5369d47989f6885d2c403d76cfdc32c0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 CPF Multiplier Seminar “IS PROPERTY A GOOD HEDGE AGAINST INFLATION? Sing Tien Foo Centre for Real Estate Studies National University of Singapore 3 August 2002
CPF Multiplier Seminar “IS PROPERTY A GOOD HEDGE AGAINST INFLATION? Sing Tien Foo Centre for Real Estate Studies National University of Singapore 3 August 2002
 Outline of Presentation Investing in Property Market l Why invest in Property? l Historical performance of property vs. financial assets l Is Property a good hedge against inflation? l ¡ l Evidence in overseas markets Research Methodology ¡ Types of inflation Empirical Results l Implications for investors – Diversification Strategies l Conclusion l
Outline of Presentation Investing in Property Market l Why invest in Property? l Historical performance of property vs. financial assets l Is Property a good hedge against inflation? l ¡ l Evidence in overseas markets Research Methodology ¡ Types of inflation Empirical Results l Implications for investors – Diversification Strategies l Conclusion l
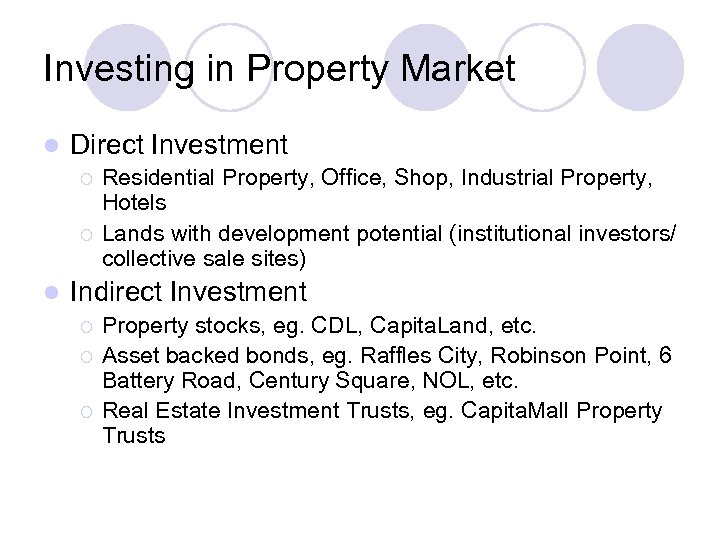 Investing in Property Market l Direct Investment ¡ ¡ l Residential Property, Office, Shop, Industrial Property, Hotels Lands with development potential (institutional investors/ collective sale sites) Indirect Investment ¡ ¡ ¡ Property stocks, eg. CDL, Capita. Land, etc. Asset backed bonds, eg. Raffles City, Robinson Point, 6 Battery Road, Century Square, NOL, etc. Real Estate Investment Trusts, eg. Capita. Mall Property Trusts
Investing in Property Market l Direct Investment ¡ ¡ l Residential Property, Office, Shop, Industrial Property, Hotels Lands with development potential (institutional investors/ collective sale sites) Indirect Investment ¡ ¡ ¡ Property stocks, eg. CDL, Capita. Land, etc. Asset backed bonds, eg. Raffles City, Robinson Point, 6 Battery Road, Century Square, NOL, etc. Real Estate Investment Trusts, eg. Capita. Mall Property Trusts
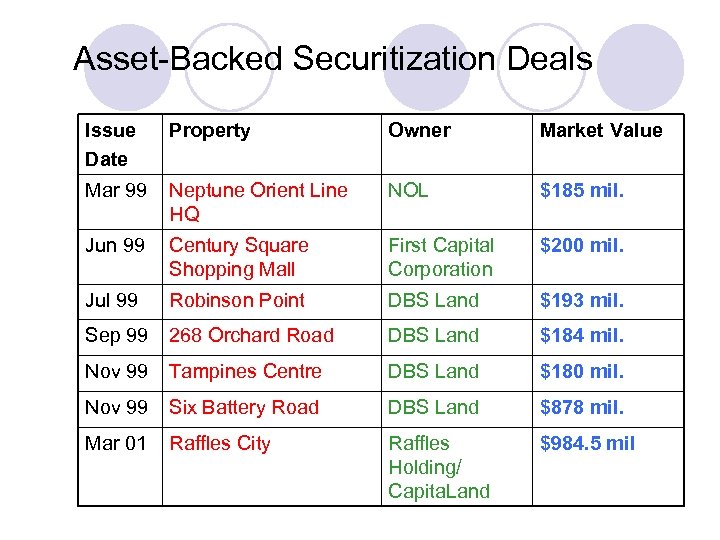 Asset-Backed Securitization Deals Issue Date Property Owner Market Value Mar 99 Neptune Orient Line HQ NOL $185 mil. Jun 99 Century Square Shopping Mall First Capital Corporation $200 mil. Jul 99 Robinson Point DBS Land $193 mil. Sep 99 268 Orchard Road DBS Land $184 mil. Nov 99 Tampines Centre DBS Land $180 mil. Nov 99 Six Battery Road DBS Land $878 mil. Mar 01 Raffles City Raffles Holding/ Capita. Land $984. 5 mil
Asset-Backed Securitization Deals Issue Date Property Owner Market Value Mar 99 Neptune Orient Line HQ NOL $185 mil. Jun 99 Century Square Shopping Mall First Capital Corporation $200 mil. Jul 99 Robinson Point DBS Land $193 mil. Sep 99 268 Orchard Road DBS Land $184 mil. Nov 99 Tampines Centre DBS Land $180 mil. Nov 99 Six Battery Road DBS Land $878 mil. Mar 01 Raffles City Raffles Holding/ Capita. Land $984. 5 mil
