b923c2d935b8457fc491ecdc7bfc8f2b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 Coupled esterification reaction in ionic liquids and product recovery by pervaporation P. Izák 1, N. M. M. Mateus 2, C. A. M. Afonso 2, J. G. Crespo 2 1 Department of Separation Processes, Institute of Chemical Process Fundamentals, Rozvojová 135, 16502 Prague 6, CZ 2 Institute of Chemistry, University of Rostock, Albert Einstein Str. 3 a, 18059 Rostock, Germany 3 Institute of Chemical Sciences and Engineering, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland 4 Department of Physical Chemistry, Institute of Chemical Technology, Technická 5, 16628 Prague 6, Czech Republic http: //www. icpf. cas. cz/
Coupled esterification reaction in ionic liquids and product recovery by pervaporation P. Izák 1, N. M. M. Mateus 2, C. A. M. Afonso 2, J. G. Crespo 2 1 Department of Separation Processes, Institute of Chemical Process Fundamentals, Rozvojová 135, 16502 Prague 6, CZ 2 Institute of Chemistry, University of Rostock, Albert Einstein Str. 3 a, 18059 Rostock, Germany 3 Institute of Chemical Sciences and Engineering, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland 4 Department of Physical Chemistry, Institute of Chemical Technology, Technická 5, 16628 Prague 6, Czech Republic http: //www. icpf. cas. cz/
 The aim • Conversion enhancement of esterification reactions taking place in RTILs by pervaporation • Modeling of the esterification reaction coupled with pervaporation • Prediction of process variables influence on the esterification reaction
The aim • Conversion enhancement of esterification reactions taking place in RTILs by pervaporation • Modeling of the esterification reaction coupled with pervaporation • Prediction of process variables influence on the esterification reaction
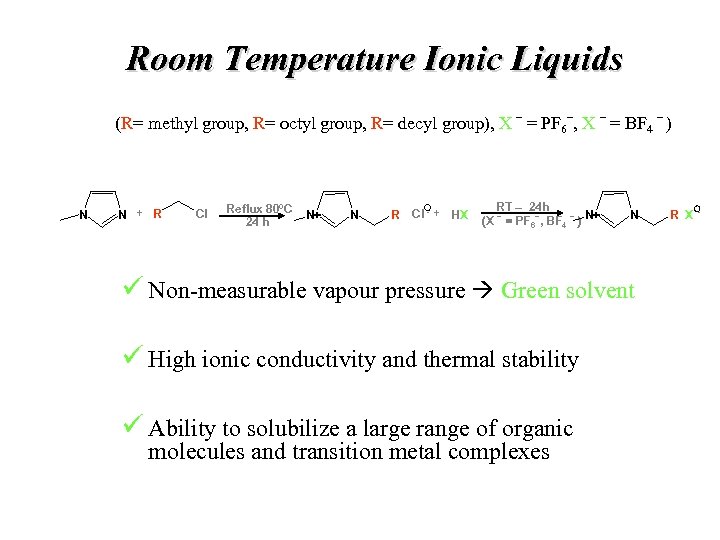 Room Temperature Ionic Liquids _ _ (R= methyl group, R= octyl group, R= decyl group), X = PF 6 , X = BF 4 ) N N + R Cl Reflux 80ºC 24 h N+ N R Cl - + HX RT – 24 h _ _ _ (X = PF 6 , BF 4 ) N+ N ü Non-measurable vapour pressure Green solvent ü High ionic conductivity and thermal stability ü Ability to solubilize a large range of organic molecules and transition metal complexes R X-
