d81a973a852cfedca35b07772e2b1ad9.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

Cournot Competition, Financial Option Markets and Efficiency Bert Willems

Long Term Contracts? l Historically: Regulators opposed long term contracts § § l Currently: Regulators more in favor of long run contracts § § § l Entry might be slowed down Decrease liquidity and transparency of the spot market Reduce market power (Bushnell et al. ) Allow Hedging (Bankruptcy California) Security of supply issues / New Entry Policy Question: § § Regulation of amount of contracts signed? Type of contracts? £ Options – Futures // Financial – Physical contracts? £ Virtual power plants / Capacity payments Bert Willems

This paper l Strategic effect of financial call options Generators freely decide about number of option contracts they sell 1 Option with 1 strike price (endogenous in model) l NOT l l § Hedging issues § Entry decisions § Security of supply issues § Regulation = obligation to buy/sell contracts Bert Willems

Paper = Extension of A&V l Allaz and Villa (1993) § Strategic reasons to sell Futures contract = commitment to produce more in spot market § Prisoners dilemma: markets become more efficient l My paper § Replace Futures with Call Option l Results of A&V – my paper rely on § Cournot competition (Mahenc and Salanie, 2004) § Observability of the futures position (Hughes and Kao) § Perfect inter-temporal arbitrage Bert Willems

Why Options? l Why look at options? § Hedge quantity risks § Retailers can counter market power of generators in peak period § Incomplete markets solved by options l Two types § Physical options £a plant is assigned to the option contract £ production decision is delegated to market § Financial option £ monetary transfer £ production decision stays with firm Bert Willems

Comparison with C&W (2004) CHAO & WILSON Oblige generators to sell physical call options l l l Perfect regulation of options sold Entry in the contracting stage Bundle of options one option of each strike price Linear supply functions Physical options Bert Willems DISCLAIMER: My interpretation of earlier work ! Ø Ø Allowing for entry and imposing optimal regulation voids any comparison of contract types Non-standard assumptions on § § option types type of competition

Solution CHAO & WILSON THIS PAPER Oblige generators to sell physical call options l l l Perfect regulation of options sold Entry in the contracting stage Bundle of options one option of each strike price Linear supply functions Physical options l Quantity is endogenous l Number of generators is fixed One option one pre-specified strike price Cournot competition Financial options l l l comparison with A&V Bert Willems
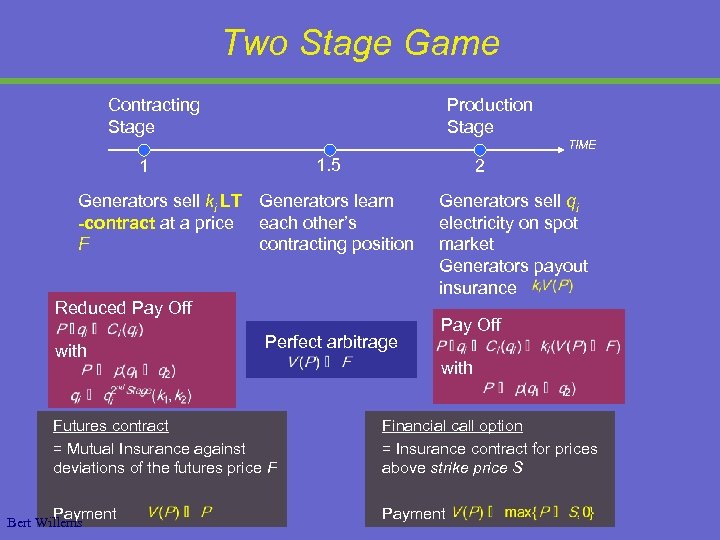
Two Stage Game Contracting Stage Production Stage TIME 1. 5 1 2 Generators sell ki LT Generators learn -contract at a price each other’s F contracting position Reduced Pay Off with Perfect arbitrage Generators sell qi electricity on spot market Generators payout insurance Pay Off with Futures contract = Mutual Insurance against deviations of the futures price F Financial call option = Insurance contract for prices above strike price S Payment Bert Willems
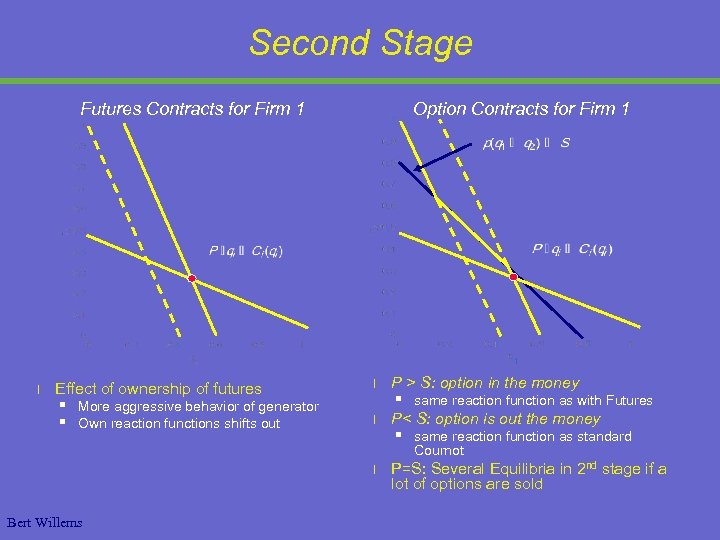
Second Stage Futures Contracts for Firm 1 l Effect of ownership of futures § § More aggressive behavior of generator Own reaction functions shifts out Option Contracts for Firm 1 l l l Bert Willems P > S: option in the money § same reaction function as with Futures P< S: option is out the money § same reaction function as standard Cournot P=S: Several Equilibria in 2 nd stage if a lot of options are sold

