Interval ØSuggested parameters for evaluating significance of unplanned and undesired weight loss are: ØSee detailed information under 401, Significant Loss Severe Loss 1 month 5% Greater than 5% 3 months 7. 5% Greater than 7. 5% 6 months 10% Greater than 10% 122
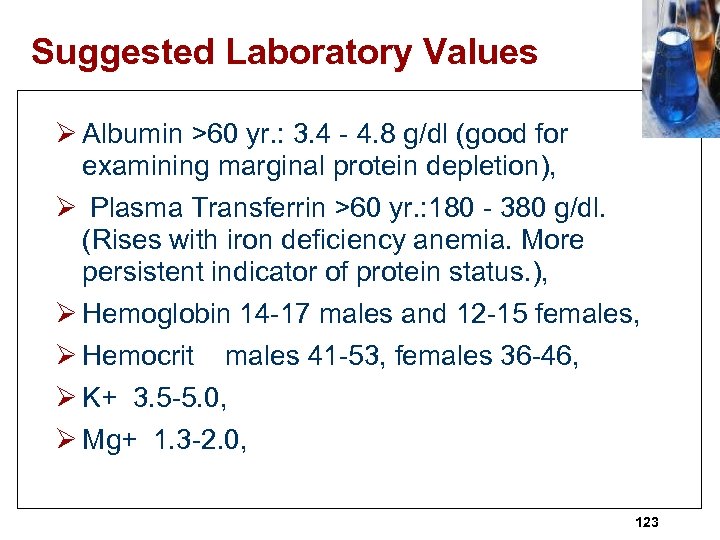 Suggested Laboratory Values Ø Albumin >60 yr. : 3. 4 - 4. 8 g/dl (good for examining marginal protein depletion), Ø Plasma Transferrin >60 yr. : 180 - 380 g/dl. (Rises with iron deficiency anemia. More persistent indicator of protein status. ), Ø Hemoglobin 14 -17 males and 12 -15 females, Ø Hemocrit males 41 -53, females 36 -46, Ø K+ 3. 5 -5. 0, Ø Mg+ 1. 3 -2. 0, 123
Suggested Laboratory Values Ø Albumin >60 yr. : 3. 4 - 4. 8 g/dl (good for examining marginal protein depletion), Ø Plasma Transferrin >60 yr. : 180 - 380 g/dl. (Rises with iron deficiency anemia. More persistent indicator of protein status. ), Ø Hemoglobin 14 -17 males and 12 -15 females, Ø Hemocrit males 41 -53, females 36 -46, Ø K+ 3. 5 -5. 0, Ø Mg+ 1. 3 -2. 0, 123
 Rehab Services 402 ØIf specialized rehabilitative services such as, but not limited to, Øphysical therapy, speech-language pathology, occupational therapy, and mental health rehabilitative services for mental illness and mental retardation, are required in the resident’s comprehensive plan of care, ØFacility must provide the required service, 124
Rehab Services 402 ØIf specialized rehabilitative services such as, but not limited to, Øphysical therapy, speech-language pathology, occupational therapy, and mental health rehabilitative services for mental illness and mental retardation, are required in the resident’s comprehensive plan of care, ØFacility must provide the required service, 124
 Rehab Services (continued) 402 ØNeed physician order (403) ØMay get from outside source, ØNo fee can be charged a Medicaid recipient for specialized rehabilitative services because they are covered facility services. 125
Rehab Services (continued) 402 ØNeed physician order (403) ØMay get from outside source, ØNo fee can be charged a Medicaid recipient for specialized rehabilitative services because they are covered facility services. 125
 Occupational Therapy 402 Ø What did the facility do to decrease the amount of assistance needed to perform a task? Ø What did the facility do to decrease behavioral symptoms? Ø What did the facility do to improve gross and fine motor coordination? Ø What did the facility do to improve sensory awareness, visual-spatial awareness, and body integration? Ø What did the facility do to improve memory, problem solving, attention span, and the ability to recognize safety hazards? 126
Occupational Therapy 402 Ø What did the facility do to decrease the amount of assistance needed to perform a task? Ø What did the facility do to decrease behavioral symptoms? Ø What did the facility do to improve gross and fine motor coordination? Ø What did the facility do to improve sensory awareness, visual-spatial awareness, and body integration? Ø What did the facility do to improve memory, problem solving, attention span, and the ability to recognize safety hazards? 126
 Speech, Language Pathology Ø What did the facility do to improve auditory comprehension? Ø What did the facility do to improve speech production and expressive behavior? Ø What did the facility do to improve the functional abilities of residents with moderate to severe hearing loss who have received an audiology evaluation? Ø For the resident who cannot speak, did the facility assess for a communication board or an alternate means of communication? 127
