61b6eae972959549f5c7f0cd07482c1d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 17
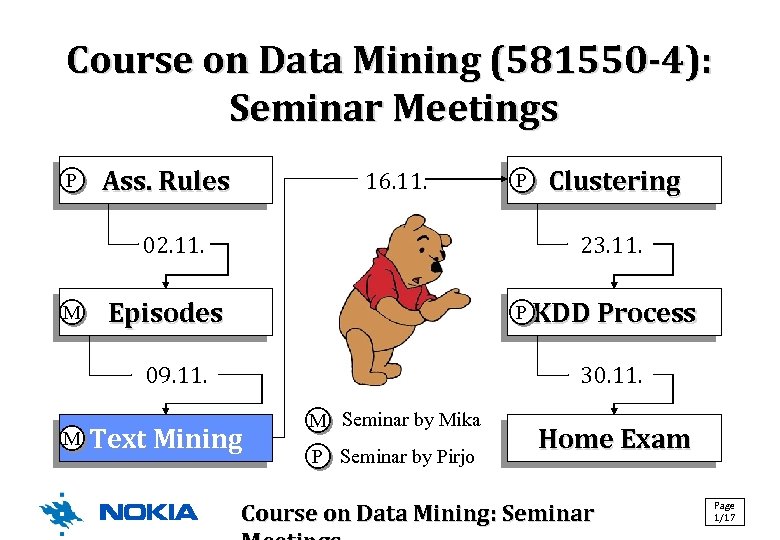 Course on Data Mining (581550 -4): Seminar Meetings P Ass. Rules 16. 11. 02. 11. M Clustering 23. 11. Episodes P KDD Process 09. 11. M P 30. 11. Text Mining M Seminar by Mika P Seminar by Pirjo Home Exam Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 1/17
Course on Data Mining (581550 -4): Seminar Meetings P Ass. Rules 16. 11. 02. 11. M Clustering 23. 11. Episodes P KDD Process 09. 11. M P 30. 11. Text Mining M Seminar by Mika P Seminar by Pirjo Home Exam Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 1/17
 Course on Data Mining (581550 -4): Seminar Meetings Today 16. 11. 2001 • R. Feldman, M. Fresko, H. Hirsh, et. al. : "Knowledge Management: A Text Mining Approach", Proc of the 2 nd Int'l Conf. on Practical Aspects of Knowledge Management (PAKM 98), 1998 • B. Lent, R. Agrawal, R. Srikant: "Discovering Trends in Text Databases", Proc. of the 3 rd Int'l Conference on Knowledge Discovery in Databases and Data Mining, 1997. Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 2/17
Course on Data Mining (581550 -4): Seminar Meetings Today 16. 11. 2001 • R. Feldman, M. Fresko, H. Hirsh, et. al. : "Knowledge Management: A Text Mining Approach", Proc of the 2 nd Int'l Conf. on Practical Aspects of Knowledge Management (PAKM 98), 1998 • B. Lent, R. Agrawal, R. Srikant: "Discovering Trends in Text Databases", Proc. of the 3 rd Int'l Conference on Knowledge Discovery in Databases and Data Mining, 1997. Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 2/17
 Course on Data Mining (581550 -4): Seminar Meetings Good to Read as Background • Both papers refer to the Agrawal and Srikant paper we had last week: Rakesh Agrawal and Ramakrishnan Srikant: Mining Sequential Patterns. Int'l Conference on Data Engineering, 1995. Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 3/17
