654b41d13d7cc89102a613e860833c27.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 96
 Crisis Management and Prevention (Management of Crises in case of Floods and Volcanic Eruptions) Giovanni Marizza gianni. marizza@yahoo. it 14 May 2014, 15, 00 – 17, 00
Crisis Management and Prevention (Management of Crises in case of Floods and Volcanic Eruptions) Giovanni Marizza gianni. marizza@yahoo. it 14 May 2014, 15, 00 – 17, 00
 Aim of the Module: • Focusing on Crisis Management in different situations in order to find lessons learned
Aim of the Module: • Focusing on Crisis Management in different situations in order to find lessons learned
 Crises produced by Floods Case Studies: • Mediterranean tsunami, 8. 000 years ago • Vajont dam, 1963 • Central Europe, 2002 • Asia Tsunami, 2004 • Katrina hurricane, 2005 • Future, possible events
Crises produced by Floods Case Studies: • Mediterranean tsunami, 8. 000 years ago • Vajont dam, 1963 • Central Europe, 2002 • Asia Tsunami, 2004 • Katrina hurricane, 2005 • Future, possible events
 Crises produced by Floods Definitions: • Flood: big, disastrous accumulation of water • Foreseable floods: monsoons, cyclons, typhoons, • • • hurricanes Non-foreseable floods: tsunami, man-made disasters Collateral effects (short-medium term): landslides, pollution of rivers, … Collateral effects (long term): alluvional plains
Crises produced by Floods Definitions: • Flood: big, disastrous accumulation of water • Foreseable floods: monsoons, cyclons, typhoons, • • • hurricanes Non-foreseable floods: tsunami, man-made disasters Collateral effects (short-medium term): landslides, pollution of rivers, … Collateral effects (long term): alluvional plains


 6000 b. C
6000 b. C
 (Pre)historical framework • Sumerians and Babilonians producing beer • Bosphorus opens, Mediterranean waters invade Black Sea basin • Rice cultivation in China • Agriculture spreads in Nile valley, Greece, Italy • First cattle-farms in the Near/Middle East
(Pre)historical framework • Sumerians and Babilonians producing beer • Bosphorus opens, Mediterranean waters invade Black Sea basin • Rice cultivation in China • Agriculture spreads in Nile valley, Greece, Italy • First cattle-farms in the Near/Middle East
 According to recent archeological findings: • Huge tsunami in the Mediterranean, • Coasts of Sicily, Southern Italy, Albania, Greece, • • Northern Africa from Tunisia to Egypt, Palestine, Lebanon, Syria, Turkey, Reason: sinking of 35 km 3 of terrain from Etna Volcano after an earthquake, Waves 50 m high, at high speed Many neolitic human structures disappeared Bosphorus, Black Sea, TU: Asia or Europe?
According to recent archeological findings: • Huge tsunami in the Mediterranean, • Coasts of Sicily, Southern Italy, Albania, Greece, • • Northern Africa from Tunisia to Egypt, Palestine, Lebanon, Syria, Turkey, Reason: sinking of 35 km 3 of terrain from Etna Volcano after an earthquake, Waves 50 m high, at high speed Many neolitic human structures disappeared Bosphorus, Black Sea, TU: Asia or Europe?
