9db3679b7ebc02521c900233e33718c7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 57
 CP US History Unit #1 – Civil War & Reconstruction
CP US History Unit #1 – Civil War & Reconstruction
 Key Learning • Compare historical interpretations of the Civil War and Reconstruction Unit Essential Question • How do historical interpretations of the Civil War and Reconstruction differ between Northern and Southern interpretations?
Key Learning • Compare historical interpretations of the Civil War and Reconstruction Unit Essential Question • How do historical interpretations of the Civil War and Reconstruction differ between Northern and Southern interpretations?
 Concept and Standard • Standard – History #3 A • Concept – How do historical interpretations of the causes and outcomes of the Civil War differ between Northern and Southern historians?
Concept and Standard • Standard – History #3 A • Concept – How do historical interpretations of the causes and outcomes of the Civil War differ between Northern and Southern historians?
 Lesson Essential Question #1 • Why did the Civil War begin? Key Ideas and Vocabulary • • • Uncle Tom’s Cabin Compromise of 1850 Fugitive Slave Act Charles Sumner Dred Scott John Brown • Election of 1860 • Secession • Confederate States of America • Abraham Lincoln • Jefferson Davis • Fort Sumter
Lesson Essential Question #1 • Why did the Civil War begin? Key Ideas and Vocabulary • • • Uncle Tom’s Cabin Compromise of 1850 Fugitive Slave Act Charles Sumner Dred Scott John Brown • Election of 1860 • Secession • Confederate States of America • Abraham Lincoln • Jefferson Davis • Fort Sumter
 What do you know? • With a partner, brain storm what you know about the American Civil War. • Create a list of people, places, events that occurred during the war. • Create another list of reasons for why the American Civil War began. • Be prepared to share with class.
What do you know? • With a partner, brain storm what you know about the American Civil War. • Create a list of people, places, events that occurred during the war. • Create another list of reasons for why the American Civil War began. • Be prepared to share with class.
 The Civil War Causes and Impact
The Civil War Causes and Impact
 Thomas Jefferson • “In the gloomiest moments of the Revolutionary War, I never had any fear equal to what I feel from this source… We have a wolf by the ears, and we can neither hold him nor safely let him go. ” What do you think I was talking about when I made this statement?
Thomas Jefferson • “In the gloomiest moments of the Revolutionary War, I never had any fear equal to what I feel from this source… We have a wolf by the ears, and we can neither hold him nor safely let him go. ” What do you think I was talking about when I made this statement?
 Economic and Social differences southern economy: one crop economy, based on cotton and dependant on slavery. northern economy: based more on industry and finished goods Northern cities; many cultures used to working together South: highly structured, conservative, class-conscious
Economic and Social differences southern economy: one crop economy, based on cotton and dependant on slavery. northern economy: based more on industry and finished goods Northern cities; many cultures used to working together South: highly structured, conservative, class-conscious
 Antislavery • Harriet Beecher Stowe – “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” Southern Reaction to Uncle Tom’s Cabin pg 300
Antislavery • Harriet Beecher Stowe – “Uncle Tom’s Cabin” Southern Reaction to Uncle Tom’s Cabin pg 300
 UNCLE TOM’S CABIN • READ EXCEPRT FROM UNCLE TOM’S CABIN – ANSWER QUESTIONS THAT ARE ATTACHED ON SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER
UNCLE TOM’S CABIN • READ EXCEPRT FROM UNCLE TOM’S CABIN – ANSWER QUESTIONS THAT ARE ATTACHED ON SEPARATE SHEET OF PAPER
 Do Now: Why was the North Opposed to Slavery? Why did the South Support it?
Do Now: Why was the North Opposed to Slavery? Why did the South Support it?
 The Slavery Question Missouri Compromise (1820) • Established a Balance between free and slave states A. Missouri enters union as a slave state B. Maine enters union as a free state C. Slavery is banned over the 36’ 30’ line
The Slavery Question Missouri Compromise (1820) • Established a Balance between free and slave states A. Missouri enters union as a slave state B. Maine enters union as a free state C. Slavery is banned over the 36’ 30’ line
 1846 - As a result of the Mexican War, the U. S. gains more land in the West known as the Mexican Cession. Congress now has to decide whether to allow slavery in these territories.
