b927fa88f4d8e0e3bd7a077287f19cd9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 45
 Creating a Classroom Culture of High Expectations Dr. Summer Whitmore, SPDG
Creating a Classroom Culture of High Expectations Dr. Summer Whitmore, SPDG
 Downloading Files You can download all of today’s materials in the FILES 2 Pod on the bottom left of your screen at any time during the presentation – Click on the selected file – Click DOWNLOAD FILE – Select the destination where you would like to save the file
Downloading Files You can download all of today’s materials in the FILES 2 Pod on the bottom left of your screen at any time during the presentation – Click on the selected file – Click DOWNLOAD FILE – Select the destination where you would like to save the file
 People First Language “People First Language puts the person before the disability and describes what a person has, not who a person is. ” Kathie Snow. (n. d. ) A few words about People First Language. Disability is Natural. Retrieved August 1, 2012 from http: //www. disabilityisnatural. com/images/PDF/pfl-sh 09. pdf
People First Language “People First Language puts the person before the disability and describes what a person has, not who a person is. ” Kathie Snow. (n. d. ) A few words about People First Language. Disability is Natural. Retrieved August 1, 2012 from http: //www. disabilityisnatural. com/images/PDF/pfl-sh 09. pdf
 • Gain knowledge of the importance of high expectations in the classroom • Gain knowledge of students’ responses to high expectations • Gain knowledge of examples of high expectations in the classrooms 4
• Gain knowledge of the importance of high expectations in the classroom • Gain knowledge of students’ responses to high expectations • Gain knowledge of examples of high expectations in the classrooms 4
 Vocabulary • Teacher Expectations are inferences or assumptions made about future student behavior.
Vocabulary • Teacher Expectations are inferences or assumptions made about future student behavior.
 Teacher Expectations • have both a positive and negative effect on student learning and achievement • influence the ways in which teachers evaluate students, behave toward students, and make decisions about students Good, T. L. , & Brophy, J. E. (2003). Looking in classrooms (9 th ed. ).
Teacher Expectations • have both a positive and negative effect on student learning and achievement • influence the ways in which teachers evaluate students, behave toward students, and make decisions about students Good, T. L. , & Brophy, J. E. (2003). Looking in classrooms (9 th ed. ).
 Pygmalion Effect • asserts that “ones expectations about a person can eventually lead that person to behave and achieve in ways that confirm those expectations” Rosenthal & Jacobson (1968)
Pygmalion Effect • asserts that “ones expectations about a person can eventually lead that person to behave and achieve in ways that confirm those expectations” Rosenthal & Jacobson (1968)
 Behaviors That Teachers Display for High and Low Expectations
Behaviors That Teachers Display for High and Low Expectations
 Teacher Behavior for Students with High Expectations • Praise students for success and less likely to criticize for failure in classroom task • Offer feedback on assignments at a higher rate • Correct and probe for students to answer questions • Criticism as a means of communicating high standards • Grading-given the benefit of the doubt Good and Weinstein (1986): General Dimensions of Teachers’ Communication of Differential Expectations
Teacher Behavior for Students with High Expectations • Praise students for success and less likely to criticize for failure in classroom task • Offer feedback on assignments at a higher rate • Correct and probe for students to answer questions • Criticism as a means of communicating high standards • Grading-given the benefit of the doubt Good and Weinstein (1986): General Dimensions of Teachers’ Communication of Differential Expectations
 Teacher Behavior for Students with Low Expectations • • • Wait less time for students to answer questions More likely to give the answer than probe Tend to reward inappropriate or incorrect responses Pay less attention/or do so privately more often than publicly Call on less frequently Seat student further away Smile less/less eye contact Offer less learning material Criticism as a means of degrading them, cutting them off from attempts to complete work Good and Weinstein (1986): General Dimensions of Teachers’ Communication of Differential Expectations
Teacher Behavior for Students with Low Expectations • • • Wait less time for students to answer questions More likely to give the answer than probe Tend to reward inappropriate or incorrect responses Pay less attention/or do so privately more often than publicly Call on less frequently Seat student further away Smile less/less eye contact Offer less learning material Criticism as a means of degrading them, cutting them off from attempts to complete work Good and Weinstein (1986): General Dimensions of Teachers’ Communication of Differential Expectations
 Teacher Behavior-Effect on Learning • Widen the gap between low and high achieving students • Affect students’ own beliefs about their competencies
Teacher Behavior-Effect on Learning • Widen the gap between low and high achieving students • Affect students’ own beliefs about their competencies
 Student Responses To Expectations
Student Responses To Expectations
 Student Passivity • Defined-inactive; a lack of initiative • Due to students being called on less often, teachers giving answers, students having a shorter wait time and students not likely to have the correct response.
