94c312eaf25eb20a311394adfe4f711a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 11
 CREATING AND DEVELOPING INNOVATION CENTERS: GUIDE technologies and key principles Dmitry Grishankov, April 2012 Director General Expert RA Rating Agency
CREATING AND DEVELOPING INNOVATION CENTERS: GUIDE technologies and key principles Dmitry Grishankov, April 2012 Director General Expert RA Rating Agency
 We have selected the very best innovation centers and science parks out of thousands all over the world The world’s top 50 leading innovation centers The world’s top 30 innovative managers Shaping innovation policies of over 40 countries of the world 2
We have selected the very best innovation centers and science parks out of thousands all over the world The world’s top 50 leading innovation centers The world’s top 30 innovative managers Shaping innovation policies of over 40 countries of the world 2
 Selection criteria Innovation centers • Assessment of innovation center upward development • Contribution to economic development • Brand awareness and citations • Level of tenants importance • Scale of innovation center • Venture capital availability • Information availability Innovation managers • Contribution to innovation infrastructure development • Experts’ and colleagues’ assessment • Scope of activity • Demand influence on national innovation systems • Involvement in innovation community and knowledge of innovation environment • Citations in authoritative newspapers and magazines (The Economist, Time, Scientific American, Wired, Nature, etc. ) • Experience in business • International awards 3
Selection criteria Innovation centers • Assessment of innovation center upward development • Contribution to economic development • Brand awareness and citations • Level of tenants importance • Scale of innovation center • Venture capital availability • Information availability Innovation managers • Contribution to innovation infrastructure development • Experts’ and colleagues’ assessment • Scope of activity • Demand influence on national innovation systems • Involvement in innovation community and knowledge of innovation environment • Citations in authoritative newspapers and magazines (The Economist, Time, Scientific American, Wired, Nature, etc. ) • Experience in business • International awards 3
 Тор 30 innovative managers of the world Wiiliam Miller, Dov Frohman, Israel USA Paulo Arruda, Brazil John Kao, USA Joseph Vardi, Israel Tony Tan, Singapore Nagavara Murthy, India Shiv Nadar, India Russell Hancock, USA Nandan Nilekani, India Wang Yangyuan, Sven-Thore Holm, Sweden Mei Meng, China Fernando Reinach, Brazil John Hennessy, USA Peter Dobson, Great Britain Pertti Huuskonen, Finland Philip Yeo, Singapore Chin-Tay Shih, Taiwan Masayoshi Son, Japan Chang-Gyu Hwang, South Korea Yigal Erlich, Israel Herbert Chen, South Korea Mervi Kaki, Finland Gilbert Pastor, France Julian Webb, Australia Se-Jung Oh, South Korea Kazuo Inamori, Japan Carlota Perez, Venezuela Anthony Tan, Hong Kong PRC 4
