f62d9997f2e6b02f5ef7f94d9628b564.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 12
 CQA Assessment for Glycosylation and Oxidation of a Monoclonal Antibody: An FDA OBP Pilot Program Case Study Andrew Weiskopf, Ph. D. 2010 WCBP CMC Strategy Forum 19 July 2010
CQA Assessment for Glycosylation and Oxidation of a Monoclonal Antibody: An FDA OBP Pilot Program Case Study Andrew Weiskopf, Ph. D. 2010 WCBP CMC Strategy Forum 19 July 2010
 Biogen Idec & The FDA Pilot Program • Biogen Idec a participant in the FDA’s OBP Pilot Program for Qb. D – Meetings with OBP senior staff and reviewers to discuss approach to product and process risk assessments, design space development, and control strategy • Case Study for Pilot Program: Antibody X (Ab. X) – Monoclonal Ig. G 1, standard Fc N-glycosylation – Oncology drug entering late-stage clinical development – Mechanism-of-Action • CDR of Ab. X binds to cellular receptor of target cells • Fc of Ab. X is involved in promoting apoptosis, but Fc-binding entity in vivo is unknown – In vitro assessment indicates ADCC capability is modest Isotype – CDC is not involved Antibody X control – Fcg. RIIIa binding used as metric of Fc integrity • Risk Assessment Examples – Glycosylation: Galactosylation & Fucosylation – Methionine Oxidation
Biogen Idec & The FDA Pilot Program • Biogen Idec a participant in the FDA’s OBP Pilot Program for Qb. D – Meetings with OBP senior staff and reviewers to discuss approach to product and process risk assessments, design space development, and control strategy • Case Study for Pilot Program: Antibody X (Ab. X) – Monoclonal Ig. G 1, standard Fc N-glycosylation – Oncology drug entering late-stage clinical development – Mechanism-of-Action • CDR of Ab. X binds to cellular receptor of target cells • Fc of Ab. X is involved in promoting apoptosis, but Fc-binding entity in vivo is unknown – In vitro assessment indicates ADCC capability is modest Isotype – CDC is not involved Antibody X control – Fcg. RIIIa binding used as metric of Fc integrity • Risk Assessment Examples – Glycosylation: Galactosylation & Fucosylation – Methionine Oxidation
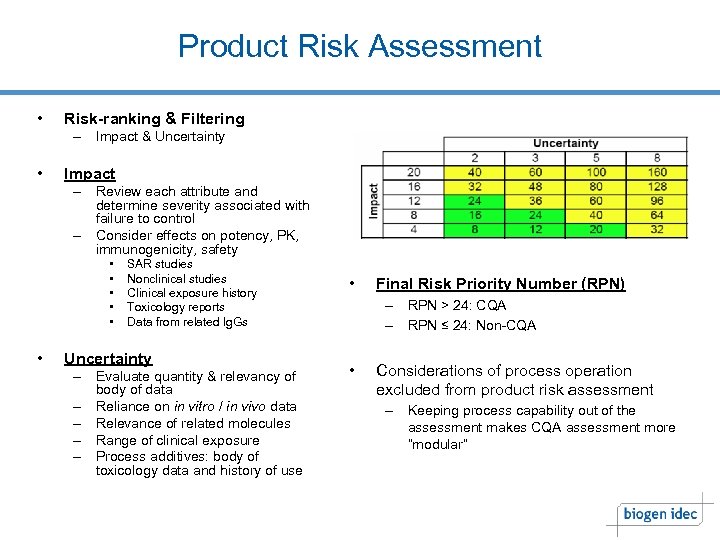 Product Risk Assessment • Risk-ranking & Filtering – Impact & Uncertainty • Impact – Review each attribute and determine severity associated with failure to control – Consider effects on potency, PK, immunogenicity, safety • • • SAR studies Nonclinical studies Clinical exposure history Toxicology reports Data from related Ig. Gs Uncertainty – Evaluate quantity & relevancy of body of data – Reliance on in vitro / in vivo data – Relevance of related molecules – Range of clinical exposure – Process additives: body of toxicology data and history of use • Final Risk Priority Number (RPN) – RPN > 24: CQA – RPN ≤ 24: Non-CQA • Considerations of process operation excluded from product risk assessment – Keeping process capability out of the assessment makes CQA assessment more “modular”
