3148e920a312e7fe39e2a9fe5ab81acc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 39
 Course Contents PART I : INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER § Essential Basic Concepts. § Data Representation Inside Computer. § Computer System Components. § Computer Classes. § Computer Networks & Internet. § Computer Applications. § Computer Generations. 1
Course Contents PART I : INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER § Essential Basic Concepts. § Data Representation Inside Computer. § Computer System Components. § Computer Classes. § Computer Networks & Internet. § Computer Applications. § Computer Generations. 1
 Course Contents PART II : SOLVING PROBLEMS USING COMPUTER § Problem Solving Technique. § Programming with C Language. Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 2
Course Contents PART II : SOLVING PROBLEMS USING COMPUTER § Problem Solving Technique. § Programming with C Language. Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 2
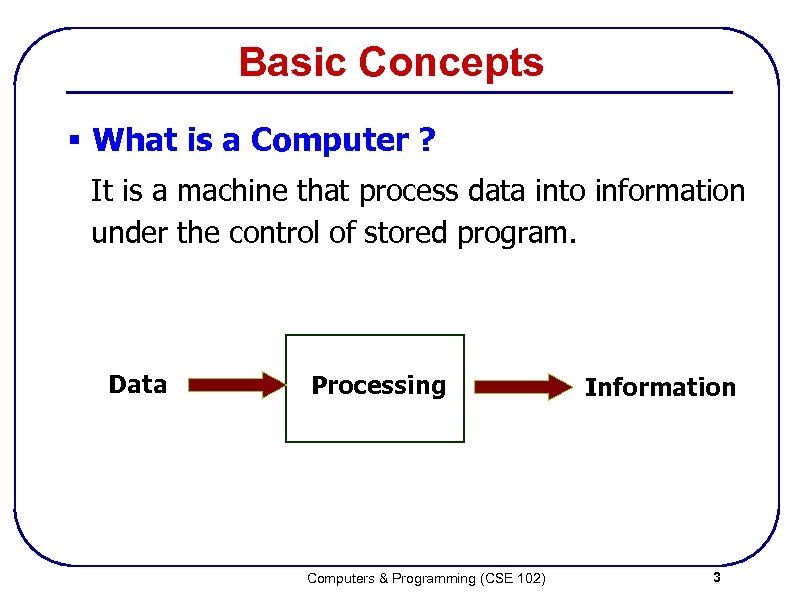 Basic Concepts § What is a Computer ? It is a machine that process data into information under the control of stored program. Data Processing Computers & Programming (CSE 102) Information 3
Basic Concepts § What is a Computer ? It is a machine that process data into information under the control of stored program. Data Processing Computers & Programming (CSE 102) Information 3
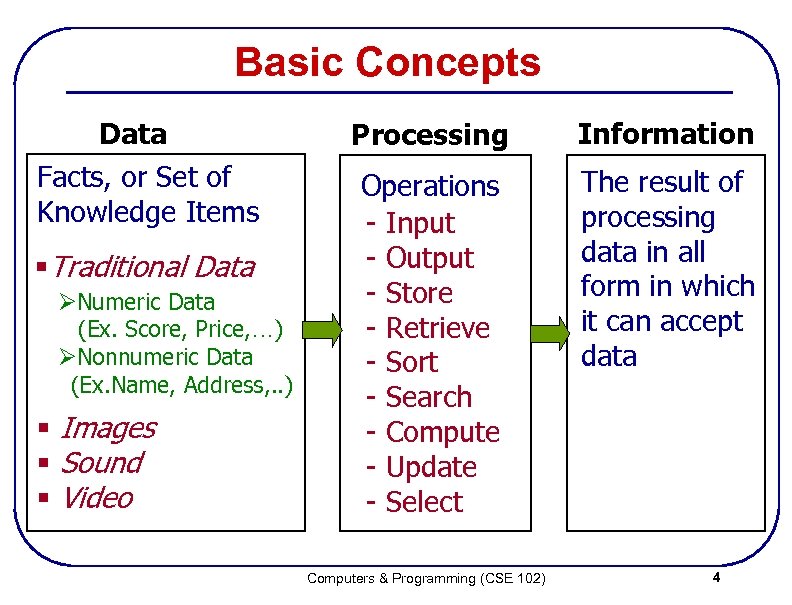 Basic Concepts Data Facts, or Set of Knowledge Items § Traditional Data ØNumeric Data (Ex. Score, Price, …) ØNonnumeric Data (Ex. Name, Address, . . ) § Images § Sound § Video Processing Information Operations - Input - Output - Store - Retrieve - Sort - Search - Compute - Update - Select The result of processing data in all form in which it can accept data Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 4
Basic Concepts Data Facts, or Set of Knowledge Items § Traditional Data ØNumeric Data (Ex. Score, Price, …) ØNonnumeric Data (Ex. Name, Address, . . ) § Images § Sound § Video Processing Information Operations - Input - Output - Store - Retrieve - Sort - Search - Compute - Update - Select The result of processing data in all form in which it can accept data Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 4
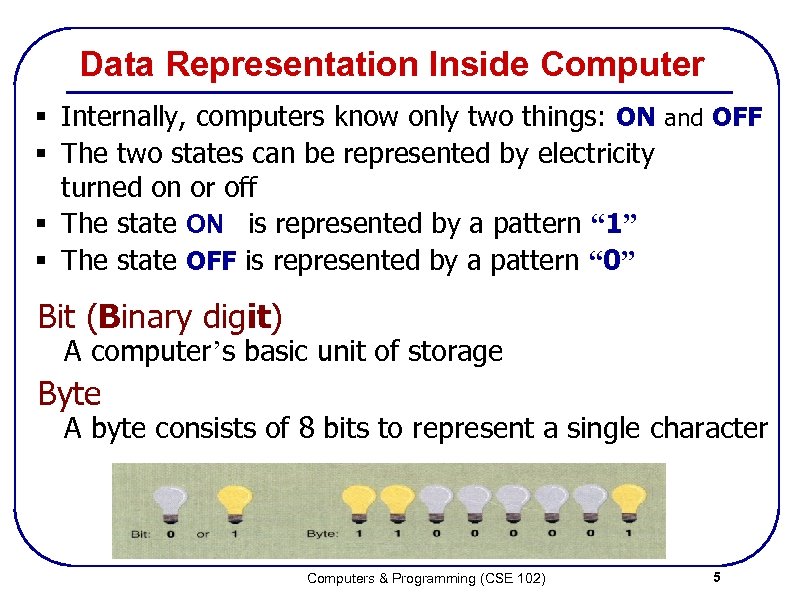 Data Representation Inside Computer § Internally, computers know only two things: ON and OFF § The two states can be represented by electricity turned on or off § The state ON is represented by a pattern “ 1” § The state OFF is represented by a pattern “ 0” Bit (Binary digit) A computer’s basic unit of storage Byte A byte consists of 8 bits to represent a single character Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 5
Data Representation Inside Computer § Internally, computers know only two things: ON and OFF § The two states can be represented by electricity turned on or off § The state ON is represented by a pattern “ 1” § The state OFF is represented by a pattern “ 0” Bit (Binary digit) A computer’s basic unit of storage Byte A byte consists of 8 bits to represent a single character Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 5
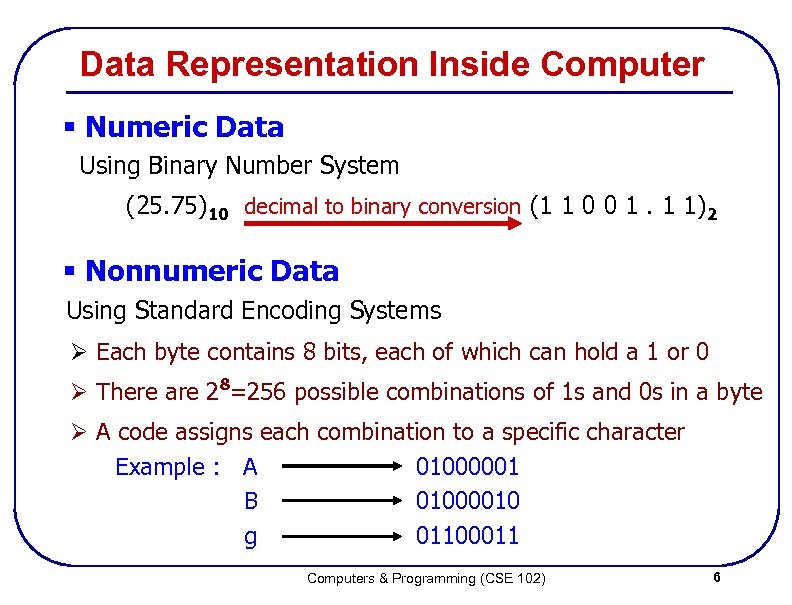 Data Representation Inside Computer § Numeric Data Using Binary Number System (25. 75)10 decimal to binary conversion (1 1 0 0 1. 1 1)2 § Nonnumeric Data Using Standard Encoding Systems Ø Each byte contains 8 bits, each of which can hold a 1 or 0 Ø There are 28=256 possible combinations of 1 s and 0 s in a byte Ø A code assigns each combination to a specific character Example : A 01000001 B 01000010 g 01100011 Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 6
