cfdb6398df580a99ea59529e9d69a933.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18

Covalent Bonds Sharing Electrons

Quick Review • What is an ionic bond? • The a bond between cations and anions.

Cations and Anions? • Cation-an ion with a positive charge. • Easy way to remember: cation has a “t, ” which looks like a + sign.

Cations and Anions? • Anion-an ion with a negative charge. • Easy way to remember: think “A N” for “a negative” ion.

Why do ionic bonds form? • There is an attraction between positive and negative ions. + Na Cl

How do elements bond if they don’t have opposite charges? Elements can share electrons to form a covalent bond.

Covalent? • Co- means to share. . • -valent refers to valence electrons… • “Covalent” means “sharing valence electrons. ”
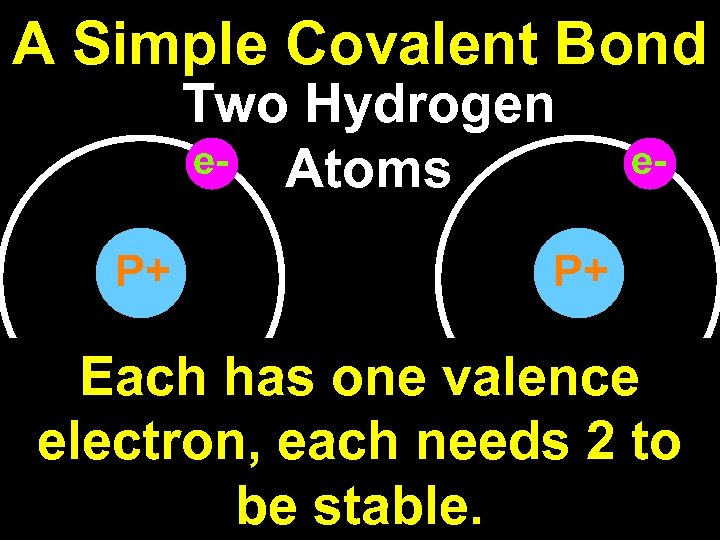
A Simple Covalent Bond Two Hydrogen e- Atoms P+ e- P+ Each has one valence electron, each needs 2 to be stable.
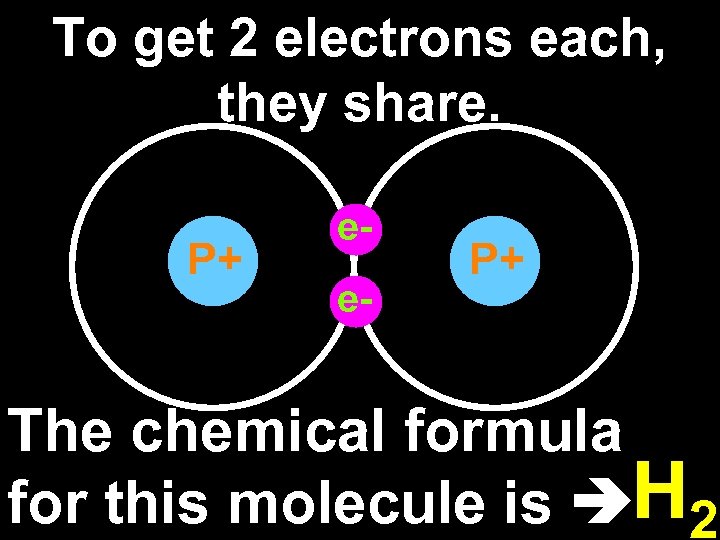
To get 2 electrons each, they share. P+ ee- P+ The chemical formula for this molecule is H 2

Two hydrogen atoms form a diatomic (two atom) molecule. Molecule: a neutral group of atoms joined together by one or more covalent bonds.
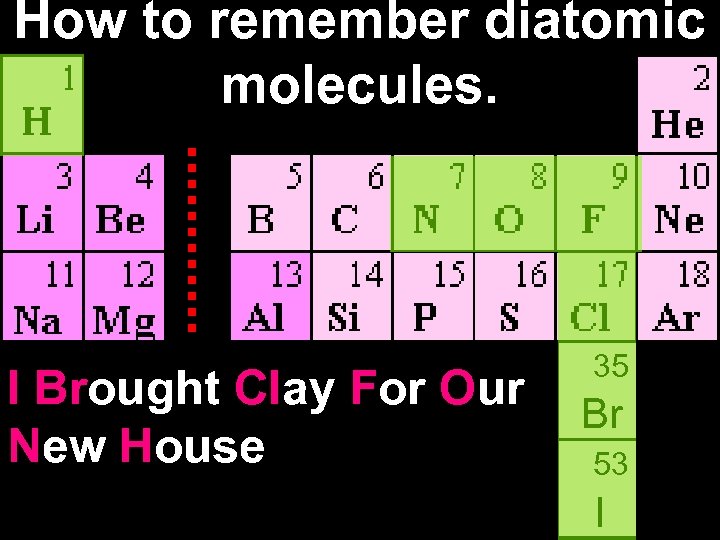
How to remember diatomic molecules. I Brought Clay For Our New House 35 Br 53 I

Properties of Covalently Bonded Molecules • Occur between two or more NONMETALS. • Do not conduct electricity. • Have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds.