 Other Secondary Property Market Instruments l Hedging ¡ Single l New instrument Property Future mortgage instruments (Potential) ¡ Mortgage REITs ¡ Mortgage Backed Securities ¡ Commercial Mortgage Backed Obligations
Other Secondary Property Market Instruments l Hedging ¡ Single l New instrument Property Future mortgage instruments (Potential) ¡ Mortgage REITs ¡ Mortgage Backed Securities ¡ Commercial Mortgage Backed Obligations
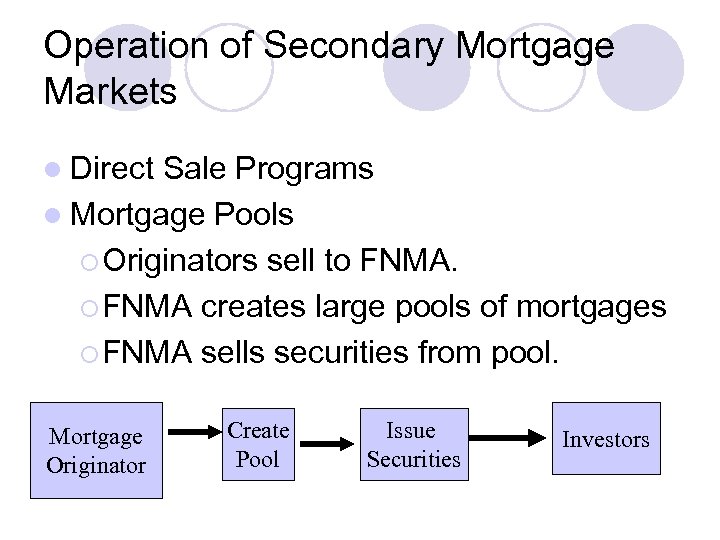 Operation of Secondary Mortgage Markets l Direct Sale Programs l Mortgage Pools ¡ Originators sell to FNMA. ¡ FNMA creates large pools of mortgages ¡ FNMA sells securities from pool. Mortgage Originator Create Pool Issue Securities Investors
Operation of Secondary Mortgage Markets l Direct Sale Programs l Mortgage Pools ¡ Originators sell to FNMA. ¡ FNMA creates large pools of mortgages ¡ FNMA sells securities from pool. Mortgage Originator Create Pool Issue Securities Investors
 Why invest in Property? For a wealth maximizing investor: l Pride of ownership l Desired rate of return l Capital appreciation l Risk diversification l Hedge against inflation
Why invest in Property? For a wealth maximizing investor: l Pride of ownership l Desired rate of return l Capital appreciation l Risk diversification l Hedge against inflation
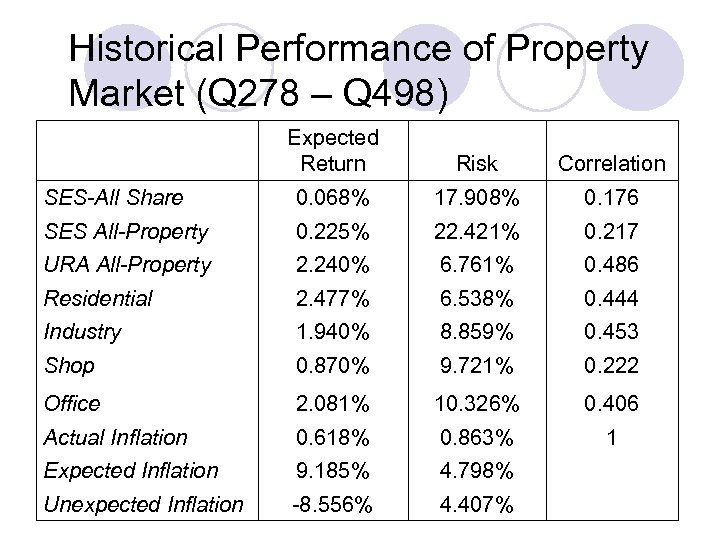 Historical Performance of Property Market (Q 278 – Q 498) Expected Return Risk Correlation SES-All Share 0. 068% 17. 908% 0. 176 SES All-Property 0. 225% 22. 421% 0. 217 URA All-Property 2. 240% 6. 761% 0. 486 Residential 2. 477% 6. 538% 0. 444 Industry 1. 940% 8. 859% 0. 453 Shop 0. 870% 9. 721% 0. 222 Office 2. 081% 10. 326% 0. 406 Actual Inflation 0. 618% 0. 863% 1 Expected Inflation 9. 185% 4. 798% Unexpected Inflation -8. 556% 4. 407%
Historical Performance of Property Market (Q 278 – Q 498) Expected Return Risk Correlation SES-All Share 0. 068% 17. 908% 0. 176 SES All-Property 0. 225% 22. 421% 0. 217 URA All-Property 2. 240% 6. 761% 0. 486 Residential 2. 477% 6. 538% 0. 444 Industry 1. 940% 8. 859% 0. 453 Shop 0. 870% 9. 721% 0. 222 Office 2. 081% 10. 326% 0. 406 Actual Inflation 0. 618% 0. 863% 1 Expected Inflation 9. 185% 4. 798% Unexpected Inflation -8. 556% 4. 407%
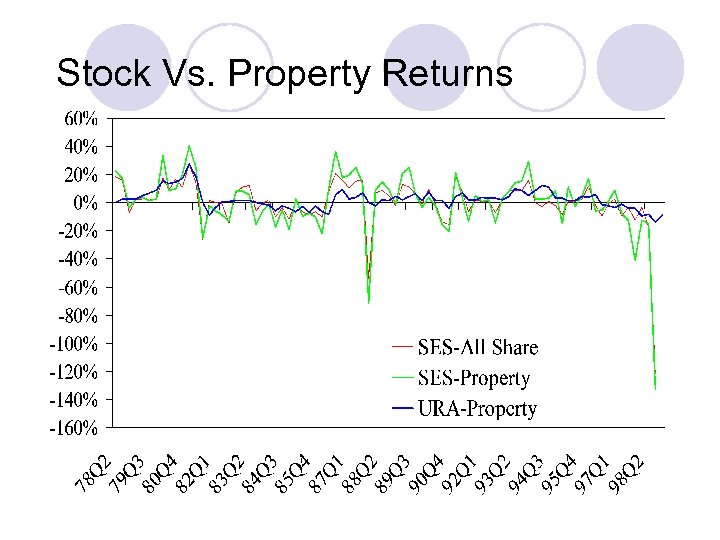 Stock Vs. Property Returns
Stock Vs. Property Returns
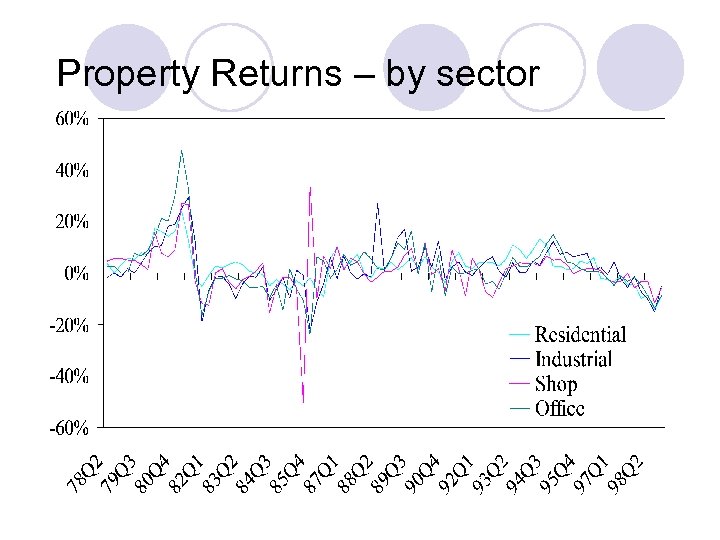 Property Returns – by sector
Property Returns – by sector
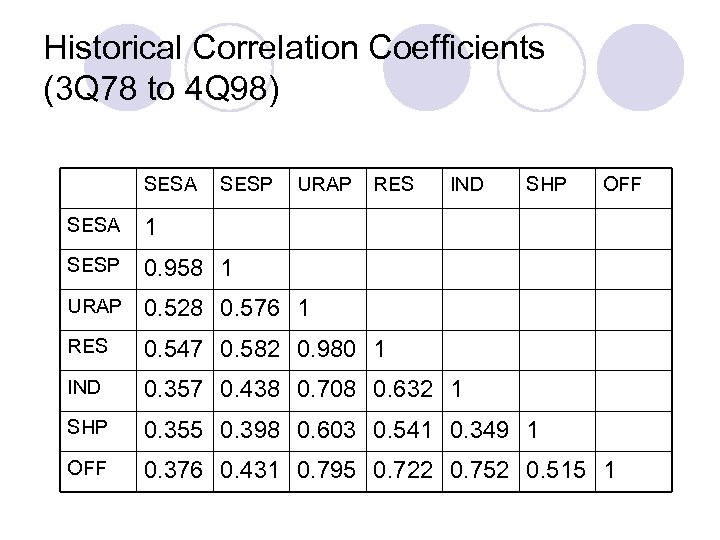 Historical Correlation Coefficients (3 Q 78 to 4 Q 98) SESA SESP URAP RES IND SHP OFF SESA 1 SESP 0. 958 1 URAP 0. 528 0. 576 1 RES 0. 547 0. 582 0. 980 1 IND 0. 357 0. 438 0. 708 0. 632 1 SHP 0. 355 0. 398 0. 603 0. 541 0. 349 1 OFF 0. 376 0. 431 0. 795 0. 722 0. 752 0. 515 1