Product Risk Assessment • Risk-ranking & Filtering – Impact & Uncertainty • Impact – Review each attribute and determine severity associated with failure to control – Consider effects on potency, PK, immunogenicity, safety • • • SAR studies Nonclinical studies Clinical exposure history Toxicology reports Data from related Ig. Gs Uncertainty – Evaluate quantity & relevancy of body of data – Reliance on in vitro / in vivo data – Relevance of related molecules – Range of clinical exposure – Process additives: body of toxicology data and history of use • Final Risk Priority Number (RPN) – RPN > 24: CQA – RPN ≤ 24: Non-CQA • Considerations of process operation excluded from product risk assessment – Keeping process capability out of the assessment makes CQA assessment more “modular”
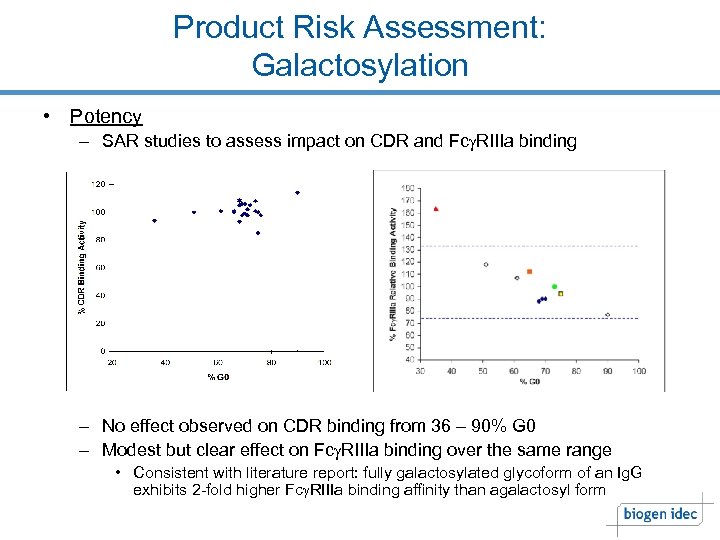 Product Risk Assessment: Galactosylation • Potency – SAR studies to assess impact on CDR and Fcg. RIIIa binding – No effect observed on CDR binding from 36 – 90% G 0 – Modest but clear effect on Fcg. RIIIa binding over the same range • Consistent with literature report: fully galactosylated glycoform of an Ig. G exhibits 2 -fold higher Fcg. RIIIa binding affinity than agalactosyl form
Product Risk Assessment: Galactosylation • Potency – SAR studies to assess impact on CDR and Fcg. RIIIa binding – No effect observed on CDR binding from 36 – 90% G 0 – Modest but clear effect on Fcg. RIIIa binding over the same range • Consistent with literature report: fully galactosylated glycoform of an Ig. G exhibits 2 -fold higher Fcg. RIIIa binding affinity than agalactosyl form
 Product Risk Assessment: Galactosylation • Pharmacokinetics – Literature: Fc glycans of Ig. G molecules not involved in Fc. Rn binding, thus not expected to impact clearance of Ab. X • Nonclinical & Clinical Experience – Wide range of terminal galactosylation exposure established with Ab. X in both nonclinical and clinical development history (36 – 75% G 0) – Ab. X Fc glycosylation variants are typical of human Ig. G’s, and are not novel structures • Conclusion: CQA – Impact = Moderate (12) – Uncertainty = Low-to-Moderate (3) – Risk Priority Number: 12 x 3 = 36
Product Risk Assessment: Galactosylation • Pharmacokinetics – Literature: Fc glycans of Ig. G molecules not involved in Fc. Rn binding, thus not expected to impact clearance of Ab. X • Nonclinical & Clinical Experience – Wide range of terminal galactosylation exposure established with Ab. X in both nonclinical and clinical development history (36 – 75% G 0) – Ab. X Fc glycosylation variants are typical of human Ig. G’s, and are not novel structures • Conclusion: CQA – Impact = Moderate (12) – Uncertainty = Low-to-Moderate (3) – Risk Priority Number: 12 x 3 = 36