 1963
1963
 Historical framework: • Reconstruction of Europe after WW 2 • 3 June: Pope Giovanni XXIII dies • 16 June: Valentina Tereshkova 1 st woman in the Space • 28 August, MLK at Lincoln Memorial: “I have a dream!” • 22 November: JFK killed at Dallas • 12 December: Kenya independent from UK • Italy: “economic miracle”
Historical framework: • Reconstruction of Europe after WW 2 • 3 June: Pope Giovanni XXIII dies • 16 June: Valentina Tereshkova 1 st woman in the Space • 28 August, MLK at Lincoln Memorial: “I have a dream!” • 22 November: JFK killed at Dallas • 12 December: Kenya independent from UK • Italy: “economic miracle”
 Vajont Dam, 9 October 1963
Vajont Dam, 9 October 1963
 • hydroelectric plant, aim: energy for Venice and Northeastern Italy • Dam: 115 million m 3 water of Piave river • Landslide: 270 million m 3 terrain (Mt Toc) • 5 villages destroyed (Longarone* +) • 2. 000 victims • 2008: “international year of Planet Earth”, Vajont declared “avoidable disaster” failure by engineers and geologists, who didn’t understand what they were doing… • Trials ended 10 years later, without serious consequences *Rommel
• hydroelectric plant, aim: energy for Venice and Northeastern Italy • Dam: 115 million m 3 water of Piave river • Landslide: 270 million m 3 terrain (Mt Toc) • 5 villages destroyed (Longarone* +) • 2. 000 victims • 2008: “international year of Planet Earth”, Vajont declared “avoidable disaster” failure by engineers and geologists, who didn’t understand what they were doing… • Trials ended 10 years later, without serious consequences *Rommel
 Lessons (not) learned: • Gaius Valerius Catullus (1 st century b. C), born in Verona, describes similar events in the same valley • Crisis prevention. Don’t underestimate historical events (landslides in the same area in 1347, 1737, 1748, 1814, 1868, 1908, 1925, 1960)
Lessons (not) learned: • Gaius Valerius Catullus (1 st century b. C), born in Verona, describes similar events in the same valley • Crisis prevention. Don’t underestimate historical events (landslides in the same area in 1347, 1737, 1748, 1814, 1868, 1908, 1925, 1960)
 2002
2002
 Historical framework: • 1 year after 911 and GWOT • USA activates Guantanamo prison • Netherlands: Pim Fortuyn killed, trial against Milosevic begins • Yugoslav Federation becomes Serbia and Montenegro • NATO-Russia Council established • Turkey abolishes death penalty • 1 year before 2 nd war in Iraq
Historical framework: • 1 year after 911 and GWOT • USA activates Guantanamo prison • Netherlands: Pim Fortuyn killed, trial against Milosevic begins • Yugoslav Federation becomes Serbia and Montenegro • NATO-Russia Council established • Turkey abolishes death penalty • 1 year before 2 nd war in Iraq
 Central Europe, 2002
Central Europe, 2002
 August 2002
August 2002
 “Political” Crisis Management: • Flood just before elections in Germany • Opinion polls: Chancellor Schroeder losing, Mr. Stoiber winning • Ace: picture of Mr. Schroeder in the mud • Victory of SPD • 2003: GE (+ FR) vs USA, UK about Iraq
“Political” Crisis Management: • Flood just before elections in Germany • Opinion polls: Chancellor Schroeder losing, Mr. Stoiber winning • Ace: picture of Mr. Schroeder in the mud • Victory of SPD • 2003: GE (+ FR) vs USA, UK about Iraq
