c8eaa461558e3bd4eb51f14fbe00a399.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006 Execution Management and SLA Enforcement in Akogrimo Antonios Litke, Kleopatra Konstanteli, Vassiliki Litke Andronikou, Sotirios Chatzis, and Theodora Varvarigou e-mail: ali@telecom. ntua. gr

Presentation Outline Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 ØArchitectural overview of Akogrimo ØThe need for SLAs ØComponent descriptions and interactions ØImplementation issues ØRelated work ØConclusions ØQuestions/answers 17 October 2006
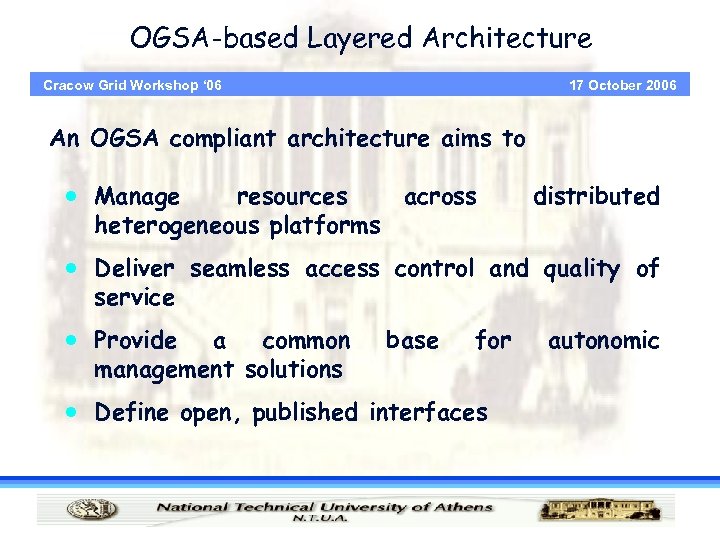
OGSA-based Layered Architecture 17 October 2006 Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 An OGSA compliant architecture aims to · Manage resources across heterogeneous platforms distributed · Deliver seamless access control and quality of service · Provide a common management solutions base for · Define open, published interfaces autonomic
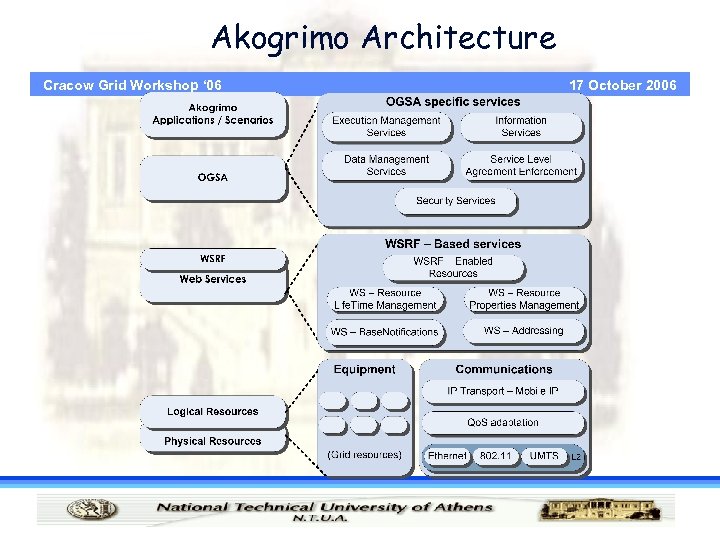
Akogrimo Architecture Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006

Akogrimo Architecture 17 October 2006 Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 • Physical and logical resources layer · Resources comprise each and every capability of the Grid • Physical resources, which include servers, storage, and network and Logical resources. • Logical resources are above the physical and provide additional functionality by virtualizing and aggregating the resources in the physical layer. • In Akogrimo communication incorporated in logical resources are also