Historical Correlation Coefficients (3 Q 78 to 4 Q 98) SESA SESP URAP RES IND SHP OFF SESA 1 SESP 0. 958 1 URAP 0. 528 0. 576 1 RES 0. 547 0. 582 0. 980 1 IND 0. 357 0. 438 0. 708 0. 632 1 SHP 0. 355 0. 398 0. 603 0. 541 0. 349 1 OFF 0. 376 0. 431 0. 795 0. 722 0. 752 0. 515 1
 Overview of Historical Inflation Rates Inflation is defined as an increase in general price level in the economy l Measured by CPI, GDP deflator, RPI l Inflation rate in Singapore has been relatively stable, especially over the last 10 years l Average 0. 62% per quarter (or 2. 48% annualized) 1978 -1998 l
Overview of Historical Inflation Rates Inflation is defined as an increase in general price level in the economy l Measured by CPI, GDP deflator, RPI l Inflation rate in Singapore has been relatively stable, especially over the last 10 years l Average 0. 62% per quarter (or 2. 48% annualized) 1978 -1998 l
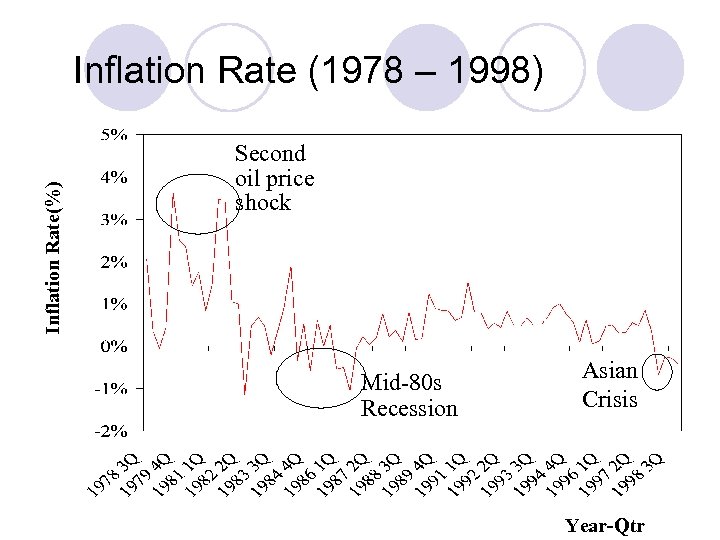 Inflation Rate(%) Inflation Rate (1978 – 1998) Second oil price shock Mid-80 s Recession Asian Crisis Year-Qtr
Inflation Rate(%) Inflation Rate (1978 – 1998) Second oil price shock Mid-80 s Recession Asian Crisis Year-Qtr
 Is real estate a good hedge against inflation? Real estate has been widely regarded as a good hedge against inflation vis-à-vis other financial assets l The study aims to empirically test the inflation hedging characteristics of the returns of real estate and other financial assets l l Related research questions: ¡ ¡ ¡ Real Estate by sectors: residential, shop, industry, and office Type of inflation: actual, expected and unexpected Over different sample periods Different inflation regimes Compared with different financial assets
Is real estate a good hedge against inflation? Real estate has been widely regarded as a good hedge against inflation vis-à-vis other financial assets l The study aims to empirically test the inflation hedging characteristics of the returns of real estate and other financial assets l l Related research questions: ¡ ¡ ¡ Real Estate by sectors: residential, shop, industry, and office Type of inflation: actual, expected and unexpected Over different sample periods Different inflation regimes Compared with different financial assets
 Country-studies on Inflation Hedging l l l Mainly in US and other countries Comparing real estate and other assets In the US, REITs is used as proxy of real estate Using the classical Fama and Schwert (1977) framework Serial-correlation is taken care of in the model In general, findings show that real estate is good inflation hedge