 Lessons Learned: • European Commission engagement • Sinergy between National States and EU • European Civil Protection still missing (14 years • • • after the Italian proposal) Public disasters influence elections Without this flood: Chancellor Stoiber, GE (and FR) supporting campaign in Iraq Public disasters influence also international relations, alliances, coalitions, Geopolitics
Lessons Learned: • European Commission engagement • Sinergy between National States and EU • European Civil Protection still missing (14 years • • • after the Italian proposal) Public disasters influence elections Without this flood: Chancellor Stoiber, GE (and FR) supporting campaign in Iraq Public disasters influence also international relations, alliances, coalitions, Geopolitics
 2004
2004
 Historical framework: • 1 February: Saudi Arabia: 250 pilgrims dye at Mecca • Asia: chicken flu spreads • 11 March: terrorist attacks in Spain • Cyprus: failure of referendum about reunification • April: Iraq, Abu-Ghraib abuses • 1 May: EU incorporates 10 new members
Historical framework: • 1 February: Saudi Arabia: 250 pilgrims dye at Mecca • Asia: chicken flu spreads • 11 March: terrorist attacks in Spain • Cyprus: failure of referendum about reunification • April: Iraq, Abu-Ghraib abuses • 1 May: EU incorporates 10 new members
 Tsunami, 26 December 2004 energy of 23. 000 Hiroshima-type atomic bombs
Tsunami, 26 December 2004 energy of 23. 000 Hiroshima-type atomic bombs

 • 230. 000 victims (incl. hundreds in Somalia, 1 in Kenya!) • Nations affected: Bangladesh, Burma, India, Indonesia, Kenya, Tanzania, Maldives, Madagascar, Somalia, South Africa, Sri-Lanka, Thailand
• 230. 000 victims (incl. hundreds in Somalia, 1 in Kenya!) • Nations affected: Bangladesh, Burma, India, Indonesia, Kenya, Tanzania, Maldives, Madagascar, Somalia, South Africa, Sri-Lanka, Thailand

 • 230. 000 victims (hundreds in Somalia, 1 in Kenya!) • Nations affected: Bangladesh, Burma, India, Indonesia, Kenya, Maldives, Somalia, Sri-Lanka, Thailand • Damages: 2 billion USD • Danger: epidemic diseases
• 230. 000 victims (hundreds in Somalia, 1 in Kenya!) • Nations affected: Bangladesh, Burma, India, Indonesia, Kenya, Maldives, Somalia, Sri-Lanka, Thailand • Damages: 2 billion USD • Danger: epidemic diseases

 tsunami
tsunami
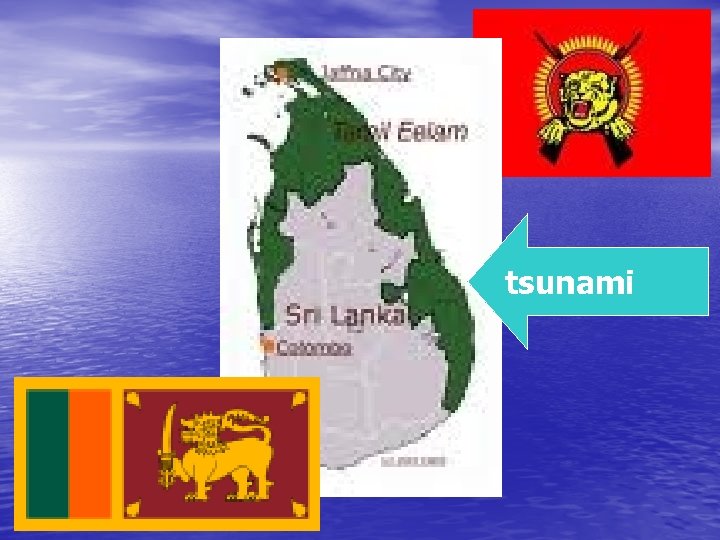
 Influence on Sri Lanka civil war • Tsunami hits mostly Tamil-controlled zones • 27. 008 victims in Government-controlled areas, • • • 16. 656 victims + 18. 481 missing in Tamilcontrolled areas. 16. 236 wounded, 578. 224 displaced people. Foreigners: 107 victims 4 years after: May 2009, Tamil Tigers defeated (by Government or tsunami? )
Influence on Sri Lanka civil war • Tsunami hits mostly Tamil-controlled zones • 27. 008 victims in Government-controlled areas, • • • 16. 656 victims + 18. 481 missing in Tamilcontrolled areas. 16. 236 wounded, 578. 224 displaced people. Foreigners: 107 victims 4 years after: May 2009, Tamil Tigers defeated (by Government or tsunami? )
 Lessons Learned: • Importance of communications (lack of early • • • warning systems) Natural disasters can influence the final result of wars (example: Waterloo) International aid benefits Governments, not oppositions (example: Sri Lanka) International aid used not only for humanitarian purposes (Sri Lanka, Marshall Plan)
Lessons Learned: • Importance of communications (lack of early • • • warning systems) Natural disasters can influence the final result of wars (example: Waterloo) International aid benefits Governments, not oppositions (example: Sri Lanka) International aid used not only for humanitarian purposes (Sri Lanka, Marshall Plan)