The need for management of SLA Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006 Grids and mobile Grids are dynamic environments subject to unpredictable changes: · system or network failures, system performance degradation, removal of machines, variations in the cost of resources, Execution Management components should take care of conformance to the contractual terms of SLAs · EMS system monitors and manages the execution of the job until its completion · In case of violations, it takes actions to dynamically rectify them in such a way as to meet the terms defined in the related SLA
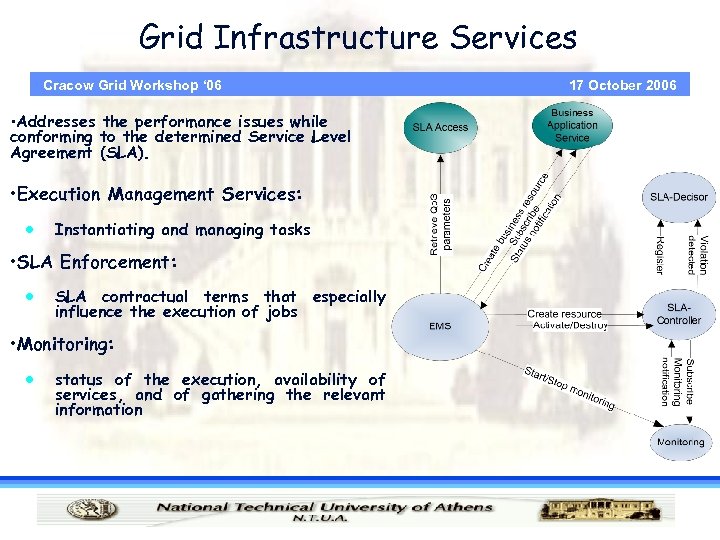
Grid Infrastructure Services Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 • Addresses the performance issues while conforming to the determined Service Level Agreement (SLA). • Execution Management Services: · Instantiating and managing tasks • SLA Enforcement: · SLA contractual terms that especially influence the execution of jobs • Monitoring: · status of the execution, availability of services, and of gathering the relevant information 17 October 2006

Example of Qo. S Parameters in SLAs Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006