Country-studies on Inflation Hedging l l l Mainly in US and other countries Comparing real estate and other assets In the US, REITs is used as proxy of real estate Using the classical Fama and Schwert (1977) framework Serial-correlation is taken care of in the model In general, findings show that real estate is good inflation hedge
 Overseas Evidence (1) – Real Estate In the US, real estate has positive hedge against expected inflation, but office and industrial property offer no significant hedge against unexpected inflation l In the UK, real estate offer good protection against inflation, and office and shop did not hedge against unexpected inflation l Capital returns hedge against unexpected inflation l Results of studies in Switzerland, Canada, New Zealand an d. Hong Kong are consistent l
Overseas Evidence (1) – Real Estate In the US, real estate has positive hedge against expected inflation, but office and industrial property offer no significant hedge against unexpected inflation l In the UK, real estate offer good protection against inflation, and office and shop did not hedge against unexpected inflation l Capital returns hedge against unexpected inflation l Results of studies in Switzerland, Canada, New Zealand an d. Hong Kong are consistent l
 Overseas Evidence (2) - Stocks l l l In the US & UK, studies showed that stocks offer no significant hedge against inflation In the UK, when returns were decomposed into capital and income returns, income did significantly hedge against inflation Swiss stock market also offers no hedge against inflation In New Zealand Hong Kong, stocks offer negative hedge against inflation REITs in the US, UK and Australia show no hedge against inflation
Overseas Evidence (2) - Stocks l l l In the US & UK, studies showed that stocks offer no significant hedge against inflation In the UK, when returns were decomposed into capital and income returns, income did significantly hedge against inflation Swiss stock market also offers no hedge against inflation In New Zealand Hong Kong, stocks offer negative hedge against inflation REITs in the US, UK and Australia show no hedge against inflation
 Overseas Evidence (3) – Bonds offer no hedge against inflation in the US, UK, New Zealand Australia l In summary, real estate offer good hedge against expected inflation, but not against unexpected inflation l Stock, real estate stocks (REITs), and bonds offer poor hedge against inflation in most of the countries under studies l
Overseas Evidence (3) – Bonds offer no hedge against inflation in the US, UK, New Zealand Australia l In summary, real estate offer good hedge against expected inflation, but not against unexpected inflation l Stock, real estate stocks (REITs), and bonds offer poor hedge against inflation in most of the countries under studies l