Data Representation Inside Computer § Numeric Data Using Binary Number System (25. 75)10 decimal to binary conversion (1 1 0 0 1. 1 1)2 § Nonnumeric Data Using Standard Encoding Systems Ø Each byte contains 8 bits, each of which can hold a 1 or 0 Ø There are 28=256 possible combinations of 1 s and 0 s in a byte Ø A code assigns each combination to a specific character Example : A 01000001 B 01000010 g 01100011 Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 6
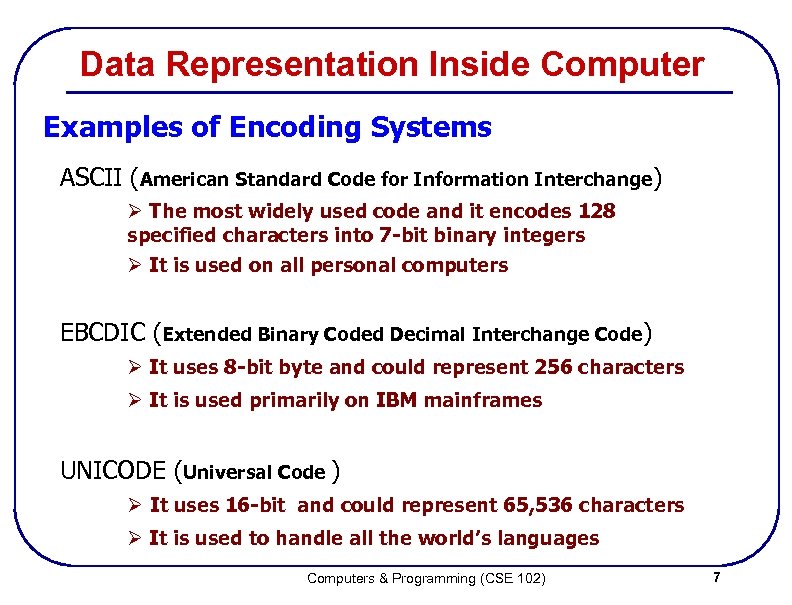 Data Representation Inside Computer Examples of Encoding Systems ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) Ø The most widely used code and it encodes 128 specified characters into 7 -bit binary integers Ø It is used on all personal computers EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code) Ø It uses 8 -bit byte and could represent 256 characters Ø It is used primarily on IBM mainframes UNICODE (Universal Code ) Ø It uses 16 -bit and could represent 65, 536 characters Ø It is used to handle all the world’s languages Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 7
Data Representation Inside Computer Examples of Encoding Systems ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) Ø The most widely used code and it encodes 128 specified characters into 7 -bit binary integers Ø It is used on all personal computers EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code) Ø It uses 8 -bit byte and could represent 256 characters Ø It is used primarily on IBM mainframes UNICODE (Universal Code ) Ø It uses 16 -bit and could represent 65, 536 characters Ø It is used to handle all the world’s languages Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 7
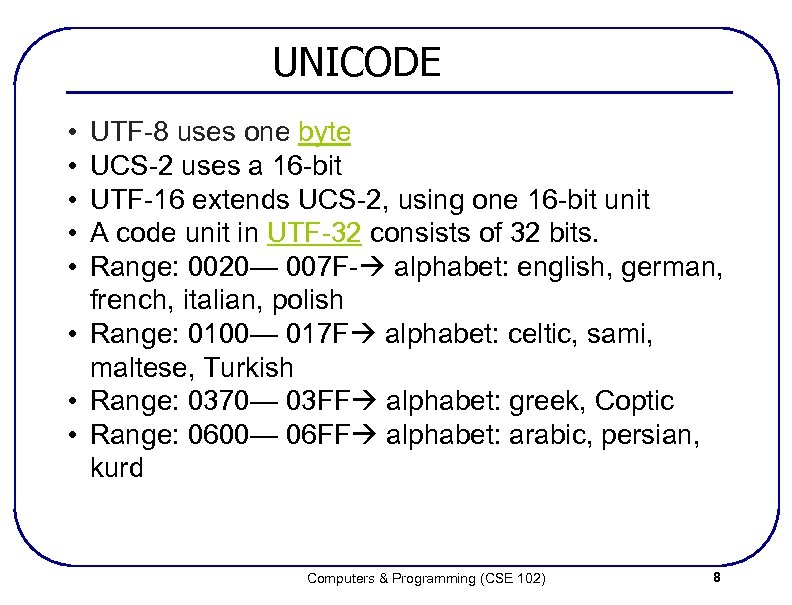 UNICODE • • • UTF-8 uses one byte UCS-2 uses a 16 -bit UTF-16 extends UCS-2, using one 16 -bit unit A code unit in UTF-32 consists of 32 bits. Range: 0020— 007 F- alphabet: english, german, french, italian, polish • Range: 0100— 017 F alphabet: celtic, sami, maltese, Turkish • Range: 0370— 03 FF alphabet: greek, Coptic • Range: 0600— 06 FF alphabet: arabic, persian, kurd Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 8
UNICODE • • • UTF-8 uses one byte UCS-2 uses a 16 -bit UTF-16 extends UCS-2, using one 16 -bit unit A code unit in UTF-32 consists of 32 bits. Range: 0020— 007 F- alphabet: english, german, french, italian, polish • Range: 0100— 017 F alphabet: celtic, sami, maltese, Turkish • Range: 0370— 03 FF alphabet: greek, Coptic • Range: 0600— 06 FF alphabet: arabic, persian, kurd Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 8
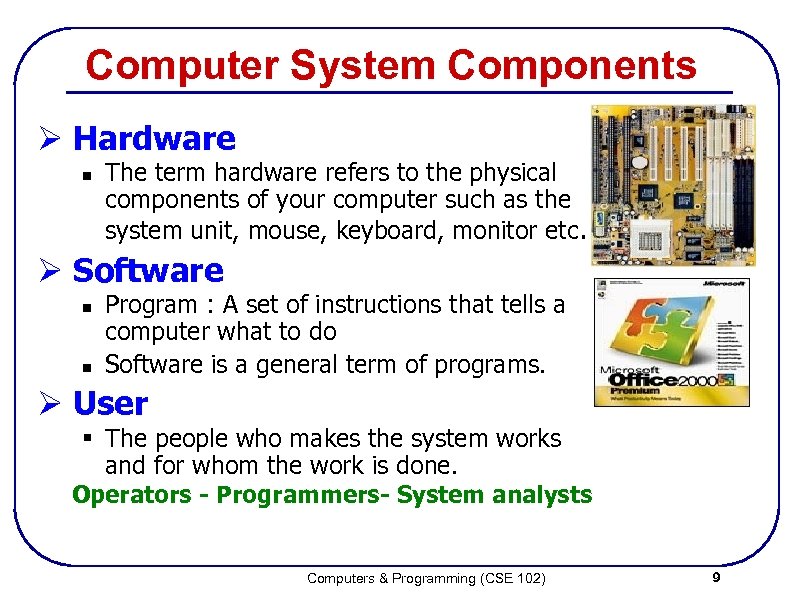 Computer System Components Ø Hardware n The term hardware refers to the physical components of your computer such as the system unit, mouse, keyboard, monitor etc. Ø Software n n Program : A set of instructions that tells a computer what to do Software is a general term of programs. Ø User § The people who makes the system works and for whom the work is done. Operators - Programmers- System analysts Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 9