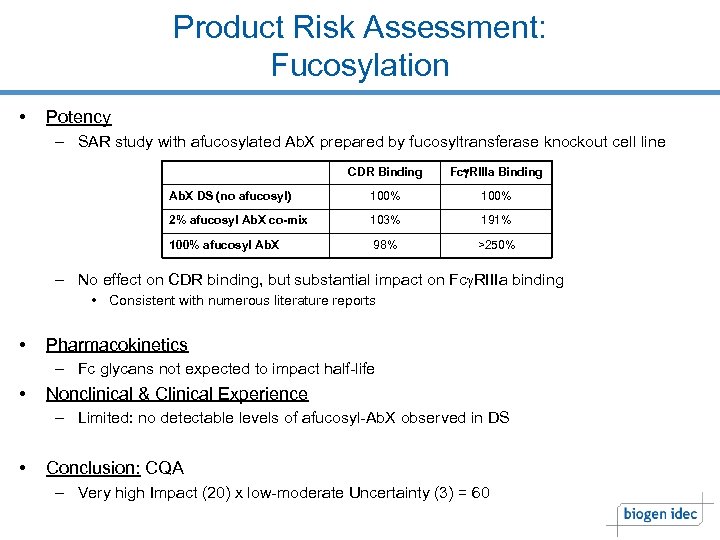 Product Risk Assessment: Fucosylation • Potency – SAR study with afucosylated Ab. X prepared by fucosyltransferase knockout cell line CDR Binding Fcg. RIIIa Binding Ab. X DS (no afucosyl) 100% 2% afucosyl Ab. X co-mix 103% 191% 100% afucosyl Ab. X 98% >250% – No effect on CDR binding, but substantial impact on Fcg. RIIIa binding • Consistent with numerous literature reports • Pharmacokinetics – Fc glycans not expected to impact half-life • Nonclinical & Clinical Experience – Limited: no detectable levels of afucosyl-Ab. X observed in DS • Conclusion: CQA – Very high Impact (20) x low-moderate Uncertainty (3) = 60
Product Risk Assessment: Fucosylation • Potency – SAR study with afucosylated Ab. X prepared by fucosyltransferase knockout cell line CDR Binding Fcg. RIIIa Binding Ab. X DS (no afucosyl) 100% 2% afucosyl Ab. X co-mix 103% 191% 100% afucosyl Ab. X 98% >250% – No effect on CDR binding, but substantial impact on Fcg. RIIIa binding • Consistent with numerous literature reports • Pharmacokinetics – Fc glycans not expected to impact half-life • Nonclinical & Clinical Experience – Limited: no detectable levels of afucosyl-Ab. X observed in DS • Conclusion: CQA – Very high Impact (20) x low-moderate Uncertainty (3) = 60
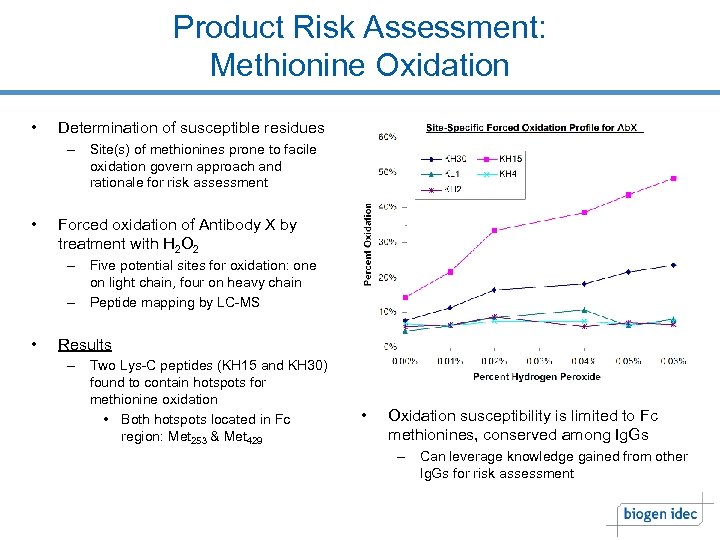 Product Risk Assessment: Methionine Oxidation • Determination of susceptible residues – Site(s) of methionines prone to facile oxidation govern approach and rationale for risk assessment • Forced oxidation of Antibody X by treatment with H 2 O 2 – Five potential sites for oxidation: one on light chain, four on heavy chain – Peptide mapping by LC-MS • Results – Two Lys-C peptides (KH 15 and KH 30) found to contain hotspots for methionine oxidation • Both hotspots located in Fc region: Met 253 & Met 429 • Oxidation susceptibility is limited to Fc methionines, conserved among Ig. Gs – Can leverage knowledge gained from other Ig. Gs for risk assessment
Product Risk Assessment: Methionine Oxidation • Determination of susceptible residues – Site(s) of methionines prone to facile oxidation govern approach and rationale for risk assessment • Forced oxidation of Antibody X by treatment with H 2 O 2 – Five potential sites for oxidation: one on light chain, four on heavy chain – Peptide mapping by LC-MS • Results – Two Lys-C peptides (KH 15 and KH 30) found to contain hotspots for methionine oxidation • Both hotspots located in Fc region: Met 253 & Met 429 • Oxidation susceptibility is limited to Fc methionines, conserved among Ig. Gs – Can leverage knowledge gained from other Ig. Gs for risk assessment