Student Passivity • Defined-inactive; a lack of initiative • Due to students being called on less often, teachers giving answers, students having a shorter wait time and students not likely to have the correct response.
 Silent Students Why? • Personal anxiety or anticipation of possible embarrassment • Low self-confidence vs. low knowledge • Cultural reasons • Prefer to learn by listening and thinking
Silent Students Why? • Personal anxiety or anticipation of possible embarrassment • Low self-confidence vs. low knowledge • Cultural reasons • Prefer to learn by listening and thinking
 Silent Students: Perspectives on More Verbal Classmates • Irritating • Self-Centered • Keeping others from having a turn • Smart (know it all) Rosenthal, R. (1991). Teacher expectancy effects: A brief update 25 years after the Pygmalion experiment. Journal of Research in Education
Silent Students: Perspectives on More Verbal Classmates • Irritating • Self-Centered • Keeping others from having a turn • Smart (know it all) Rosenthal, R. (1991). Teacher expectancy effects: A brief update 25 years after the Pygmalion experiment. Journal of Research in Education
 Self-Fulfilling Prophecy • Defined -- The process by which a person’s expectations about someone can lead to that someone behaving in ways which confirm to the expectations • Pygmalion in the Classroom -- Research by Rosenthal and Jacobson
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy • Defined -- The process by which a person’s expectations about someone can lead to that someone behaving in ways which confirm to the expectations • Pygmalion in the Classroom -- Research by Rosenthal and Jacobson
 Students’ Perceptions of Teacher Expectations • Expectations, either high or low, can become a self-fulfilling prophecy. • Teachers’ beliefs about student potential are particularly powerful for students of color and students from poor families. Lisa Delpit (2012). Multiplication is for White People
Students’ Perceptions of Teacher Expectations • Expectations, either high or low, can become a self-fulfilling prophecy. • Teachers’ beliefs about student potential are particularly powerful for students of color and students from poor families. Lisa Delpit (2012). Multiplication is for White People
 High Expectations • High expectations is both a belief about student capability and specific actions undertaken to make those beliefs a reality.
High Expectations • High expectations is both a belief about student capability and specific actions undertaken to make those beliefs a reality.
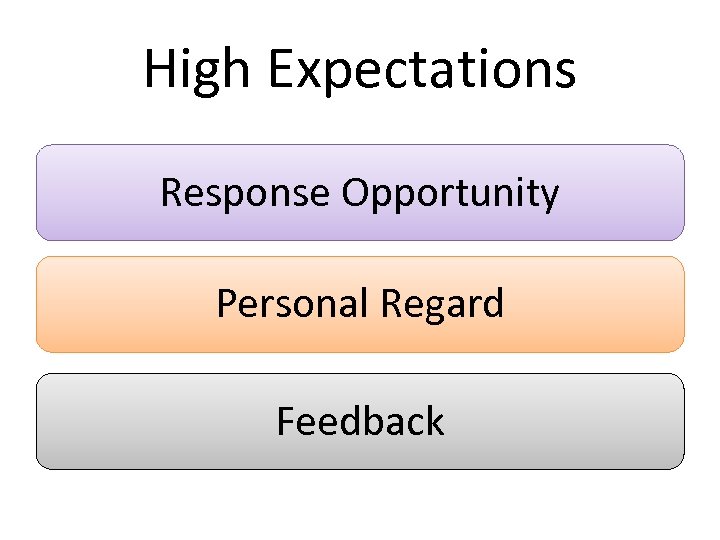 High Expectations Response Opportunity Personal Regard Feedback
High Expectations Response Opportunity Personal Regard Feedback
 Response Opportunities • Individual Help • Probing, Rephrasing, and Clues • Wait Time • Equitable Response Opportunities • Higher Level Questions
Response Opportunities • Individual Help • Probing, Rephrasing, and Clues • Wait Time • Equitable Response Opportunities • Higher Level Questions
 Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Wait Time • Students who volunteer to answer will increase as will the length of their responses • Responses will demonstrate critical thinking supported by evidence or logic
Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Wait Time • Students who volunteer to answer will increase as will the length of their responses • Responses will demonstrate critical thinking supported by evidence or logic
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=d. Bnu. SUL 0 ym. M
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=d. Bnu. SUL 0 ym. M
 Equitable Response Opportunities • The number of times teachers call on students is directly related to the level of expectations they have for them • Teachers call on students when they have confidence in their ability to answer a question • Teachers call on less students in whom they have little confidence