Speech, Language Pathology Ø What did the facility do to improve auditory comprehension? Ø What did the facility do to improve speech production and expressive behavior? Ø What did the facility do to improve the functional abilities of residents with moderate to severe hearing loss who have received an audiology evaluation? Ø For the resident who cannot speak, did the facility assess for a communication board or an alternate means of communication? 127
 Dental Services 404 Ø The facility must assist residents in obtaining routine and 24 -hour emergency dental care. Ø This requirement makes the facility directly responsible for the dental care needs of its residents. Ø The facility must ensure that a dentist is available for residents, Ø Make appt and arrange transportation (408), Ø Can’t charge Medicaid patients, Ø For Medicare and private pay can impose additional charge, 128
Dental Services 404 Ø The facility must assist residents in obtaining routine and 24 -hour emergency dental care. Ø This requirement makes the facility directly responsible for the dental care needs of its residents. Ø The facility must ensure that a dentist is available for residents, Ø Make appt and arrange transportation (408), Ø Can’t charge Medicaid patients, Ø For Medicare and private pay can impose additional charge, 128
 AHA Website on CAH Øwww. aha. org/member. Relations/cah. asp ØProvides updates, ØDirectory of resources, ØFederal legislation, ØGrowth of the program, ØGrants, ØState hospital association links, 129
AHA Website on CAH Øwww. aha. org/member. Relations/cah. asp ØProvides updates, ØDirectory of resources, ØFederal legislation, ØGrowth of the program, ØGrants, ØState hospital association links, 129
 Ø Statement of Deficiencies and Plan of corrections, Ø Based on documentation of surveyor worksheet or notes and form CMS-2567, 130
Ø Statement of Deficiencies and Plan of corrections, Ø Based on documentation of surveyor worksheet or notes and form CMS-2567, 130
 131
131
 The End Questions? ? ? Ø Sue Dill Calloway RN, Esq. CPHRM ØAD, BA, BSN, MSN, JD ØPresident ØAttorney at Law Ø 614 791 -1468 Øsdill 1@columbus. rr. com 132
The End Questions? ? ? Ø Sue Dill Calloway RN, Esq. CPHRM ØAD, BA, BSN, MSN, JD ØPresident ØAttorney at Law Ø 614 791 -1468 Øsdill 1@columbus. rr. com 132
 The End ØAre you up to the challenge? ? Ø See additional resources including patient safety resources, 133
The End ØAre you up to the challenge? ? Ø See additional resources including patient safety resources, 133
 Websites ØTools and Resources Rural Health Resource Center at http: //www. ruralcenter. org/tasc/ Ø American Association for Respiratory Care AARC- www. aarc. org, ØAmerican College of Surgeons ACSwww. facs. org, ØAmerican Nurses Association ANAwww. ana. org 134
Websites ØTools and Resources Rural Health Resource Center at http: //www. ruralcenter. org/tasc/ Ø American Association for Respiratory Care AARC- www. aarc. org, ØAmerican College of Surgeons ACSwww. facs. org, ØAmerican Nurses Association ANAwww. ana. org 134
 Websites Ø Center for Disease Control CDC – www. cdc. gov, Ø Food and Drug Administration- www. fda. gov, Ø Association of peri. Operative Registered Nurses at AORN- www. aorn. org, Ø American Institute of Architects AIAwww. aia. org, Ø Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA – www. osha. gov, Ø National Institutes of Health NIH-www. nih. gov, 135