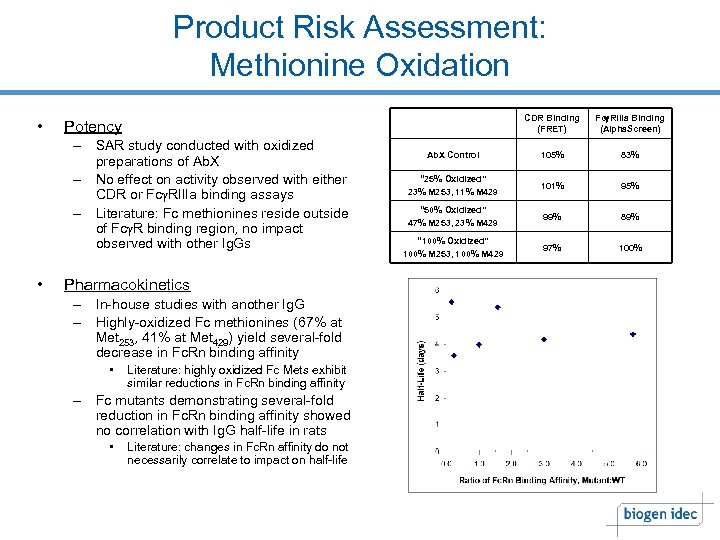 Product Risk Assessment: Methionine Oxidation • CDR Binding (FRET) – SAR study conducted with oxidized preparations of Ab. X – No effect on activity observed with either CDR or Fcg. RIIIa binding assays – Literature: Fc methionines reside outside of Fcg. R binding region, no impact observed with other Ig. Gs • Fcg. RIIIa Binding (Alpha. Screen) Ab. X Control 105% 83% “ 25% Oxidized” 23% M 253, 11% M 429 101% 95% “ 50% Oxidized” 47% M 253, 23% M 429 99% 89% “ 100% Oxidized” 100% M 253, 100% M 429 97% 100% Potency Pharmacokinetics – In-house studies with another Ig. G – Highly-oxidized Fc methionines (67% at Met 253, 41% at Met 429) yield several-fold decrease in Fc. Rn binding affinity • Literature: highly oxidized Fc Mets exhibit similar reductions in Fc. Rn binding affinity – Fc mutants demonstrating several-fold reduction in Fc. Rn binding affinity showed no correlation with Ig. G half-life in rats • Literature: changes in Fc. Rn affinity do not necessarily correlate to impact on half-life
Product Risk Assessment: Methionine Oxidation • CDR Binding (FRET) – SAR study conducted with oxidized preparations of Ab. X – No effect on activity observed with either CDR or Fcg. RIIIa binding assays – Literature: Fc methionines reside outside of Fcg. R binding region, no impact observed with other Ig. Gs • Fcg. RIIIa Binding (Alpha. Screen) Ab. X Control 105% 83% “ 25% Oxidized” 23% M 253, 11% M 429 101% 95% “ 50% Oxidized” 47% M 253, 23% M 429 99% 89% “ 100% Oxidized” 100% M 253, 100% M 429 97% 100% Potency Pharmacokinetics – In-house studies with another Ig. G – Highly-oxidized Fc methionines (67% at Met 253, 41% at Met 429) yield several-fold decrease in Fc. Rn binding affinity • Literature: highly oxidized Fc Mets exhibit similar reductions in Fc. Rn binding affinity – Fc mutants demonstrating several-fold reduction in Fc. Rn binding affinity showed no correlation with Ig. G half-life in rats • Literature: changes in Fc. Rn affinity do not necessarily correlate to impact on half-life
 Product Risk Assessment: Methionine Oxidation • Nonclinical & Clinical Experience – 3 -8% oxidized Met 253 in clinical lots of Ab. X – No adverse effects traced to differences – Wider range of experience with other Ig. G products • Other Considerations – Oxidation-induced increase in aggregation rates not studied in isolation for Ab. X, though reported in literature • Conclusion: Non-CQA – Low-Moderate Impact (8) x Low Uncertainty (2) = 16
Product Risk Assessment: Methionine Oxidation • Nonclinical & Clinical Experience – 3 -8% oxidized Met 253 in clinical lots of Ab. X – No adverse effects traced to differences – Wider range of experience with other Ig. G products • Other Considerations – Oxidation-induced increase in aggregation rates not studied in isolation for Ab. X, though reported in literature • Conclusion: Non-CQA – Low-Moderate Impact (8) x Low Uncertainty (2) = 16