Course on Data Mining (581550 -4): Seminar Meetings Good to Read as Background • Both papers refer to the Agrawal and Srikant paper we had last week: Rakesh Agrawal and Ramakrishnan Srikant: Mining Sequential Patterns. Int'l Conference on Data Engineering, 1995. Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 3/17
 Knowledge Management: A Text Mining Approach R. Feldman, M. Fresko, H. Hirsh, et. al Bar-Ilan University and Instict Software, ISRAEL; Rutgers University, USA; LIA-EPFL, Switzerland Published in PAKM'98 (Int'l Conf. on Practical Aspects of Knowledge Management) Data Mining course Autumn 2001/University of Helsinki Summary by Mika Klemettinen Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 4/17
Knowledge Management: A Text Mining Approach R. Feldman, M. Fresko, H. Hirsh, et. al Bar-Ilan University and Instict Software, ISRAEL; Rutgers University, USA; LIA-EPFL, Switzerland Published in PAKM'98 (Int'l Conf. on Practical Aspects of Knowledge Management) Data Mining course Autumn 2001/University of Helsinki Summary by Mika Klemettinen Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 4/17
 KM: A Text Mining Approach • Basic idea (see selected phases on the next slides): 1. Get input data in SGML (or XML) format Select only the contents of desired elements! (title, abstract, etc. ) 2. Do linguistic preprocessing: 2. 1 Term extraction (use linguistic software for this) 2. 2 Term generation (combine adjacent terms to morphosyntactic patterns like "noun-noun", "adj. -noun", etc. by calculating association coefficients) 2. 3 Term filtering (select only the top M most frequent ones) 3. Create taxonomies (there is a tool for this) 4. Generate associations (you may constrain the creation) Page Course on Data Mining: Seminar 5/17 5. Visualize/explore the results