 Inflation & Inflation Hedging CPI is compiled by the Dept of Statistics (DOS) l Laspeye Index – a fixed basket of goods and services in CPI l ¡ 7 broad categories of goods & services in CPI basket: food, housing, transport & communications, clothing, health, education and miscellaneous Inflation hedging – the real return of an asset is independent of the rate of inflation l An asset is a complete hedge against inflation, if and only if the nominal return of the asset changes in a one-to-one relationship with both expected & unexpected inflation l
Inflation & Inflation Hedging CPI is compiled by the Dept of Statistics (DOS) l Laspeye Index – a fixed basket of goods and services in CPI l ¡ 7 broad categories of goods & services in CPI basket: food, housing, transport & communications, clothing, health, education and miscellaneous Inflation hedging – the real return of an asset is independent of the rate of inflation l An asset is a complete hedge against inflation, if and only if the nominal return of the asset changes in a one-to-one relationship with both expected & unexpected inflation l
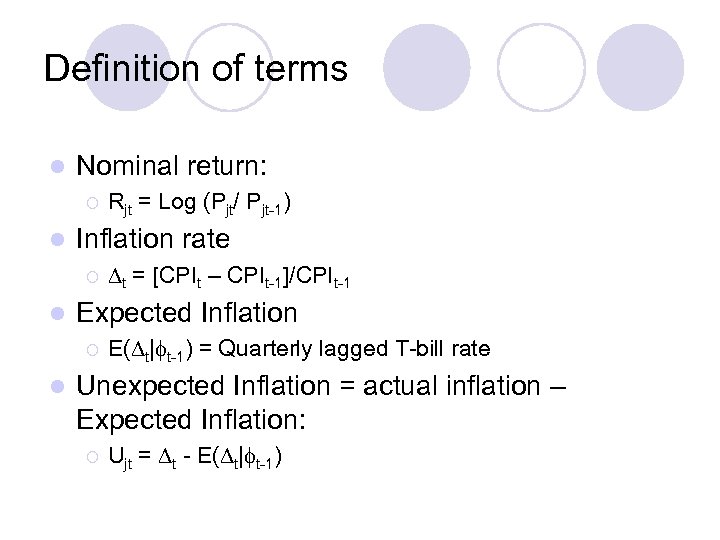 Definition of terms l Nominal return: ¡ l Inflation rate ¡ l t = [CPIt – CPIt-1]/CPIt-1 Expected Inflation ¡ l Rjt = Log (Pjt/ Pjt-1) E( t| t-1) = Quarterly lagged T-bill rate Unexpected Inflation = actual inflation – Expected Inflation: ¡ Ujt = t - E( t| t-1)
Definition of terms l Nominal return: ¡ l Inflation rate ¡ l t = [CPIt – CPIt-1]/CPIt-1 Expected Inflation ¡ l Rjt = Log (Pjt/ Pjt-1) E( t| t-1) = Quarterly lagged T-bill rate Unexpected Inflation = actual inflation – Expected Inflation: ¡ Ujt = t - E( t| t-1)
 Data Source l l l Sample period 1978 Q 3– 1998 Q 4 URA all property price index and related subindices SES all-share index Consumer Price Index (CPI) Treasury bill rate Nominal return ¡ Rjt = Log (Pjt/ Pjt-1)
Data Source l l l Sample period 1978 Q 3– 1998 Q 4 URA all property price index and related subindices SES all-share index Consumer Price Index (CPI) Treasury bill rate Nominal return ¡ Rjt = Log (Pjt/ Pjt-1)
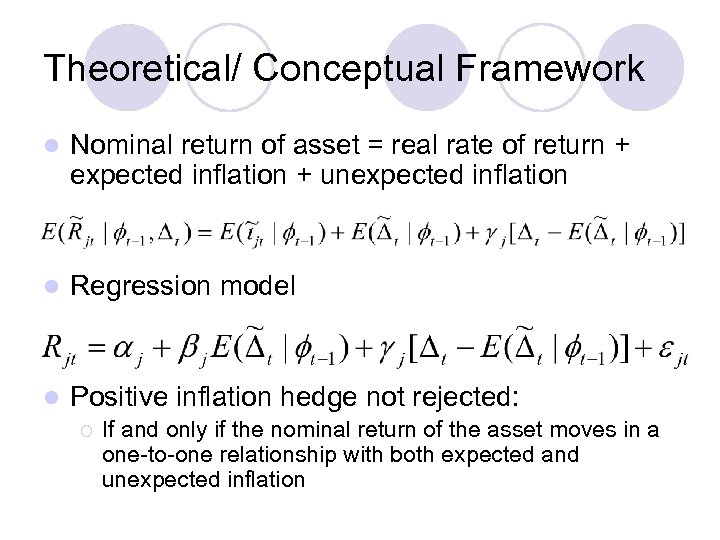 Theoretical/ Conceptual Framework l Nominal return of asset = real rate of return + expected inflation + unexpected inflation l Regression model l Positive inflation hedge not rejected: ¡ If and only if the nominal return of the asset moves in a one-to-one relationship with both expected and unexpected inflation
Theoretical/ Conceptual Framework l Nominal return of asset = real rate of return + expected inflation + unexpected inflation l Regression model l Positive inflation hedge not rejected: ¡ If and only if the nominal return of the asset moves in a one-to-one relationship with both expected and unexpected inflation
