4e343b706297411bfc07b57ffb805028.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 32

Creating Value Through External Collaboration
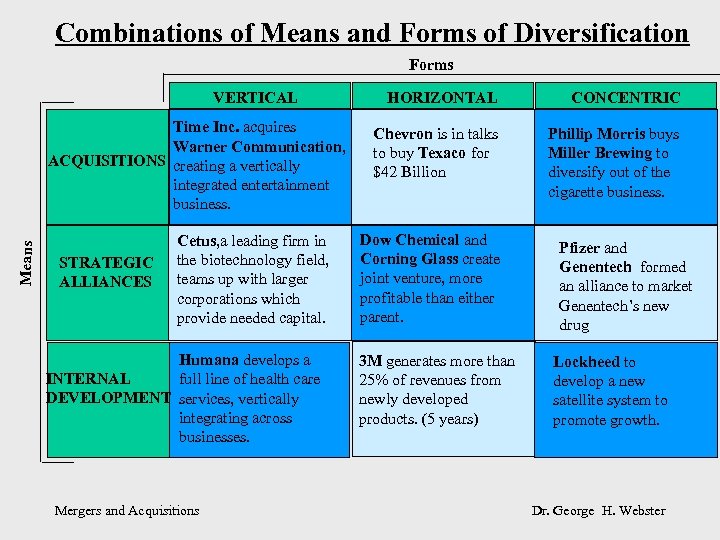
Combinations of Means and Forms of Diversification Forms VERTICAL Means Time Inc. acquires Warner Communication, ACQUISITIONS creating a vertically integrated entertainment business. STRATEGIC ALLIANCES Cetus, a leading firm in the biotechnology field, teams up with larger corporations which provide needed capital. Humana develops a INTERNAL full line of health care DEVELOPMENT services, vertically integrating across businesses. Mergers and Acquisitions HORIZONTAL CONCENTRIC Chevron is in talks to buy Texaco for $42 Billion Phillip Morris buys Miller Brewing to diversify out of the cigarette business. Dow Chemical and Corning Glass create joint venture, more profitable than either parent. 3 M generates more than 25% of revenues from newly developed products. (5 years) Pfizer and Genentech formed an alliance to market Genentech’s new drug Lockheed to develop a new satellite system to promote growth. Dr. George H. Webster

Mergers and Acquisitions Dr. George H. Webster

Financial Transactions • Operating changes • New controlling shareholder • New board of directors • Change in business strategy Mergers and Acquisitions Dr. George H. Webster

Who Buys? • An operating company • A group of managers • A group of financial investors Mergers and Acquisitions Dr. George H. Webster

Objective To increase the per-share value of the acquirer • Long term • Discounted cash flows Mergers and Acquisitions Dr. George H. Webster

Merger and Acquisition Types • Horizontal • Vertical • Congeneric • Conglomerate Mergers and Acquisitions Dr. George H. Webster

Valuation of an Acquisition Candidate Mergers and Acquisitions Dr. George H. Webster

Value to Parties to the Transaction • Value to Buyer – Discounted present value of cash flows – Value represents maximum price • Value to Seller – Similar discounted cash flow analysis – Value may be lower for seller Mergers and Acquisitions Dr. George H. Webster
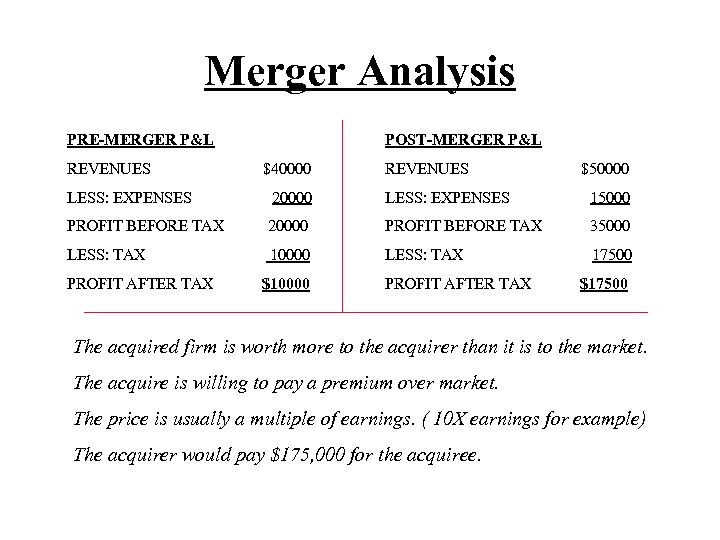
Merger Analysis PRE-MERGER P&L REVENUES POST-MERGER P&L $40000 REVENUES $50000 LESS: EXPENSES 20000 LESS: EXPENSES 15000 PROFIT BEFORE TAX 20000 PROFIT BEFORE TAX 35000 LESS: TAX 10000 LESS: TAX 17500 PROFIT AFTER TAX $10000 PROFIT AFTER TAX $17500 The acquired firm is worth more to the acquirer than it is to the market. The acquire is willing to pay a premium over market. The price is usually a multiple of earnings. ( 10 X earnings for example) The acquirer would pay $175, 000 for the acquiree.