KM: A Text Mining Approach • Basic idea (see selected phases on the next slides): 1. Get input data in SGML (or XML) format Select only the contents of desired elements! (title, abstract, etc. ) 2. Do linguistic preprocessing: 2. 1 Term extraction (use linguistic software for this) 2. 2 Term generation (combine adjacent terms to morphosyntactic patterns like "noun-noun", "adj. -noun", etc. by calculating association coefficients) 2. 3 Term filtering (select only the top M most frequent ones) 3. Create taxonomies (there is a tool for this) 4. Generate associations (you may constrain the creation) Page Course on Data Mining: Seminar 5/17 5. Visualize/explore the results
 2. 1: Term Extraction Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 6/17
2. 1: Term Extraction Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 6/17
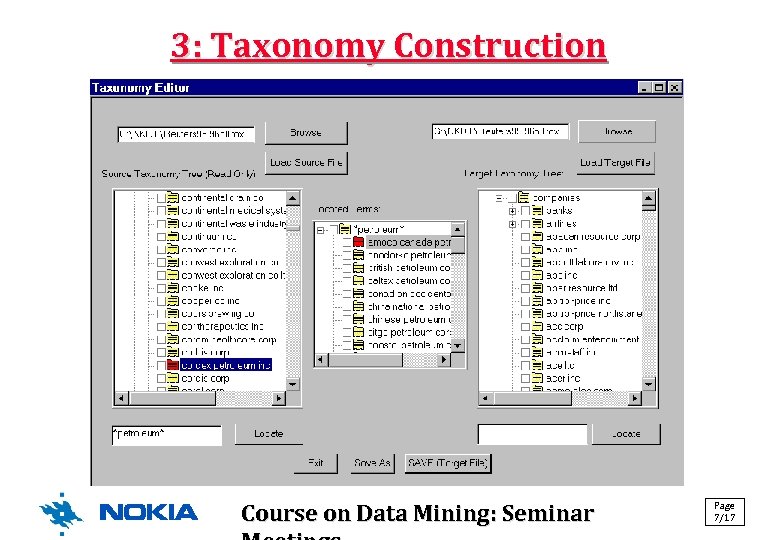 3: Taxonomy Construction Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 7/17
3: Taxonomy Construction Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 7/17
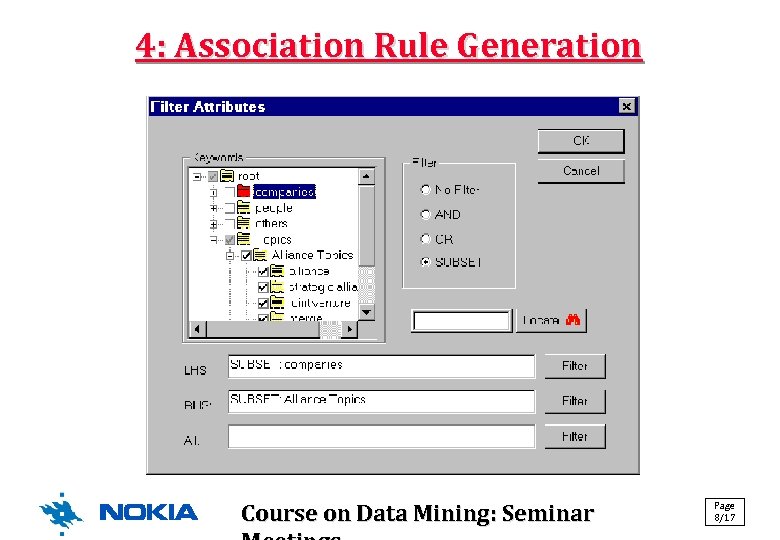 4: Association Rule Generation Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 8/17
4: Association Rule Generation Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 8/17
 4: Association Rule Generation Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 9/17
4: Association Rule Generation Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 9/17
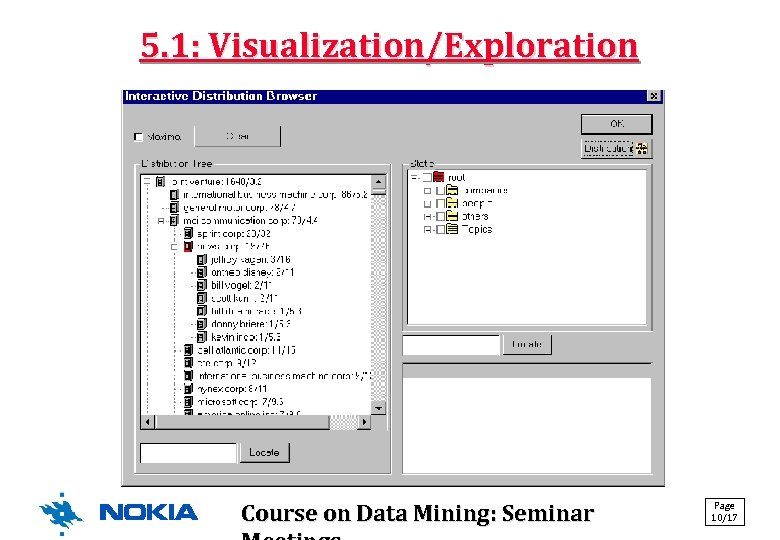 5. 1: Visualization/Exploration Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 10/17
5. 1: Visualization/Exploration Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 10/17
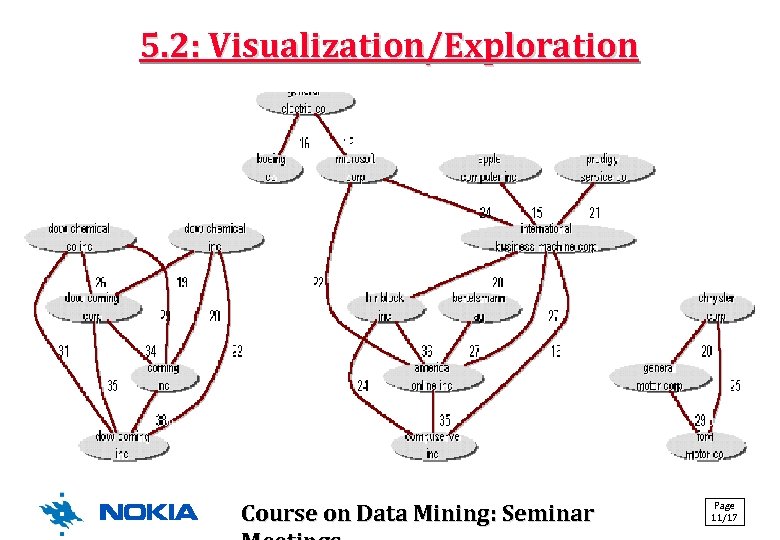 5. 2: Visualization/Exploration Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 11/17