Computer System Components Ø Hardware n The term hardware refers to the physical components of your computer such as the system unit, mouse, keyboard, monitor etc. Ø Software n n Program : A set of instructions that tells a computer what to do Software is a general term of programs. Ø User § The people who makes the system works and for whom the work is done. Operators - Programmers- System analysts Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 9
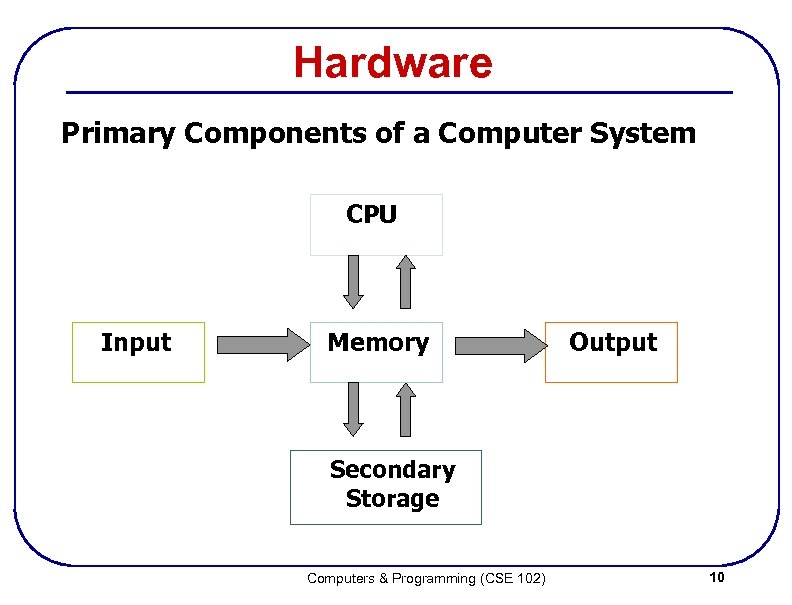 Hardware Primary Components of a Computer System CPU Input Memory Output Secondary Storage Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 10
Hardware Primary Components of a Computer System CPU Input Memory Output Secondary Storage Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 10
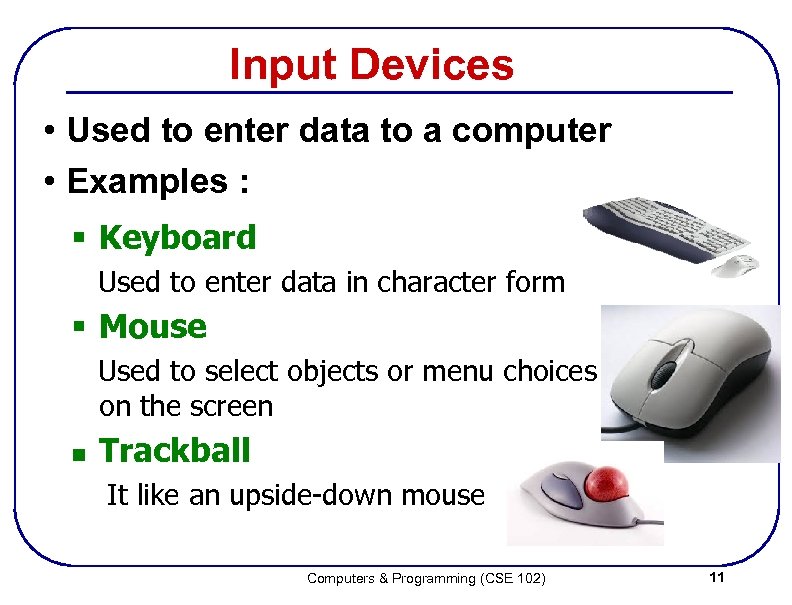 Input Devices • Used to enter data to a computer • Examples : § Keyboard Used to enter data in character form § Mouse Used to select objects or menu choices on the screen n Trackball It like an upside-down mouse Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 11
Input Devices • Used to enter data to a computer • Examples : § Keyboard Used to enter data in character form § Mouse Used to select objects or menu choices on the screen n Trackball It like an upside-down mouse Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 11
 Input Devices n Scanner Used to capture images from paper n Touch Pad A device that lays on the desktop and responds to pressure n Light Pen Used to enter hand written input n Joysticks Used for the proper playing of the game Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 12
Input Devices n Scanner Used to capture images from paper n Touch Pad A device that lays on the desktop and responds to pressure n Light Pen Used to enter hand written input n Joysticks Used for the proper playing of the game Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 12
 Input Devices Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 13
Input Devices Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 13
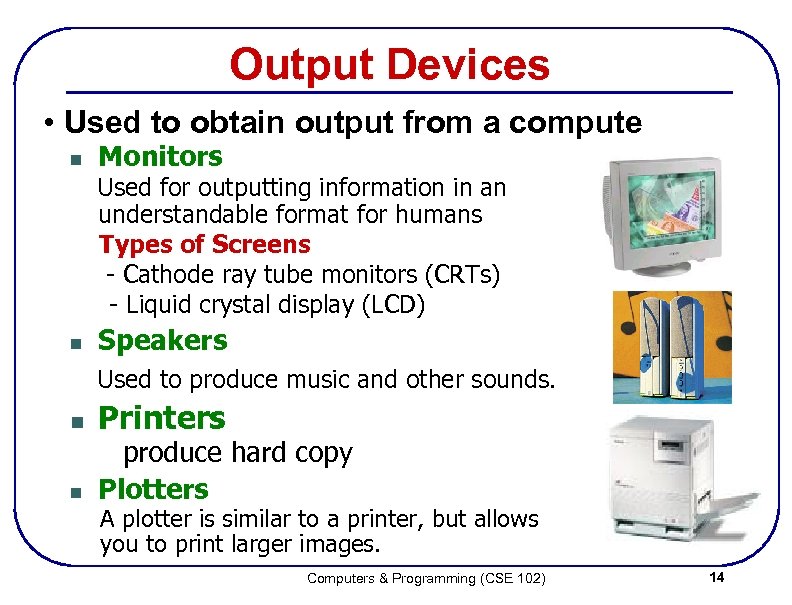 Output Devices • Used to obtain output from a compute n Monitors Used for outputting information in an understandable format for humans Types of Screens - Cathode ray tube monitors (CRTs) - Liquid crystal display (LCD) n Speakers Used to produce music and other sounds. n n Printers produce hard copy Plotters A plotter is similar to a printer, but allows you to print larger images. Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 14
Output Devices • Used to obtain output from a compute n Monitors Used for outputting information in an understandable format for humans Types of Screens - Cathode ray tube monitors (CRTs) - Liquid crystal display (LCD) n Speakers Used to produce music and other sounds. n n Printers produce hard copy Plotters A plotter is similar to a printer, but allows you to print larger images. Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 14
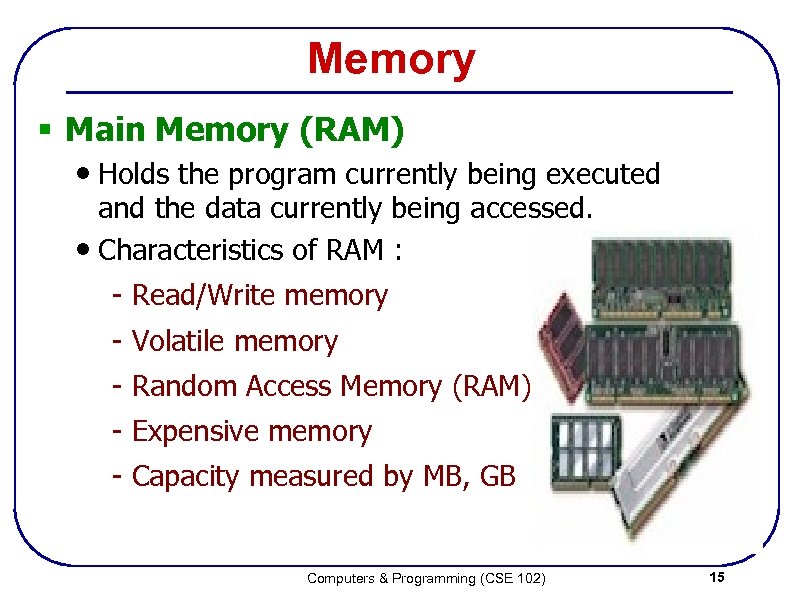 Memory § Main Memory (RAM) • Holds the program currently being executed and the data currently being accessed. • Characteristics of RAM : - Read/Write memory - Volatile memory - Random Access Memory (RAM) - Expensive memory - Capacity measured by MB, GB Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 15
Memory § Main Memory (RAM) • Holds the program currently being executed and the data currently being accessed. • Characteristics of RAM : - Read/Write memory - Volatile memory - Random Access Memory (RAM) - Expensive memory - Capacity measured by MB, GB Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 15