Websites Ø Center for Disease Control CDC – www. cdc. gov, Ø Food and Drug Administration- www. fda. gov, Ø Association of peri. Operative Registered Nurses at AORN- www. aorn. org, Ø American Institute of Architects AIAwww. aia. org, Ø Occupational Safety and Health Administration OSHA – www. osha. gov, Ø National Institutes of Health NIH-www. nih. gov, 135
 Websites Ø United States Dept of Agriculture USDAwww. usda. gov, Ø Emergency Nurses Association ENAwww. ena. org, Ø American College of Emergency Physicians ACE - www. acep. org, Ø Joint Commissionwww. Joint. Commission. org, Ø Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services CMS www. cms. hhs. gov, 136
Websites Ø United States Dept of Agriculture USDAwww. usda. gov, Ø Emergency Nurses Association ENAwww. ena. org, Ø American College of Emergency Physicians ACE - www. acep. org, Ø Joint Commissionwww. Joint. Commission. org, Ø Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services CMS www. cms. hhs. gov, 136
 Websites Ø American Association for Respiratory Care AARC- www. aarc. org, Ø American College of Surgeons ACSwww. facs. org, Ø American Nurses Association ANAwww. ana. org, Ø AHRQ is www. ahrq. gov, 137
Websites Ø American Association for Respiratory Care AARC- www. aarc. org, Ø American College of Surgeons ACSwww. facs. org, Ø American Nurses Association ANAwww. ana. org, Ø AHRQ is www. ahrq. gov, 137
 Websites Ø American Hospital Association AHAwww. aha. org, Ø CMS Life Safety Code page http: //new. cms. hhs. gov/CFCs. And. Co. Ps/07_ LSC. asp, Ø COPs available in word and PDR at http: //www. access. gpo. gov/nara/cfr/waisidx _04/42 cfr 485_04. html, Ø American College of Radiologywww. acr. org, 138
Websites Ø American Hospital Association AHAwww. aha. org, Ø CMS Life Safety Code page http: //new. cms. hhs. gov/CFCs. And. Co. Ps/07_ LSC. asp, Ø COPs available in word and PDR at http: //www. access. gpo. gov/nara/cfr/waisidx _04/42 cfr 485_04. html, Ø American College of Radiologywww. acr. org, 138
 Websites Ø Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)- www. fema. gov, Ø Drug Enforcement Administration –www. dea. gov (copy of controlled substance act), Ø US Pharmacopeia- www. usp. org, (USP 797 book for sale), Ø Rural Assistance Center or RAC at http: //www. raconline. org/ Ø CAH seminar Oct 2007 handouts at http: //www. nrharural. org/conferences/sub/CAH. html 139
Websites Ø Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA)- www. fema. gov, Ø Drug Enforcement Administration –www. dea. gov (copy of controlled substance act), Ø US Pharmacopeia- www. usp. org, (USP 797 book for sale), Ø Rural Assistance Center or RAC at http: //www. raconline. org/ Ø CAH seminar Oct 2007 handouts at http: //www. nrharural. org/conferences/sub/CAH. html 139
 Websites Ø National Patient Safety Foundation at the AMAwww. ama-assn. org/med-sci/npsf/htm, Ø The Institute for Safe Medication Practiceswww. ismp. org Ø U. S. Pharmacopeia (USP) Convention, Inc. www. usp. org Ø U. S. Food and Drug Administration Med. Watchwww. fda. gov/medwatch Ø Institute for Healthcare Improvement- www. ihi. org, Ø AHRQ at www. ahrq. gov, Ø Sentinel event alerts at www. jointcommission. org, 140
Websites Ø National Patient Safety Foundation at the AMAwww. ama-assn. org/med-sci/npsf/htm, Ø The Institute for Safe Medication Practiceswww. ismp. org Ø U. S. Pharmacopeia (USP) Convention, Inc. www. usp. org Ø U. S. Food and Drug Administration Med. Watchwww. fda. gov/medwatch Ø Institute for Healthcare Improvement- www. ihi. org, Ø AHRQ at www. ahrq. gov, Ø Sentinel event alerts at www. jointcommission. org, 140