First Union- Core. States • Takeover was a $19. 7 Billion deal • Core. States 1997 net income - $830 million • First Union forecast $258 Million savings in after tax expenses from synergy • In 1998 FUC missed goal by $50 Million • Payback period is about 18 years- Does this make sense? • Why else spend that much money? Expand into the Northeast Capture Core. States investment banking business Position itself to merge with another large bank (Chase Manhattan)

The Ford-Volvo Merger • Bought Volvo’s Car Business for $6 billion • Worldwide sales now 7. 2 million units • Ford will achieve three goals; boost market share, fill a hole in the lineup, gain momentum in battle with G. M. • Volvo forecasts 200, 000 units sold in U. S. by 2001 • Ford will now compete in the $30, 000 -$40, 000 range • Analysts see only six major players by 2010

CLASS EXERCISE Time Warner is joining forces with Advance Publications to create a new TV network for women. France’s Aerosatiale and Lockheed are in talks to develop military surveillance and refueling aircraft. Pharmacia Upjohn agreed to buy Sugen, a California biotech firm for $728 Million. Seagram’s Universal Music is planning to begin selling digital music on the internet Boeing will develop its own high capacity satellite system and services. Georgia-Pacific acquired Unisource, a full line paper distributor, for $1. 2 Billion Wal-Mart made a cash offer to buy a British Supermarket chain to position themselves in Europe Thomson Multimedia is expected to unveil a portable device that plays music files from the internet. Lockheed, TRW, and Telecom Italia will begin to develop their $3. 5 Billion Astrolink Global satellite system.
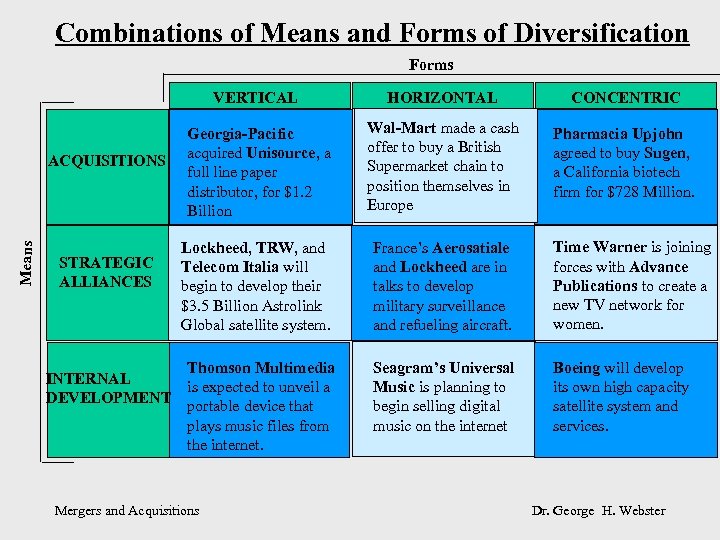
Combinations of Means and Forms of Diversification Forms VERTICAL HORIZONTAL CONCENTRIC Georgia-Pacific acquired Unisource, a full line paper distributor, for $1. 2 Billion Wal-Mart made a cash offer to buy a British Supermarket chain to position themselves in Europe Pharmacia Upjohn agreed to buy Sugen, a California biotech firm for $728 Million. Lockheed, TRW, and Telecom Italia will begin to develop their $3. 5 Billion Astrolink Global satellite system. France’s Aerosatiale and Lockheed are in talks to develop military surveillance and refueling aircraft. Time Warner is joining forces with Advance Publications to create a new TV network for women. Thomson Multimedia INTERNAL is expected to unveil a DEVELOPMENT portable device that plays music files from the internet. Seagram’s Universal Music is planning to begin selling digital music on the internet Boeing will develop its own high capacity satellite system and services. Means ACQUISITIONS STRATEGIC ALLIANCES Mergers and Acquisitions Dr. George H. Webster