 Memory § Read Only Memory (ROM) • A non volatile memory that can be read and used, but not written. • Contains programs that permanently recorded at factory. - Start up program that execute when a computer is turned on - BIOS (Basic Input/Output system) Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 16
Memory § Read Only Memory (ROM) • A non volatile memory that can be read and used, but not written. • Contains programs that permanently recorded at factory. - Start up program that execute when a computer is turned on - BIOS (Basic Input/Output system) Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 16
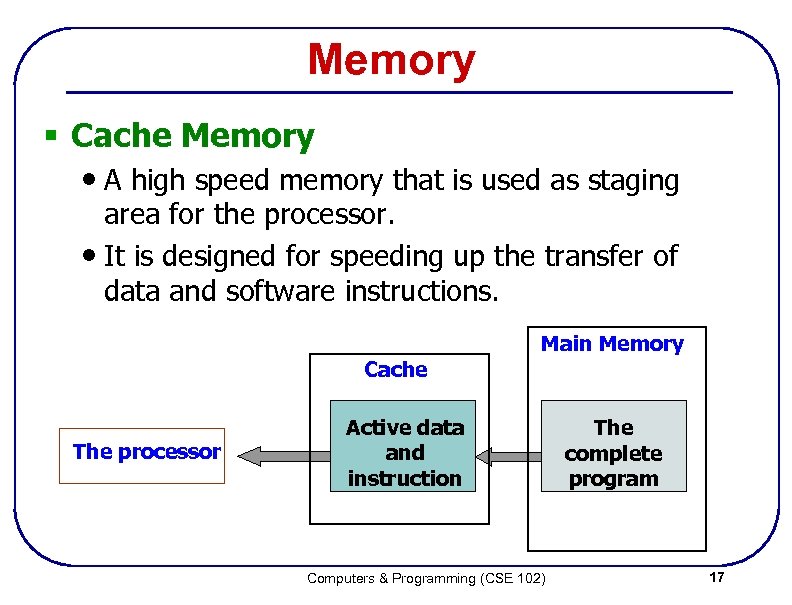 Memory § Cache Memory • A high speed memory that is used as staging area for the processor. • It is designed for speeding up the transfer of data and software instructions. Main Memory Cache The processor Active data and instruction Computers & Programming (CSE 102) The complete program 17
Memory § Cache Memory • A high speed memory that is used as staging area for the processor. • It is designed for speeding up the transfer of data and software instructions. Main Memory Cache The processor Active data and instruction Computers & Programming (CSE 102) The complete program 17
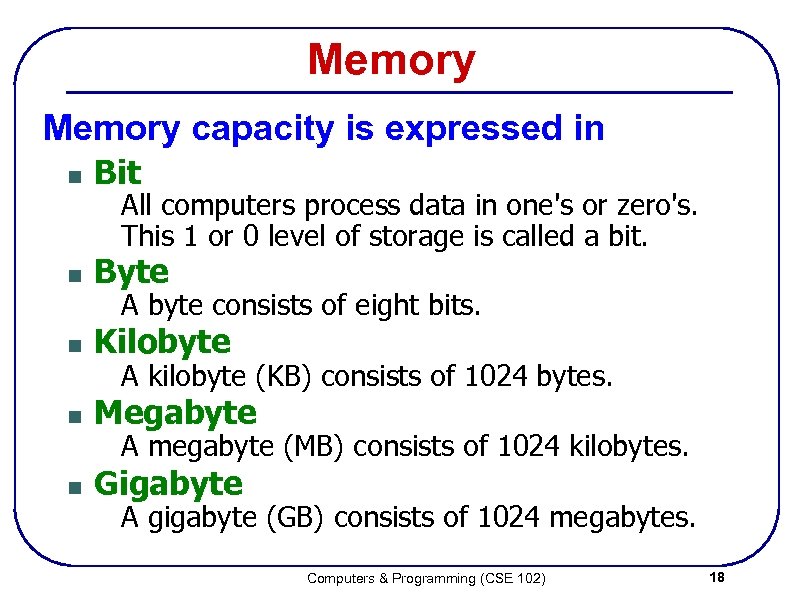 Memory capacity is expressed in n Bit n Byte n Kilobyte n Megabyte n Gigabyte All computers process data in one's or zero's. This 1 or 0 level of storage is called a bit. A byte consists of eight bits. A kilobyte (KB) consists of 1024 bytes. A megabyte (MB) consists of 1024 kilobytes. A gigabyte (GB) consists of 1024 megabytes. Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 18
Memory capacity is expressed in n Bit n Byte n Kilobyte n Megabyte n Gigabyte All computers process data in one's or zero's. This 1 or 0 level of storage is called a bit. A byte consists of eight bits. A kilobyte (KB) consists of 1024 bytes. A megabyte (MB) consists of 1024 kilobytes. A gigabyte (GB) consists of 1024 megabytes. Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 18
 Memory n Word fixed number of bits processed as a unit which varies from computer to computer but is fixed for each computer. Tera. Byte n Peta. Byte n Exa. Byte n Zetta. Byte n Yotta. Byte n Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 19
Memory n Word fixed number of bits processed as a unit which varies from computer to computer but is fixed for each computer. Tera. Byte n Peta. Byte n Exa. Byte n Zetta. Byte n Yotta. Byte n Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 19
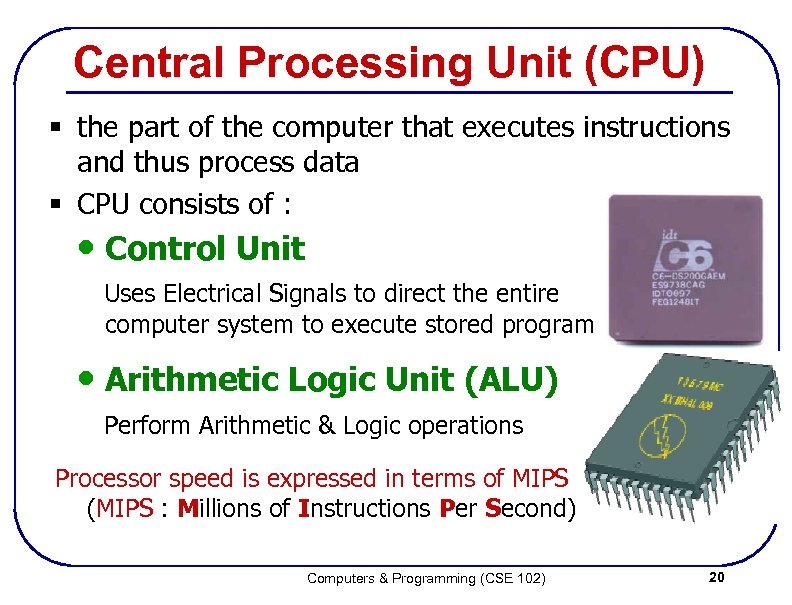 Central Processing Unit (CPU) § the part of the computer that executes instructions and thus process data § CPU consists of : • Control Unit Uses Electrical Signals to direct the entire computer system to execute stored program • Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Perform Arithmetic & Logic operations Processor speed is expressed in terms of MIPS (MIPS : Millions of Instructions Per Second) Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 20
Central Processing Unit (CPU) § the part of the computer that executes instructions and thus process data § CPU consists of : • Control Unit Uses Electrical Signals to direct the entire computer system to execute stored program • Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) Perform Arithmetic & Logic operations Processor speed is expressed in terms of MIPS (MIPS : Millions of Instructions Per Second) Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 20