1846 - As a result of the Mexican War, the U. S. gains more land in the West known as the Mexican Cession. Congress now has to decide whether to allow slavery in these territories.
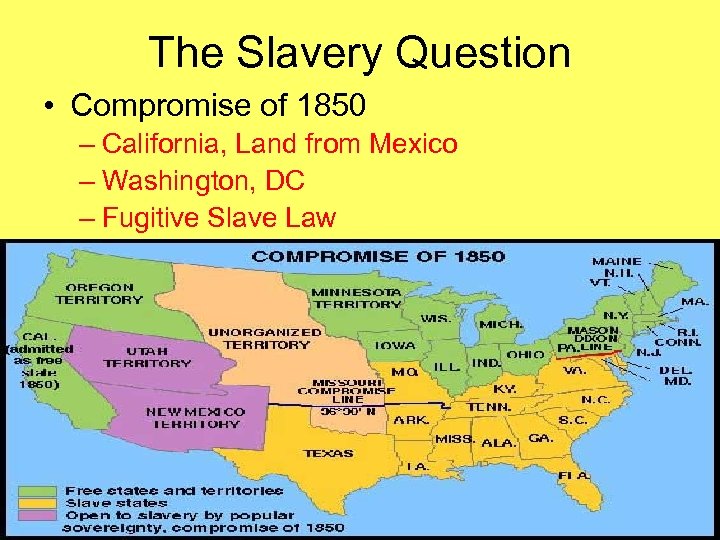 The Slavery Question • Compromise of 1850 – California, Land from Mexico – Washington, DC – Fugitive Slave Law
The Slavery Question • Compromise of 1850 – California, Land from Mexico – Washington, DC – Fugitive Slave Law
 Fugitive Slave Law of 1850 A. Required all citizens to help catch runaway slaves B. People who let slaves escape could be fined $1000 and get 6 months in jail
Fugitive Slave Law of 1850 A. Required all citizens to help catch runaway slaves B. People who let slaves escape could be fined $1000 and get 6 months in jail
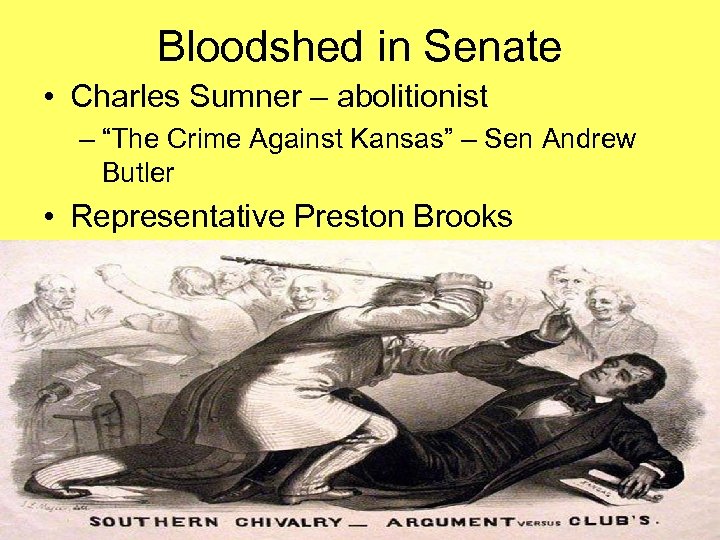 Bloodshed in Senate • Charles Sumner – abolitionist – “The Crime Against Kansas” – Sen Andrew Butler • Representative Preston Brooks
Bloodshed in Senate • Charles Sumner – abolitionist – “The Crime Against Kansas” – Sen Andrew Butler • Representative Preston Brooks
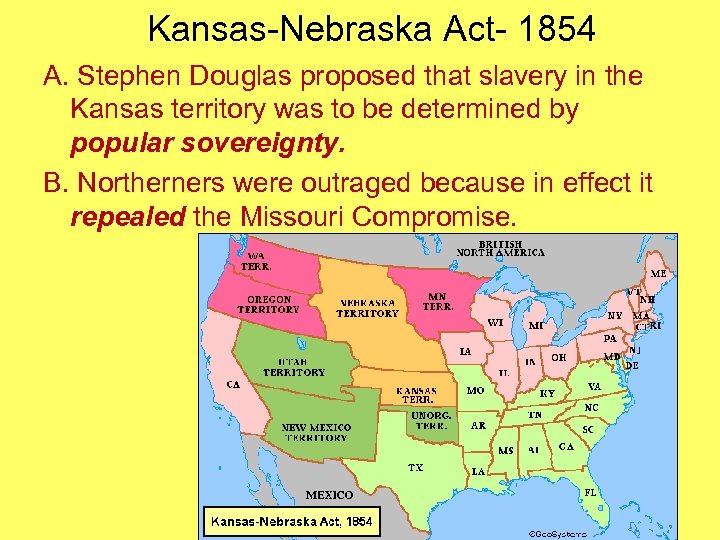 Kansas-Nebraska Act- 1854 A. Stephen Douglas proposed that slavery in the Kansas territory was to be determined by popular sovereignty. B. Northerners were outraged because in effect it repealed the Missouri Compromise.
