c1d55f2d4776e84ecfd9584f84622dfb.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 29

Crew Resource Management © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Introduction § § § Name Position History/Career Experience of CRM A/C Type & Routes Interests & Activities © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Domestic Arrangements § § § § Timings Food & Refreshments Toilets Smoking Policy Fire or Emergency – Exits & Assembly Point Mobile Phones Language Course pack © Global Air Training Limited 2010

CRM ? ? ? § What does CRM stand for? § Define CRM – What does the term mean to you? § The origin of CRM © Global Air Training Limited 2010

CRM Objective To enhance the communication and management skills of the flight crew members by the effective utilisation of all available resources to achieve a safe and efficient operation TGL 44 © Global Air Training Limited 2010

In the days of early technology, human error was the cause of many safety related incidents © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Human errors continued to repeat even with advanced technology © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Lessons Learnt § Research carried out by: § NASA § Leading Airline Corporations § International Civil Aviation Authorities and Accident Investigation Units § Universities Worldwide § Human performance cited as the causal factor in 3 out of 4 accidents § Study & Application of an error avoidance programme called CRM has now become mandatory for both civil and military aircraft operations © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Error Management Strategies § Understanding the nature and extent of error or risk § Changing the conditions that induce the error § Determining the behaviours that prevent or mitigate error © Global Air Training Limited 2010 Who is at risk?

Requirements & Blocks to CRM Success § Requirements for CRM Success § Support from Top & Middle Management § CRM Instructors who have the core competencies of good CRM & role model CRM in their words & actions § Dedicated Team § Blocks to CRM Success § Resistance to Change § Fear of Failure § CRM delivery methodology © Global Air Training Limited 2010
H S L L © Global Air Training Limited 2010 E

Liveware Variations in Performance & limitations § § § L Physical size & shape Physical needs (sustenance, sleep etc) Input/Output Characteristics Information processing Environmental tolerances (temp, pressure, humidity, enclosed space, stress & boredom) © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Liveware – Hardware § Ergonomics § Displays § Instrument interpretation § Scanning & detection § Work space § Controls with proper movement, coding and location © Global Air Training Limited 2010 H L

Liveware – Software S § § § L Non-physical aspects of systems Symbology and computer programmes Procedures (SOP’s, normal, abnormal or emergency drills) Rules and regulations i. e. company and authority Training manuals & document design i. e. content and layout © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Liveware – Environment L E § Disturbed biological rhythms - Sleep disturbance and deprivation / transmeridian travel § Pressurised cabin § Noise & vibration § Weather conditions © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Liveware – Liveware § Leadership, cooperation, teamwork, personality interactions § Staff/management relationships, corporate culture & climate, company operating pressures © Global Air Training Limited 2010 L L
H S L L © Global Air Training Limited 2010 E
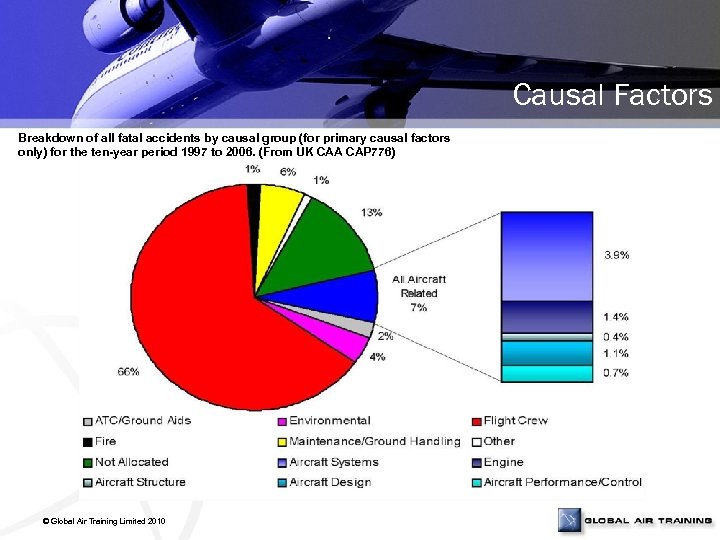
Causal Factors Breakdown of all fatal accidents by causal group (for primary causal factors only) for the ten-year period 1997 to 2006. (From UK CAA CAP 776) © Global Air Training Limited 2010