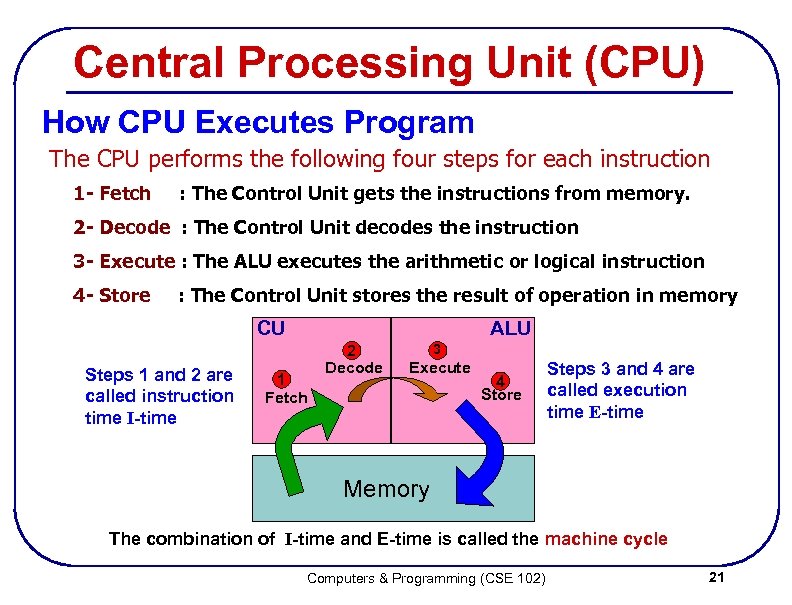 Central Processing Unit (CPU) How CPU Executes Program The CPU performs the following four steps for each instruction 1 - Fetch : The Control Unit gets the instructions from memory. 2 - Decode : The Control Unit decodes the instruction 3 - Execute : The ALU executes the arithmetic or logical instruction 4 - Store : The Control Unit stores the result of operation in memory ALU CU Steps 1 and 2 are called instruction time I-time 1 Fetch 2 Decode 3 Execute 4 Store Steps 3 and 4 are called execution time E-time Memory The combination of I-time and E-time is called the machine cycle Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 21
Central Processing Unit (CPU) How CPU Executes Program The CPU performs the following four steps for each instruction 1 - Fetch : The Control Unit gets the instructions from memory. 2 - Decode : The Control Unit decodes the instruction 3 - Execute : The ALU executes the arithmetic or logical instruction 4 - Store : The Control Unit stores the result of operation in memory ALU CU Steps 1 and 2 are called instruction time I-time 1 Fetch 2 Decode 3 Execute 4 Store Steps 3 and 4 are called execution time E-time Memory The combination of I-time and E-time is called the machine cycle Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 21
 Secondary Storage The Benefits of Secondary Storage Space - Reliability – Economy 1) Magnetic Disk Memories § Diskettes - Portability - Backup - New software delivery - Slow access - Low capacity § Hard disks - Fast access – High capacity Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 22
Secondary Storage The Benefits of Secondary Storage Space - Reliability – Economy 1) Magnetic Disk Memories § Diskettes - Portability - Backup - New software delivery - Slow access - Low capacity § Hard disks - Fast access – High capacity Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 22
 Secondary Storage 2) Magnetic Tape Memory § It stores very large quantity of information. § The cost is very low § But, it is not the main storage because its long access time. § It is a plastic tape with a magnetic coating 1/2 inch-wide tape 1/4 inch-wide tape Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 23
Secondary Storage 2) Magnetic Tape Memory § It stores very large quantity of information. § The cost is very low § But, it is not the main storage because its long access time. § It is a plastic tape with a magnetic coating 1/2 inch-wide tape 1/4 inch-wide tape Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 23
 Secondary Storage 3) Optical Disk Memories Ø Its technology uses a laser beams to enter data as a spots on the disk surface. Ø To read the data, the laser scans the disk, and a lens picks up different light reflections from the various spots § CD-ROM Disks Much slower than Hard disk – 650 MB § DVD Drives Much faster than CD – Up to 17 GB § Blue-ray Drives Much faster than CD – Up to 128 GB Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 24
Secondary Storage 3) Optical Disk Memories Ø Its technology uses a laser beams to enter data as a spots on the disk surface. Ø To read the data, the laser scans the disk, and a lens picks up different light reflections from the various spots § CD-ROM Disks Much slower than Hard disk – 650 MB § DVD Drives Much faster than CD – Up to 17 GB § Blue-ray Drives Much faster than CD – Up to 128 GB Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 24