Kansas-Nebraska Act- 1854 A. Stephen Douglas proposed that slavery in the Kansas territory was to be determined by popular sovereignty. B. Northerners were outraged because in effect it repealed the Missouri Compromise.
 C. During elections to choose lawmakers, hundreds of Border Ruffians crossed into Kansas. Fighting erupted and Kansas was in chaos. D. 200 people died, known as “Bleeding Kansas”
C. During elections to choose lawmakers, hundreds of Border Ruffians crossed into Kansas. Fighting erupted and Kansas was in chaos. D. 200 people died, known as “Bleeding Kansas”
 Dred Scott Case • Dred Scott’s Journey • Filed suit for Freedom • Supreme Court Decision – Enslaved people were property – Only citizens could sue others HW – Read “North and South”
Dred Scott Case • Dred Scott’s Journey • Filed suit for Freedom • Supreme Court Decision – Enslaved people were property – Only citizens could sue others HW – Read “North and South”
 Elections and Revolts: The Last Straw I. Republican Party is formed -1854 main goal -> to stop the spread of slavery.
Elections and Revolts: The Last Straw I. Republican Party is formed -1854 main goal -> to stop the spread of slavery.
 III. John Brown’s Raid on Harper’s Ferry A. was anti-slave B. raided an arsenal -> weapons for a slave revolt at Harper’s Ferry, Virginia C. Northerners saw him as a martyr D. Southerners were convinced that northerners wanted to destroy slavery
III. John Brown’s Raid on Harper’s Ferry A. was anti-slave B. raided an arsenal -> weapons for a slave revolt at Harper’s Ferry, Virginia C. Northerners saw him as a martyr D. Southerners were convinced that northerners wanted to destroy slavery
 DVD – JOHN BROWN • WATCH DVD OF JOHN BROWN’S ATTACK ON HARPER’S FERRY, VA • ANSWER QUESTIONS WHILE WATCHING DVD
DVD – JOHN BROWN • WATCH DVD OF JOHN BROWN’S ATTACK ON HARPER’S FERRY, VA • ANSWER QUESTIONS WHILE WATCHING DVD
 John Brown’s Body John Brown’s body lies a-mouldering in the grave But his soul goes marching on. Glory, glory, hallelujah (3 x) His soul goes marching on. He captured Harper’s Ferry with his nineteen men so few, And he frightened "Old Virginny" till she trembled through and through, They hung him for a traitor, themselves a traitor crew, But his soul is marching on. Glory, glory, hallelujah (3 x) His soul goes marching on. John Brown died so the slaves might be free John brown died so the slaves might be free john brown died so the slaves might be free but his soul goes marching on Glory, glory, hallelujah (3 x) His soul goes marching on.
John Brown’s Body John Brown’s body lies a-mouldering in the grave But his soul goes marching on. Glory, glory, hallelujah (3 x) His soul goes marching on. He captured Harper’s Ferry with his nineteen men so few, And he frightened "Old Virginny" till she trembled through and through, They hung him for a traitor, themselves a traitor crew, But his soul is marching on. Glory, glory, hallelujah (3 x) His soul goes marching on. John Brown died so the slaves might be free John brown died so the slaves might be free john brown died so the slaves might be free but his soul goes marching on Glory, glory, hallelujah (3 x) His soul goes marching on.