 Websites Ø American Pharmaceutical Associationwww. aphanet. org Ø American Society of Heath-System Pharmacistswww. ashp. org Ø Enhancing Patient Safety and Errors in Healthcarewww. mederrors. com Ø National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention-www. nccmerp. org, Ø FDA's Recalls, Market Withdrawals and Safety Alerts Page: http: //www. fda. gov/opacom/7 alerts. html 141
Websites Ø American Pharmaceutical Associationwww. aphanet. org Ø American Society of Heath-System Pharmacistswww. ashp. org Ø Enhancing Patient Safety and Errors in Healthcarewww. mederrors. com Ø National Coordinating Council for Medication Error Reporting and Prevention-www. nccmerp. org, Ø FDA's Recalls, Market Withdrawals and Safety Alerts Page: http: //www. fda. gov/opacom/7 alerts. html 141
 Infection Control Websites Ø Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC) infection control guidelines at www. apic. org, Ø Centers for Disease Control and Preventionwww. cdc. gov, Ø Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) at www. osha. gov, Ø The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health NIOSH at www. cdc. gov/niosh/homepage. html, Ø AORN at www. aorn. org, Ø Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) at www. shea-online. org, 142
Infection Control Websites Ø Association for Professionals in Infection Control and Epidemiology (APIC) infection control guidelines at www. apic. org, Ø Centers for Disease Control and Preventionwww. cdc. gov, Ø Occupational Health and Safety Administration (OSHA) at www. osha. gov, Ø The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health NIOSH at www. cdc. gov/niosh/homepage. html, Ø AORN at www. aorn. org, Ø Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) at www. shea-online. org, 142
 www. flexmonitoring. org/links. shtml 143
www. flexmonitoring. org/links. shtml 143
 Helpful Websites 144
Helpful Websites 144
 145
145
 Federal Office of Rural Health Policy ØFederal Office or Rural Health Policy Room 9 A-55 5600 Fishers Lane Rockville, MD 20857 301 443 -0835 301 443 -2803 fax 146
Federal Office of Rural Health Policy ØFederal Office or Rural Health Policy Room 9 A-55 5600 Fishers Lane Rockville, MD 20857 301 443 -0835 301 443 -2803 fax 146
 Office of Rural Health Policy Ø Advises DHHS on matters affecting rural hospitals, Ø Has resources for CAH, Ø Furnishes selected articles, Ø Articles on rural issues on their web site Ø http: //www. ruralhealth. hrsa. gov/index. htm 147
Office of Rural Health Policy Ø Advises DHHS on matters affecting rural hospitals, Ø Has resources for CAH, Ø Furnishes selected articles, Ø Articles on rural issues on their web site Ø http: //www. ruralhealth. hrsa. gov/index. htm 147
 148
148
 149
149
 Physical Environment ØHow do you provide emergency power? ØCan emergency generator provide power for emergency equipment and lighting, ØReview maintenance records and policies of test runs and how often on emergency equipment, 150
Physical Environment ØHow do you provide emergency power? ØCan emergency generator provide power for emergency equipment and lighting, ØReview maintenance records and policies of test runs and how often on emergency equipment, 150
 Resources Ø AHRQ published patient safety primer in 2008 that is designed to help users to understand key concepts in patient safety at http: //psnet. ahrq. gov/primer. Home. aspx, Ø Team. STEPPS is a teamwork system with tons of free resources on this at http: //teamstepps. ahrq. gov/ 151
Resources Ø AHRQ published patient safety primer in 2008 that is designed to help users to understand key concepts in patient safety at http: //psnet. ahrq. gov/primer. Home. aspx, Ø Team. STEPPS is a teamwork system with tons of free resources on this at http: //teamstepps. ahrq. gov/ 151