Тор 30 innovative managers of the world Wiiliam Miller, Dov Frohman, Israel USA Paulo Arruda, Brazil John Kao, USA Joseph Vardi, Israel Tony Tan, Singapore Nagavara Murthy, India Shiv Nadar, India Russell Hancock, USA Nandan Nilekani, India Wang Yangyuan, Sven-Thore Holm, Sweden Mei Meng, China Fernando Reinach, Brazil John Hennessy, USA Peter Dobson, Great Britain Pertti Huuskonen, Finland Philip Yeo, Singapore Chin-Tay Shih, Taiwan Masayoshi Son, Japan Chang-Gyu Hwang, South Korea Yigal Erlich, Israel Herbert Chen, South Korea Mervi Kaki, Finland Gilbert Pastor, France Julian Webb, Australia Se-Jung Oh, South Korea Kazuo Inamori, Japan Carlota Perez, Venezuela Anthony Tan, Hong Kong PRC 4
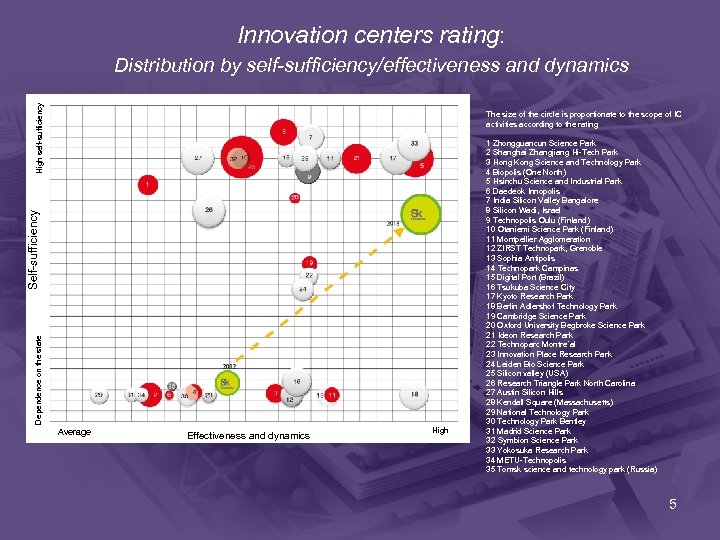 Innovation centers rating: High self-sufficiency Distribution by self-sufficiency/effectiveness and dynamics Dependence on the state Self-sufficiency The size of the circle is proportionate to the scope of IC activities according to the rating Average Effectiveness and dynamics High 1 Zhongguancun Science Park 2 Shanghai Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park 3 Hong Kong Science and Technology Park 4 Biopolis (One North) 5 Hsinchu Science and Industrial Park 6 Daedeok Innopolis 7 India Silicon Valley Bangalore 8 Silicon Wadi, Israel 9 Technopolis Oulu (Finland) 10 Otaniemi Science Park (Finland) 11 Montpellier Agglomeration 12 ZIRST Technopark, Grenoble 13 Sophia Antipolis 14 Technopark Campinas 15 Digital Port (Brazil) 16 Tsukuba Science City 17 Kyoto Research Park 18 Berlin Adlershof Technology Park 19 Cambridge Science Park 20 Oxford University Begbroke Science Park 21 Ideon Research Park 22 Technoparc Montre`al 23 Innovation Place Research Park 24 Leiden Bio Science Park 25 Silicon valley (USA) 26 Research Triangle Park North Carolina 27 Austin Silicon Hills 28 Kendall Square (Massachusetts) 29 National Technology Park 30 Technology Park Bentley 31 Madrid Science Park 32 Symbion Science Park 33 Yokosuka Research Park 34 METU-Technopolis 35 Tomsk science and technology park (Russia) 5
Innovation centers rating: High self-sufficiency Distribution by self-sufficiency/effectiveness and dynamics Dependence on the state Self-sufficiency The size of the circle is proportionate to the scope of IC activities according to the rating Average Effectiveness and dynamics High 1 Zhongguancun Science Park 2 Shanghai Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park 3 Hong Kong Science and Technology Park 