Room Temperature Ionic Liquids _ _ (R= methyl group, R= octyl group, R= decyl group), X = PF 6 , X = BF 4 ) N N + R Cl Reflux 80ºC 24 h N+ N R Cl - + HX RT – 24 h _ _ _ (X = PF 6 , BF 4 ) N+ N ü Non-measurable vapour pressure Green solvent ü High ionic conductivity and thermal stability ü Ability to solubilize a large range of organic molecules and transition metal complexes R X-
 Room Temperature Ionic Liquids ü Do not permeate through either organophilic or hydrophilic dense membranes ü Possibly an environmentally benign alternative to classical organic solvents v High viscosity and low heat transfer v Purification of ionic liquids
Room Temperature Ionic Liquids ü Do not permeate through either organophilic or hydrophilic dense membranes ü Possibly an environmentally benign alternative to classical organic solvents v High viscosity and low heat transfer v Purification of ionic liquids
![Experimental [bmim] [BF 4] A + CH 3 COOH H 2 O + p-Ts. Experimental [bmim] [BF 4] A + CH 3 COOH H 2 O + p-Ts.](https://present5.com/presentation/b923c2d935b8457fc491ecdc7bfc8f2b/image-5.jpg) Experimental [bmim] [BF 4] A + CH 3 COOH H 2 O + p-Ts. OH 60°C B W E § Hydrophobic RTIL [bmim] [PF 6] at temperatures over 50°C - hydrolysis producing HF and PO 43 - § The selected “dried” [bmim] [BF 4] had viscosity 26 c. P at 60°C § Due to crystallization on the lid of the vessel, a 50% excess of (-)-Borneol was used
Experimental [bmim] [BF 4] A + CH 3 COOH H 2 O + p-Ts. OH 60°C B W E § Hydrophobic RTIL [bmim] [PF 6] at temperatures over 50°C - hydrolysis producing HF and PO 43 - § The selected “dried” [bmim] [BF 4] had viscosity 26 c. P at 60°C § Due to crystallization on the lid of the vessel, a 50% excess of (-)-Borneol was used
 Experimental § Esterification in closed vessel with minimized headspace • Water content in the reaction mixture was determined by automatic Karl-Fisher titration (Aquapal III) • Esterification reaction was monitored by GC (CP-9001) using a FFAP polar capillary column • Pervaporation membrane for water removal – PVA membrane PERVAP® 2205, SULZER (suitable for organic acids without limitation)