 AHRQ Website http: //www. ahrq. gov/qual/ 152
AHRQ Website http: //www. ahrq. gov/qual/ 152
 IHI Website www. ihi. org/ihi 153
IHI Website www. ihi. org/ihi 153
 Safety. Leaders. org Website 154
Safety. Leaders. org Website 154
 AHA Quality Center http: //www. ahaqualitycenter. org/ahaqualitycenter/jsp/home. jsp 155
AHA Quality Center http: //www. ahaqualitycenter. org/ahaqualitycenter/jsp/home. jsp 155
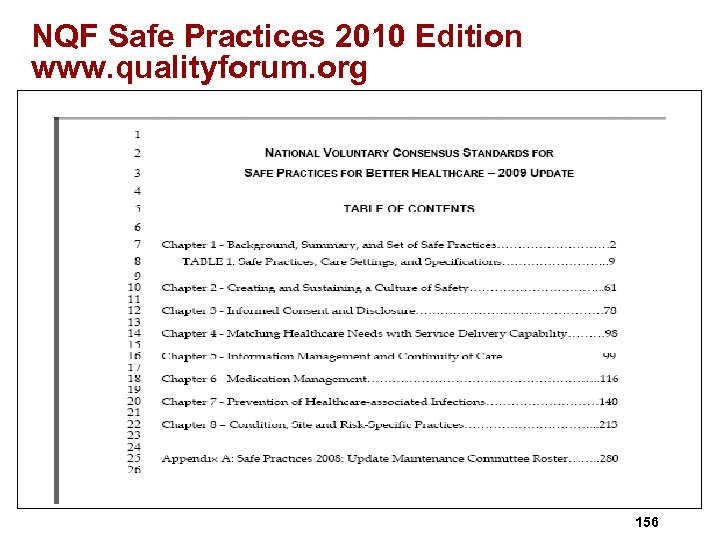 NQF Safe Practices 2010 Edition www. qualityforum. org 156
NQF Safe Practices 2010 Edition www. qualityforum. org 156
 NCP VA National Safety for Patient Safety ØHas multiple resources available at www. patientsafety. gov/bravo. htm ØTIPS Newsletter - topics concerning patient safety, ØNCPS Patient Safety Handbook developed by the National Center for Patient Safety, ØFall incident report by Morse Fall Scale and tools for falls, ØPatient elopement tools, ØMedication tips, 157
NCP VA National Safety for Patient Safety ØHas multiple resources available at www. patientsafety. gov/bravo. htm ØTIPS Newsletter - topics concerning patient safety, ØNCPS Patient Safety Handbook developed by the National Center for Patient Safety, ØFall incident report by Morse Fall Scale and tools for falls, ØPatient elopement tools, ØMedication tips, 157
 158
158
 AHRQ Ø Medical Error and Patient Safety at http: //www. ahrq. gov/qual/errorsix. htm, Web M&M, Mortality and Morbidity Monthly, at http: //www. webmm. ahrq. gov/, Ø PSNet, AHRQ Patient Safety Network, http: //psnet. ahrq. gov/, contains articles on medication errors and other patient safety issues that come out, Ø Are you signed up to get this? You can browse under medication errors/ADE 159 topic. (866 articles)
AHRQ Ø Medical Error and Patient Safety at http: //www. ahrq. gov/qual/errorsix. htm, Web M&M, Mortality and Morbidity Monthly, at http: //www. webmm. ahrq. gov/, Ø PSNet, AHRQ Patient Safety Network, http: //psnet. ahrq. gov/, contains articles on medication errors and other patient safety issues that come out, Ø Are you signed up to get this? You can browse under medication errors/ADE 159 topic. (866 articles)
 160
160
 ISMP Ø Institute for Safe Medication Practice is a rich source of information, Ø www. ismp. org, Ø Has medication tools and resources, Ø Has high alert list, self assessment tools Ø Error prone abbreviation, Ø FDA Med. Watch, Ø Confused drug name list, anticoagulant safety, Ø Sign up nurses for free newsletter via email called Nurse Advise-ERR at https: //www. ismp. org/orderforms/advise. ERRsubscri 161 ption. asp
ISMP Ø Institute for Safe Medication Practice is a rich source of information, Ø www. ismp. org, Ø Has medication tools and resources, Ø Has high alert list, self assessment tools Ø Error prone abbreviation, Ø FDA Med. Watch, Ø Confused drug name list, anticoagulant safety, Ø Sign up nurses for free newsletter via email called Nurse Advise-ERR at https: //www. ismp. org/orderforms/advise. ERRsubscri 161 ption. asp
 162
162
 USP US Pharmacopeia Ø Good source of information and have the MEDMARX program, Ø Have drug error finder for LASA, Ø Revises heparin monograph at http: //www. usp. org/hottopics/heparin. ht ml? hlc. Ø Has newletters at http: //www. usp. org/about. USP/newslett er. html Ø Has USP email notices –monthly updates, Ø www. usp. org 163
USP US Pharmacopeia Ø Good source of information and have the MEDMARX program, Ø Have drug error finder for LASA, Ø Revises heparin monograph at http: //www. usp. org/hottopics/heparin. ht ml? hlc. Ø Has newletters at http: //www. usp. org/about. USP/newslett er. html Ø Has USP email notices –monthly updates, Ø www. usp. org 163