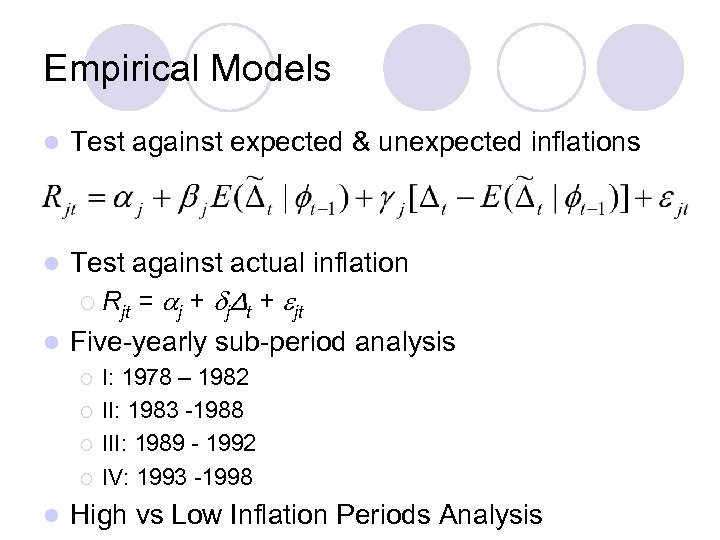 Empirical Models l Test against expected & unexpected inflations Test against actual inflation ¡ Rjt = j + jΔt + jt l Five-yearly sub-period analysis l ¡ ¡ l I: 1978 – 1982 II: 1983 -1988 III: 1989 - 1992 IV: 1993 -1998 High vs Low Inflation Periods Analysis
Empirical Models l Test against expected & unexpected inflations Test against actual inflation ¡ Rjt = j + jΔt + jt l Five-yearly sub-period analysis l ¡ ¡ l I: 1978 – 1982 II: 1983 -1988 III: 1989 - 1992 IV: 1993 -1998 High vs Low Inflation Periods Analysis
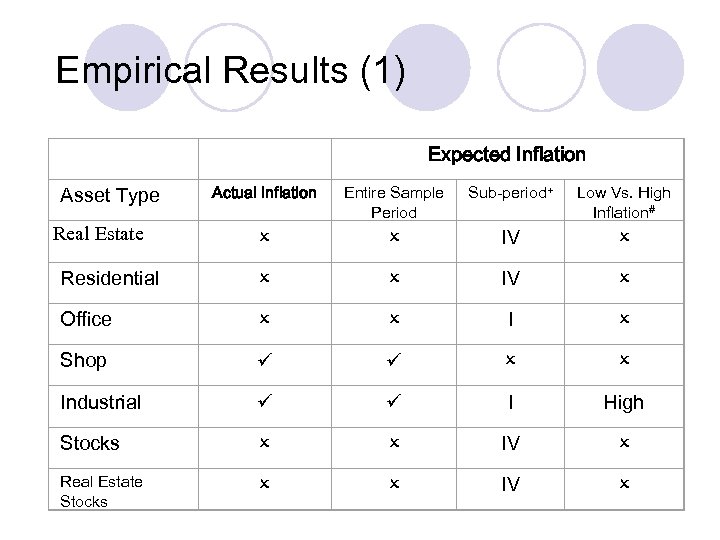 Empirical Results (1) Asset Type Actual Inflation Entire Sample Period Sub-period+ Low Vs. High Inflation# IV Residential IV Office I Shop Industrial I High Stocks IV Real Estate Expected Inflation
Empirical Results (1) Asset Type Actual Inflation Entire Sample Period Sub-period+ Low Vs. High Inflation# IV Residential IV Office I Shop Industrial I High Stocks IV Real Estate Expected Inflation
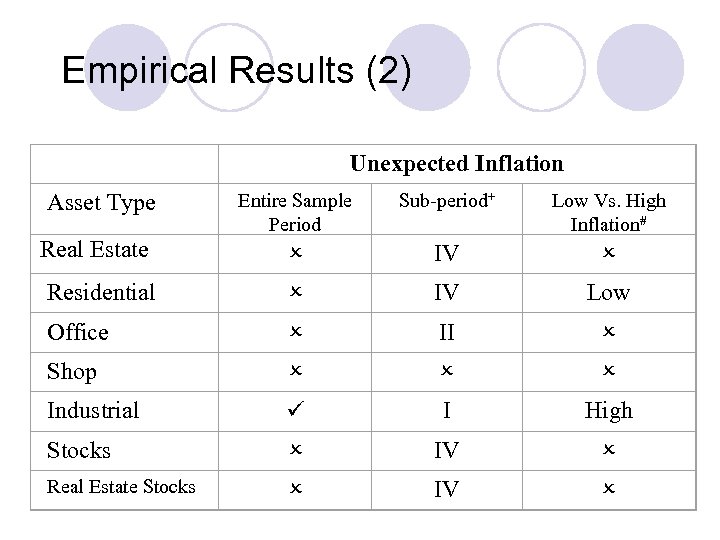 Empirical Results (2) Unexpected Inflation Entire Sample Period Sub-period+ Low Vs. High Inflation# Real Estate IV Residential IV Low Office II Shop Industrial I High Stocks IV Real Estate Stocks IV Asset Type
Empirical Results (2) Unexpected Inflation Entire Sample Period Sub-period+ Low Vs. High Inflation# Real Estate IV Residential IV Low Office II Shop Industrial I High Stocks IV Real Estate Stocks IV Asset Type
 Analysis of Results (1) See tables l Real estate assets (industrial & shop) are better hedges against inflation compared to financial assets l Industry show significant hedges against expected and unexpected inflations & shop hedge effectively against expected inflation l Residential property offers good hedge against expected and unexpected inflations for sub-period IV (1993 -1998) l
Analysis of Results (1) See tables l Real estate assets (industrial & shop) are better hedges against inflation compared to financial assets l Industry show significant hedges against expected and unexpected inflations & shop hedge effectively against expected inflation l Residential property offers good hedge against expected and unexpected inflations for sub-period IV (1993 -1998) l
 Analysis of Results (2) Stock and property stocks also provide good hedge against expected and unexpected inflation in sub-period IV l Office and industrial property perform better in sub-period I (1978 -1982) l In high inflation period, industrial is good asset for inflation hedging, whereas residential is more suitable during inflation period. l
