e99cf549318698a8af60d01de91f1d84.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 CPSC- 120 Principle of Computer Science I Computer = Hardware + Software
CPSC- 120 Principle of Computer Science I Computer = Hardware + Software
 Hardware b. Main Memory b. Secondary Memory b. Central Processing Unit (CPU) b. Input Devises b. Output Devises
Hardware b. Main Memory b. Secondary Memory b. Central Processing Unit (CPU) b. Input Devises b. Output Devises
 Main Memory b Random Access Memory (RAM) b storing information and programs b information such as numbers, names, lists, pictures b An ordered sequence of storage locations called memory cell b each memory cell has associated with it a unique address
Main Memory b Random Access Memory (RAM) b storing information and programs b information such as numbers, names, lists, pictures b An ordered sequence of storage locations called memory cell b each memory cell has associated with it a unique address
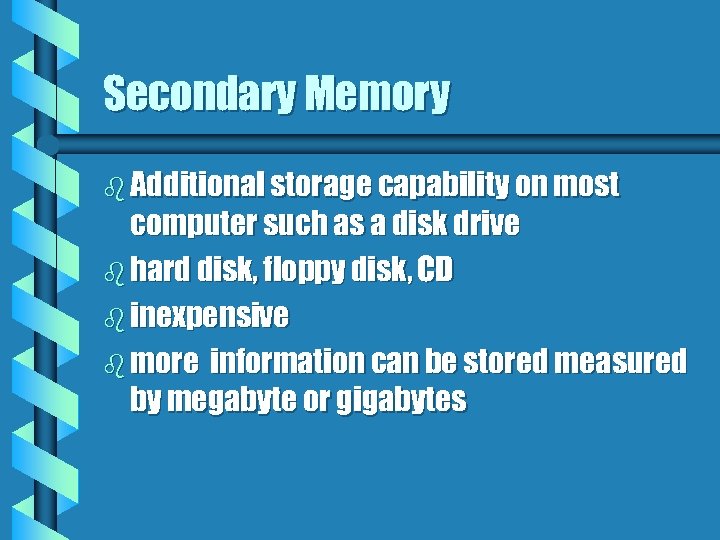 Secondary Memory b Additional storage capability on most computer such as a disk drive b hard disk, floppy disk, CD b inexpensive b more information can be stored measured by megabyte or gigabytes
Secondary Memory b Additional storage capability on most computer such as a disk drive b hard disk, floppy disk, CD b inexpensive b more information can be stored measured by megabyte or gigabytes
 Central Processing Unit (CPU) b Control computer operations b Perform arithmetic and logical operations b each operation is performed less than one millionth of a second b To process a program, CPU • fetches each instruction • decodes the instruction • executes the instruction
Central Processing Unit (CPU) b Control computer operations b Perform arithmetic and logical operations b each operation is performed less than one millionth of a second b To process a program, CPU • fetches each instruction • decodes the instruction • executes the instruction
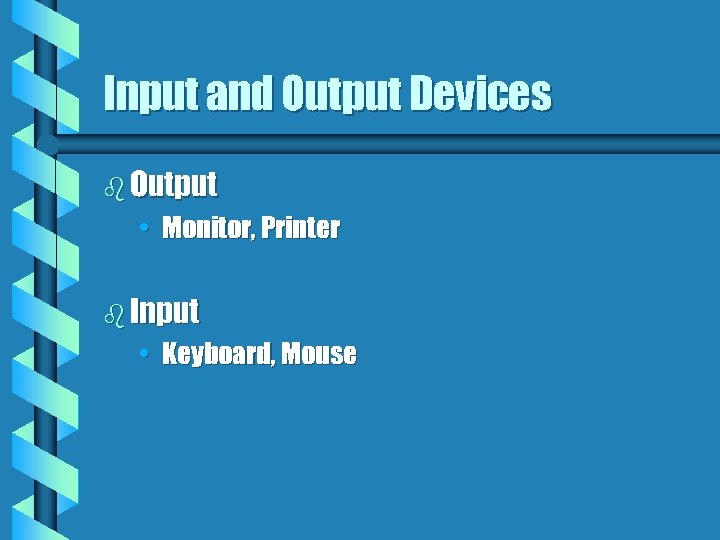 Input and Output Devices b Output • Monitor, Printer b Input • Keyboard, Mouse
Input and Output Devices b Output • Monitor, Printer b Input • Keyboard, Mouse
 Software b. Operating Systems- - UNIX, Windows b. Application Programs - - Word Processor, Spreadsheet b. Software Development Tools - - compiler, editor
Software b. Operating Systems- - UNIX, Windows b. Application Programs - - Word Processor, Spreadsheet b. Software Development Tools - - compiler, editor
 Steps in the Software Development Method b Problem Specification b Analysis b Design b Test Plan b Implementation or coding b Testing