 164
164
 CAPSlink Ø Every hospital should have someone on their medication management team to get this publication, Ø It is available at no charge, Ø Includes data from MEDMARX and Medication error reporting program, Ø Guidelines from different organizations, Ø Recommendations for problem prone error issues, Ø At http: //www. usp. org/hqi/practitioner. Programs/newsletters/caps. Link/ 165
CAPSlink Ø Every hospital should have someone on their medication management team to get this publication, Ø It is available at no charge, Ø Includes data from MEDMARX and Medication error reporting program, Ø Guidelines from different organizations, Ø Recommendations for problem prone error issues, Ø At http: //www. usp. org/hqi/practitioner. Programs/newsletters/caps. Link/ 165
 166
166
 Sign Up for FDA Alerts Ø Sign up to get safety alerts from FDA, Ø At http: //www. fda. gov/opacom/7 alerts. html Ø Example; Advil and ASA taken together- if heart patient takes ASA 81 mg for heart- ibuprofen can interfere with anti-platelet effect, Ø Take 30 minutes or longer, Ø Minimal risk with occasional use, Ø Lots of information on medications! Ø See also Drug Safety newsletter at http: //www. fda. gov/cder/dsn/2008_winter/2008_wint er. pdf 167
Sign Up for FDA Alerts Ø Sign up to get safety alerts from FDA, Ø At http: //www. fda. gov/opacom/7 alerts. html Ø Example; Advil and ASA taken together- if heart patient takes ASA 81 mg for heart- ibuprofen can interfere with anti-platelet effect, Ø Take 30 minutes or longer, Ø Minimal risk with occasional use, Ø Lots of information on medications! Ø See also Drug Safety newsletter at http: //www. fda. gov/cder/dsn/2008_winter/2008_wint er. pdf 167
 168
168
 FDA Patient Safety News 2008 Ø Mixups between insulin U-100 and U-500 which occurred when selecting from computer screens, Ø Severe pain, muscle or joint pain, with osteoporosis drug with bisphosphate drugs such as Fosamax, Actonel, Boniva, and Reclast, Ø More patients die with luer misconnections, Ø Deaths from Fentanyl patches continue, Ø http: //www. accessdata. fda. gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/psn/index. cfm 169
FDA Patient Safety News 2008 Ø Mixups between insulin U-100 and U-500 which occurred when selecting from computer screens, Ø Severe pain, muscle or joint pain, with osteoporosis drug with bisphosphate drugs such as Fosamax, Actonel, Boniva, and Reclast, Ø More patients die with luer misconnections, Ø Deaths from Fentanyl patches continue, Ø http: //www. accessdata. fda. gov/scripts/cdrh/cfdocs/psn/index. cfm 169
 170
170
 IHI Institute for Healthcare Improvement Ø Excellent source of resources for patient safety and quality resources, toolkits, how to kits, Ø Prevent ADEs by implementing medication reconciliation, Ø Reduce harm from high alert medications, Ø Reduce MRSA infections, Ø Many resources related to medication issues, At www. ihi. org, 171
IHI Institute for Healthcare Improvement Ø Excellent source of resources for patient safety and quality resources, toolkits, how to kits, Ø Prevent ADEs by implementing medication reconciliation, Ø Reduce harm from high alert medications, Ø Reduce MRSA infections, Ø Many resources related to medication issues, At www. ihi. org, 171
 172
172