 Product Risk Assessment: Attribute Criticality & Control Strategy • Galactosylation – Classified as a CQA, due to modest impact on Fcg. RIIIa binding – Only critical control parameters linked to galactosylation are readily controlled • Cell culture duration, p. H, and temperature – Primary controls achievable through process, justifying in-process testing • Incorporate into comparability assesssments • Fucosylation – Classified as a CQA, due to high impact on Fcg. RIII binding activity – No critical control parameters identified within the design space – Monitor by proxy through release test for Fcg. RIIIa binding activity • Variations will be evident due to sensitivity of assay to afucosyl content • Afucosyl levels controlled indirectly by Fcg. RIIIa binding activity specification • Fcg. RIIIa binding activity evaluated in comparability assessment • Methionine Oxidation – Classified as a non-CQA, due to low impact on potency & PK – Comparability assessment, selected process monitoring
Product Risk Assessment: Attribute Criticality & Control Strategy • Galactosylation – Classified as a CQA, due to modest impact on Fcg. RIIIa binding – Only critical control parameters linked to galactosylation are readily controlled • Cell culture duration, p. H, and temperature – Primary controls achievable through process, justifying in-process testing • Incorporate into comparability assesssments • Fucosylation – Classified as a CQA, due to high impact on Fcg. RIII binding activity – No critical control parameters identified within the design space – Monitor by proxy through release test for Fcg. RIIIa binding activity • Variations will be evident due to sensitivity of assay to afucosyl content • Afucosyl levels controlled indirectly by Fcg. RIIIa binding activity specification • Fcg. RIIIa binding activity evaluated in comparability assessment • Methionine Oxidation – Classified as a non-CQA, due to low impact on potency & PK – Comparability assessment, selected process monitoring
 Take-Home Messages From the Pilot Program • Keep process considerations separate from product risk assessment – Process changes shouldn’t have to trigger review of attribute criticality – Maintains CQA assessment as an evaluation of the biology, efficacy, and safety of the product • Certainty scoring for CQAs is helpful, but take care with implementation – Scoring system should not overweigh certainty at expense of impact – Don’t mathematically de-risk a critical attribute on the basis of having data – RPNs should accurately reflect degree of criticality and convince one of the risk • Attributes reside on a “continuum of criticality” – “CQA” and “Non-CQA” are useful terms, but developing an appropriate control strategy looks beyond the name • How critical is the attribute? • What process controls can be implemented to control the attribute? • How readily controlled are those parameters? – Control strategy should be proportional to overall degree of risk • Not all CQAs need to be controlled through release testing