4 Biopolis (One North) 5 Hsinchu Science and Industrial Park 6 Daedeok Innopolis 7 India Silicon Valley Bangalore 8 Silicon Wadi, Israel 9 Technopolis Oulu (Finland) 10 Otaniemi Science Park (Finland) 11 Montpellier Agglomeration 12 ZIRST Technopark, Grenoble 13 Sophia Antipolis 14 Technopark Campinas 15 Digital Port (Brazil) 16 Tsukuba Science City 17 Kyoto Research Park 18 Berlin Adlershof Technology Park 19 Cambridge Science Park 20 Oxford University Begbroke Science Park 21 Ideon Research Park 22 Technoparc Montre`al 23 Innovation Place Research Park 24 Leiden Bio Science Park 25 Silicon valley (USA) 26 Research Triangle Park North Carolina 27 Austin Silicon Hills 28 Kendall Square (Massachusetts) 29 National Technology Park 30 Technology Park Bentley 31 Madrid Science Park 32 Symbion Science Park 33 Yokosuka Research Park 34 METU-Technopolis 35 Tomsk science and technology park (Russia) 5
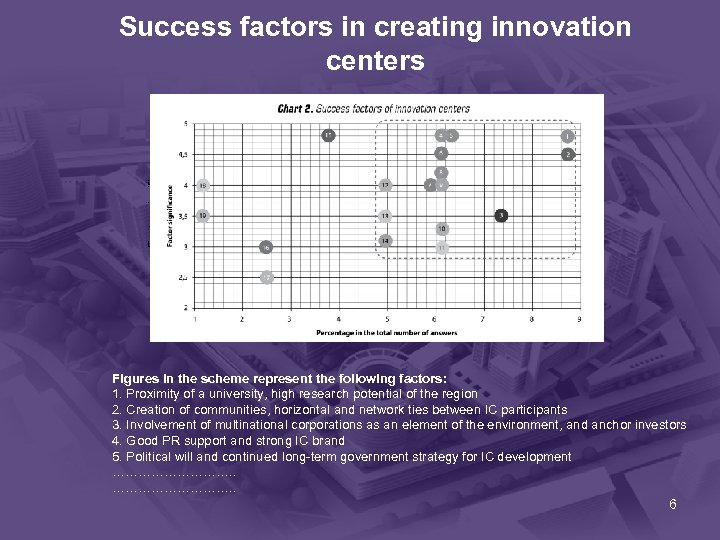 Factor significance Success factors in creating innovation centers Figures in the scheme represent the following factors: 1. Proximity of a university, high research potential of the region 2. Creation of communities, horizontal and network ties between IC participants 3. Involvement of multinational corporations as an element of the environment, and anchor investors 4. Good PR support and strong IC brand 5. Political will and continued long-term government strategy for IC development ………………………. . 6
Factor significance Success factors in creating innovation centers Figures in the scheme represent the following factors: 1. Proximity of a university, high research potential of the region 2. Creation of communities, horizontal and network ties between IC participants 3. Involvement of multinational corporations as an element of the environment, and anchor investors 4. Good PR support and strong IC brand 5. Political will and continued long-term government strategy for IC development ………………………. . 6
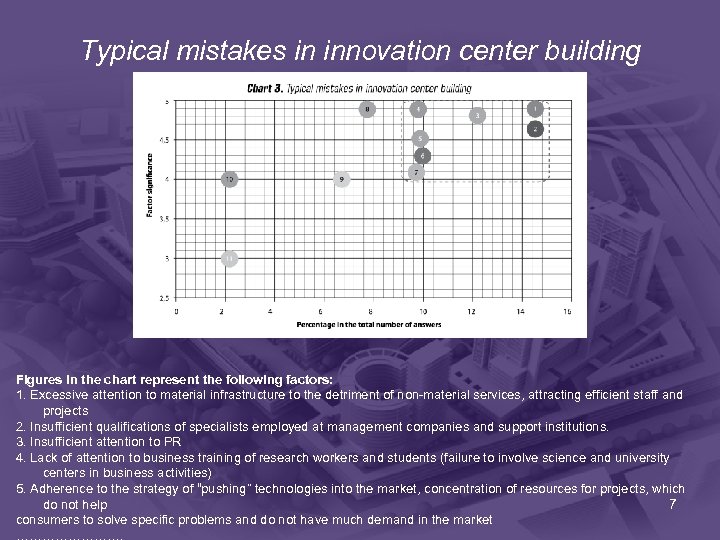 Factor significance Typical mistakes in innovation center building Figures in the chart represent the following factors: 1. Excessive attention to material infrastructure to the detriment of non-material services, attracting efficient staff and projects 2. Insufficient qualifications of specialists employed at management companies and support institutions. 3. Insufficient attention to PR 4. Lack of attention to business training of research workers and students (failure to involve science and university centers in business activities) 5. Adherence to the strategy of “pushing” technologies into the market, concentration of resources for projects, which do not help 7 consumers to solve specific problems and do not have much demand in the market ………….