 ERP (Marshall Plan) • No Eastern Europe • It supported mostly the winners • It also supported who didn’t fight • It supported who didn’t receive damages • Did it support FR, UK nuclear plans? (FR 1952, UK 1960)
ERP (Marshall Plan) • No Eastern Europe • It supported mostly the winners • It also supported who didn’t fight • It supported who didn’t receive damages • Did it support FR, UK nuclear plans? (FR 1952, UK 1960)
 2005
2005
 Historical framework • 2 nd Iraq war ongoing (since 2003) • Italy: voluntary service substitutes compulsory • • • military service Viktor Yushenko President of Ukraine Kyoto Protocol in effect (141 countries, no USA) 28 March: earthquake off Sumatra 23 July: AQ attacks Sharm El-Sheikh, 90 victims Piracy in Somalia/Gulf of Aden erupts
Historical framework • 2 nd Iraq war ongoing (since 2003) • Italy: voluntary service substitutes compulsory • • • military service Viktor Yushenko President of Ukraine Kyoto Protocol in effect (141 countries, no USA) 28 March: earthquake off Sumatra 23 July: AQ attacks Sharm El-Sheikh, 90 victims Piracy in Somalia/Gulf of Aden erupts
 Katrina hurricane, 2005
Katrina hurricane, 2005
 Katrina hurricane, 2005 Winds: 280 km/h
Katrina hurricane, 2005 Winds: 280 km/h
 Katrina hurricane, 2005 New Orleans: 2 weeks after
Katrina hurricane, 2005 New Orleans: 2 weeks after
 Reasons: -building a big city under the level of sea, between a river and a lake : acceptable 2 -3 centuries ago, -building embankments and pumping water: risky idea in NL, bad idea in hurricane-area, -NASA 2000: “within 100 years, New Orleans will be the new Atlantis”, -2005: funds for the reinforcement of dams: to Iraqi War, -2004: 94 M$ from hurricanes to GWOT, -Nat Guard: 30% personnel, 50% equipment: in Iraq
Reasons: -building a big city under the level of sea, between a river and a lake : acceptable 2 -3 centuries ago, -building embankments and pumping water: risky idea in NL, bad idea in hurricane-area, -NASA 2000: “within 100 years, New Orleans will be the new Atlantis”, -2005: funds for the reinforcement of dams: to Iraqi War, -2004: 94 M$ from hurricanes to GWOT, -Nat Guard: 30% personnel, 50% equipment: in Iraq
 Consequences: -thousands of victims, 1 million homeless, -many oil platforms destroyed, -12 oil refineries out of order, -95% oil and 88% gas produced in the Gulf of Mexico: paralyzed, -energy crisis, -political consequences: USA forced to accept foreign aid, -doubts about Iraqi war, -doubts about US capabilities (war + homeland security? )
Consequences: -thousands of victims, 1 million homeless, -many oil platforms destroyed, -12 oil refineries out of order, -95% oil and 88% gas produced in the Gulf of Mexico: paralyzed, -energy crisis, -political consequences: USA forced to accept foreign aid, -doubts about Iraqi war, -doubts about US capabilities (war + homeland security? )
 A recent example: “Katrina” hurricane Solution: NATO Response Force (again!) Like in Pakistan earthquake
A recent example: “Katrina” hurricane Solution: NATO Response Force (again!) Like in Pakistan earthquake
 NATO Response Force http: //www. nato. int/cps/en/natolive/topics_49755. htm Launched at Prague Summit, 2002 Proposed by Mr. Rumsfeld 21. 000 troops from Army, Navy, Air Force Aim: oblige European Allies to do more
NATO Response Force http: //www. nato. int/cps/en/natolive/topics_49755. htm Launched at Prague Summit, 2002 Proposed by Mr. Rumsfeld 21. 000 troops from Army, Navy, Air Force Aim: oblige European Allies to do more