5. 2: Visualization/Exploration Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 11/17
 Discovering Trends in Text Databases Brian Lent, Rakesh Agrawal and Ramakrishnan Srikant IBM Almaden Research Center, USA Published in KDD'97 Data Mining course Autumn 2001/University of Helsinki Summary by Mika Klemettinen Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 12/17
Discovering Trends in Text Databases Brian Lent, Rakesh Agrawal and Ramakrishnan Srikant IBM Almaden Research Center, USA Published in KDD'97 Data Mining course Autumn 2001/University of Helsinki Summary by Mika Klemettinen Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 12/17
 Discovering Trends in Text Databases • Basic ideas: • Identify frequent phrases using sequential patterns mining (see the slides & summaries from the Agrawal et. al paper "Mining Sequential Patterns" (MSP)) • Generate histories of phrases • Find phrases that satisfy a specified trend • Definitions: • Phrase: phrase p is (w 1)(w 2) … (wn ) , where w is a word • 1 -phrase: (IBM) (data)(mining) • 2 -phrase: (IBM) (data)(mining) (Anderson) (Consulting) (decision)(support) • Itemset, sequence, is contained, etc. : as in MSP paper Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 13/17
Discovering Trends in Text Databases • Basic ideas: • Identify frequent phrases using sequential patterns mining (see the slides & summaries from the Agrawal et. al paper "Mining Sequential Patterns" (MSP)) • Generate histories of phrases • Find phrases that satisfy a specified trend • Definitions: • Phrase: phrase p is (w 1)(w 2) … (wn ) , where w is a word • 1 -phrase: (IBM) (data)(mining) • 2 -phrase: (IBM) (data)(mining) (Anderson) (Consulting) (decision)(support) • Itemset, sequence, is contained, etc. : as in MSP paper Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 13/17