Factor significance Typical mistakes in innovation center building Figures in the chart represent the following factors: 1. Excessive attention to material infrastructure to the detriment of non-material services, attracting efficient staff and projects 2. Insufficient qualifications of specialists employed at management companies and support institutions. 3. Insufficient attention to PR 4. Lack of attention to business training of research workers and students (failure to involve science and university centers in business activities) 5. Adherence to the strategy of “pushing” technologies into the market, concentration of resources for projects, which do not help 7 consumers to solve specific problems and do not have much demand in the market ………….
 Stages of innovation centers development I. II. IV. Concentration of resources (building up regional R&D potential and fostering favourable business climate); Innovation ecosystem development (symbiosis of technological start-ups, small businesses and large businesses; proactive regional policy to support innovative entrepreneurship); Breakthrough (rapid revenue growth of big – anchor – companies that are turning into global players; significant increase in the number of technological start-ups; venture investment market development); Mature development (highly efficient infrastructure to foster innovative entrepreneurship; integration into existing technological chains and building of new ones on the basis of international cooperation). 8
Stages of innovation centers development I. II. IV. Concentration of resources (building up regional R&D potential and fostering favourable business climate); Innovation ecosystem development (symbiosis of technological start-ups, small businesses and large businesses; proactive regional policy to support innovative entrepreneurship); Breakthrough (rapid revenue growth of big – anchor – companies that are turning into global players; significant increase in the number of technological start-ups; venture investment market development); Mature development (highly efficient infrastructure to foster innovative entrepreneurship; integration into existing technological chains and building of new ones on the basis of international cooperation). 8
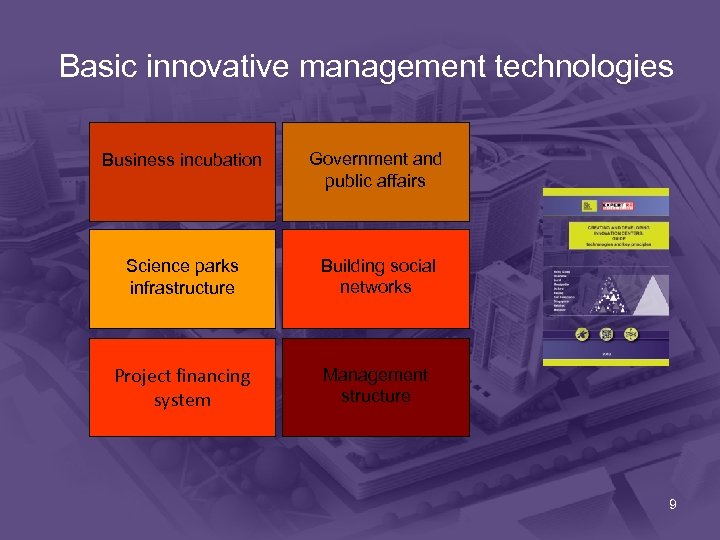 Basic innovative management technologies Business incubation Government and public affairs Science parks infrastructure Building social networks Project financing system Management structure 9
Basic innovative management technologies Business incubation Government and public affairs Science parks infrastructure Building social networks Project financing system Management structure 9
 Russia aspires to become a global innovation leader I. History and solid basis for innovative development (competitive fundamental science, education and high-tech productions); II. Availability of necessary resources and political will of the country’s leadership (a major innovation state-run project is under way in Russia); III. Institutional environment has been built (all necessary innovation development instruments have been created in Russia); 10
Russia aspires to become a global innovation leader I. History and solid basis for innovative development (competitive fundamental science, education and high-tech productions); II. Availability of necessary resources and political will of the country’s leadership (a major innovation state-run project is under way in Russia); III. Institutional environment has been built (all necessary innovation development instruments have been created in Russia); 10
 Thank you! Dmitry Grishankov Director General Expert RA Rating Agency grishankov@raexpert. ru 11
Thank you! Dmitry Grishankov Director General Expert RA Rating Agency grishankov@raexpert. ru 11