 IV. The election of Abraham Lincoln. South believed Lincoln was pro abolition; states began to secede upon his election in 1860
IV. The election of Abraham Lincoln. South believed Lincoln was pro abolition; states began to secede upon his election in 1860

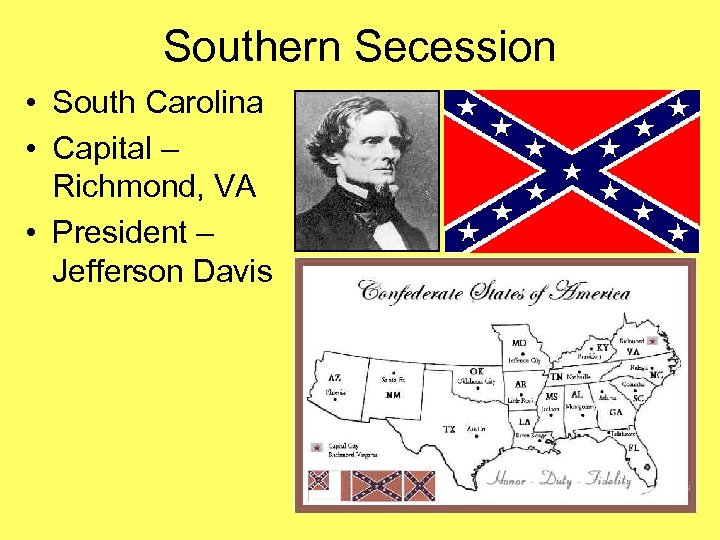 Southern Secession • South Carolina • Capital – Richmond, VA • President – Jefferson Davis
Southern Secession • South Carolina • Capital – Richmond, VA • President – Jefferson Davis
 Fort Sumter • Charleston, South Carolina
Fort Sumter • Charleston, South Carolina
 EXIT TICKET • ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTION BEFORE LEAVING CLASS… – Was there just one cause to the American Civil War? If so, what was it? If there were multiple causes, what were they? Why were they so significant? Explain. Homework – Purpose of Civil War
EXIT TICKET • ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTION BEFORE LEAVING CLASS… – Was there just one cause to the American Civil War? If so, what was it? If there were multiple causes, what were they? Why were they so significant? Explain. Homework – Purpose of Civil War
 LESSON ESSENTIAL QUESTION • HOW DID THE CIVIL WAR AFFECT THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH? KEY TOPICS & VOCABULARY • BLOCKADE • EMANCAPATION PROCLAMATION • CONTRABAND • GETTYSBURG ADDRESS • Battle of GETTYSBURG • 13 th Amendment • DEFENSIVE WAR • 54 TH MASSACHUSETTS REGIMENT • TOTAL WAR • Robert E. Lee • BULL RUN, VIRGINIA • Stonewall Jackson • Draft • Ulysses S Grant
LESSON ESSENTIAL QUESTION • HOW DID THE CIVIL WAR AFFECT THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH? KEY TOPICS & VOCABULARY • BLOCKADE • EMANCAPATION PROCLAMATION • CONTRABAND • GETTYSBURG ADDRESS • Battle of GETTYSBURG • 13 th Amendment • DEFENSIVE WAR • 54 TH MASSACHUSETTS REGIMENT • TOTAL WAR • Robert E. Lee • BULL RUN, VIRGINIA • Stonewall Jackson • Draft • Ulysses S Grant
 What were the strategies and major battles of the Civil War?
What were the strategies and major battles of the Civil War?
 Union Plans A. Planned to use its Navy to blockade Southern ports. B. Capture the Confederate capitol- Richmond. C. Seize control of the Mississippi River
Union Plans A. Planned to use its Navy to blockade Southern ports. B. Capture the Confederate capitol- Richmond. C. Seize control of the Mississippi River
 Confederate Plans A. Fight a defensive war B. Make war unpopular in the North… C. Trade with Europe for supplies. WHY?
Confederate Plans A. Fight a defensive war B. Make war unpopular in the North… C. Trade with Europe for supplies. WHY?