Experimental § Esterification in closed vessel with minimized headspace • Water content in the reaction mixture was determined by automatic Karl-Fisher titration (Aquapal III) • Esterification reaction was monitored by GC (CP-9001) using a FFAP polar capillary column • Pervaporation membrane for water removal – PVA membrane PERVAP® 2205, SULZER (suitable for organic acids without limitation)
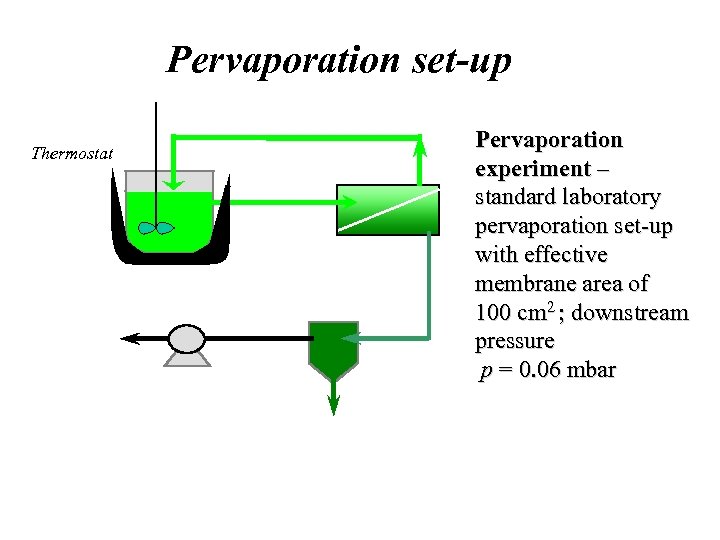 Pervaporation set-up Retentate Thermostat Feed Permeate Reaction vessel Vacuum pump Cold trap Permeate Pervaporation experiment – standard laboratory pervaporation set-up with effective membrane area of 100 cm 2 ; downstream pressure p = 0. 06 mbar
Pervaporation set-up Retentate Thermostat Feed Permeate Reaction vessel Vacuum pump Cold trap Permeate Pervaporation experiment – standard laboratory pervaporation set-up with effective membrane area of 100 cm 2 ; downstream pressure p = 0. 06 mbar
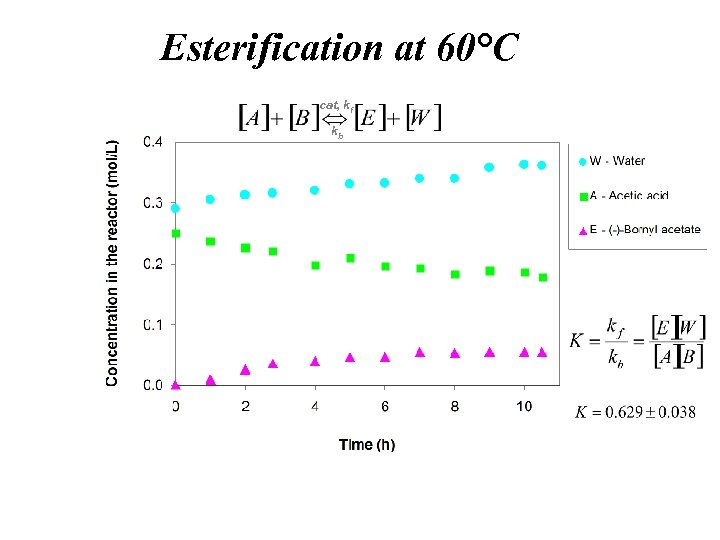 Esterification at 60°C cat, kf kb
Esterification at 60°C cat, kf kb
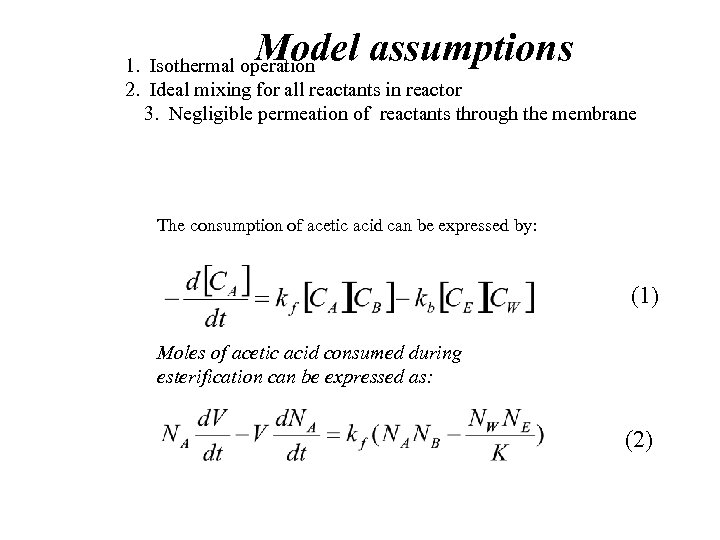 Model assumptions 1. Isothermal operation 2. Ideal mixing for all reactants in reactor 3. Negligible permeation of reactants through the membrane The consumption of acetic acid can be expressed by: (1) Moles of acetic acid consumed during esterification can be expressed as: (2)
Model assumptions 1. Isothermal operation 2. Ideal mixing for all reactants in reactor 3. Negligible permeation of reactants through the membrane The consumption of acetic acid can be expressed by: (1) Moles of acetic acid consumed during esterification can be expressed as: (2)
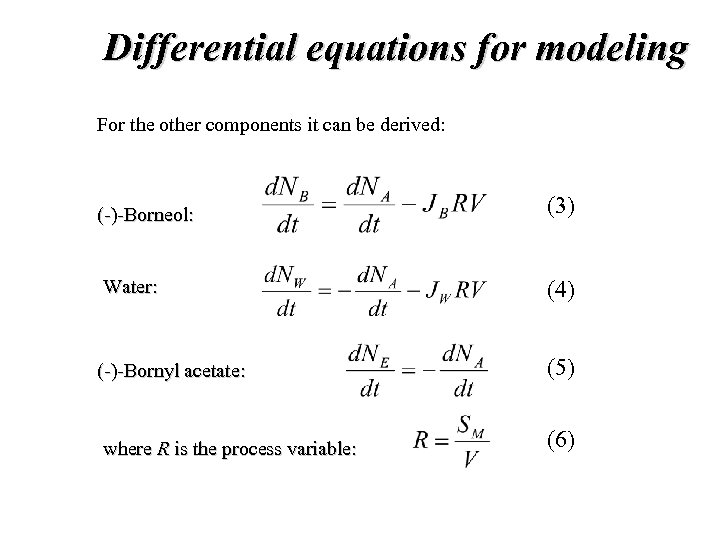 Differential equations for modeling For the other components it can be derived: (-)-Borneol: (3) Water: (4) (-)-Bornyl acetate: (5) where R is the process variable: (6)
Differential equations for modeling For the other components it can be derived: (-)-Borneol: (3) Water: (4) (-)-Bornyl acetate: (5) where R is the process variable: (6)
 Volume change in the reactor Taking into consideration that the ionic liquid does not permeate through the PVA membrane, d. V/dt can be expressed by: (7) All differential Eqs. (2 -5, 7) were solved by the least square method using Scientist software.