Analysis of Results (2) Stock and property stocks also provide good hedge against expected and unexpected inflation in sub-period IV l Office and industrial property perform better in sub-period I (1978 -1982) l In high inflation period, industrial is good asset for inflation hedging, whereas residential is more suitable during inflation period. l
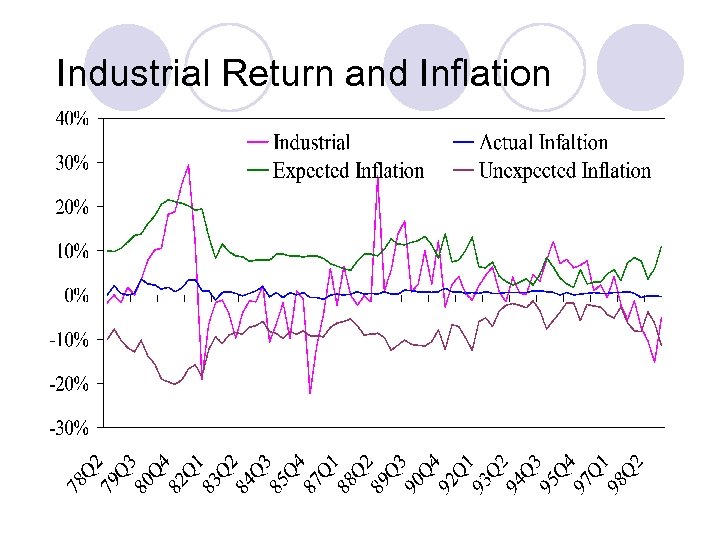 Industrial Return and Inflation
Industrial Return and Inflation
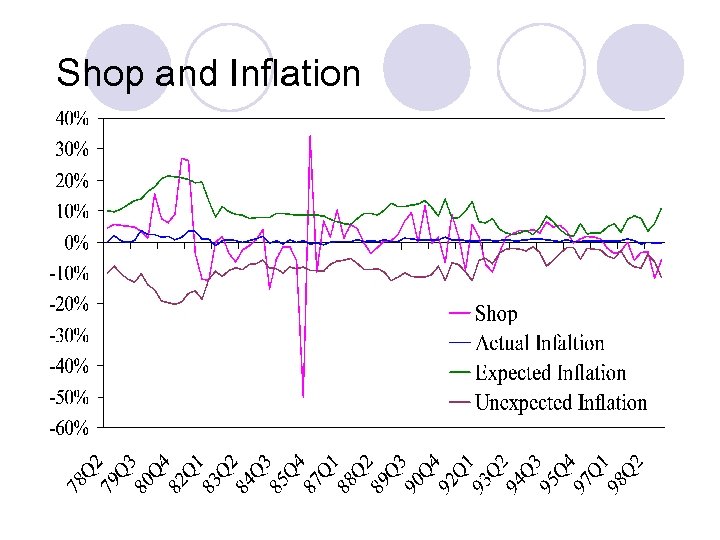 Shop and Inflation
Shop and Inflation
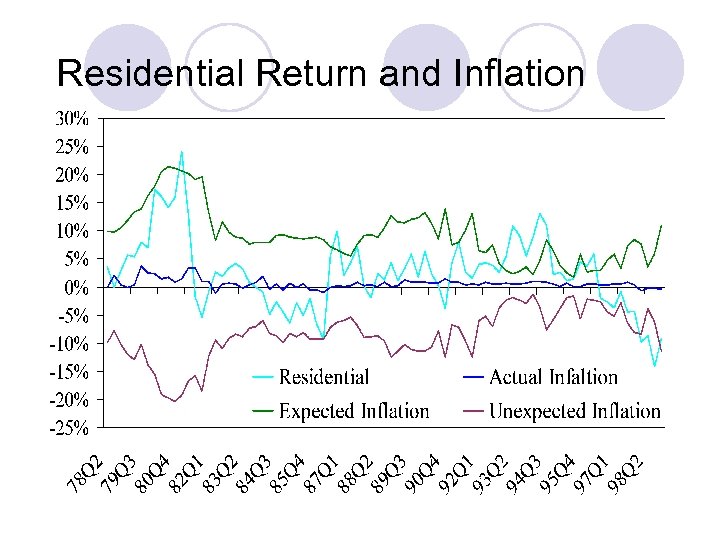 Residential Return and Inflation
Residential Return and Inflation
 Implications for investors’ Strategies It is strategic to improve hedging capability of institutional portfolio by increasing the asset weight of industrial and retail properties l However, in Singapore, investment in industrial property is limited and dominated by public agency like Ascendas and JTC l Strict restrictions on industrial land uses limit the upside potential l For retail properties, majority of prime shopping centers are developed and managed by institutional investors for long term investment purposes l
Implications for investors’ Strategies It is strategic to improve hedging capability of institutional portfolio by increasing the asset weight of industrial and retail properties l However, in Singapore, investment in industrial property is limited and dominated by public agency like Ascendas and JTC l Strict restrictions on industrial land uses limit the upside potential l For retail properties, majority of prime shopping centers are developed and managed by institutional investors for long term investment purposes l
 Implications for Investors’ Strategies l l l Economies of scale for single ownership for shopping centers – resources could be optimized for implementing crowd-pulling tenant mix strategies New investment vehicles, new launched retail REITs and the proposed industrial REITs For residential property, good news for investors/owners of CPF financed private residential property, their property value will be preserved in low inflation period Residential property has performed well in 1993 -1998 period Stock and property stocks have also performed well against expected and unexpected inflation
Implications for Investors’ Strategies l l l Economies of scale for single ownership for shopping centers – resources could be optimized for implementing crowd-pulling tenant mix strategies New investment vehicles, new launched retail REITs and the proposed industrial REITs For residential property, good news for investors/owners of CPF financed private residential property, their property value will be preserved in low inflation period Residential property has performed well in 1993 -1998 period Stock and property stocks have also performed well against expected and unexpected inflation