 Lessons Learned: • NRF established for GWOT, employed twice in 12 • • • years, always for humanitarian reasons NRF: keep it ready Natural disasters influence domestic policy Katrina: political, internal consequences for Bush administration (and re-election) Gulf of Mexico: same problems for Mr. Obama? Natural disasters also influence foreign policy and Geopolitics (Iraq)
Lessons Learned: • NRF established for GWOT, employed twice in 12 • • • years, always for humanitarian reasons NRF: keep it ready Natural disasters influence domestic policy Katrina: political, internal consequences for Bush administration (and re-election) Gulf of Mexico: same problems for Mr. Obama? Natural disasters also influence foreign policy and Geopolitics (Iraq)
 Mediterranean, 2020 (? ) • Is a tsunami possible in the Mediterranean? • Events already occurred: -8. 000 years ago (the biggest ever), -365 b. C: tsunami (origin: south of Creta) destroys the coastal zone of Egypt, -1693: submarine earthquake hits eastern coast of Sicily -1831 -32: Ferdinandea island / Graham
Mediterranean, 2020 (? ) • Is a tsunami possible in the Mediterranean? • Events already occurred: -8. 000 years ago (the biggest ever), -365 b. C: tsunami (origin: south of Creta) destroys the coastal zone of Egypt, -1693: submarine earthquake hits eastern coast of Sicily -1831 -32: Ferdinandea island / Graham
 Ferdinand II Borbone King of Two Sicilies
Ferdinand II Borbone King of Two Sicilies

 Mediterranean, 2020 (? ) • Is a tsunami possible in the Mediterranean? • Events already occurred: -8. 000 years ago (the biggest ever), -365 b. C: tsunami (origin: south of Creta) destroys coasts of Egypt, -1693: submarine earthquake hits east coast of Sicily -1831 -32: Ferdinandea / Graham -1908: Messina earthquake generates a tsunami provoking thousands victims -2002: small tsunami off Stromboli
Mediterranean, 2020 (? ) • Is a tsunami possible in the Mediterranean? • Events already occurred: -8. 000 years ago (the biggest ever), -365 b. C: tsunami (origin: south of Creta) destroys coasts of Egypt, -1693: submarine earthquake hits east coast of Sicily -1831 -32: Ferdinandea / Graham -1908: Messina earthquake generates a tsunami provoking thousands victims -2002: small tsunami off Stromboli
 Marsili, Magnaghi, Vavilov, Cassini, Secchi, Issel, Poseidone, Marchi, Flavio Gioia, Palinuro, … • www. naturamediterraneo. com Flavio Gioia Vavilov Marsili
Marsili, Magnaghi, Vavilov, Cassini, Secchi, Issel, Poseidone, Marchi, Flavio Gioia, Palinuro, … • www. naturamediterraneo. com Flavio Gioia Vavilov Marsili
 Lessons learned? ? ? Mt. Epomeo, Ischia: a volcano Last eruption: AD 1302
Lessons learned? ? ? Mt. Epomeo, Ischia: a volcano Last eruption: AD 1302
 ALARMISM? SUPERFICIALITY?
ALARMISM? SUPERFICIALITY?
 Crises produced by Volcanic Eruptions 6 case studies: -Vesuvius, … -Tambora, 1815 -Krakatoa, 1883 -Pinatubo, 1991 -Anatahan, 2005 -Eyjafjallayokull, 2010
Crises produced by Volcanic Eruptions 6 case studies: -Vesuvius, … -Tambora, 1815 -Krakatoa, 1883 -Pinatubo, 1991 -Anatahan, 2005 -Eyjafjallayokull, 2010
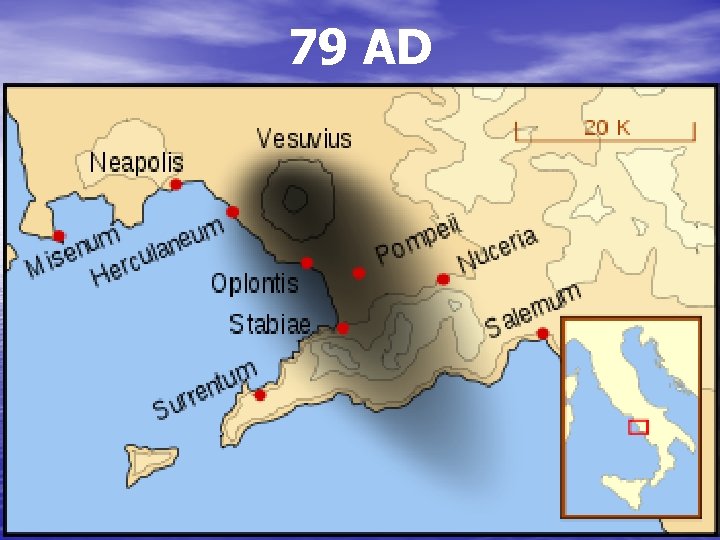 79 AD
79 AD
 1631
1631
 1760
1760
 1794
1794
 1872
1872
![March 1944 [Picture taken by US troops] March 1944 [Picture taken by US troops]](https://present5.com/presentation/654b41d13d7cc89102a613e860833c27/image-58.jpg) March 1944 [Picture taken by US troops]