Volume change in the reactor Taking into consideration that the ionic liquid does not permeate through the PVA membrane, d. V/dt can be expressed by: (7) All differential Eqs. (2 -5, 7) were solved by the least square method using Scientist software.
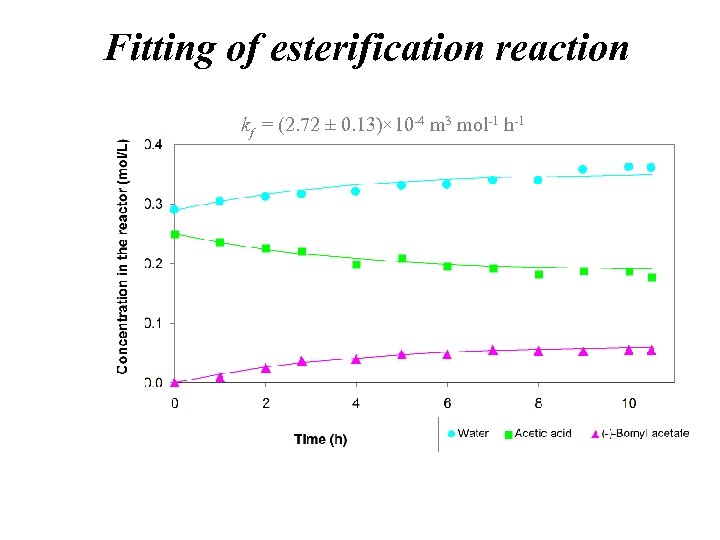 Fitting of esterification reaction kf = (2. 72 ± 0. 13)× 10 -4 m 3 mol-1 h-1
Fitting of esterification reaction kf = (2. 72 ± 0. 13)× 10 -4 m 3 mol-1 h-1
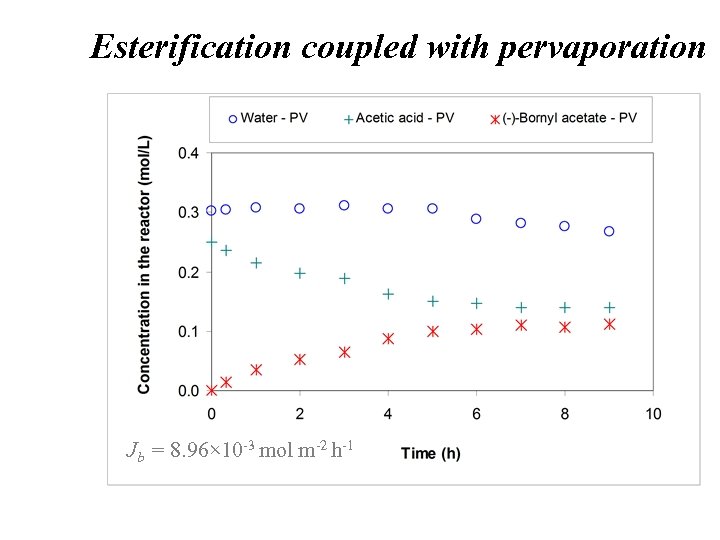 Esterification coupled with pervaporation Jb = 8. 96× 10 -3 mol m-2 h-1
Esterification coupled with pervaporation Jb = 8. 96× 10 -3 mol m-2 h-1
![Drying of [bmim] [BF 4] by PV Drying of [bmim] [BF 4] by PV](https://present5.com/presentation/b923c2d935b8457fc491ecdc7bfc8f2b/image-14.jpg) Drying of [bmim] [BF 4] by PV
Drying of [bmim] [BF 4] by PV
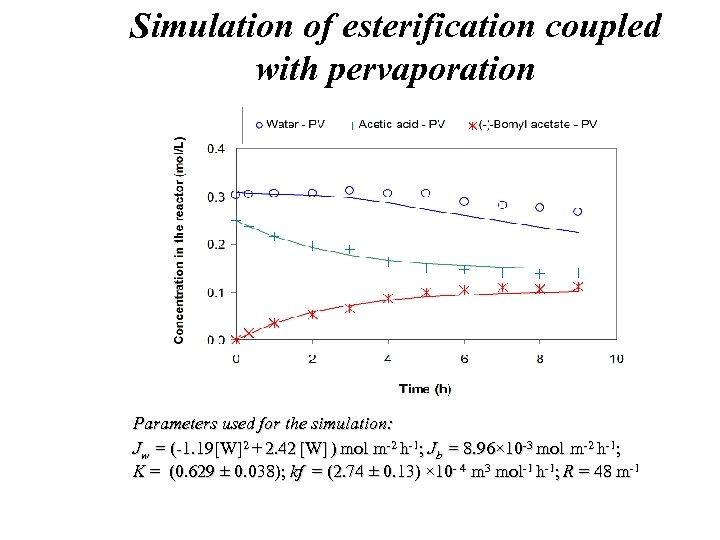 Simulation of esterification coupled with pervaporation Parameters used for the simulation: . . . simulation: Jw = (-1. 19[W]2 + 2. 42 [W] ) mol m-2 h-1; Jb = 8. 96× 10 -3 mol m-2 h-1; . . K ; K = (0. 629 ± 0. 038); kf = (2. 74 ± 0. 13) × 10 - 4 m 3 mol-1 h-1; R = 48 m-1