 BULL RUN, VIRGINIA • FIRST BATTLE OF CIVIL WAR • Battle Strategies • Point of view of war – Over quickly – Citizens saw as show
BULL RUN, VIRGINIA • FIRST BATTLE OF CIVIL WAR • Battle Strategies • Point of view of war – Over quickly – Citizens saw as show
 Phases of the war: 1861 -1863: Secession, South takes control of the war, union loses key battles, builds its strength, Lincoln battles war weariness 1863 -1864: Turning points, union makes major gains, south is weakened, union advantages come into play (Vicksburg, Gettysburg) 1864 -1865: Union grinds south down – TOTAL WAR, southern armies defeated, south surrenders (Petersburg, Appomattox courthouse)
Phases of the war: 1861 -1863: Secession, South takes control of the war, union loses key battles, builds its strength, Lincoln battles war weariness 1863 -1864: Turning points, union makes major gains, south is weakened, union advantages come into play (Vicksburg, Gettysburg) 1864 -1865: Union grinds south down – TOTAL WAR, southern armies defeated, south surrenders (Petersburg, Appomattox courthouse)
 Lincoln’s Speeches • Emancipation Proclamation (Jan 1, 1863) – – Beginning to end of slavery in US Freed slaves in states still in rebellion Did not free slaves living in loyal border states Changed cause of war = END SLAVERY • More blacks able to join military – Video • Gettysburg Address (Nov 19, 1863) – Following Union victory at Gettysburg – Video
Lincoln’s Speeches • Emancipation Proclamation (Jan 1, 1863) – – Beginning to end of slavery in US Freed slaves in states still in rebellion Did not free slaves living in loyal border states Changed cause of war = END SLAVERY • More blacks able to join military – Video • Gettysburg Address (Nov 19, 1863) – Following Union victory at Gettysburg – Video





 Movement towards freedom Initially: “preserve the union”, slavery not addressed Congress: The confiscation Act of 1861 -> encouraged slaves to escape Emancipation Proclamation (1863): freed slaves in areas of rebellion, not union controlled areas Over 185, 000 black soldiers serve in Union army and navy (85% of eligible men) Emancipation: 13 th amendment, ratified in 1865
Movement towards freedom Initially: “preserve the union”, slavery not addressed Congress: The confiscation Act of 1861 -> encouraged slaves to escape Emancipation Proclamation (1863): freed slaves in areas of rebellion, not union controlled areas Over 185, 000 black soldiers serve in Union army and navy (85% of eligible men) Emancipation: 13 th amendment, ratified in 1865
 54 th Massachusetts Regiment • All black regiment, white officers only – Blacks unable to fight or lead • Men Born free …. . WHY? • Paid less than white soldiers ($13/$10) • Fort Wagner
54 th Massachusetts Regiment • All black regiment, white officers only – Blacks unable to fight or lead • Men Born free …. . WHY? • Paid less than white soldiers ($13/$10) • Fort Wagner
 DVD – 54 TH MASSACHUSETTS REGIMENT • WATCH DVD ON 54 TH MASSACHUSETTS REGIMENT • ANSWER QUESTIONS WHILE WATCHING DVD