March 1944 [Picture taken by US troops]
 • “These Italians show an apparent indifference, very remarkable, towards the disaster. I expected demonstrations of panic, desperate women, crazy men and children. Nothing at all. People gathered in groups, looking at the slow sacrifice of the village, as it was a casual fire. The doctor of the village interrupted saving some goods of him and showed me a good observation point. There were also some signs of humor” (Manchester Guardian’s envoy, 22 March, 1944)
• “These Italians show an apparent indifference, very remarkable, towards the disaster. I expected demonstrations of panic, desperate women, crazy men and children. Nothing at all. People gathered in groups, looking at the slow sacrifice of the village, as it was a casual fire. The doctor of the village interrupted saving some goods of him and showed me a good observation point. There were also some signs of humor” (Manchester Guardian’s envoy, 22 March, 1944)
 Lessons NOT learned:
Lessons NOT learned:
 Lessons NOT learned:
Lessons NOT learned:

 1815
1815
 Historical framework: -26 February: Napoleon escapes from Elba, -April: eruption of Tambora volcano, Indonesia, -9 June: end of Vienna Congress (started in Nov 1814), -18 June: Napoleon defeated at Waterloo, -26 September: Austria, Russia, Prussia: Holy Alliance,
Historical framework: -26 February: Napoleon escapes from Elba, -April: eruption of Tambora volcano, Indonesia, -9 June: end of Vienna Congress (started in Nov 1814), -18 June: Napoleon defeated at Waterloo, -26 September: Austria, Russia, Prussia: Holy Alliance,
 Tambora, 1815 -Sumbawa island, 1. 000 km far from Jakarta, -10. 000 victims immediately, 85. 000 later (hunger, disease), -before explosion: 4. 000 mt, after: 1. 000, -heavy ash: 2, 5 million km 2 -light ash: huge cloud, athmosphere, stratosphere, up to Europe, America for 2 years -1815: “year without summer” -climatic changes, rainshowers and thunderstorms in Europe and America, famine in Ireland, emigration,
Tambora, 1815 -Sumbawa island, 1. 000 km far from Jakarta, -10. 000 victims immediately, 85. 000 later (hunger, disease), -before explosion: 4. 000 mt, after: 1. 000, -heavy ash: 2, 5 million km 2 -light ash: huge cloud, athmosphere, stratosphere, up to Europe, America for 2 years -1815: “year without summer” -climatic changes, rainshowers and thunderstorms in Europe and America, famine in Ireland, emigration,
 INTERVENTION IN DISASTER RELIEF napoleone -18 June: Napoleon unable to employ his Cavalry and Artillery, Major General -tactical result: Napoleon defeated (by Anglo-Prussians Giovanni MARIZZA or by a volcano? ) TURIN, April 18 th, 2008 -strategic result: new world order
INTERVENTION IN DISASTER RELIEF napoleone -18 June: Napoleon unable to employ his Cavalry and Artillery, Major General -tactical result: Napoleon defeated (by Anglo-Prussians Giovanni MARIZZA or by a volcano? ) TURIN, April 18 th, 2008 -strategic result: new world order
 Lessons Learned: -serious consequences, even on the other side of the world, -volcanic eruptions can influence Geopolitics
Lessons Learned: -serious consequences, even on the other side of the world, -volcanic eruptions can influence Geopolitics
 1883
1883
 Historical framework: -24 May: New York, Brooklin Bridge inauguration, -28 July: earthquake in Ischia: 2. 333 victims, -29 July: Benito Mussolini is born, -30 October: treaty between Austria-Hungary and Romania to counter Russian influence in the Balkans,