STRATEGY IN ACTION- AMETEK Ametek Inc, Paoli PA, makes devices that measure physical properties- temperature and pressure gauges, motors, sensors, and tank gauges, for example. “The objective is to double the size of the company in five years. ” The Three Part Strategy Acquisitions- Adding to existing businesses directly or adjacent product lines to existing businesses. (Fastest method of growth) Internal Development- create more products through R&D. Penetrate New Markets- The company will concentrate on increasing international sales.

Strategic Alliances An Alternative to Mergers and Acquisitions Strategic Allinaces Dr. George H. Webster

Creating Value Through Strategic Alliances • Mergers and alliances are not substitutes for each other • For each situation there is a best structure Strategic Alliances Dr. George H. Webster

Global Logic of Strategic Alliances • National identity of products has disappeared - markets not defined by geographic borders • Dispersion of technology • The importance of fixed costs Strategic Alliances Dr. George H. Webster
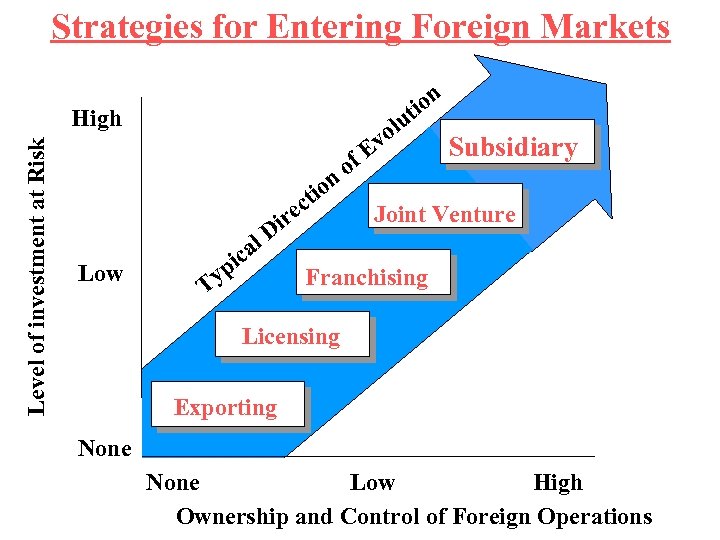
Strategies for Entering Foreign Markets ion t lu o Level of investment at Risk High ion ct Low ire l. D ica yp T Ev f o Subsidiary Joint Venture Franchising Licensing Exporting None Low High Ownership and Control of Foreign Operations