Steps in the Software Development Method b Problem Specification b Analysis b Design b Test Plan b Implementation or coding b Testing
 Case Study b Refer to page 21
Case Study b Refer to page 21
 Programming languages b Machine Languages b Assembly Languages b High-Level Languages
Programming languages b Machine Languages b Assembly Languages b High-Level Languages
 Example Ada Program WITH Ada. Text_IO; PRODECURE Hello IS ----------------------------------- A very simple program; it is just displays a greeting. ---------------------------------BEGIN -- Hello Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => “Hello there. “); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => “We hope you enjoy studying Ada!”); Ada. Text_IO. New_Line; END Hello;
Example Ada Program WITH Ada. Text_IO; PRODECURE Hello IS ----------------------------------- A very simple program; it is just displays a greeting. ---------------------------------BEGIN -- Hello Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => “Hello there. “); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => “We hope you enjoy studying Ada!”); Ada. Text_IO. New_Line; END Hello;
 Chapter 3 The General Structure of Ada Programs
Chapter 3 The General Structure of Ada Programs
 Displaying Initials Program WITH Ada. Text_IO; PROCEDURE Hello_Initials IS -------------------------------| Requests, then displays, user's first and last initials. --| ------------------------------Initial 1 : Character; -- objects that hold initials Initial 2 : Character;
Displaying Initials Program WITH Ada. Text_IO; PROCEDURE Hello_Initials IS -------------------------------| Requests, then displays, user's first and last initials. --| ------------------------------Initial 1 : Character; -- objects that hold initials Initial 2 : Character;
 Cont. BEGIN -- Hello_Initials -- Prompt for (request user to enter) user's initials Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => "Enter your two initials> "); Ada. Text_IO. Get(Item => Initial 1); Ada. Text_IO. Get(Item => Initial 2); -- Display user's initials, with a greeting Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => "Hello "); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => Initial 1); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => Initial 2); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => ". Enjoy studying Ada!"); Ada. Text_IO. New_Line; END Hello_Initials;