Equitable Response Opportunities • The number of times teachers call on students is directly related to the level of expectations they have for them • Teachers call on students when they have confidence in their ability to answer a question • Teachers call on less students in whom they have little confidence
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=1 W 0 Yrk 3 GZ_U
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=1 W 0 Yrk 3 GZ_U
 Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Questioning • Leveling questions is a good practice, it helps students to stretch their thinking • Rephrase questions to aid students understanding • Give students clues rather than pass over them
Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Questioning • Leveling questions is a good practice, it helps students to stretch their thinking • Rephrase questions to aid students understanding • Give students clues rather than pass over them
 Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Questioning • If students are only asked questions that require low levels of intellectual involvement they will tend to think accordingly • Students who are given questions based on higher levels of thinking will tend to think more creatively
Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Questioning • If students are only asked questions that require low levels of intellectual involvement they will tend to think accordingly • Students who are given questions based on higher levels of thinking will tend to think more creatively
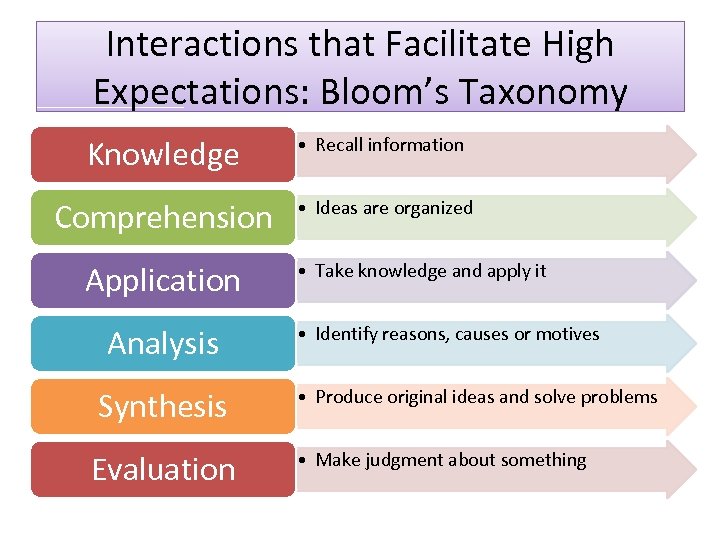 Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Bloom’s Taxonomy Knowledge • Recall information Comprehension • Ideas are organized Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation • Take knowledge and apply it • Identify reasons, causes or motives • Produce original ideas and solve problems • Make judgment about something
Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Bloom’s Taxonomy Knowledge • Recall information Comprehension • Ideas are organized Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation • Take knowledge and apply it • Identify reasons, causes or motives • Produce original ideas and solve problems • Make judgment about something
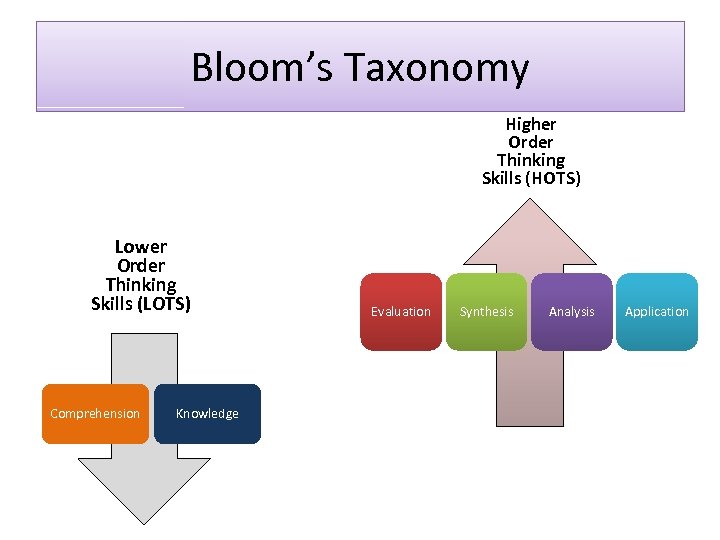 Bloom’s Taxonomy Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Lower Order Thinking Skills (LOTS) Comprehension Knowledge Evaluation Synthesis Analysis Application
Bloom’s Taxonomy Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Lower Order Thinking Skills (LOTS) Comprehension Knowledge Evaluation Synthesis Analysis Application
 http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=CW 8 JQfjmh. CE&feature=youtu. be
http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=CW 8 JQfjmh. CE&feature=youtu. be
 Personal Regard • • Proximity Courtesy Touch Personal Interest
Personal Regard • • Proximity Courtesy Touch Personal Interest
 Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Proximity • Proximity communicates value • Provides the teacher an opportunity to develop a bond with each individual
Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Proximity • Proximity communicates value • Provides the teacher an opportunity to develop a bond with each individual
 Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Touching • • Shake hands High five Thumbs up Smile Boynton & Boynton (2005) Educator's Guide to Preventing and Solving Discipline Problems
Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Touching • • Shake hands High five Thumbs up Smile Boynton & Boynton (2005) Educator's Guide to Preventing and Solving Discipline Problems
 http: //vimeo. com/41421052
http: //vimeo. com/41421052
 Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Personal Interest • Incorporating students’ personal interests into academics • Noticing individual accomplishments and important events in students' lives • Interacting with students as individuals Good, T. L. , & Brophy, J. E. (2003). Looking in classrooms (9 th ed. ).