First Stage l Futures § increases number of futures £ Market share increases £ Spot price goes down § Prisoner’s Dilemma: sell forwards l Options § Multiple Nash equilibria in second stage £ No obvious focal point £ Punishment equilibria possible § Assumption: generators co-ordinate on equilibrium highest price £ Low price: generators sell a lot of options in the first stage Risky, assumes perfect co-ordination in the N. E. £ High Bert Willems price: Lower profit in general with higher prices
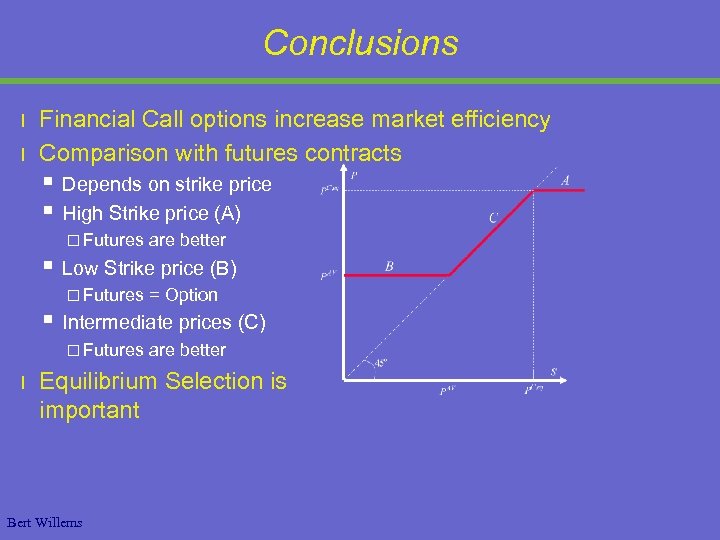
Conclusions l l Financial Call options increase market efficiency Comparison with futures contracts § § Depends on strike price High Strike price (A) £ Futures § Low Strike price (B) £ Futures § = Option Intermediate prices (C) £ Futures l are better Equilibrium Selection is important Bert Willems

Extensions l Physical options vs. Financial options § Two different types of property rights § Prisoner’s dilemma with Physical options is not there § See Working Paper l Other types of Financial insurance contracts § Insurance contracts which pay relatively more when prices are high: more competitive market § Work in progress Bert Willems

Future Work: Investments + Entry l LT-contracts + Entry § Lower risk (risk aversion) § Retailer and entrant (partially) internalize reduction of market power l Role of options? § Better hedging of quantity risks l NEEDED: § Extend model with uncertainty – risk aversion Bert Willems

Future Work: Regulation l l Under-contracting by retailers § § § W. r. t. market power mitigation and reliability Reason: missing markets Contracting is public good Regulation of long term contracts? § Should retailers / producers be obliged to buy/sell? Role of options § § § Options might be cheaper regulatory instruments Only put constraints on markets when there is a problem Market conform NEEDED § § § Model for market imperfection £ £ missing markets (Explaining under-contracting by private players) market power Model for regulation costs £ £ Asymmetric information? Incomplete contracting? Regulatory efficiency Bert Willems
d81a973a852cfedca35b07772e2b1ad9.ppt