 Leapfrog Ø Represents half a million Americans by corporations that purchase health insurance, Ø Rewards for improving safety and quality, Ø Aims CPOE, 27 procedures to preventing medical errors, high risk treatments, ICU staffing with intensivists Ø If 3 followed would prevent 907, 600 medication errors, 65, 341 lives and $41 billion dollars a year! Ø www. leapfroggroup. org 173
Leapfrog Ø Represents half a million Americans by corporations that purchase health insurance, Ø Rewards for improving safety and quality, Ø Aims CPOE, 27 procedures to preventing medical errors, high risk treatments, ICU staffing with intensivists Ø If 3 followed would prevent 907, 600 medication errors, 65, 341 lives and $41 billion dollars a year! Ø www. leapfroggroup. org 173
 National Quality Forum Ø 30 Safe Practices published in October, 2006, Ø 34 Safe Practices Update 2009, Ø Includes CPOE, unit dose, anticoagulant therapy, culture of safety, standardize labeling and storage of medication, identification of high alert medications, medication reconciliation, Ø Chapter 6 was on Medication Management, 174
National Quality Forum Ø 30 Safe Practices published in October, 2006, Ø 34 Safe Practices Update 2009, Ø Includes CPOE, unit dose, anticoagulant therapy, culture of safety, standardize labeling and storage of medication, identification of high alert medications, medication reconciliation, Ø Chapter 6 was on Medication Management, 174
 Culture 2007 NQF Report Culture SP 1 CHAPTER 1: Background q Summary, and Set of Safe Practices Structures & Systems ID Mitigation Risk & Hazards Consent & Disclosure Informed Consent CHAPTERS 2 -8 : Practices By Subject Team Training & Team Interv. Culture Meas. , F. B. , & Interv. CHAPTER 2: Creating and Sustaining a Culture of Patient Safety • Leadership Structures & Systems • Culture Measurement, Feedback and Interventions • Teamwork Training and Team Interventions • Identification and Mitigation of Risks and Hazards Life-Sustaining Treatment Disclosure Workforce Nursing Workforce Direct Caregivers ICU Care Information Management & Continuity of Care Critical Care Info. Order Read-back CHAPTER 3: Informed Consent & Disclosure • Informed Consent • Life-Sustaining Treatment • Disclosure CHAPTER 4: Workforce • Nursing Workforce • Direct Caregivers • ICU Care CHAPTER 5: Information Management & Continuity of Care • Critical Care Information • Order Read-back • Labeling Studies • Discharge Systems • Safe Adoption of Integrated Clinical Systems including CPOE • Abbreviations CHAPTER 6: Medication Management • Pharmacist Role Medication Management • Medication Reconciliation. • High-Alert Medications • Standardized Medication Labeling & Packaging • Unit-Dose Medications Hospital Acquired Infections Labeling Studies Discharge System CPOE Abbreviations Med Recon Pharmacist Central Role High Alert Meds Std. Med Labeling & Pkg Unit Dose Medications Asp. + VAP Prevention Hand Hygiene Influenza Prevention Central V. Cath BSI Prevention Sx Site Inf. Prevention Condition- & Site-Specific Practices Evidence. Based Ref. Press. Ulcer Prevention Anticoag. Therapy Wrong-site Sx Prevention DVT/VTE Prevention Periop. MI Prevention Contrast Media Use CHAPTER 6: Medication Management • Medication Reconciliation • Pharmacist Role • Standardized Medication Labeling & Packaging • High-Alert Medications • Unit-Dose Medications CHAPTER 7: Hospital-Acquired Infections • Prevention of Aspiration and Ventilator. Associated Pneumonia • Central Venous Catheter-Related Blood Stream Infection Prevention • Surgical Site Infection Prevention • Hand Hygiene • Influenza Prevention CHAPTER 8: • Evidence-Based Referrals • Wrong-Site, Wrong Procedure, Wrong Person Surgery Prevention • Perioperative Myocardial Infarct/Ischemia Prevention • Pressure Ulcer Prevention • DVT/VTE Prevention • Anticoagulation Therapy • Contrast Media-Induced Renal Failure Prevention 175