Take-Home Messages From the Pilot Program • Keep process considerations separate from product risk assessment – Process changes shouldn’t have to trigger review of attribute criticality – Maintains CQA assessment as an evaluation of the biology, efficacy, and safety of the product • Certainty scoring for CQAs is helpful, but take care with implementation – Scoring system should not overweigh certainty at expense of impact – Don’t mathematically de-risk a critical attribute on the basis of having data – RPNs should accurately reflect degree of criticality and convince one of the risk • Attributes reside on a “continuum of criticality” – “CQA” and “Non-CQA” are useful terms, but developing an appropriate control strategy looks beyond the name • How critical is the attribute? • What process controls can be implemented to control the attribute? • How readily controlled are those parameters? – Control strategy should be proportional to overall degree of risk • Not all CQAs need to be controlled through release testing
 Acknowledgments Analytical Development • Testing Support – – – – • • Joseph Siemiatkoski Michael Molony Martha Berardino Namrata Chansarkar Tongjun Lu Christine Poliks Molly Roudabush – – – Svetlana Bergelson Yucai Peng Aeona Wasserman Kazumi Kobayashi Helena Madden Rohin Mhatre • Yelena Lyubarskaya Zoran Sosic Richard Strong Li Zang Andy Blum Tyler Carlage Hans Fajardo Damian Houde Amy Diggle Moran Samnang Tep • Damian Cunningham Mia Kiistala Maria Lacap • Graham Farrington Ann Mac. Laren Nuzhat Pathan Bioprocess Development – – – – – AD CMC Management Group – – – Research – – – Method Development / Characterization – – – – – Bioassay Development • Lynn Conley Eric Cunningham Victoria Delerue Tia Estey John Pieracci Valerie Tsang Michael Villacorta Matt Westoby Helena Yusuf-Makagiansar Qb. D Project Team – – – Vince Narbut Stephen Notarnicola Suzanne Stella
Acknowledgments Analytical Development • Testing Support – – – – • • Joseph Siemiatkoski Michael Molony Martha Berardino Namrata Chansarkar Tongjun Lu Christine Poliks Molly Roudabush – – – Svetlana Bergelson Yucai Peng Aeona Wasserman Kazumi Kobayashi Helena Madden Rohin Mhatre • Yelena Lyubarskaya Zoran Sosic Richard Strong Li Zang Andy Blum Tyler Carlage Hans Fajardo Damian Houde Amy Diggle Moran Samnang Tep • Damian Cunningham Mia Kiistala Maria Lacap • Graham Farrington Ann Mac. Laren Nuzhat Pathan Bioprocess Development – – – – – AD CMC Management Group – – – Research – – – Method Development / Characterization – – – – – Bioassay Development • Lynn Conley Eric Cunningham Victoria Delerue Tia Estey John Pieracci Valerie Tsang Michael Villacorta Matt Westoby Helena Yusuf-Makagiansar Qb. D Project Team – – – Vince Narbut Stephen Notarnicola Suzanne Stella