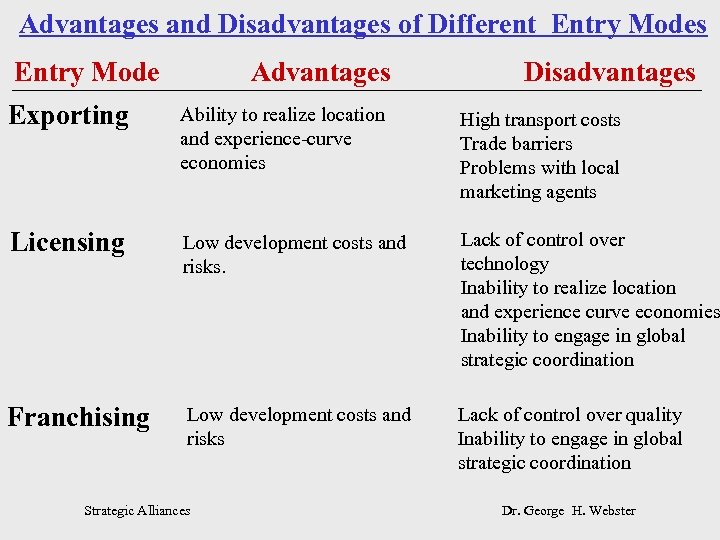
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Entry Modes Entry Mode Advantages Disadvantages Exporting Ability to realize location and experience-curve economies High transport costs Trade barriers Problems with local marketing agents Licensing Low development costs and risks. Lack of control over technology Inability to realize location and experience curve economies Inability to engage in global strategic coordination Franchising Low development costs and risks Lack of control over quality Inability to engage in global strategic coordination Strategic Alliances Dr. George H. Webster
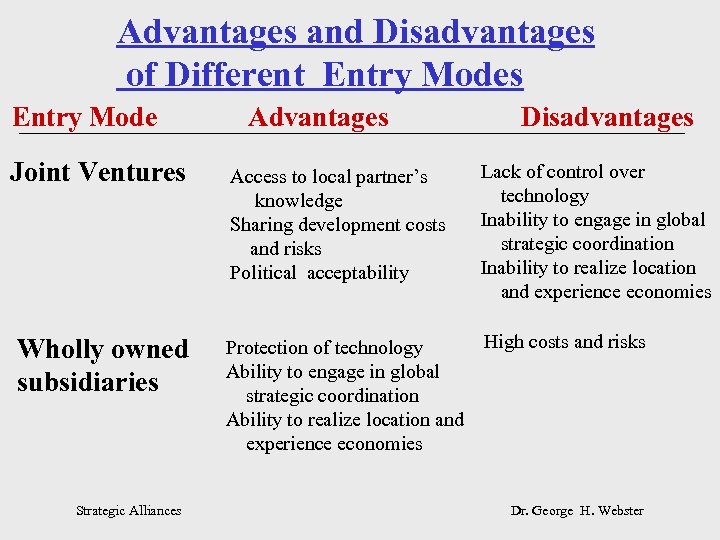
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Entry Modes Entry Mode Joint Ventures Wholly owned subsidiaries Strategic Alliances Advantages Access to local partner’s knowledge Sharing development costs and risks Political acceptability Disadvantages Lack of control over technology Inability to engage in global strategic coordination Inability to realize location and experience economies High costs and risks Protection of technology Ability to engage in global strategic coordination Ability to realize location and experience economies Dr. George H. Webster