Ions are needed to conduct electricity • Ionic compounds vs Covalent compounds

Why is the hydrogen molecule neutral? Two Protons It has two protons (one from each eatom) and P+ P+ etwo electrons (one from each atom). Two Electrons
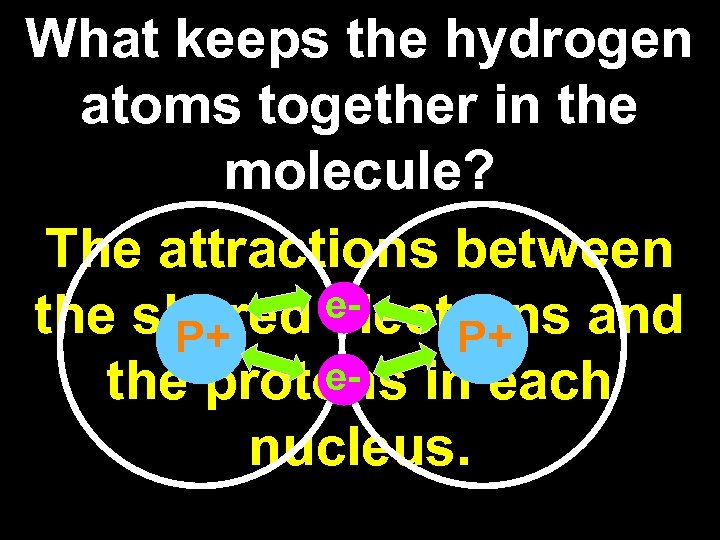
What keeps the hydrogen atoms together in the molecule? The attractions between ethe shared electrons and P+ P+ ethe protons in each nucleus.
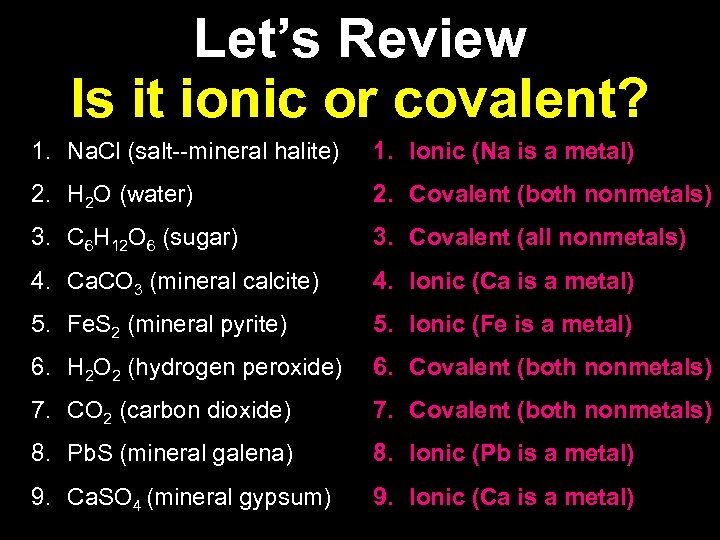
Let’s Review Is it ionic or covalent? 1. Na. Cl (salt--mineral halite) 1. Ionic (Na is a metal) 2. H 2 O (water) 2. Covalent (both nonmetals) 3. C 6 H 12 O 6 (sugar) 3. Covalent (all nonmetals) 4. Ca. CO 3 (mineral calcite) 4. Ionic (Ca is a metal) 5. Fe. S 2 (mineral pyrite) 5. Ionic (Fe is a metal) 6. H 2 O 2 (hydrogen peroxide) 6. Covalent (both nonmetals) 7. CO 2 (carbon dioxide) 7. Covalent (both nonmetals) 8. Pb. S (mineral galena) 8. Ionic (Pb is a metal) 9. Ca. SO 4 (mineral gypsum) 9. Ionic (Ca is a metal)

Let’s Review Would it conduct electricity? 1. Na. Cl (salt--mineral halite) 1. Yes- Ionic 2. H 2 O (water) 2. No-Covalent 3. C 6 H 12 O 6 (sugar) 3. No- Covalent 4. Ca. CO 3 (mineral calcite) 4. Yes- Ionic 5. Fe. S 2 (mineral pyrite) 5. Yes- Ionic 6. H 2 O 2 (hydrogen peroxide) 6. No- Covalent 7. CO 2 (carbon dioxide) 7. No- covalent 8. Pb. S (mineral galena) 8. Yes- Ionic 9. Ca. SO 4 (mineral gypsum) 9. Yes-Ionic

Covalent Songs & Tutorial • Covalent Song #1 • Covalent Song #2 • Covalent Bonding Tutorial
cfdb6398df580a99ea59529e9d69a933.ppt