Simulation of esterification coupled with pervaporation Parameters used for the simulation: . . . simulation: Jw = (-1. 19[W]2 + 2. 42 [W] ) mol m-2 h-1; Jb = 8. 96× 10 -3 mol m-2 h-1; . . K ; K = (0. 629 ± 0. 038); kf = (2. 74 ± 0. 13) × 10 - 4 m 3 mol-1 h-1; R = 48 m-1
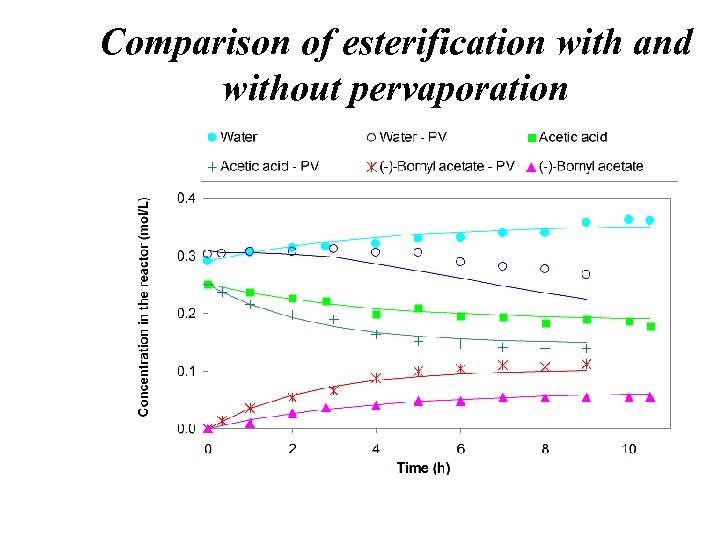 Comparison of esterification with and without pervaporation
Comparison of esterification with and without pervaporation
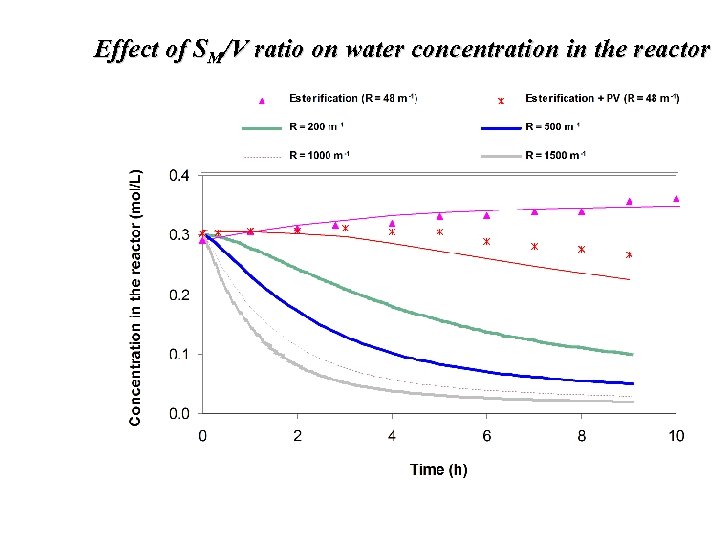 Effect of SM/V ratio on water concentration in the reactor
Effect of SM/V ratio on water concentration in the reactor
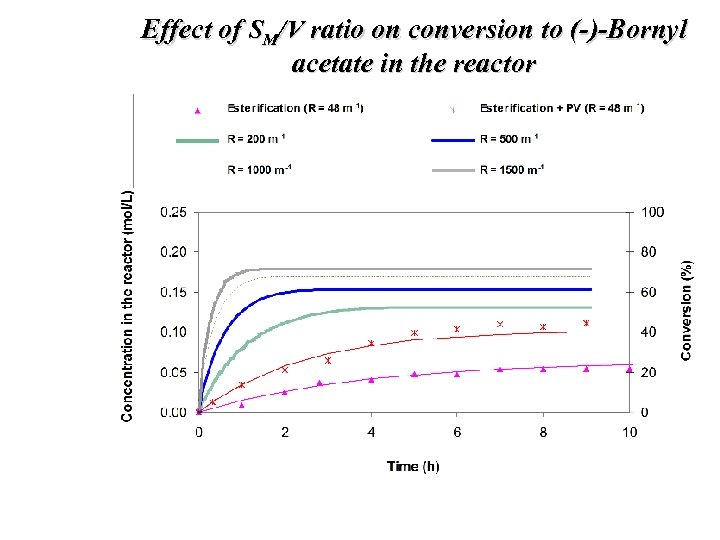 Effect of SM/V ratio on conversion to (-)-Bornyl acetate in the reactor
Effect of SM/V ratio on conversion to (-)-Bornyl acetate in the reactor
 Conclusions • Thanks to pervaporation, the reaction conversion increased from 22. 0% to 44. 4% (increase by 102%) • Numerical simulation and experimental results showed a good agreement • The process variable SM/V has a significant impact on the esterification conversion
Conclusions • Thanks to pervaporation, the reaction conversion increased from 22. 0% to 44. 4% (increase by 102%) • Numerical simulation and experimental results showed a good agreement • The process variable SM/V has a significant impact on the esterification conversion
 Acknowledgement • This research was supported by Marie Curie Intra. European and Marie Curie Reintegration Fellowships within the 6 th European Community Framework Programme and by Purkyne Fellowship from Czech Academy of Science. • Thank you for your attention!
Acknowledgement • This research was supported by Marie Curie Intra. European and Marie Curie Reintegration Fellowships within the 6 th European Community Framework Programme and by Purkyne Fellowship from Czech Academy of Science. • Thank you for your attention!


