30db42e0f07c808383402ad3809598f1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23
 Creating the Constitution
Creating the Constitution
 1. Constitutional Convention § Framers met in Philadelphia in 1787 § Divided over views of the appropriate power and responsibilities of government § Some thought current gov’t (under Articles of Confederation) was weak and ineffective § Others thought changes to the Articles would infringe on state gov’ts and the lives of citizens § All agreed that a stronger central government was needed
1. Constitutional Convention § Framers met in Philadelphia in 1787 § Divided over views of the appropriate power and responsibilities of government § Some thought current gov’t (under Articles of Confederation) was weak and ineffective § Others thought changes to the Articles would infringe on state gov’ts and the lives of citizens § All agreed that a stronger central government was needed
 Washington Addressing the Convention
Washington Addressing the Convention
 2. Creating a New Constitution § Issue: Representation in Congress § Virginia Plan § Representing large states § 2 house legislature § Both houses with proportional representation § 3 branches of government § Clause that national gov’ts laws are supreme in dispute with state law --> supremacy clause
2. Creating a New Constitution § Issue: Representation in Congress § Virginia Plan § Representing large states § 2 house legislature § Both houses with proportional representation § 3 branches of government § Clause that national gov’ts laws are supreme in dispute with state law --> supremacy clause
 Edmund Randolph- Proposed Virginia Plan
Edmund Randolph- Proposed Virginia Plan
 Issue: Representation in Congress New Jersey Plan § Represented small states § One house legislature with equal representation § Federal judges appointed for life § Plural executive § Instituted even stronger supremacy clause
Issue: Representation in Congress New Jersey Plan § Represented small states § One house legislature with equal representation § Federal judges appointed for life § Plural executive § Instituted even stronger supremacy clause
 William Paterson, author of the New Jersey Plan
William Paterson, author of the New Jersey Plan
 Issue: Representation in Congress Connecticut (“Great”) Compromise § 2 house legislature (bi-cameral) § Upper house (Senate) would have equal representation and be elected by the lower house § Lower house (House of Representatives) would be based on proportional representation § Federal judges appointed for life
Issue: Representation in Congress Connecticut (“Great”) Compromise § 2 house legislature (bi-cameral) § Upper house (Senate) would have equal representation and be elected by the lower house § Lower house (House of Representatives) would be based on proportional representation § Federal judges appointed for life
 Roger Sherman, author of the CT Compromise
Roger Sherman, author of the CT Compromise