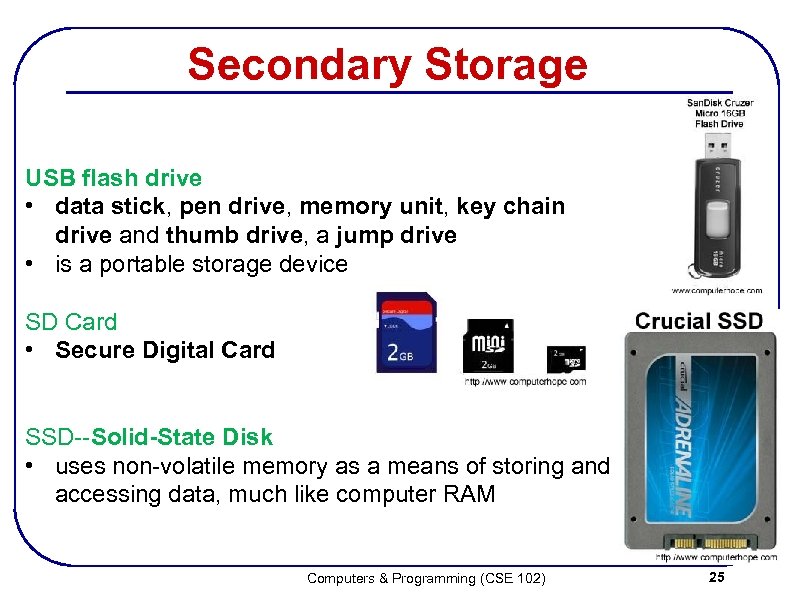 Secondary Storage USB flash drive • data stick, pen drive, memory unit, key chain drive and thumb drive, a jump drive • is a portable storage device SD Card • Secure Digital Card SSD--Solid-State Disk • uses non-volatile memory as a means of storing and accessing data, much like computer RAM Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 25
Secondary Storage USB flash drive • data stick, pen drive, memory unit, key chain drive and thumb drive, a jump drive • is a portable storage device SD Card • Secure Digital Card SSD--Solid-State Disk • uses non-volatile memory as a means of storing and accessing data, much like computer RAM Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 25
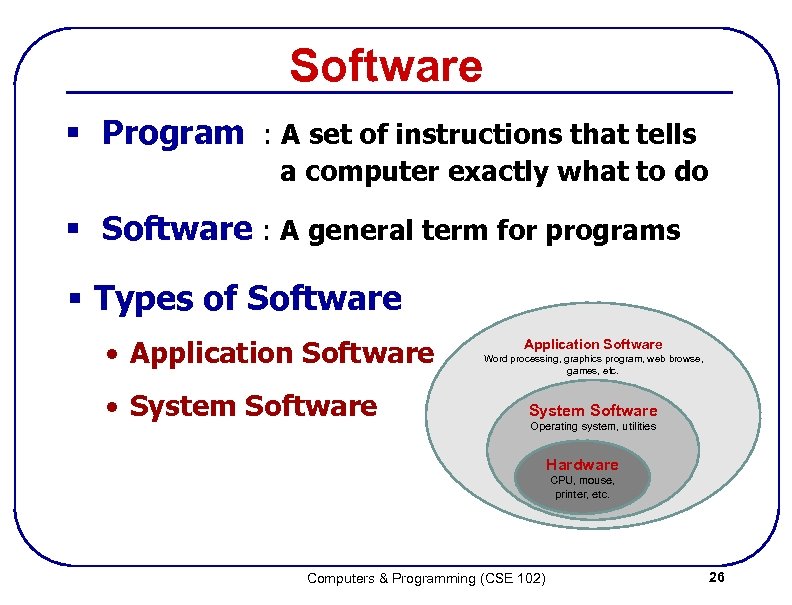 Software § Program : A set of instructions that tells a computer exactly what to do § Software : A general term for programs § Types of Software • Application Software • System Software Application Software Word processing, graphics program, web browse, games, etc. System Software Operating system, utilities Hardware CPU, mouse, printer, etc. Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 26
Software § Program : A set of instructions that tells a computer exactly what to do § Software : A general term for programs § Types of Software • Application Software • System Software Application Software Word processing, graphics program, web browse, games, etc. System Software Operating system, utilities Hardware CPU, mouse, printer, etc. Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 26
 Application Software Programs that perform tasks that users want to do such as play games, write a report, . . . § Types of Application Software • Custom Software A software that is written to solve a specific problem or perform a specific task. • Packages Software A software that is prewritten to perform a common task. Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 27
Application Software Programs that perform tasks that users want to do such as play games, write a report, . . . § Types of Application Software • Custom Software A software that is written to solve a specific problem or perform a specific task. • Packages Software A software that is prewritten to perform a common task. Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 27
 Application Software Package Classes § Word Processing (Microsoft Word - Word. Perfect) § Spreadsheet (Microsoft Excel - Lotus 123 - Quattro) § Database (Microsoft Access - Oracle - DB 3+ ) § Design (Auto. CAD – 3 D Studio) § Graphics & Presentation (Microsoft Power. Point - Harvard - Visio) § Games and Entertainment Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 28
Application Software Package Classes § Word Processing (Microsoft Word - Word. Perfect) § Spreadsheet (Microsoft Excel - Lotus 123 - Quattro) § Database (Microsoft Access - Oracle - DB 3+ ) § Design (Auto. CAD – 3 D Studio) § Graphics & Presentation (Microsoft Power. Point - Harvard - Visio) § Games and Entertainment Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 28
 System Software Programs that directly controls and manages the computer hardware (resources) § Types of System Software • Operating Systems DOS – Windows – Mac OS – Unix • Programming Languages & Compilers Java - Basic - Pascal - Fortran - C • Utility Programs Backup – Virus Scanning - Firewalls Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 29