Cont. BEGIN -- Hello_Initials -- Prompt for (request user to enter) user's initials Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => "Enter your two initials> "); Ada. Text_IO. Get(Item => Initial 1); Ada. Text_IO. Get(Item => Initial 2); -- Display user's initials, with a greeting Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => "Hello "); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => Initial 1); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => Initial 2); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => ". Enjoy studying Ada!"); Ada. Text_IO. New_Line; END Hello_Initials;
 Reserve Words and Identifiers b Reserve Words With Procedure IS Begin END
Reserve Words and Identifiers b Reserve Words With Procedure IS Begin END
 b Predefined Identifiers Ada. Text_IO Put New_Line Character Get
b Predefined Identifiers Ada. Text_IO Put New_Line Character Get
 Displaying the User’s Name WITH Ada. Text_IO; PROCEDURE Hello_Name IS -------------------------------------| Requests, then displays, user's name --| ------------------------------------First. Name: String(1. . 10); -- object to hold user's name
Displaying the User’s Name WITH Ada. Text_IO; PROCEDURE Hello_Name IS -------------------------------------| Requests, then displays, user's name --| ------------------------------------First. Name: String(1. . 10); -- object to hold user's name
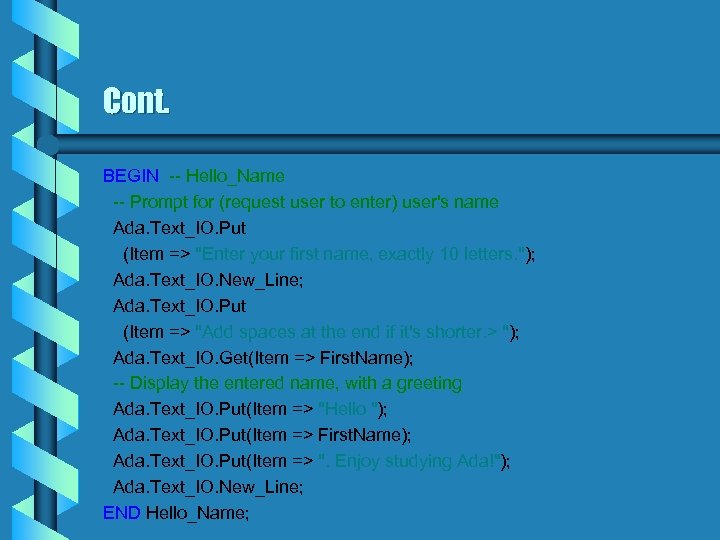 Cont. BEGIN -- Hello_Name -- Prompt for (request user to enter) user's name Ada. Text_IO. Put (Item => "Enter your first name, exactly 10 letters. "); Ada. Text_IO. New_Line; Ada. Text_IO. Put (Item => "Add spaces at the end if it's shorter. > "); Ada. Text_IO. Get(Item => First. Name); -- Display the entered name, with a greeting Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => "Hello "); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => First. Name); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => ". Enjoy studying Ada!"); Ada. Text_IO. New_Line; END Hello_Name;
Cont. BEGIN -- Hello_Name -- Prompt for (request user to enter) user's name Ada. Text_IO. Put (Item => "Enter your first name, exactly 10 letters. "); Ada. Text_IO. New_Line; Ada. Text_IO. Put (Item => "Add spaces at the end if it's shorter. > "); Ada. Text_IO. Get(Item => First. Name); -- Display the entered name, with a greeting Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => "Hello "); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => First. Name); Ada. Text_IO. Put(Item => ". Enjoy studying Ada!"); Ada. Text_IO. New_Line; END Hello_Name;
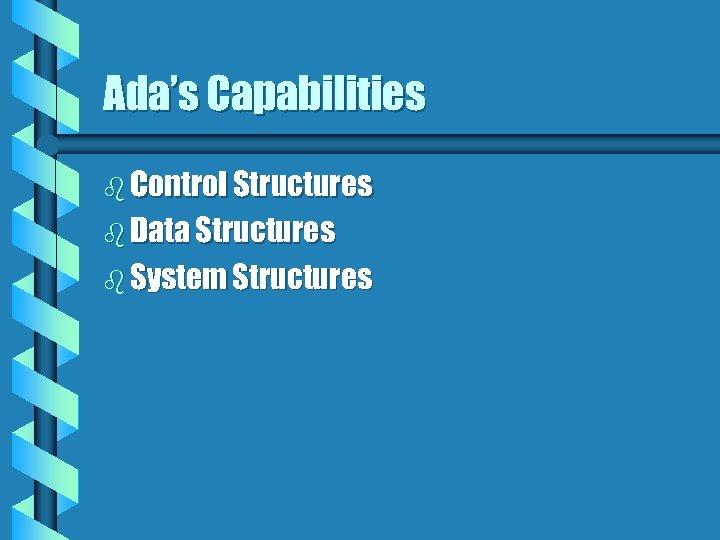 Ada’s Capabilities b Control Structures b Data Structures b System Structures
Ada’s Capabilities b Control Structures b Data Structures b System Structures