 Issue: Regulation of Interstate and Foreign Trade Commerce and Slave Trade Compromise § Gave Congress power to regulate interstate and foreign trade § Denied Congress right to tax exports § Denied Congress right to end the importation of slaves until 1808
Issue: Regulation of Interstate and Foreign Trade Commerce and Slave Trade Compromise § Gave Congress power to regulate interstate and foreign trade § Denied Congress right to tax exports § Denied Congress right to end the importation of slaves until 1808
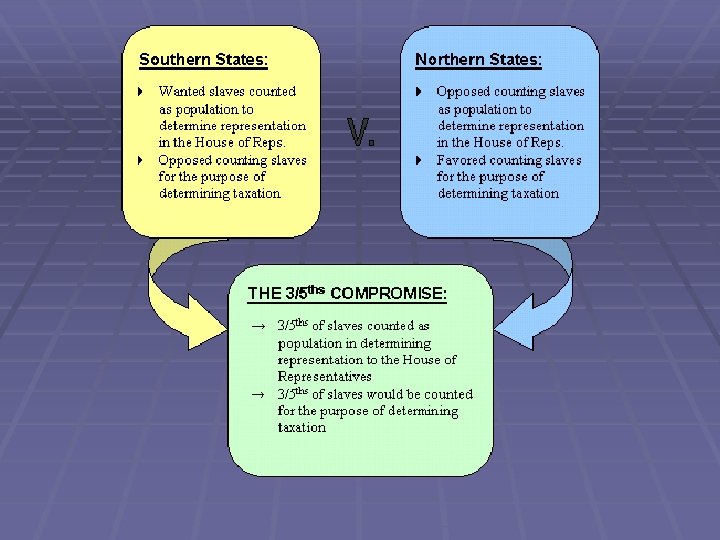
 Issue: Regulation of Slavery § Fierce debate between the North & South § North wanted slaves counted for taxation, not representation § South wanted slaves counted for representation, not taxation § Three-Fifths Compromise § For every 5 slaves, 3 slaves would be counted as part of the population for the purpose of determining both representation and taxation
Issue: Regulation of Slavery § Fierce debate between the North & South § North wanted slaves counted for taxation, not representation § South wanted slaves counted for representation, not taxation § Three-Fifths Compromise § For every 5 slaves, 3 slaves would be counted as part of the population for the purpose of determining both representation and taxation
 Issue: Method of Choosing a Chief Executive Electoral College § Provides for an indirect method of choosing a president § No way for one person/group to control election § Established to pacify those who were against an independent executive branch
Issue: Method of Choosing a Chief Executive Electoral College § Provides for an indirect method of choosing a president § No way for one person/group to control election § Established to pacify those who were against an independent executive branch
 Electoral College Map 2012
Electoral College Map 2012
 3. Ratification Battle § Securing ratification of the Constitution proved to be difficult § Convention approved the Constitution in September 1787 § Final draft written by Governor Morris (NY) § Battle within state ratifying conventions quickly ensued between Federalists and Anti-Federalists
3. Ratification Battle § Securing ratification of the Constitution proved to be difficult § Convention approved the Constitution in September 1787 § Final draft written by Governor Morris (NY) § Battle within state ratifying conventions quickly ensued between Federalists and Anti-Federalists
 3. Ratification Battle § Main issues included: § Representation: direct democracy vs. representative democracy § Tyranny: government is too far removed from the people vs. tyranny of the majority § Governmental Power: attacked supremacy clause and elastic clause, lack of bill of rights vs. checks and balances and the need to take risks to achieve goals
3. Ratification Battle § Main issues included: § Representation: direct democracy vs. representative democracy § Tyranny: government is too far removed from the people vs. tyranny of the majority § Governmental Power: attacked supremacy clause and elastic clause, lack of bill of rights vs. checks and balances and the need to take risks to achieve goals

 3. Ratification Battle § Federalist Papers § 85 essays written under the name “Publius” by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay § They defended the principles of the Constitution and sought to dispel fears of a national authority § Antifederalists published essays of their own, arguing that the new Constitution betrayed the revolution and was a step toward monarchy
3. Ratification Battle § Federalist Papers § 85 essays written under the name “Publius” by Alexander Hamilton, James Madison, and John Jay § They defended the principles of the Constitution and sought to dispel fears of a national authority § Antifederalists published essays of their own, arguing that the new Constitution betrayed the revolution and was a step toward monarchy

 Federalist Papers § Federalist #10 § Warnings about factions (often called “special interests”) today and “tyranny of the majority” § Strategies to deal with factions and protect minorities § Checks & balances § Separation of 3 branches
Federalist Papers § Federalist #10 § Warnings about factions (often called “special interests”) today and “tyranny of the majority” § Strategies to deal with factions and protect minorities § Checks & balances § Separation of 3 branches
 Federalist Papers Federalist #51 § Elaborates on checks and balances as the solution to factions § Based on common distrust of human nature § Idea of representative democracy
Federalist Papers Federalist #51 § Elaborates on checks and balances as the solution to factions § Based on common distrust of human nature § Idea of representative democracy
 4. Ratification § Went into effect March 4, 1789 § Delaware the first state to approve on December 7, 1787 § 1791, Constitution finally ratified by all states with Rhode Island’s vote
4. Ratification § Went into effect March 4, 1789 § Delaware the first state to approve on December 7, 1787 § 1791, Constitution finally ratified by all states with Rhode Island’s vote