DVD – 54 TH MASSACHUSETTS REGIMENT • WATCH DVD ON 54 TH MASSACHUSETTS REGIMENT • ANSWER QUESTIONS WHILE WATCHING DVD
 EXIT TICKET • The economy of a country is vastly important, beyond just making money. Explain the impact that the economies of the North and South had on their ability to fight the war. Homework – Teenager’s Account of War
EXIT TICKET • The economy of a country is vastly important, beyond just making money. Explain the impact that the economies of the North and South had on their ability to fight the war. Homework – Teenager’s Account of War
 Reading Assignment • Read one of the following articles and complete the worksheet that is attached. – Article #1 Who Really Won the Civil War? – Article #2 Gettysburg Address HW – Cause & Effect, Reading a Chart
Reading Assignment • Read one of the following articles and complete the worksheet that is attached. – Article #1 Who Really Won the Civil War? – Article #2 Gettysburg Address HW – Cause & Effect, Reading a Chart
 LESSON ESSENTIAL QUESTION • HOW DID THE OUTCOMES FO THE CIVIL WAR AFFECT THE ECONOMIC, SOCIAL AND POLITICAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH? Key Aspects & Vocabulary • Appomattox Court House • Ford’s Theater • John Wilkes Booth
LESSON ESSENTIAL QUESTION • HOW DID THE OUTCOMES FO THE CIVIL WAR AFFECT THE ECONOMIC, SOCIAL AND POLITICAL DEVELOPMENT OF THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH? Key Aspects & Vocabulary • Appomattox Court House • Ford’s Theater • John Wilkes Booth
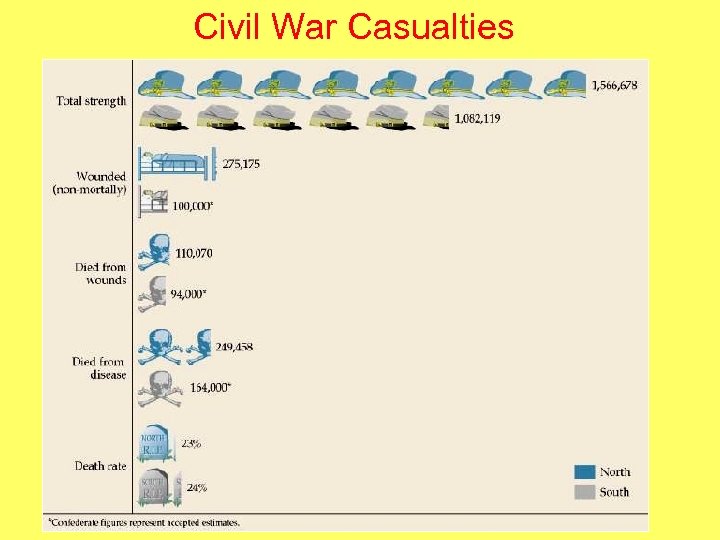 Civil War Casualties
Civil War Casualties
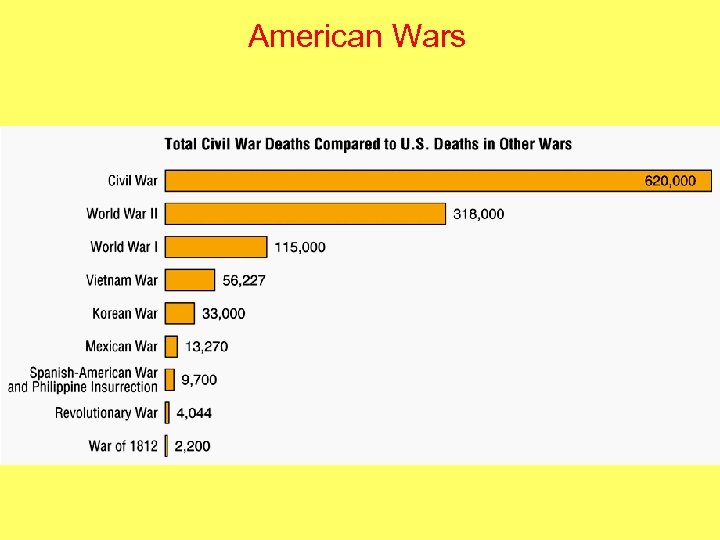 American Wars
American Wars
 Surrender at Appomattox April 9 th 1865
Surrender at Appomattox April 9 th 1865
 Ford’s Theatre April 14, 1865
Ford’s Theatre April 14, 1865
 The Assassin John Wilkes Booth
The Assassin John Wilkes Booth
 The Assassination
The Assassination
 Wanted!
Wanted!

 The execution
The execution
 RESULTS OF THE CIVIL WAR • 620, 000 soldiers dead (2% of population!); over 1 million total casualties • 25% of able-bodied southern men killed or maimed. • Southern economy ruined • Slavery abolished • Total cost of war: $15 billion (immediate costs) (about $1. 5 trillion in today’s dollars) • U. S. becomes a true, unified nation-state
RESULTS OF THE CIVIL WAR • 620, 000 soldiers dead (2% of population!); over 1 million total casualties • 25% of able-bodied southern men killed or maimed. • Southern economy ruined • Slavery abolished • Total cost of war: $15 billion (immediate costs) (about $1. 5 trillion in today’s dollars) • U. S. becomes a true, unified nation-state
 EXIT TICKET • “Those who do not learn from history are doomed to repeat it. ” What lessons can we take from the American Civil War? Why are they so important? Homework – STUDY FOR TEST
EXIT TICKET • “Those who do not learn from history are doomed to repeat it. ” What lessons can we take from the American Civil War? Why are they so important? Homework – STUDY FOR TEST