© Global Air Training Limited 2010
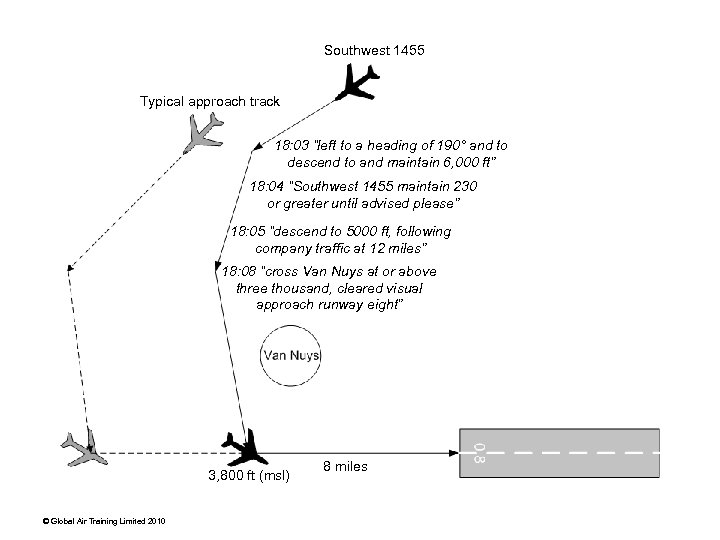
Southwest 1455 Typical approach track 18: 03 “left to a heading of 190° and to descend to and maintain 6, 000 ft” 18: 04 “Southwest 1455 maintain 230 or greater until advised please” 18: 05 “descend to 5000 ft, following company traffic at 12 miles” 18: 08 “cross Van Nuys at or above three thousand, cleared visual approach runway eight” 3, 800 ft (msl) © Global Air Training Limited 2010 8 miles
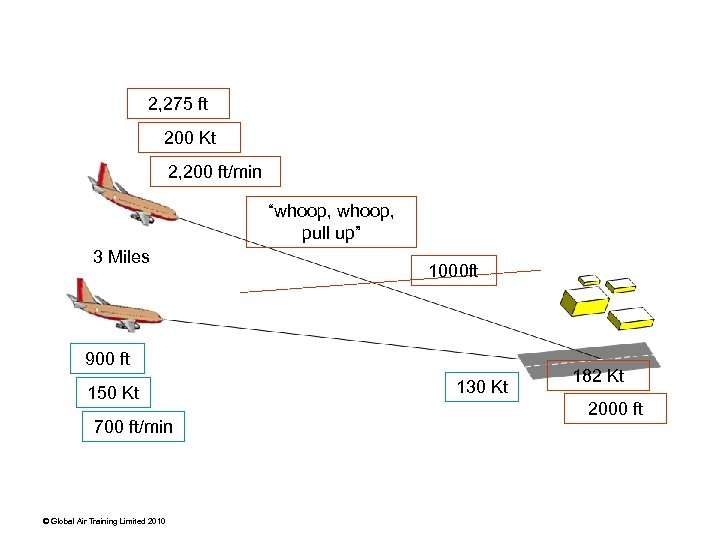
2, 275 ft 200 Kt 2, 200 ft/min “whoop, pull up” 3 Miles 1000 ft 900 ft 150 Kt 700 ft/min © Global Air Training Limited 2010 130 Kt 182 Kt 2000 ft
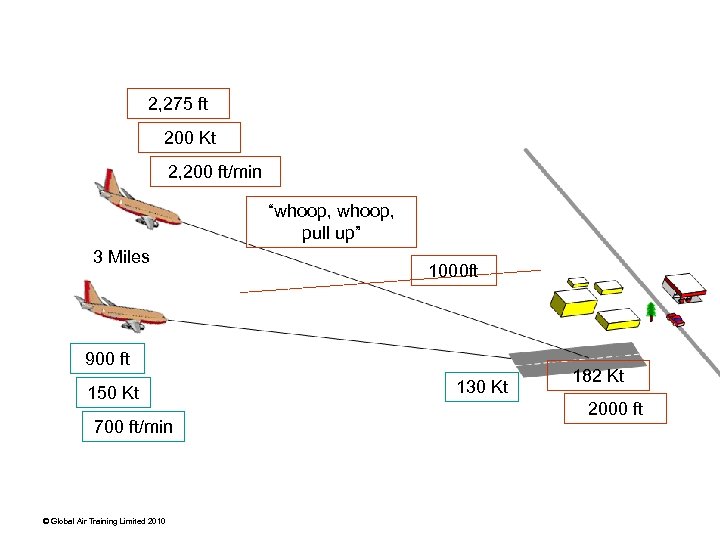
2, 275 ft 200 Kt 2, 200 ft/min “whoop, pull up” 3 Miles 1000 ft 900 ft 150 Kt 700 ft/min © Global Air Training Limited 2010 130 Kt 182 Kt 2000 ft
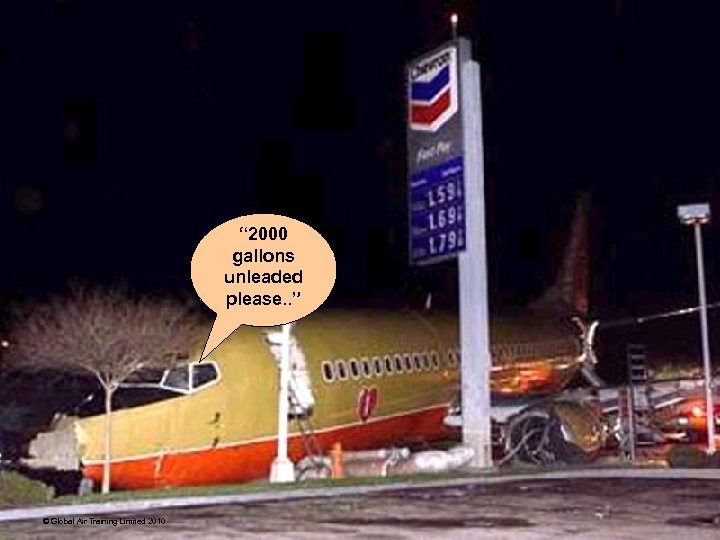