 Discovering Trends in Text Databases Gaps: Minimum and maximum gaps between adjacent words: identify relations of words/phrases inside sentences/paragraphs, between words/phrases in different sections, etc. • Sentence boundary: 1000 • Paragraph boundary: 100. 000 • Section boundary: 10. 000 • Phases: • Partition data/documents based on their time stamps, create phrases for each partition (Lent & al. have patent data documents) • Select the frequent phrases and save their frequences • Define shape queries using SDL (Shape Definition Language) Page Course on Data Mining: Seminar 14/17 •
Discovering Trends in Text Databases Gaps: Minimum and maximum gaps between adjacent words: identify relations of words/phrases inside sentences/paragraphs, between words/phrases in different sections, etc. • Sentence boundary: 1000 • Paragraph boundary: 100. 000 • Section boundary: 10. 000 • Phases: • Partition data/documents based on their time stamps, create phrases for each partition (Lent & al. have patent data documents) • Select the frequent phrases and save their frequences • Define shape queries using SDL (Shape Definition Language) Page Course on Data Mining: Seminar 14/17 •
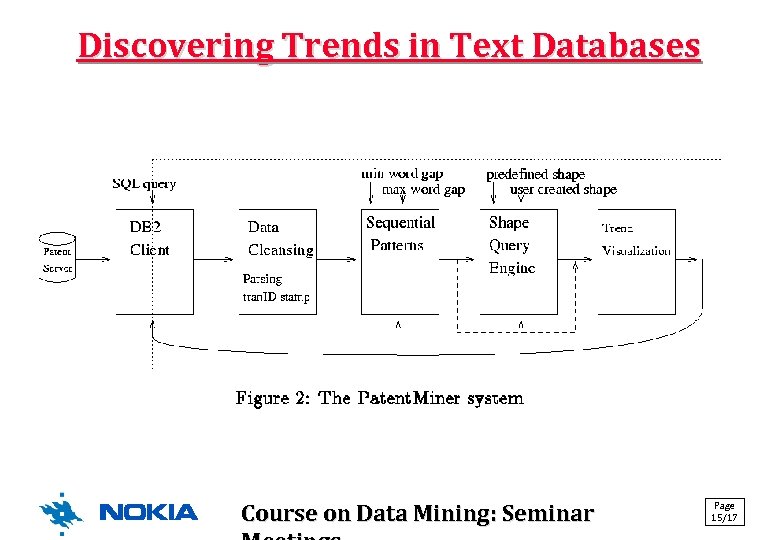 Discovering Trends in Text Databases Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 15/17
Discovering Trends in Text Databases Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 15/17
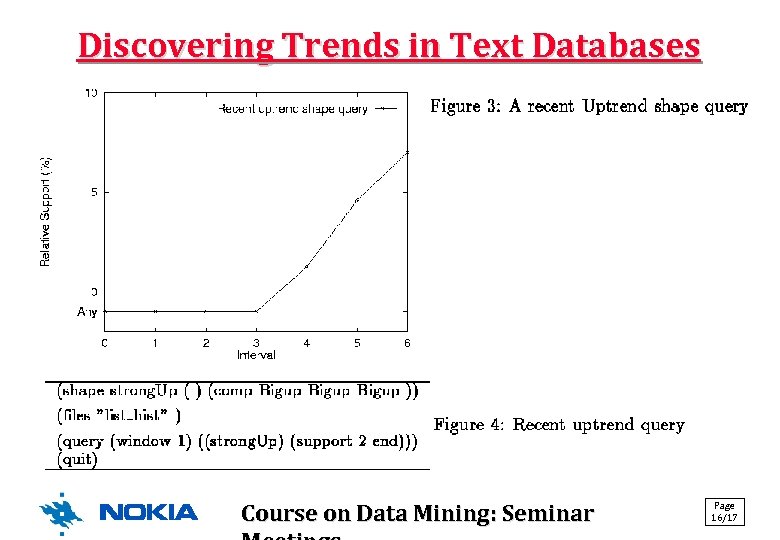 Discovering Trends in Text Databases Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 16/17
Discovering Trends in Text Databases Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 16/17
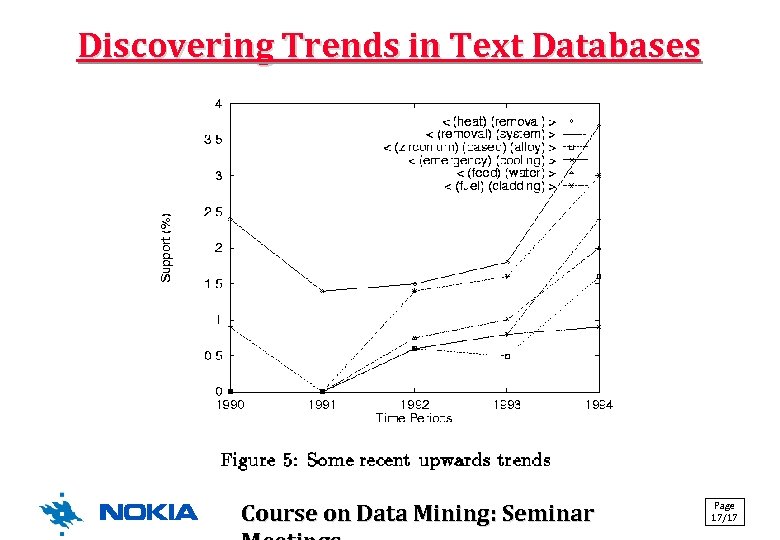 Discovering Trends in Text Databases Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 17/17
Discovering Trends in Text Databases Course on Data Mining: Seminar Page 17/17