Creating Value Through Strategic Alliances • The potential for merger synergy is greatest where both partners have significant overlapping geographic positions. Important sources of synergy are: – Consolidation on a national basis – Improving skills transfers across borders • By contrast strong overlapping geographic markets frequently suggest trouble for strategic alliances

Creating Value Through Strategic Alliances • Keys to success in alliances are complementary activities and well-matched functional strengths • Keys to success in M. &A. are often overlapping activities and skills • In cross-border M. &A. much of the value is based on sharing skills, products and customers across national borders Strategic Alliances Dr. George H. Webster

Advantages of Global Strategic Alliances • Facilitates entry into a foreign market • Share costs and risks associated with development of new products or processes • Bring together complementary skills and assets that neither company could easily develop on its own • Might help the company set technological standards for its industry

Disadvantages of Global Strategic Alliances • Give competitors a low cost route to gain new technology and market access Strategic Alliances Dr. George H. Webster
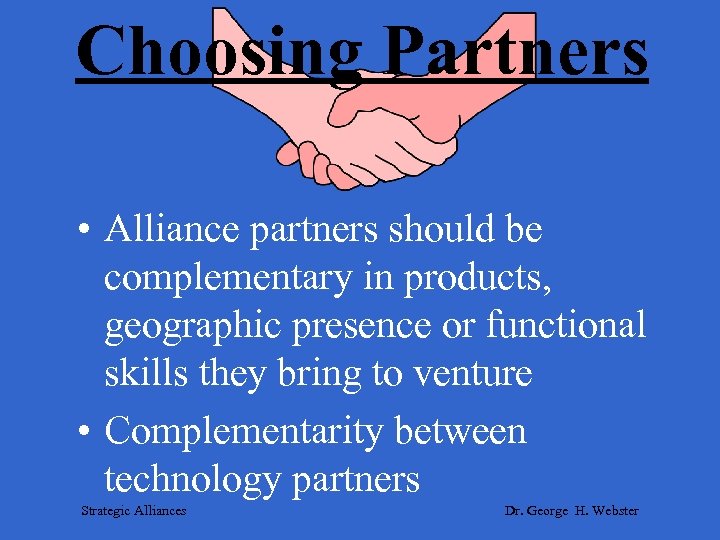
Choosing Partners • Alliance partners should be complementary in products, geographic presence or functional skills they bring to venture • Complementarity between technology partners Strategic Alliances Dr. George H. Webster
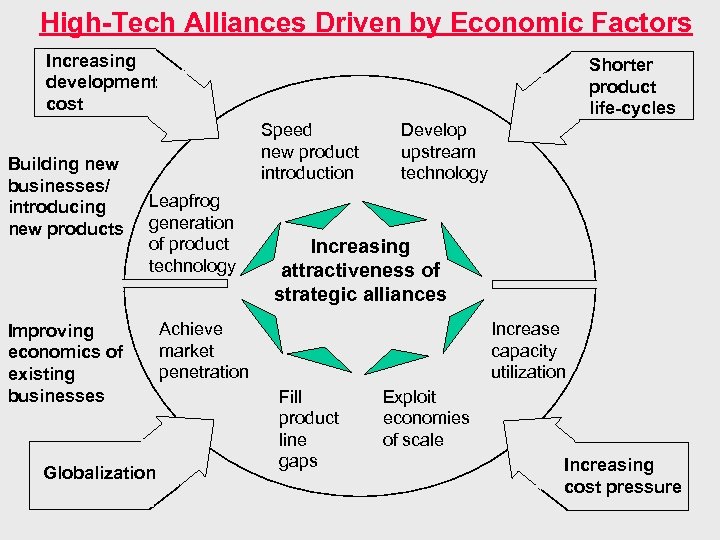
High-Tech Alliances Driven by Economic Factors Increasing development cost Building new businesses/ introducing new products Shorter product life-cycles Speed new product introduction Leapfrog generation of product technology Improving economics of existing businesses Globalization Develop upstream technology Increasing attractiveness of strategic alliances Achieve market penetration Increase capacity utilization Fill product line gaps Exploit economies of scale Increasing cost pressure

Final Thoughts on Strategic Alliances • Expanding existing businesses into new geographic regions • Acquisitions successful in building core business in existing geographic market • Alliances work well for moving into new businesses Strategic Alliances Dr. George H. Webster

Final Thoughts on Strategic Alliances • Equal strength partners more likely to be successful • Autonomy and flexibility • Issue of ownership should be separated from managerial control • Realize that joint venture fill intermediate-term needs but may mortgage long-term global future Strategic Alliances Dr. George H. Webster

Pirelli-Cooper- a Strategic Alliance Example • Pirelli designated Cooper as exclusive distributor of Pirelli tires in N. A. • Cooper supplies tires for the replacement market • Cooper needs a major brand to complement its own • Pirelli gives Cooper a “ tier one” product (meets O. E. M. standards) • Cooper can now supply a complete line of tires • Pirelli will use Cooper’s strong dealer relationships in U. S.

“Let’s Make a Deal”- A Proposed Strategic Alliance • General Electric’s contribution: G. E. will invest $500 million to develop an enlarged version of the GE 90 (777) The engine will have a 5, 000 -pound thrust margin over the competition G. E. Capital will finance 747 sales, either through lease or sale in Asia • Boeing’s contribution: Boeing must proceed to develop the 777 (by 2003) Cost of development will be at least $1 Billion Boeing must make G. E. the sole engine supplier

“Let’s Make a Deal”- A Proposed Strategic Alliance • General Electric receives: $20 Billion contract from Boeing Engine sales for 20 years Approximately 20 per cent return on 747 sales/lease • Boeing receives: Exclusive use of an engine that which will make the 777 competitive with the Airbus A 340 Financing help with the sale of 747’s (critical in Asia)
4e343b706297411bfc07b57ffb805028.ppt