 Diversification Strategy l l l How much investment should be allocated to property and non-property assets? Diversification benefits – not putting all your eggs in one basket Using empirical returns data from 4 Q 1993 to 4 Q 2000 Using Markowitz’s risk-return optimization framework Minimizing portfolio risks for a given portfolio return No short-selling and no borrowing in the portfolio
Diversification Strategy l l l How much investment should be allocated to property and non-property assets? Diversification benefits – not putting all your eggs in one basket Using empirical returns data from 4 Q 1993 to 4 Q 2000 Using Markowitz’s risk-return optimization framework Minimizing portfolio risks for a given portfolio return No short-selling and no borrowing in the portfolio
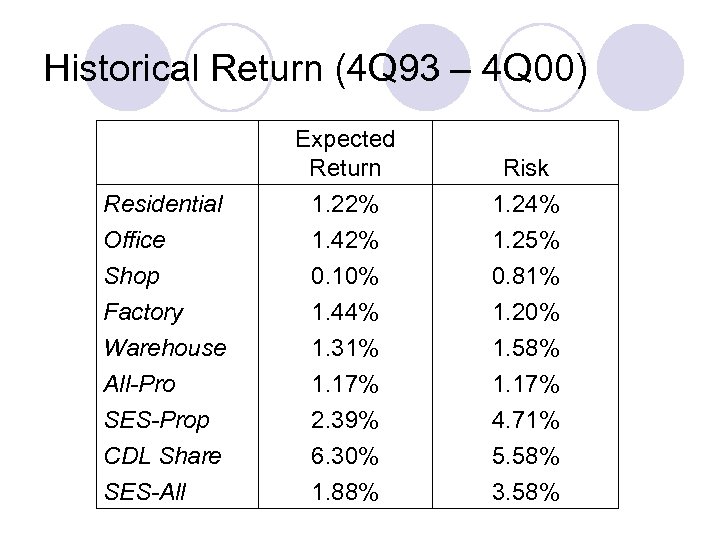 Historical Return (4 Q 93 – 4 Q 00) Residential Office Shop Factory Warehouse All-Pro SES-Prop CDL Share SES-All Expected Return 1. 22% 1. 42% 0. 10% 1. 44% 1. 31% 1. 17% 2. 39% 6. 30% 1. 88% Risk 1. 24% 1. 25% 0. 81% 1. 20% 1. 58% 1. 17% 4. 71% 5. 58% 3. 58%
Historical Return (4 Q 93 – 4 Q 00) Residential Office Shop Factory Warehouse All-Pro SES-Prop CDL Share SES-All Expected Return 1. 22% 1. 42% 0. 10% 1. 44% 1. 31% 1. 17% 2. 39% 6. 30% 1. 88% Risk 1. 24% 1. 25% 0. 81% 1. 20% 1. 58% 1. 17% 4. 71% 5. 58% 3. 58%
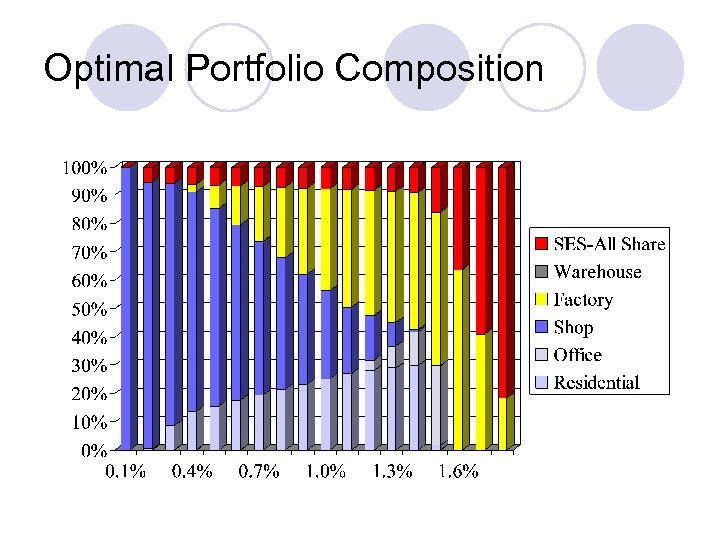 Optimal Portfolio Composition
Optimal Portfolio Composition
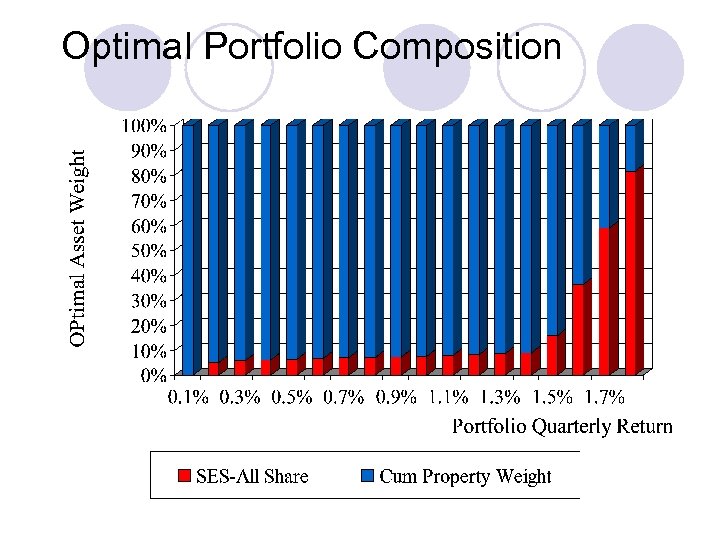 Optimal Portfolio Composition
Optimal Portfolio Composition
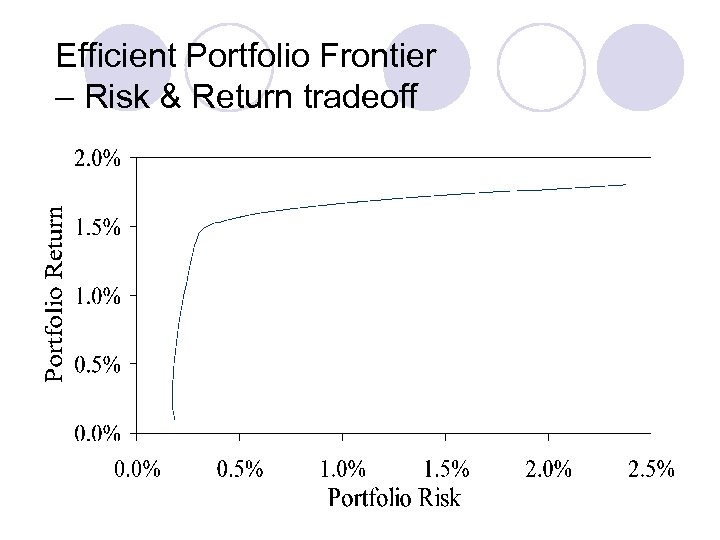 Efficient Portfolio Frontier – Risk & Return tradeoff
Efficient Portfolio Frontier – Risk & Return tradeoff
 Conclusion l l l Do not reject the null hypothesis that real estate is a good hedge against inflation Real estate assets are better hedges against inflation vis-à-vis financial assets Industrial & shop are good assets for inflation hedging purposes Industrial and retail REITs offer alternative channels for increasing asset weights in portfolio Residential property value will be preserved in low inflation regime Real Estate composition in institutional portfolio is important for risk diversification purposes
Conclusion l l l Do not reject the null hypothesis that real estate is a good hedge against inflation Real estate assets are better hedges against inflation vis-à-vis financial assets Industrial & shop are good assets for inflation hedging purposes Industrial and retail REITs offer alternative channels for increasing asset weights in portfolio Residential property value will be preserved in low inflation regime Real Estate composition in institutional portfolio is important for risk diversification purposes
 l Thank you
l Thank you