Discovery and Reservation phase Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006
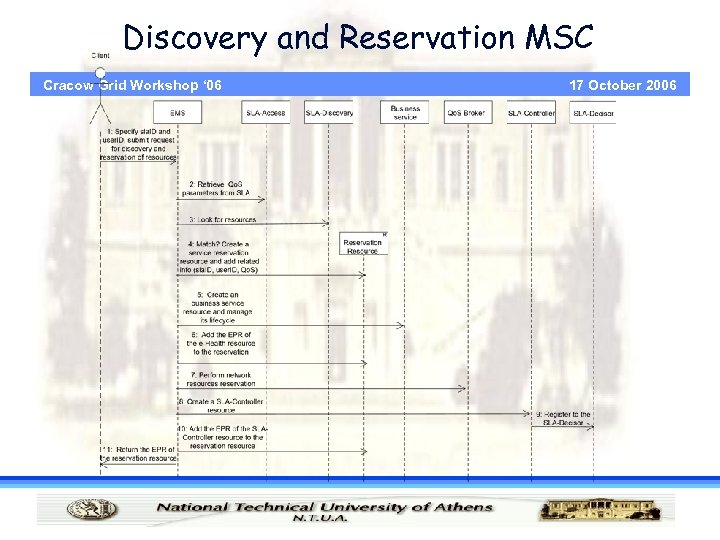
Discovery and Reservation MSC Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006
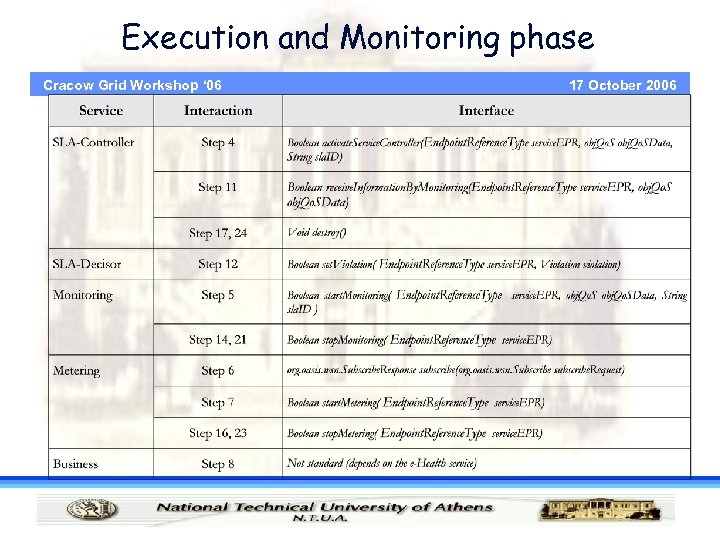
Execution and Monitoring phase Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006
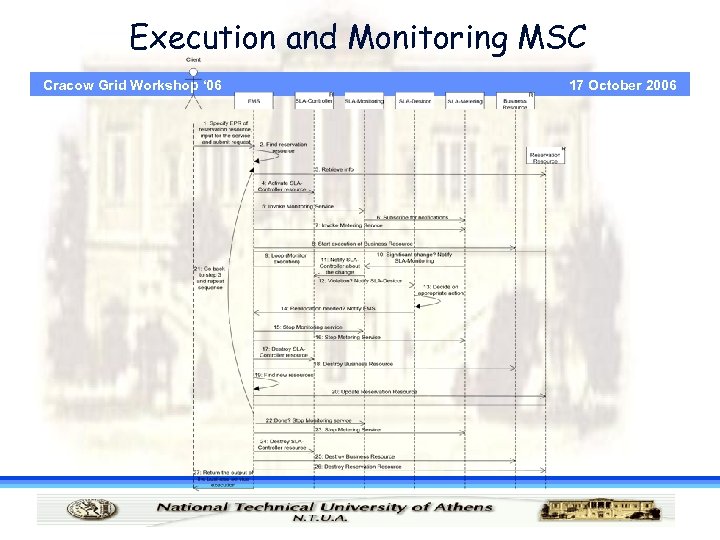
Execution and Monitoring MSC Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006
Implementation issues 17 October 2006 Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 · Globus Toolkit 4, and especially WS-GRAM and MDS 4 · SLA contracts management are developed using the WSRF. NET platform · Compelling implementation challenge to see whether: and technological • The 2 main grid services development tools, implement the WS-related specifications in a transparent and interoperable way

Related work Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006 · GRIA (Grid Resources for Industrial Applications) • designed and developed the GRIA middleware based on Web Services • supports the confirmation of a service offer through establishment of SLA and extensions of existing SLAs · GRASP (Grid-based Application Service Provision) • SLA management subsystem including the service provision negotiation based on Qo. S criteria and monitoring of the feasibility of the contract · Unigrids (Uniform Interface to Grid Services) • SLA framework and cross-Grid brokering services in order to support Grid economics • integrating a Web Services Agreement-based resource management framework into the Unicore Grid middleware

. . . and what is special in Akogrimo? 17 October 2006 Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 1) SLA parameters do include network Qo. S 2) Negotiation, reservation and execution are made on this basis also 3) Utilization of both toolkits: GT 4 and WSRF. NET 4) Decision on appropriate action when violation and estimation of the significance of the violation through a dedicated component

Conclusion Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006 • We presented an architecture to manage execution and enforce SLA in OGSA based grids and mobile Grids · Discovery and reservation phase · Execution and monitoring phase • The proposed design has been implemented in GT 4 and WSRF. NET • Advancing attributes of SLA mangement with use of network resources • For future research: To define an economic model based on how these violations affect the efficiency of Grids