Historical framework: -24 May: New York, Brooklin Bridge inauguration, -28 July: earthquake in Ischia: 2. 333 victims, -29 July: Benito Mussolini is born, -30 October: treaty between Austria-Hungary and Romania to counter Russian influence in the Balkans,
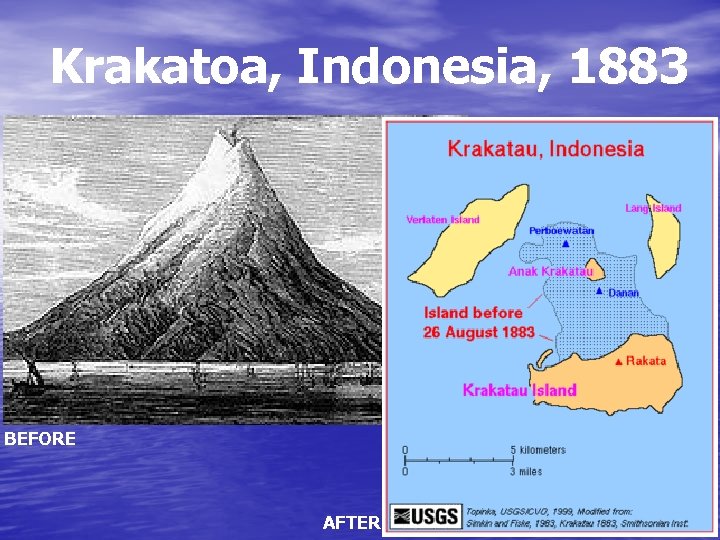 Krakatoa, Indonesia, 1883 BEFORE AFTER
Krakatoa, Indonesia, 1883 BEFORE AFTER
 • The biggest ever eruption in the world, • Biggest ever noise in the history (heard at 5. 000 km), • Power: 200 Megatons, • Air waves: 7 times around the world, • Spectacular sunsets everywhere for years Munch: “Shrijk” (1893)
• The biggest ever eruption in the world, • Biggest ever noise in the history (heard at 5. 000 km), • Power: 200 Megatons, • Air waves: 7 times around the world, • Spectacular sunsets everywhere for years Munch: “Shrijk” (1893)
 Lessons Learned: -still active (last eruption: 1994), -keep distant (not less than 3 km), -biological aspect: life disappeared, after 50 years: 270 new species, -according to experts: a new destructive explosion in the near future (like in 1883, but with a much higher density of population)
Lessons Learned: -still active (last eruption: 1994), -keep distant (not less than 3 km), -biological aspect: life disappeared, after 50 years: 270 new species, -according to experts: a new destructive explosion in the near future (like in 1883, but with a much higher density of population)
 1991
1991
 Historical framework: -first call by a GSM cellphone, -9 January: Soviet troops occupy Vilnius trying to stop the independence of Lithuania, -11 January: US Congress authorizes President Bush to attack Iraq, -Gulf war, Iraq launches 45 SCUD missiles on Israel, -1 February: South Africa, end of apartheid, -9 April: Georgia declares the independence, -21 May: India, Rajiv Gandhi killed, -25 June: Croatia, Slovenia independent, -6 August: www, -19 August: coup in USSR, solved by Eltsin, -26 December: URSS disbanded
Historical framework: -first call by a GSM cellphone, -9 January: Soviet troops occupy Vilnius trying to stop the independence of Lithuania, -11 January: US Congress authorizes President Bush to attack Iraq, -Gulf war, Iraq launches 45 SCUD missiles on Israel, -1 February: South Africa, end of apartheid, -9 April: Georgia declares the independence, -21 May: India, Rajiv Gandhi killed, -25 June: Croatia, Slovenia independent, -6 August: www, -19 August: coup in USSR, solved by Eltsin, -26 December: URSS disbanded
 Pinatubo, Philippines, 1991 -June: eruption, 1. 000 dead, 1 million homeless, -US military bases: Subic Bay (75 km from the volcano) and Clark (25 km), -everything transferred to USA, Guam, Okinawa, Hawaii, -Clark Mil Base (633 km 2, built in 1903 after the war with Spain) destroyed, -Subic Bay Naval Base to the local Government, -huge ash cloud up to Russia and North America, -in other times: no operations during WWII and Vietnam conflict, -in August 1945: no “Enola Gay” to Hiroshima
Pinatubo, Philippines, 1991 -June: eruption, 1. 000 dead, 1 million homeless, -US military bases: Subic Bay (75 km from the volcano) and Clark (25 km), -everything transferred to USA, Guam, Okinawa, Hawaii, -Clark Mil Base (633 km 2, built in 1903 after the war with Spain) destroyed, -Subic Bay Naval Base to the local Government, -huge ash cloud up to Russia and North America, -in other times: no operations during WWII and Vietnam conflict, -in August 1945: no “Enola Gay” to Hiroshima