System Software Programs that directly controls and manages the computer hardware (resources) § Types of System Software • Operating Systems DOS – Windows – Mac OS – Unix • Programming Languages & Compilers Java - Basic - Pascal - Fortran - C • Utility Programs Backup – Virus Scanning - Firewalls Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 29
 PC Operating Systems 1 - DOS (Disk Operating System) § Single user & Single task § Command line interface Example : c> copy a: report. doc c: Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 30
PC Operating Systems 1 - DOS (Disk Operating System) § Single user & Single task § Command line interface Example : c> copy a: report. doc c: Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 30
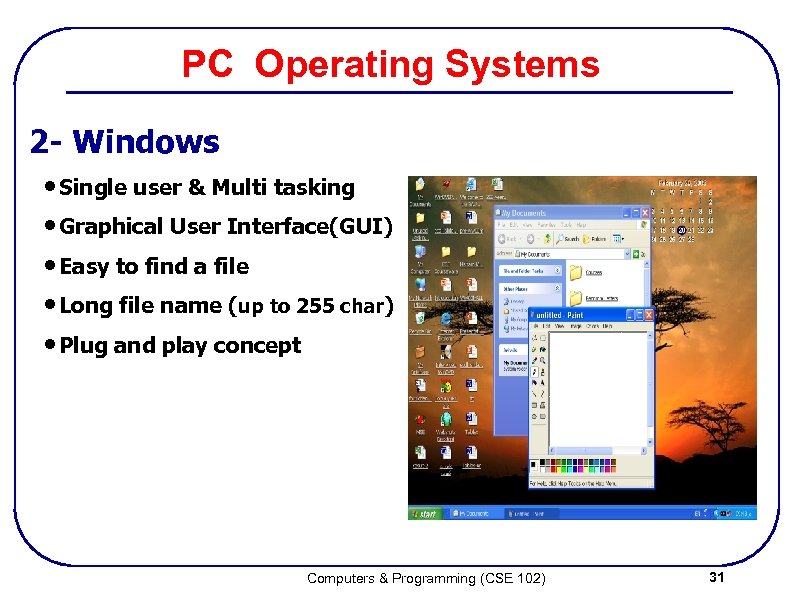 PC Operating Systems 2 - Windows • Single user & Multi tasking • Graphical User Interface(GUI) • Easy to find a file • Long file name (up to 255 char) • Plug and play concept Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 31
PC Operating Systems 2 - Windows • Single user & Multi tasking • Graphical User Interface(GUI) • Easy to find a file • Long file name (up to 255 char) • Plug and play concept Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 31
 Programming Languages A set of rules that provides a way for writing a program § Levels of Programming Languages • Machine Language 1950 -1960 • Assembly Languages 1955 -1966 • High-Level languages 1960 -Now • Very High-level languages 1980 -Now • Natural Languages 1980 -Now Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 32
Programming Languages A set of rules that provides a way for writing a program § Levels of Programming Languages • Machine Language 1950 -1960 • Assembly Languages 1955 -1966 • High-Level languages 1960 -Now • Very High-level languages 1980 -Now • Natural Languages 1980 -Now Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 32
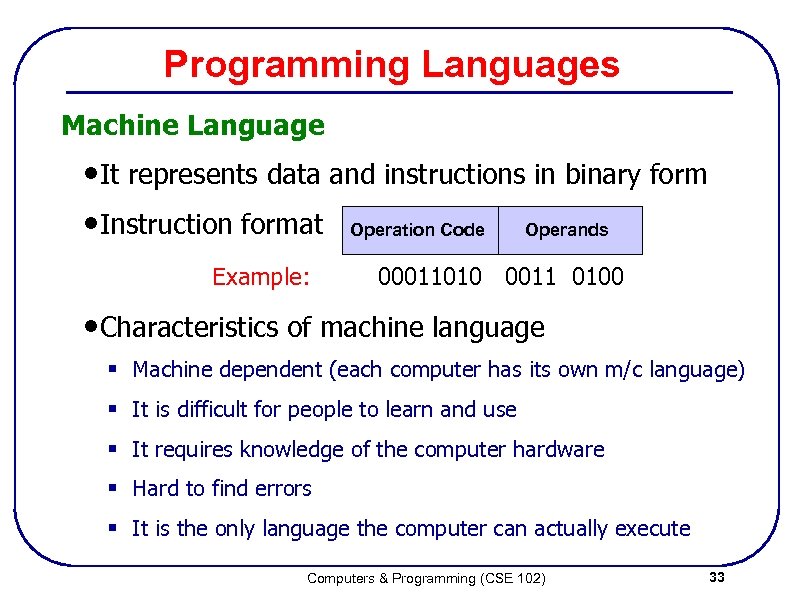 Programming Languages Machine Language • It represents data and instructions in binary form • Instruction format Operation Code Operands Example: 00011010 0011 0100 • Characteristics of machine language § Machine dependent (each computer has its own m/c language) § It is difficult for people to learn and use § It requires knowledge of the computer hardware § Hard to find errors § It is the only language the computer can actually execute Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 33
Programming Languages Machine Language • It represents data and instructions in binary form • Instruction format Operation Code Operands Example: 00011010 0011 0100 • Characteristics of machine language § Machine dependent (each computer has its own m/c language) § It is difficult for people to learn and use § It requires knowledge of the computer hardware § Hard to find errors § It is the only language the computer can actually execute Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 33
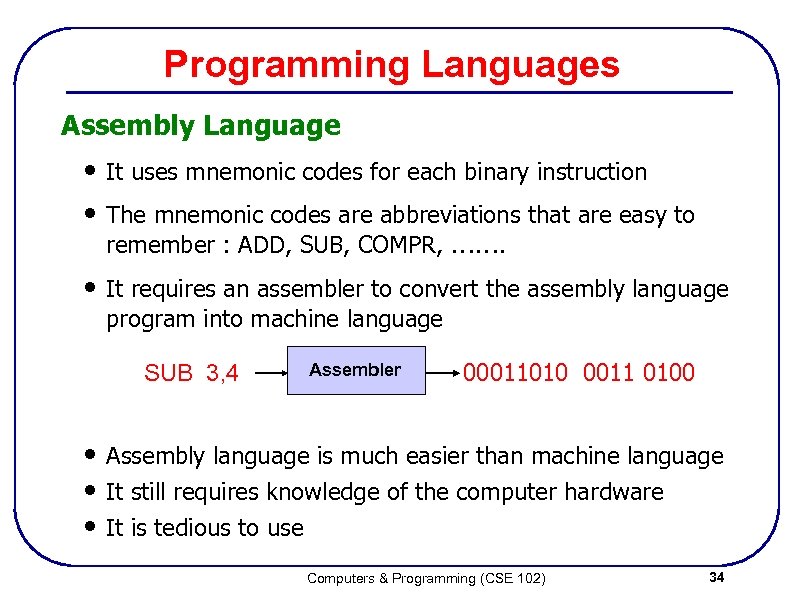 Programming Languages Assembly Language • It uses mnemonic codes for each binary instruction • The mnemonic codes are abbreviations that are easy to remember : ADD, SUB, COMPR, ……. • It requires an assembler to convert the assembly language program into machine language SUB 3, 4 Assembler 00011010 0011 0100 • Assembly language is much easier than machine language • It still requires knowledge of the computer hardware • It is tedious to use Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 34