17 October 2006 Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 Thank you! Questions?

17 October 2006 Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 Backup slides

Akogrimo Architecture 17 October 2006 Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 • Web services layer · All Grid resources are modelled as services · Web Services Resource Framework (WSRF) defines a family of specifications services for accessing stateful resources using Web • OGSA architected grid services layer · Overall grid management functionality • Grid applications layer · High – level applications a client might require · For Akogrimo we have deployed an E – Health application offering a suite of E – Health services.
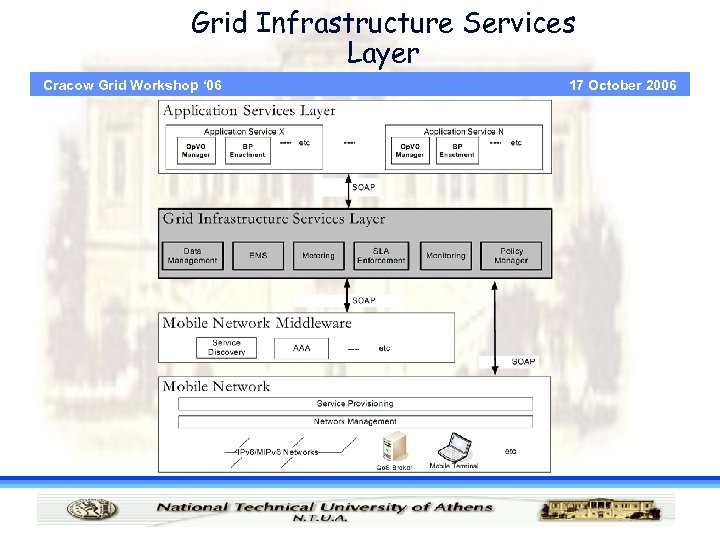
Grid Infrastructure Services Layer Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006

Network Qo. S Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006 • The Mobile Network Layer implements end-to-end Quality of Service, for all types of mobility · Make an effective use of network resources · Assure that a user can utilize the services he is entitled to without disruptions • The Qo. S implementation · Allows fine-grained Qo. S control at the access networks · Aggregates different flows with the same Qo. S requirements in the core network • The network supports well defined Qo. S bundles
Application Services Layer Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006 • Each application service requested by a client is modeled as a business process • Workflows represent the automation of the business process · Each workflow coordinates and manages component services or entities involved into the automation of business process • A Virtual Organization (VO) provides services and the means to manage and coordinate Business Processes • Implementation of a Business Process implies · Creation of an Operational Virtual Organisation (Op. VO) out of a base VO.
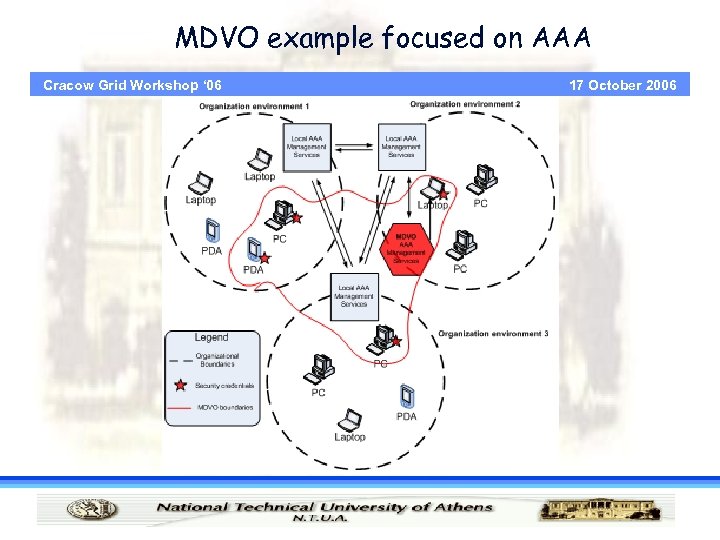
MDVO example focused on AAA Cracow Grid Workshop ‘ 06 17 October 2006
c8eaa461558e3bd4eb51f14fbe00a399.ppt