 Lessons Learned: -volcanic eruptions influence military operations (projection of power), -volcanic eruptions can change the History,
Lessons Learned: -volcanic eruptions influence military operations (projection of power), -volcanic eruptions can change the History,
 2005
2005
 Historical framework • 2 nd Iraq war ongoing (since 2003) • 10 January: Abu Mazen replaces Arafat • Italy: voluntary service substitutes compulsory • • military service Karol Wojtyla dies, Josef Ratzinger elected Viktor Yushenko President of Ukraine Kyoto Protocol in effect (141 countries, no USA) 28 March: earthquake off Sumatra 7 July: terroristic attacks in London, 23 July: AQ attacks Sharm El-Sheikh, 90 victims Piracy in Somalia/Gulf of Aden erupts
Historical framework • 2 nd Iraq war ongoing (since 2003) • 10 January: Abu Mazen replaces Arafat • Italy: voluntary service substitutes compulsory • • military service Karol Wojtyla dies, Josef Ratzinger elected Viktor Yushenko President of Ukraine Kyoto Protocol in effect (141 countries, no USA) 28 March: earthquake off Sumatra 7 July: terroristic attacks in London, 23 July: AQ attacks Sharm El-Sheikh, 90 victims Piracy in Somalia/Gulf of Aden erupts
 Anatahan, Pacific, 2005 -200 miles north of Guam, -ash cloud: temporary closure of Andersen Base, Guam, -strategic importance of Guam
Anatahan, Pacific, 2005 -200 miles north of Guam, -ash cloud: temporary closure of Andersen Base, Guam, -strategic importance of Guam
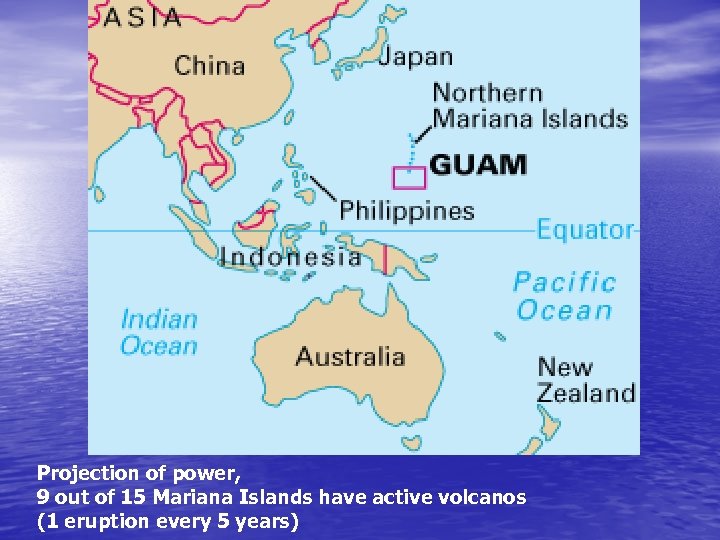 Projection of power, 9 out of 15 Mariana Islands have active volcanos (1 eruption every 5 years)
Projection of power, 9 out of 15 Mariana Islands have active volcanos (1 eruption every 5 years)
 Lessons Learned: -Andersen Air Base (Guam) in danger like Clark, -USA: “Volcano Hazards Program” (USGS and Southern Methodist University), a 250. 000 USD project monitorizing volcanic activities in SE Asia, -creation of an Early Warning System
Lessons Learned: -Andersen Air Base (Guam) in danger like Clark, -USA: “Volcano Hazards Program” (USGS and Southern Methodist University), a 250. 000 USD project monitorizing volcanic activities in SE Asia, -creation of an Early Warning System
 Eyjafjallayokull, 2010
Eyjafjallayokull, 2010

 1940 Battle of England
1940 Battle of England

 1944, Montecassino
1944, Montecassino
 1945 Dresda
1945 Dresda

 1948 -49 Berlin Air Bridge
1948 -49 Berlin Air Bridge


 Lessons Learned: - volcanic eruptions can influence military operations -… change the outcome of wars, -… endanger civil aviation, -… stop air traffic
Lessons Learned: - volcanic eruptions can influence military operations -… change the outcome of wars, -… endanger civil aviation, -… stop air traffic

 Grimsvotn, Iceland May 2011
Grimsvotn, Iceland May 2011
 Suggestions for Thesis: • How Crises influence international politics: the case of volcanic eruptions • What if? The case of a possible tsunami in the Mediterranean
Suggestions for Thesis: • How Crises influence international politics: the case of volcanic eruptions • What if? The case of a possible tsunami in the Mediterranean
 Crisis Management and Prevention (Management of Crises in case of Floods and Volcanic Eruptions) Giovanni Marizza gianni. marizza@yahoo. it 14 May 2014, 15, 00 – 17, 00
Crisis Management and Prevention (Management of Crises in case of Floods and Volcanic Eruptions) Giovanni Marizza gianni. marizza@yahoo. it 14 May 2014, 15, 00 – 17, 00