Culture 2007 NQF Report Culture SP 1 CHAPTER 1: Background q Summary, and Set of Safe Practices Structures & Systems ID Mitigation Risk & Hazards Consent & Disclosure Informed Consent CHAPTERS 2 -8 : Practices By Subject Team Training & Team Interv. Culture Meas. , F. B. , & Interv. CHAPTER 2: Creating and Sustaining a Culture of Patient Safety • Leadership Structures & Systems • Culture Measurement, Feedback and Interventions • Teamwork Training and Team Interventions • Identification and Mitigation of Risks and Hazards Life-Sustaining Treatment Disclosure Workforce Nursing Workforce Direct Caregivers ICU Care Information Management & Continuity of Care Critical Care Info. Order Read-back CHAPTER 3: Informed Consent & Disclosure • Informed Consent • Life-Sustaining Treatment • Disclosure CHAPTER 4: Workforce • Nursing Workforce • Direct Caregivers • ICU Care CHAPTER 5: Information Management & Continuity of Care • Critical Care Information • Order Read-back • Labeling Studies • Discharge Systems • Safe Adoption of Integrated Clinical Systems including CPOE • Abbreviations CHAPTER 6: Medication Management • Pharmacist Role Medication Management • Medication Reconciliation. • High-Alert Medications • Standardized Medication Labeling & Packaging • Unit-Dose Medications Hospital Acquired Infections Labeling Studies Discharge System CPOE Abbreviations Med Recon Pharmacist Central Role High Alert Meds Std. Med Labeling & Pkg Unit Dose Medications Asp. + VAP Prevention Hand Hygiene Influenza Prevention Central V. Cath BSI Prevention Sx Site Inf. Prevention Condition- & Site-Specific Practices Evidence. Based Ref. Press. Ulcer Prevention Anticoag. Therapy Wrong-site Sx Prevention DVT/VTE Prevention Periop. MI Prevention Contrast Media Use CHAPTER 6: Medication Management • Medication Reconciliation • Pharmacist Role • Standardized Medication Labeling & Packaging • High-Alert Medications • Unit-Dose Medications CHAPTER 7: Hospital-Acquired Infections • Prevention of Aspiration and Ventilator. Associated Pneumonia • Central Venous Catheter-Related Blood Stream Infection Prevention • Surgical Site Infection Prevention • Hand Hygiene • Influenza Prevention CHAPTER 8: • Evidence-Based Referrals • Wrong-Site, Wrong Procedure, Wrong Person Surgery Prevention • Perioperative Myocardial Infarct/Ischemia Prevention • Pressure Ulcer Prevention • DVT/VTE Prevention • Anticoagulation Therapy • Contrast Media-Induced Renal Failure Prevention 175
 Pa Patient Safety Authority www. psa. state. pa. us/psa/site/default. asp 176
Pa Patient Safety Authority www. psa. state. pa. us/psa/site/default. asp 176
 Federal Office of Rural Health Policy ØFederal Office or Rural Health Policy Room 9 A-55 5600 Fishers Lane Rockville, MD 20857 301 443 -0835 301 443 -2803 fax 177
Federal Office of Rural Health Policy ØFederal Office or Rural Health Policy Room 9 A-55 5600 Fishers Lane Rockville, MD 20857 301 443 -0835 301 443 -2803 fax 177
 Office of Rural Health Policy Ø Advises DHHS on matters affecting rural hospitals, Ø Has resources for CAH, Ø Furnishes selected articles, Ø Articles on rural issues on their web site Ø http: //www. ruralhealth. hrsa. gov/index. htm 178
Office of Rural Health Policy Ø Advises DHHS on matters affecting rural hospitals, Ø Has resources for CAH, Ø Furnishes selected articles, Ø Articles on rural issues on their web site Ø http: //www. ruralhealth. hrsa. gov/index. htm 178
 179
179
 180
180