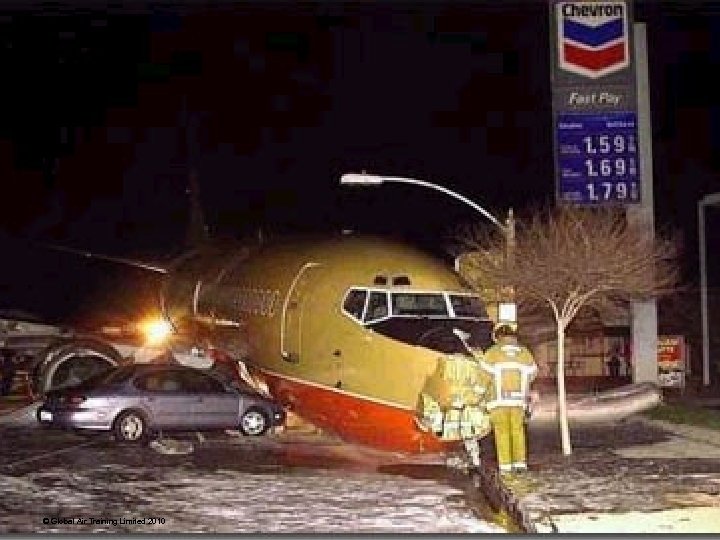
“ 2000 gallons unleaded please. . ” © Global Air Training Limited 2010

© Global Air Training Limited 2010

Crew § Captain § 11, 000 Hours § 9, 870 on 737 for South. West § congenial, mild-mannered, and someone who got along well with everyone. § First Officer § § 5, 000 hours 2, 500 hours 737 for South. West 12 years USAF F-15 above-average, good skills, good judgment © Global Air Training Limited 2010

What went wrong § The Captain failed to “Go-around” § The First Officer failed to perform his duties regarding: § calling deviations from approach normal criteria § check lists © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Why? § They were two hours behind schedule § pressure to avoid further delay caused by going around. § Peer pressure – All other crews on the radio frequency would be aware of their ‘failing’ to make the approach. § this was home base § the aircraft ahead was also Southwest § FO pressure not to challenge his superior § Risk shift § FO failed under stress to complete simple tasks § Both failed under stress to respond to the continuous GPWS warnings © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Lessons § The crew were § Skilled § Experienced § Current § They succumbed to § Peer Pressure § Operational Pressures § Under stress § Inability to perform simple tasks § Judgement was compromised © Global Air Training Limited 2010

Primary Causes of Fatal Accidents § Inadequate Communication § Deviation from SOP’s § Maintenance Error § Poor Response to, or no GPWS © Global Air Training Limited 2010
c1d55f2d4776e84ecfd9584f84622dfb.ppt