Interactions that Facilitate High Expectations: Personal Interest • Incorporating students’ personal interests into academics • Noticing individual accomplishments and important events in students' lives • Interacting with students as individuals Good, T. L. , & Brophy, J. E. (2003). Looking in classrooms (9 th ed. ).
 http: //youtu. be/x. NIJCs 0 U 1 PM
http: //youtu. be/x. NIJCs 0 U 1 PM
 Expectations and Support • Increase expectations without helping students achieve success almost always leads to frustration and failure
Expectations and Support • Increase expectations without helping students achieve success almost always leads to frustration and failure
 Feedback • Affirm or Correct Response • Praise Performance • Give Reason For Praise • Listen Attentively • Accept and Reflect Feelings
Feedback • Affirm or Correct Response • Praise Performance • Give Reason For Praise • Listen Attentively • Accept and Reflect Feelings
 Feedback: Grading Strategy • What does an “F” really mean? • Grading: A, B, C, and NY (Not Yet!) communicates what is expected from students
Feedback: Grading Strategy • What does an “F” really mean? • Grading: A, B, C, and NY (Not Yet!) communicates what is expected from students
 Feedback with Families • Effective teachers produce and share progress reports and grades weekly with families and students • Reaffirms the teachers and families approach to students learning Porterfield & Carnes (2012) Why Social Media Matters
Feedback with Families • Effective teachers produce and share progress reports and grades weekly with families and students • Reaffirms the teachers and families approach to students learning Porterfield & Carnes (2012) Why Social Media Matters
 Feedback • Beginning and ending every instructional segment with a review of past learning and the big picture • Inspiring students to probe “why? ” and “how do you know that you know? ” • Requiring students to express their thinking and learning through speaking, writing and designing
Feedback • Beginning and ending every instructional segment with a review of past learning and the big picture • Inspiring students to probe “why? ” and “how do you know that you know? ” • Requiring students to express their thinking and learning through speaking, writing and designing
 Feedback • Students need constant feedback on how well they are performing • Feedback is a two way proposition
Feedback • Students need constant feedback on how well they are performing • Feedback is a two way proposition
 High Expectations Response Opportunity Personal Regard Feedback
High Expectations Response Opportunity Personal Regard Feedback
 Building Capacity • When you leave today, what will you do with this information? • How will you share it with others in your district? • When will you share it? (Timeline)
Building Capacity • When you leave today, what will you do with this information? • How will you share it with others in your district? • When will you share it? (Timeline)
 www. laspdg. org Summer Whitmore swhitm 1@lsu. edu The contents of this Power. Point presentation were developed under a grant from the US Department of Education, #H 323 A 110003. However those contents do not necessarily represent the policy of the US Department of Education, and you should not assume endorsement by the Federal Government.
www. laspdg. org Summer Whitmore swhitm 1@lsu. edu The contents of this Power. Point presentation were developed under a grant from the US Department of Education, #H 323 A 110003. However those contents do not necessarily represent the policy of the US Department of Education, and you should not assume endorsement by the Federal Government.
 Reminder -In order to receive a certificate for 1 CLU, you must complete the online reflection at https: //www. surveymonkey. com/r/pt 2 highexp before January 22, 2016
Reminder -In order to receive a certificate for 1 CLU, you must complete the online reflection at https: //www. surveymonkey. com/r/pt 2 highexp before January 22, 2016