Programming Languages Assembly Language • It uses mnemonic codes for each binary instruction • The mnemonic codes are abbreviations that are easy to remember : ADD, SUB, COMPR, ……. • It requires an assembler to convert the assembly language program into machine language SUB 3, 4 Assembler 00011010 0011 0100 • Assembly language is much easier than machine language • It still requires knowledge of the computer hardware • It is tedious to use Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 34
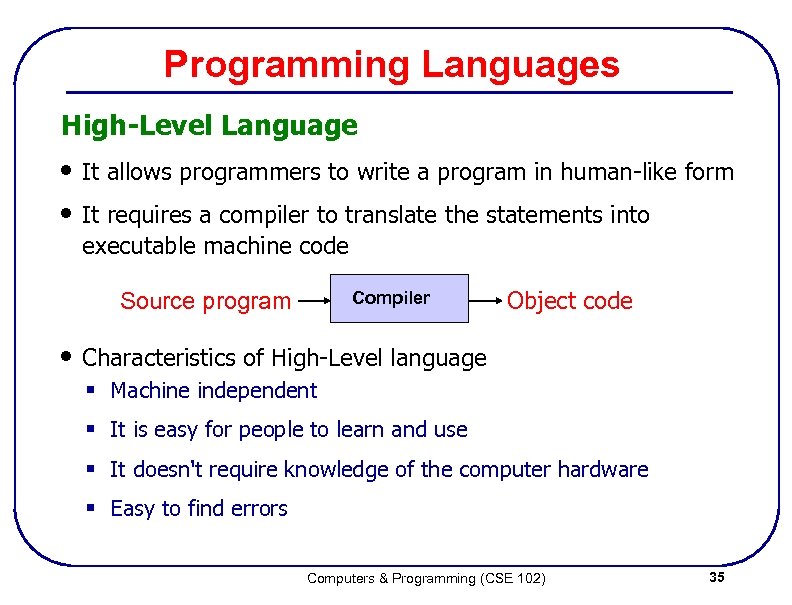 Programming Languages High-Level Language • It allows programmers to write a program in human-like form • It requires a compiler to translate the statements into executable machine code Compiler Source program Object code • Characteristics of High-Level language § Machine independent § It is easy for people to learn and use § It doesn't require knowledge of the computer hardware § Easy to find errors Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 35
Programming Languages High-Level Language • It allows programmers to write a program in human-like form • It requires a compiler to translate the statements into executable machine code Compiler Source program Object code • Characteristics of High-Level language § Machine independent § It is easy for people to learn and use § It doesn't require knowledge of the computer hardware § Easy to find errors Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 35
 Computer Classes Distinguish Between Computers in Terms of Capacity, Speed, Cost, and Typical Users. n Personal computers Ø Ø Ø Small Less powerful Cheap Single user Desktop , notebook Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 36
Computer Classes Distinguish Between Computers in Terms of Capacity, Speed, Cost, and Typical Users. n Personal computers Ø Ø Ø Small Less powerful Cheap Single user Desktop , notebook Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 36
 Computer Classes n Mini computers Ø Ø Ø Mid-sized powerful Expensive Multiple users used by a single department of an organization such as colleges! Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 37
Computer Classes n Mini computers Ø Ø Ø Mid-sized powerful Expensive Multiple users used by a single department of an organization such as colleges! Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 37
 Computer Classes n Mainframe computers Ø Ø Ø Large Very powerful Very expensive Multiple users used by large organizations such an banks to control the entire business operation. ! Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 38
Computer Classes n Mainframe computers Ø Ø Ø Large Very powerful Very expensive Multiple users used by large organizations such an banks to control the entire business operation. ! Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 38
 Computer Classes n Super computers Ø Ø Ø Very large Most powerful Most expensive Multiple users Used for tasks such as Weather forecasting and weapons research Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 39
Computer Classes n Super computers Ø Ø Ø Very large Most powerful Most expensive Multiple users Used for tasks such as Weather forecasting and weapons research Computers & Programming (CSE 102) 39


